Development and Evaluation of a New Self-Administered Near Visual Acuity Chart: Accuracy and Feasibility of Usage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample and Study Design
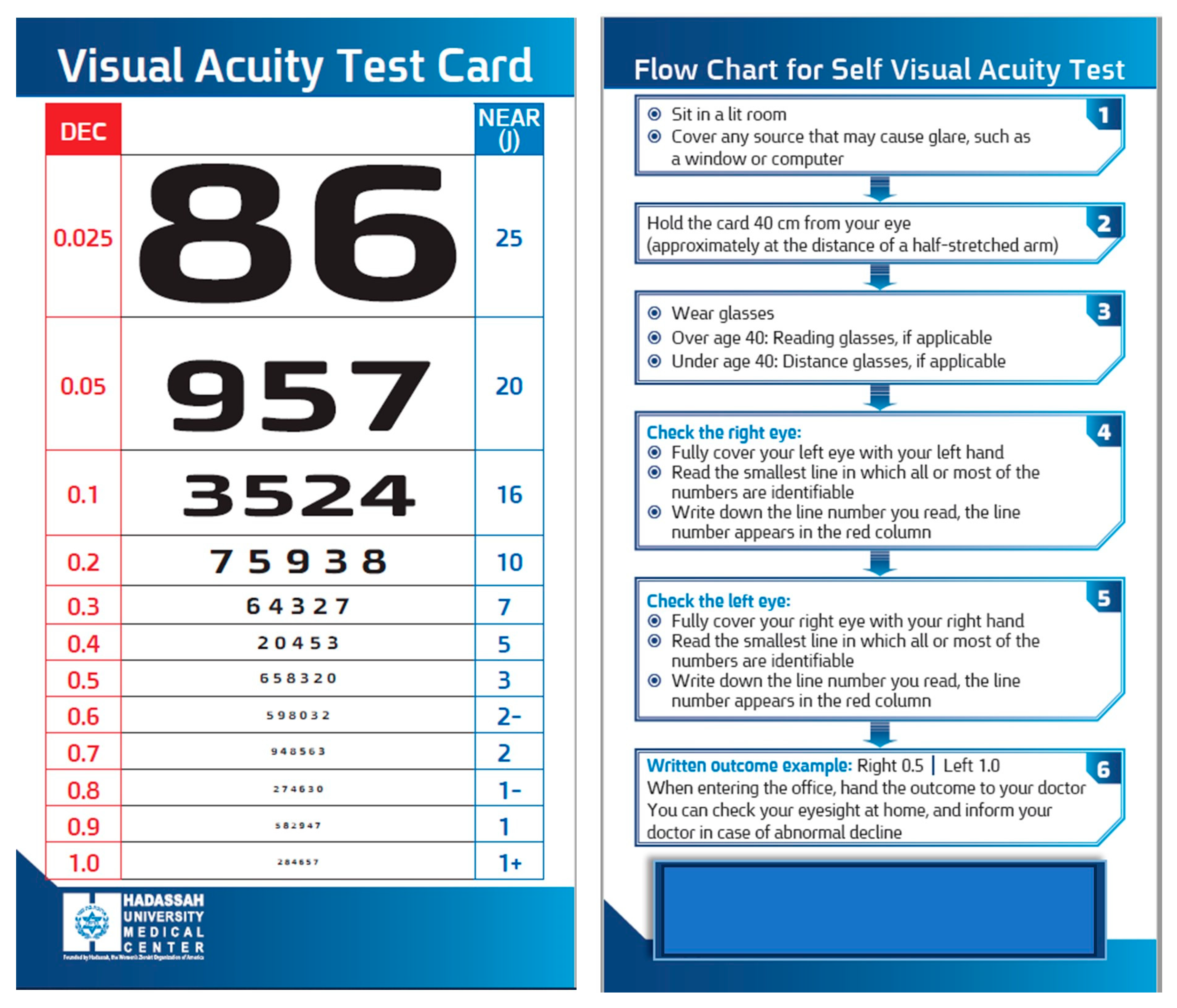
2.2. Development of the near Visual Acuity Chart
Procedure
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.4. Sample Size Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Power Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Test–Retest Reliability
3.2. Accuracy
3.3. Agreement between HSVA and RPVS Charts
3.4. Self-Test HSVA
3.5. Self-Test vs. Electronic Medical Records
3.6. Prediction Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VA | Visual acuity |
| RPVS | Rosenbaum Pocket Vision Screener |
| HSVA | Hadassah Self-Visual Acuity Screener |
| BCVA | Best-corrected visual acuity |
| ICC | Intra-class correlation coefficient |
| ETDRS | Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study |
| DDiVAT | Democritus Digital Visual Acuity Test |
| PNAC | Practical Near Acuity Chart |
References
- Silverstein, E.; Williams, J.S.; Brown, J.R.; Bylykbashi, E.; Stinnett, S.S. Teleophthalmology: Evaluation of Phone-based Visual Acuity in a Pediatric Population. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 221, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siktberg, J.; Hamdan, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Donahue, S.P.; Patel, S.N.; Sternberg, P.; Robinson, J.; Kammer, J.A.; Gangaputra, S.S. Validation of a Standardized Home Visual Acuity Test for Teleophthalmology. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2021, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.P.; Mills, M.; Gallagher, T.; Polis, A.; Blasberg, S.; Pham, P.; Gentile, R.C.; Ianchulev, T.; The Accustat Study Group. Remote vision testing of central retinal acuity and comparison with clinic-based Snellen acuity testing in patients followed for retinal conditions. Digit. Health 2023, 9, 20552076231180727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holekamp, N.M. Moving from Clinic to Home: What the Future Holds for Ophthalmic Telemedicine. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 187, xxviii–xxxv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arditi, A.; Cagenello, R. On the statistical reliability of letter-chart visual acuity measurements. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1993, 34, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, H.K.; Hall, W.D.; Hurst, J.W. (Eds.) Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Daiber, H.F.; Gnugnoli, D.M. Visual Acuity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hetherinton, R. The Shellen Chart as a test of visual acuity. Psychol. Forsch. 1954, 357, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caltrider, D.; Gupta, A.; Tripathy, K. Evaluation of Visual Acuity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, R.R.A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; Leashe, J.; Limburg, H.; et al. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e888–e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Cochrane, A.L. The practical near acuity chart (PNAC) and prediction of visual ability at near. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2000, 20, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Hassan, R.; Limonard, A.; Savant, S.V. Accuracy and reliability of self-administered visual acuity tests: Systematic review of pragmatic trials. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Scheetz, J.; Keel, S.; Liao, C.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Müller, A.; Meng, W.; He, M. Development and Validation of a Smartphone-Based Visual Acuity Test (Vision at Home). Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastawrous, A.; Rono, H.K.; Livingstone, I.A.T.; Weiss, H.A.; Jordan, S.; Kuper, H.; Burton, M.J. Development and Validation of a Smartphone-Based Visual Acuity Test (Peek Acuity) for Clinical Practice and Community-Based Fieldwork. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.G.; Webel, A.D.; Blumenkranz, M.S.; Kim, Y.; Yang, J.H.; Yu, S.Y.; Kwak, H.W.; Palanker, D.; Toy, B.; Myung, D. A Smartphone-Based Near-Vision Testing System: Design, Accuracy, and Reproducibility Compared with Standard Clinical Measures. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2022, 53, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racano, E.; Malfatti, G.; Pertile, R.; Site, R.D.; Romanelli, F.; Nicolini, A. A novel smartphone App to support the clinical practice of pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus: The validation of visual acuity tests. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 4007–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, J.; Van Egmond, J.; Wanten, J.; Bauer, N.; Nuijts, R.; Wisse, R. The Accuracy of a Web-Based Visual Acuity Self-assessment Tool Performed Independently by Eye Care Patients at Home: Method Comparison Study. JMIR Form. Res. 2023, 7, e41045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, M.; Ramamurthy, D.; Srinivasan, K.; Varadharajan, L.S. Development of Pocket Vision Screener and its effectiveness at screening visual acuity deficits. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labiris, G.; Delibasis, K.; Panagiotopoulou, E.-K.; Pigadas, V.; Bakirtzis, M.; Panagis, C.; Dardabounis, D.; Ntonti, P. Development and Validation of the First Smart TV-Based Visual Acuity Test: A Prospective Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, J.L.J.; Geuvers, J.R.; Imhof, S.M.; Wisse, R.P.L. Digital Tools for the Self-Assessment of Visual Acuity: A Systematic Review. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2021, 10, 715–730, Erratum in Ophthalmol. Ther. 2021, 10, 731—732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.C.; Jones, M.R. Warning on inaccurate Rosenbaum cards for testing near vision. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1997, 42, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A. Statistical guidelines for the analysis of data obtained from one or both eyes. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2013, 33, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, L.J.; Gomez, J.P.; Leuenberger, E.F. The Philippine Peso Bill as an Alternative Near Visual Acuity Chart in Filipino Eyes: A Pilot Study. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 3437–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, P.; Woo, G.C. Repeatability of the Waterloo Four-Contrast LogMAR Visual Acuity chart and Near Vision Test card on a group of normal young adults. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2004, 24, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.A.; Li, J.; Schallhorn, J.M.; Sun, C.Q. Comparing a Home Vision Self-Assessment Test to Office-Based Snellen Visual Acuity. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 3205–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, J. Agreement between a mobile applet-based visual acuity self-test program and the conventional method for distance and near visual acuity tests. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2023, 51, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosser, D.A.; Laidlaw, D.A.; Murdoch, I.E. The development of a “reduced logMAR” visual acuity chart for use in routine clinical practice. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 85, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, C.J.; Eghrari, A.O.; Labrique, A.B. Smartphone-Based Visual Acuity Measurement for Screening and Clinical Assessment. JAMA 2015, 314, 2682–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, M.D.; Winter, P.A.; McKenney, K.C.; Packard, K.L.; Williams, V.; Dorsey, E.A.; Szabo, A.; Visotcky, A.; Warren, C.C.; Wirostko, W.J.; et al. An innovative visual acuity chart for urgent and primary care settings: Validation of the Runge near vision card. Eye 2019, 33, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jaeger Notation Debate—Precision Vision. Available online: https://precision-vision.com/the-jaeger-notation-debate/ (accessed on 23 February 2024).

| Visual Acuity Chart | Mean | Median | SD | p * | Spearman (Rs) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snellen—1st test | 0.06 | 0.0 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.99 | <0.001 |
| Snellen—2nd test | 0.04 | 0.0 | 0.14 | |||
| RPVS—1st test | 0.02 | 0.0 | 0.11 | 1.0 | 1.0 | <0.001 |
| RPVS—2nd test | 0.02 | 0.0 | 0.11 | |||
| HSVA—1st test | 0.02 | 0.0 | 0.11 | 1.0 | 1.0 | <0.001 |
| HSVA—2nd test | 0.02 | 0.0 | 0.11 |
| Visual Acuity Chart | Mean | Median | SD | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snellen | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.22 | Snellen–RPVS: 0.001 |
| RPVS | 0.10 | 0.0 | 0.19 | Snellen–HSVA: 0.001 |
| HSVA | 0.09 | 0.0 | 0.20 | RPVS–HSVA: 0.10 |
| Test Method | Mean | Median | SD | p * | Spearman (Rs) | p | ICC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-test | 0.10 | 0.0 | 0.20 | 0.17 | |||
| Masked examiner | 0.09 | 0.0 | 0.19 | 0.87 | <0.001 | 0.96 |
| Visual Acuity Chart | Mean | Median | SD | p * | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snellen (medical records) | 0.24 | 0.1 | 0.31 | 0.12 | |
| HSVA by examiner | 0.18 | 0.0 | 0.27 | 0.04 | |
| Self-test HSVA (N = 26) | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.27 |
| Near RPVS VA | Distance Snellen VA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B (SEB) | β | p | B(SEB) | β | p | ||
| Model I | Age | 0.004 (0.001) | 0.35 | 0.003 | 0.011 (0.07) | 0.26 | 0.02 |
| F | 9.5 | 0.003 | 5.1 | 0.02 | |||
| R2 | 0.13 | 0.07 | |||||
| Model II | Age | 0.001 (0.00) | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.001 (0.001) | 0.09 | 0.37 |
| HSVA by examiner | 0.13 (0.18) | 0.91 | 0.001 | −0.50 (0.45) | −0.40 | 0.27 | |
| HSVA self-test | −0.24 (0.17) | −0.22 | 0.15 | 1.10 (0.43) | 0.93 | 0.01 | |
| F | 156.9 | 0.001 | 11.6 | 0.001 | |||
| R2 | 0.88 | 0.36 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben-Eli, H.; Banin, E.; Levy, J.; Glik, M.; Afriat, S.; Magal, Y.; Harari, R.; Benyamin, A.; Shein, S.; Chowers, I. Development and Evaluation of a New Self-Administered Near Visual Acuity Chart: Accuracy and Feasibility of Usage. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072064
Ben-Eli H, Banin E, Levy J, Glik M, Afriat S, Magal Y, Harari R, Benyamin A, Shein S, Chowers I. Development and Evaluation of a New Self-Administered Near Visual Acuity Chart: Accuracy and Feasibility of Usage. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(7):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072064
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen-Eli, Hadas, Eyal Banin, Jaime Levy, Miryam Glik, Sarah Afriat, Yasmin Magal, Rivka Harari, Aviya Benyamin, Shira Shein, and Itay Chowers. 2024. "Development and Evaluation of a New Self-Administered Near Visual Acuity Chart: Accuracy and Feasibility of Usage" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 7: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072064
APA StyleBen-Eli, H., Banin, E., Levy, J., Glik, M., Afriat, S., Magal, Y., Harari, R., Benyamin, A., Shein, S., & Chowers, I. (2024). Development and Evaluation of a New Self-Administered Near Visual Acuity Chart: Accuracy and Feasibility of Usage. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(7), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072064







