How In Vivo Alteration of Hip Replacement Wear Mode Can Cause a Voluminous Inflammatory Reaction and an Excessive Titanium Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
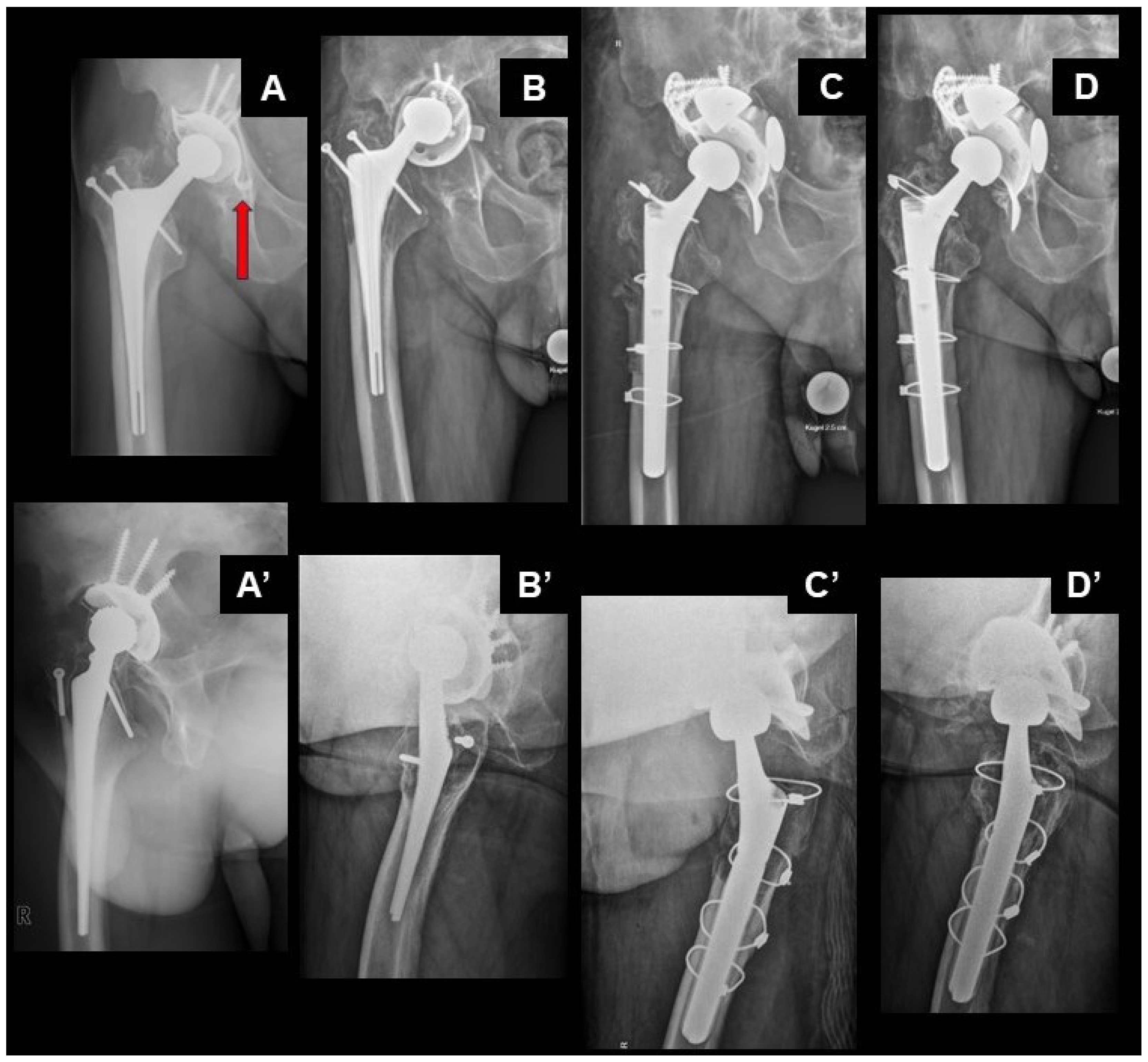
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatt, H.; Goswami, T. Implant wear mechanisms—Basic approach. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, M.R.; Endo, M.; Zachara, S.; Nielsen, T.O.; Greidanus, N.V.; Masri, B.A.; Garbuz, D.S.; Duncan, C.P. Adverse local tissue reactions in metal-on-polyethylene total hip arthroplasty due to trunnion corrosion: The risk of misdiagnosis. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97-B, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler Ransohoff, C.; Wanner, R.; Solinger, T.; Gautier, E.; Eijer, H.; Wahl, P. The different failure modes of the connecting elements of the modular hip arthroplasty revision stem Revitan. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 123, 104778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łapaj, Ł.; Woźniak, W.; Wiśniewski, T.; Rozwalka, J.; Paczesny, Ł.; Zabrzyński, J.; Janusz, P.; Kruczyński, J. Breakage of metal hip arthroplasty components: Retrieval and structural analysis. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2019, 30, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibon, E.; Amanatullah, D.F.; Loi, F.; Pajarinen, J.; Nabeshima, A.; Yao, Z.; Hamadouche, M.; Goodman, S.B. The biological response to orthopaedic implants for joint replacement: Part I: Metals. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.C.; Banerjee, S.; Cherian, J.J.; Wong, F.; Butany, J.; Gilbert, C.; Overgaard, C.; Syed, K.; Zywiel, M.G.; Jacobs, J.J.; et al. Systemic cobalt toxicity from total hip arthroplasties: Review of a rare condition Part 1—History, mechanism, measurements, and pathophysiology. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98-b, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zywiel, M.G.; Cherian, J.J.; Banerjee, S.; Cheung, A.C.; Wong, F.; Butany, J.; Gilbert, C.; Overgaard, C.; Syed, K.; Jacobs, J.J.; et al. Systemic cobalt toxicity from total hip arthroplasties: Review of a rare condition Part 2—Measurement, risk factors, and step-wise approach to treatment. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98-B, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, B.D.; Steck, T.; Woelber, E.; Tower, S.S. A systematic review of systemic cobaltism after wear or corrosion of chrome-cobalt hip implants. J. Patient Saf. 2019, 15, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.; Mandalunis, P. A review of metal exposure and its effects on bone health. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 4854152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, R.M.; Jacobs, J.J.; Tomlinson, M.J.; Gavrilovic, J.; Black, J.; Peoc’h, M. Dissemination of wear particles to the liver, spleen, and abdominal lymph nodes of patients with hip or knee replacement. JBJS 2000, 82, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarpada, S.P.; Loloi, J.; Schwechter, E.M. A Case of Titanium Pseudotumor and Systemic Toxicity After Total Hip Arthroplasty Polyethylene Failure. Arthroplast. Today 2020, 6, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paprosky, W.G.; Perona, P.G.; Lawrence, J.M. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J. Arthroplast. 1994, 9, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKellop, H.A. The lexicon of polyethylene wear in artificial joints. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5049–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hall, D.J.; Della Valle, C.J.; Walsh, M.J.; Jacobs, J.J.; Pourzal, R. Simultaneous characterization of implant wear and Tribocorrosion debris within its corresponding tissue response using infrared chemical imaging. Biotribology 2021, 26, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenn, V.; Morawietz, L.; Perino, G.; Kienapfel, H.; Ascherl, R.; Hassenpflug, G.J.; Thomsen, M.; Thomas, P.; Huber, M.; Kendoff, D.; et al. Revised histopathological consensus classification of joint implant related pathology. Pathol. Res. Pr. 2014, 210, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.; Ebramzadeh, E.; Nelson, S.; Takamura, K.; De Smet, K.; Amstutz, H.C. Histological features of pseudotumor-like tissues from metal-on-metal hips. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Grammatopoulos, G.; Adshead, S.; Tsialogiannis, E.; Tsiridis, E. Molecular and immune toxicity of CoCr nanoparticles in MoM hip arthroplasty. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourzal, R.; Catelas, I.; Theissmann, R.; Kaddick, C.; Fischer, A. Characterization of Wear Particles Generated from CoCrMo Alloy under Sliding Wear Conditions. Wear 2011, 271, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.M.; Hall, D.J.; Darrith, B.; Liu, S.; Jacobs, J.J.; Pourzal, R.; Silverton, C.D. Non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy associated with elevated serum cobalt and accelerated wear of a metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e249070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Tateiwa, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, Y.; Shishido, T.; Masaoka, T.; Sano, K.; Yamamoto, K. Do Polyethylene Supra-Macroparticles Lead to Pseudotumor Formation in Metal-on-Polyethylene Total Hip Arthroplasty? Arthroplast. Today 2020, 6, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, H.P.; Rieker, C.B.; Kottig, P. Analysis of 118 second-generation metal-on-metal retrieved hip implants. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1999, 81, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krombach, F.; Münzing, S.; Allmeling, A.M.; Gerlach, J.T.; Behr, J.; Dörger, M. Cell size of alveolar macrophages: An interspecies comparison. Env. Health Perspect. 1997, 105 (Suppl. 5), 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Paiement, G.D.; Penenberg, B.L.; Rajaee, S.S. Metallosis in Total Hip Arthroplasty. JBJS Rev. 2023, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Steiger, R.; Peng, A.; Lewis, P.; Graves, S. What Is the Long-term Survival for Primary THA With Small-head Metal-on-metal Bearings? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2018, 476, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Dorr, L.D.; Long, W.T. Impingement as a mechanism of dissociation of a metasul metal-on-metal liner. J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, e313–e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innmann, M.M.; Gotterbarm, T.; Kretzer, J.P.; Merle, C.; Ewerbeck, V.; Weiss, S.; Aldinger, P.R.; Streit, M.R. Minimum ten-year results of a 28-mm metal-on-metal bearing in cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients fifty years of age and younger. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Yu, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Progress of in vivo studies on the systemic toxicities induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.J.; Silverton, C.; Hallab, N.J.; Skipor, A.K.; Patterson, L.; Black, J.; Galante, J.O. Metal release and excretion from cementless titanium alloy total knee replacements. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1999, 358, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannemann, F.; Hartmann, A.; Schmitt, J.; Lutzner, J.; Seidler, A.; Campbell, P.; Delaunay, C.P.; Drexler, H.; Ettema, H.B.; Garcia-Cimbrelo, E.; et al. European multidisciplinary consensus statement on the use and monitoring of metal-on-metal bearings for total hip replacement and hip resurfacing. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2013, 99, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.; Ziaee, H.; Pynsent, P.; McMinn, D. The validity of serum levels as a surrogate measure of systemic exposure to metal ions in hip replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2007, 89, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutter, C.; Klüß, D.; Enz, A.; Mittelmeier, W. Impingement of metal-polyethylene hip prostheses: Potential cause of high systemic titanium levels? Der Orthopäde 2020, 49, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Wei, L.; Shao, L. A review on potential neurotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandoliya, R.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, V.; Joshi, R.; Sivanesan, I. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis, Applications and Toxicity. Plants 2024, 13, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatkowska, I.; Martin, N.G.; Henckel, J.; Apthorp, H.; Hamshere, J.; Hart, A.J. Blood and plasma titanium levels associated with well-functioning hip implants. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 57, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahl, A.; Kazim, M.A.; Kattwinkel, N.; Hauskeller, W.; Moritz, S.; Arlt, S.; Niemeier, A. Mid-term improvement of cognitive performance after total hip arthroplasty in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip: A prospective cohort study. Bone Jt. J. 2022, 104-b, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutter, L.; Hall, D.J.; Bischoff, L.; Dommann-Scherrer, C.; Schläppi, M.; Pourzal, R.; Hallab, N.; Meier, C.; Wahl, P. How In Vivo Alteration of Hip Replacement Wear Mode Can Cause a Voluminous Inflammatory Reaction and an Excessive Titanium Exposure. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010210
Sutter L, Hall DJ, Bischoff L, Dommann-Scherrer C, Schläppi M, Pourzal R, Hallab N, Meier C, Wahl P. How In Vivo Alteration of Hip Replacement Wear Mode Can Cause a Voluminous Inflammatory Reaction and an Excessive Titanium Exposure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(1):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010210
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutter, Luca, Deborah J. Hall, Lydia Bischoff, Corina Dommann-Scherrer, Michel Schläppi, Robin Pourzal, Nadim Hallab, Christoph Meier, and Peter Wahl. 2025. "How In Vivo Alteration of Hip Replacement Wear Mode Can Cause a Voluminous Inflammatory Reaction and an Excessive Titanium Exposure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 1: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010210
APA StyleSutter, L., Hall, D. J., Bischoff, L., Dommann-Scherrer, C., Schläppi, M., Pourzal, R., Hallab, N., Meier, C., & Wahl, P. (2025). How In Vivo Alteration of Hip Replacement Wear Mode Can Cause a Voluminous Inflammatory Reaction and an Excessive Titanium Exposure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(1), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010210




