Endothelial Protein C Receptor and Its Impact on Rheumatic Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Endothelial Cell Protein C Receptor
2.1. EPCR Expression and Localisation
2.2. EPCR Function
2.2.1. Regulation of Normal Homeostasis
2.2.2. Regulation of Coagulation
2.2.3. Regulation of Inflammation
2.2.4. Regulation of Stemness
2.3. EPCR Function Mediators
2.3.1. Soluble EPCR
2.3.2. Anti-EPCR Autoantibodies
2.3.3. EPCR Genetic Variants
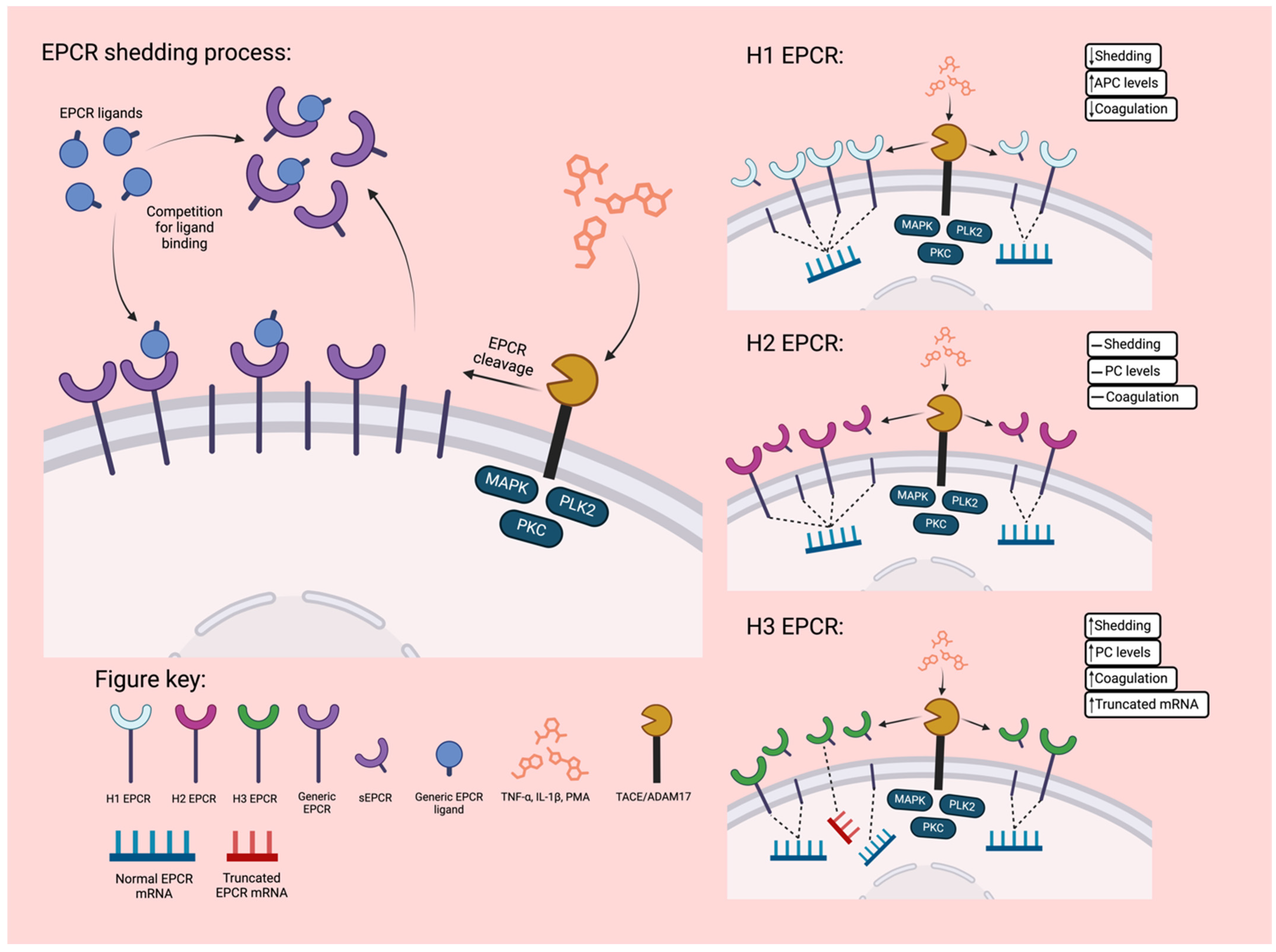
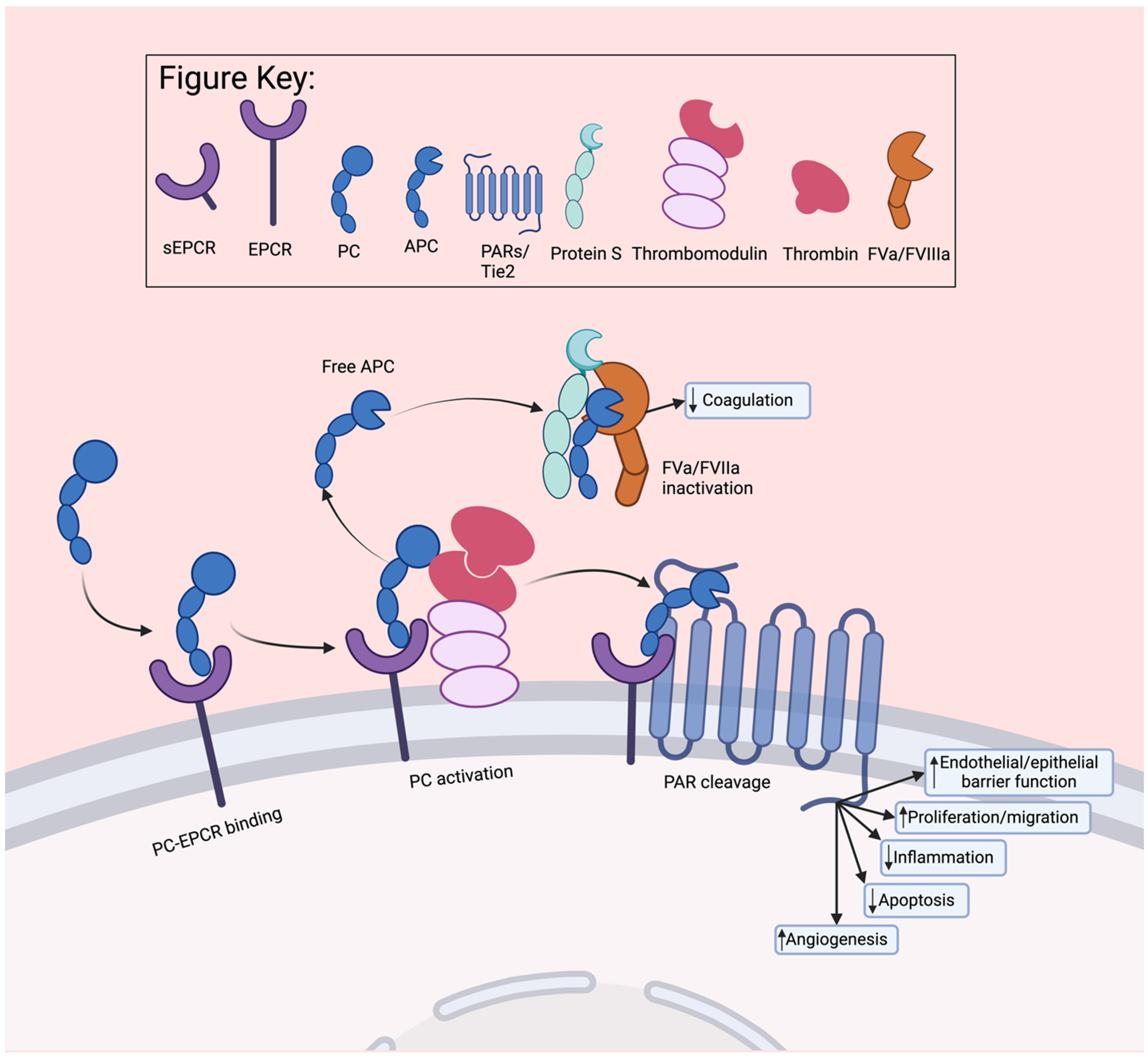
3. EPCR Ligands and Ligand Associated Functions
3.1. Activated Protein C
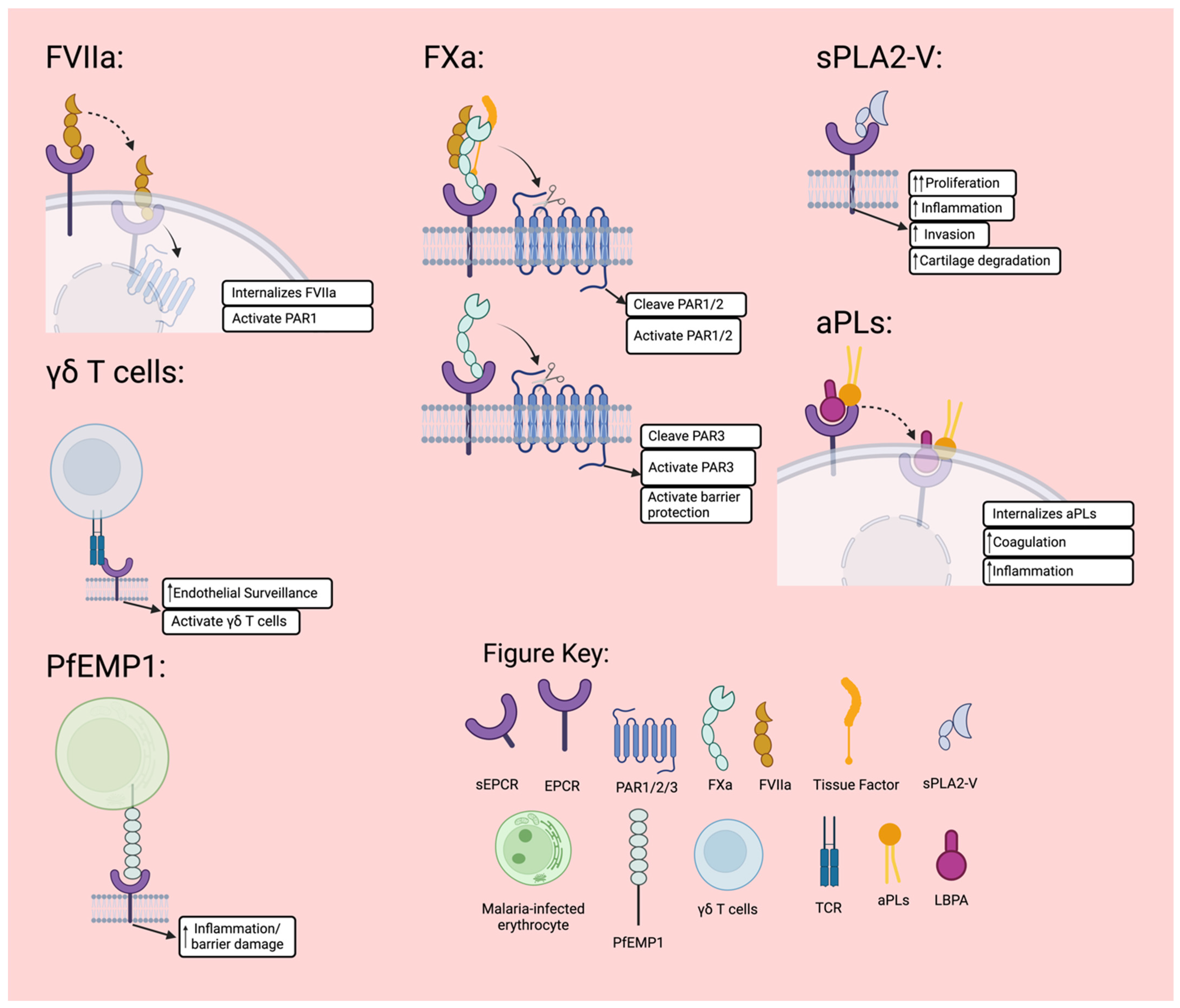
3.2. Factor VII
3.3. Factor X
3.4. γδ T Cells
3.5. Plasmodium Falciparum Erythrocyte Membrane Protein 1 (PfEMP1)
3.6. Secretory Group V Phospholipases A2 (sPLA2V)
3.7. Proteinase-3 (PR3)/Macrophage-1 Antigen (Mac-1)
3.8. Autoantibodies to Phospholipids
4. EPCR in Rheumatic Diseases
4.1. EPCR and RA
4.2. EPCR and SLE
4.3. EPCR and Other Rheumatic Diseases
5. Conclusions
6. Clinical Implications and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esmon, C.T. Structure and functions of the endothelial cell protein C receptor. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, S298–S301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukudome, K.; Esmon, C.T. Identification, cloning, and regulation of a novel endothelial cell protein c activated protein c receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 26486–26491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Rosen, E.D.; Castellino, F.J. Nucleotide structure and characterization of the murine gene encoding the endothelial cell protein C receptor. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 81, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, R.E.; Lane, D.A. Structural and functional implications of the intron/exon organization of the human endothelial cell protein C/activated protein C receptor (EPCR) gene: Comparison with the structure of CD1/major histocompatibility complex alpha1 and alpha2 domains. Blood 1999, 94, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, P.C.; Mather, T.; Oganesyan, N.; Ferrell, G.L.; Esmon, C.T. Identification of the protein C/activated protein C binding sites on the endothelial cell protein C receptor. Implications for a novel mode of ligand recognition by a major histocompatibility complex class 1-type receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8364–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erausquin, E.; Moran-Garrido, M.; Saiz, J.; Barbas, C.; Dichiara-Rodriguez, G.; Urdiciain, A.; Lopez-Sagaseta, J. Identification of a broad lipid repertoire associated to the endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oganesyan, V.; Oganesyan, N.; Terzyan, S.; Qu, D.; Dauter, Z.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. The crystal structure of the endothelial protein C receptor and a bound phospholipid. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 24851–24854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, D.; Moody, D.B. The CD1 size problem: Lipid antigens, ligands, and scaffolds. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukudome, K.; Esmon, C.T. Molecular cloning and expression of murine and bovine endothelial cell protein C/activated protein C receptor (EPCR). The structural and functional conservation in human, bovine, and murine EPCR. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5571–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbarth, K.; Dabaghian, A.R.; Stammer, H.; Werner, D. One single mRNA encodes the centrosomal protein CCD41 and the endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). FEBS Lett. 1999, 458, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbarth, K.; Petzelt, C.; Lu, X.; Todorov, I.T.; Joswig, G.; Pepperkok, R.; Ansorge, W.; Werner, D. cDNA-derived molecular characteristics and antibodies to a new centrosome-associated and G2/M phase-prevalent protein. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104 Pt 1, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukudome, K.; Kurosawa, S.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J.; He, X.; Rezaie, A.R.; Esmon, C.T. The endothelial cell protein C receptor. Cell surface expression and direct ligand binding by the soluble receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17491–17498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laszik, Z.; Mitro, A.; Taylor, F.B., Jr.; Ferrell, G.; Esmon, C.T. Human protein C receptor is present primarily on endothelium of large blood vessels: Implications for the control of the protein C pathway. Circulation 1997, 96, 3633–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, R.C.; Sen, P.; Ghosh, S.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Esmon, C.T.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V. Endothelial cell protein C receptor cellular localization and trafficking: Potential functional implications. Blood 2009, 114, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Fukudome, K.; Tsuneyoshi, N.; Satoh, T.; Tokunaga, O.; Sugawara, K.; Mizokami, H.; Kimoto, M. The endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) functions as a primary receptor for protein C activation on endothelial cells in arteries, veins, and capillaries. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 259, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerschen, E.; Hernandez, I.; Zogg, M.; Jia, S.; Hessner, M.J.; Fernandez, J.A.; Griffin, J.H.; Huettner, C.S.; Castellino, F.J.; Weiler, H. Activated protein C targets CD8+ dendritic cells to reduce the mortality of endotoxemia in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3167–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, E.M.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Preston, R.J. The endothelial cell protein C receptor: Cell surface conductor of cytoprotective coagulation factor signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Campbell, D.; Sambrook, P.N.; Fukudome, K.; Jackson, C.J. Endothelial protein C receptor and protease-activated receptor-1 mediate induction of a wound-healing phenotype in human keratinocytes by activated protein C. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feistritzer, C.; Sturn, D.H.; Kaneider, N.C.; Djanani, A.; Wiedermann, C.J. Endothelial protein C receptor-dependent inhibition of human eosinophil chemotaxis by protein C. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; March, L.; Sambrook, P.N.; Fukudome, K.; Jackson, C.J. Endothelial protein C receptor is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritic (RA) synovium and mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of activated protein C in RA monocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipitsin, M.; Campbell, L.L.; Argani, P.; Weremowicz, S.; Bloushtain-Qimron, N.; Yao, J.; Nikolskaya, T.; Serebryiskaya, T.; Beroukhim, R.; Hu, M.; et al. Molecular definition of breast tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, H.; Arai, F.; Kubota, Y.; Dahl, M.; Suda, T. Endothelial protein C receptor-expressing hematopoietic stem cells reside in the perisinusoidal niche in fetal liver. Blood 2010, 116, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.E.; Li, H.; Shipitsin, M.; Gelman, R.; Polyak, K. Heterogeneity for Stem Cell–Related Markers According to Tumor Subtype and Histologic Stage in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazs, A.B.; Fabian, A.J.; Esmon, C.T.; Mulligan, R.C. Endothelial protein C receptor (CD201) explicitly identifies hematopoietic stem cells in murine bone marrow. Blood 2006, 107, 2317–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, I.; Chagraoui, J.; Lehnertz, B.; MacRae, T.; Mayotte, N.; Tomellini, E.; Aubert, L.; Roux, P.P.; Sauvageau, G. EPCR expression marks UM171-expanded CD34(+) cord blood stem cells. Blood 2017, 129, 3344–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.L.C.; Bode, D.; Kucinski, I.; Cull, A.H.; Bain, F.; Becker, H.J.; Jassinskaja, M.; Barile, M.; Boyd, G.; Belmonte, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of in vitro expanded hematopoietic stem cells. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e55502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.S.; Trumpp, A. Differential expression of endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) in hematopoietic stem and multipotent progenitor cells in young and old mice. Cells Dev. 2023, 174, 203843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Dervish, S.; Chan, B.; Jackson, C.J. The endothelial protein C receptor is a potential stem cell marker for epidermal keratinocytes. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 1786–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.A.; Vatsyayan, R.; Hedner, U.; Esmon, C.T.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V. Endothelial cell protein C receptor-mediated redistribution and tissue-level accumulation of factor VIIa. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 2383–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.C.; Keshava, S.; Esmon, C.T.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V. Rab GTPases regulate endothelial cell protein C receptor-mediated endocytosis and trafficking of factor VIIa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.M.; Crawley, J.T.; Ferrell, G.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. Disruption of the endothelial cell protein C receptor gene in mice causes placental thrombosis and early embryonic lethality. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43335–43343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Gu, J.M.; Ferrell, G.L.; Brady, M.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. Extraembryonic expression of EPCR is essential for embryonic viability. Blood 2005, 106, 2716–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepler, L.; Yu, P.; Dwivedi, D.J.; Trigatti, B.L.; Liaw, P.C. Characterization of mice harboring a variant of EPCR with impaired ability to bind protein C: Novel role of EPCR in hematopoiesis. Blood 2015, 126, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N.; Bondeson, J.; Taylor, P.; Foxwell, B.M.; Brennan, F.M. Cytokine blockade in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2001, 490, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magisetty, J.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Esmon, C.T.; Rao, L.V.M. EPCR deficiency or function-blocking antibody protects against joint bleeding-induced pathology in hemophilia mice. Blood 2020, 135, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Gu, J.; Hunter, J.; Ferrell, G.L.; Lupu, F.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. Overexpressing endothelial cell protein C receptor alters the hemostatic balance and protects mice from endotoxin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ferrell, G.L.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. Non-hematopoietic EPCR regulates the coagulation and inflammatory responses during endotoxemia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondreddy, V.; Keshava, S.; Esmon, C.T.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V.M. A critical role of endothelial cell protein C receptor in the intestinal homeostasis in experimental colitis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, T.; Cruz, D.T.; Martin, J.A.; Castellino, F.J. A cardioprotective role for the endothelial protein C receptor in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in the mouse. Blood 2005, 105, 2364–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, F.B., Jr.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J.; Kurosawa, S.; Ferrell, G.; Chang, A.C.; Laszik, Z.; Kosanke, S.; Peer, G.; Esmon, C.T. The endothelial cell protein C receptor aids in host defense against Escherichia coli sepsis. Blood 2000, 95, 1680–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, Y.; Kondo, T.; Xiao, S.; Yosef, N.; Gaublomme, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Chihara, N.; Regev, A.; Joller, N.; et al. Protein C receptor (PROCR) is a negative regulator of Th17 pathogenicity. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2489–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Cui, L.; Yu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Infliximab modifies regulatory T cells and co-inhibitory receptor expression on circulating T cells in psoriasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kager, L.M.; Schouten, M.; Wiersinga, W.J.; de Boer, J.D.; Lattenist, L.C.; Roelofs, J.J.; Meijers, J.C.; Levi, M.; Dondorp, A.M.; Esmon, C.T.; et al. Overexpression of the endothelial protein C receptor is detrimental during pneumonia-derived gram-negative sepsis (Melioidosis). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, N.; Willcox, C.R.; Beggs, A.; Taniere, P.; Shikotra, A.; Bradding, P.; Adams, R.; Fisher, D.; Middleton, G.; Tselepis, C.; et al. Endothelial protein C receptor is overexpressed in colorectal cancer as a result of amplification and hypomethylation of chromosome 20q. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2017, 3, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, I.; Molina, E.; Luis-Ravelo, D.; Zandueta, C.; Valencia, K.; Ormazabal, C.; Martinez-Canarias, S.; Perurena, N.; Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; et al. Receptor of Activated Protein C Promotes Metastasis and Correlates with Clinical Outcome in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izmirly, P.M.; Barisoni, L.; Buyon, J.P.; Kim, M.Y.; Rivera, T.L.; Schwartzman, J.S.; Weisstuch, J.M.; Liu, D.T.; Bernstein, S.; Tseng, C.E.; et al. Expression of endothelial protein C receptor in cortical peritubular capillaries associates with a poor clinical response in lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshava, S.; Magisetty, J.; Tucker, T.A.; Kujur, W.; Mulik, S.; Esmon, C.T.; Idell, S.; Rao, L.V.M.; Pendurthi, U.R. Endothelial Cell Protein C Receptor Deficiency Attenuates Streptococcus Pneumoniae-induced Pleural Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Calleja, N.; Hollerbach, A.; Royce, J.; Ritter, S.; Pedrosa, D.; Madhusudhan, T.; Teifel, S.; Meineck, M.; Hauser, F.; Canisius, A.; et al. Lipid presentation by the protein C receptor links coagulation with autoimmunity. Science 2021, 371, eabc0956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V.M. Endothelial cell protein C receptor-dependent signaling. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2018, 25, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, D.G.; Copley, M.R.; Benz, C.; Wohrer, S.; Dykstra, B.J.; Ma, E.; Cheyne, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bowie, M.B.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Prospective isolation and molecular characterization of hematopoietic stem cells with durable self-renewal potential. Blood 2009, 113, 6342–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, A.; Talkhoncheh, M.S.; Magnusson, M.; Larsson, J. Endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) expression marks human fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells. Haematologica 2019, 104, e47–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, M.H.; Shi, W.; Ji, L.; Ladewig, E.; Zhang, X.; Srivastava, R.M.; Capistrano, K.J.; Edwards, C.; Malik, I.; Nixon, B.G.; et al. Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages to outcompete endovascular endothelial progenitor cells and suppress tumor neoangiogenesis. Immunity 2023, 56, 2555–2569.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.B.; Dimos, J.T.; Schaniel, C.; Hackney, J.A.; Moore, K.A.; Lemischka, I.R. A Stem Cell Molecular Signature. Science 2002, 298, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanpain, C.; Lowry, W.E.; Geoghegan, A.; Polak, L.; Fuchs, E. Self-renewal, multipotency, and the existence of two cell populations within an epithelial stem cell niche. Cell 2004, 118, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho-Santos, M.; Yoon, S.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Mulligan, R.C.; Melton, D.A. “Stemness”: Transcriptional profiling of embryonic and adult stem cells. Science 2002, 298, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang-Verslues, W.W.; Kuo, W.H.; Chang, P.H.; Pan, C.C.; Wang, H.H.; Tsai, S.T.; Jeng, Y.M.; Shew, J.Y.; Kung, J.T.; Chen, C.H.; et al. Multiple lineages of human breast cancer stem/progenitor cells identified by profiling with stem cell markers. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirino, Y.; Remmers, E.F. Genetic architectures of seropositive and seronegative rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Wang, Y.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. Regulated endothelial protein C receptor shedding is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme/ADAM17. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saposnik, B.; Lesteven, E.; Lokajczyk, A.; Esmon, C.T.; Aiach, M.; Gandrille, S. Alternative mRNA is favored by the A3 haplotype of the EPCR gene PROCR and generates a novel soluble form of EPCR in plasma. Blood 2008, 111, 3442–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, T.; Bae, J.S. Suppressive Effects of Pelargonidin on Endothelial Protein C Receptor Shedding via the Inhibition of TACE Activity and MAP Kinases. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.K.; Han, M.S.; Bae, J.S. Sulforaphane inhibits endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2014, 63, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.K.; Yang, E.J.; Song, K.S.; Bae, J.S. Rosmarinic acid down-regulates endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.K.; Han, M.S.; Park, E.J.; Na, D.H.; Bae, J.S. Exendin-4 inhibits endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 84, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, S.; Bonet, E.; Estellés, A.; Montes, R.; Hermida, J.; Martos, L.; España, F.; Medina, P. The endothelial cell protein C receptor: Its role in thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2011, 128, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, P.C.; Neuenschwander, P.F.; Smirnov, M.D.; Esmon, C.T. Mechanisms by which soluble endothelial cell protein C receptor modulates protein C and activated protein C function. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5447–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Wouwer, M.; Collen, D.; Conway, E.M. Thrombomodulin-protein C-EPCR system: Integrated to regulate coagulation and inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saposnik, B.; Reny, J.L.; Gaussem, P.; Emmerich, J.; Aiach, M.; Gandrille, S. A haplotype of the EPCR gene is associated with increased plasma levels of sEPCR and is a candidate risk factor for thrombosis. Blood 2004, 103, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Tian, L.; Li, M.; Jin, W.; Zhang, H.K.; Zheng, C.F. Relationship between endothelial cell protein C receptor gene 6936A/G polymorphisms and deep venous thrombosis. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J.; Swindle, K.; D’Angelo, A.; Della Valle, P.; Fattorini, A.; Caron, N.; Grimaux, M.; Woodhams, B.; Kurosawa, S. Plasma levels of endothelial protein C receptor respond to anticoagulant treatment. Blood 2002, 99, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, V.; Montes, R.; Gris, J.C.; Bertolaccini, M.L.; Alonso, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Khamashta, M.A.; Fukudome, K.; Lane, D.A.; Hermida, J. Autoantibodies against EPCR are found in antiphospholipid syndrome and are a risk factor for fetal death. Blood 2004, 104, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoh, T.; Shirai, T.; Ishii, T.; Shirota, Y.; Fujishima, F.; Takahashi, F.; Kakuta, Y.; Kanazawa, Y.; Masamune, A.; Saiki, Y.; et al. Identification of two major autoantigens negatively regulating endothelial activation in Takayasu arteritis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, T.; Kakuta, Y.; Fujii, H. Distinct Autoantibodies Against Endothelial Protein C Receptor in Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1724–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hylckama Vlieg, A.; Montes, R.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Hermida, J. Autoantibodies against endothelial protein C receptor and the risk of a first deep vein thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes, R.; Hurtado, V.; Alonso, A.; Foco, L.; Zonzin, P.; Mannucci, P.M.; Hermida, J. Autoantibodies against the endothelial receptor of protein C are associated with acute myocardial infarction in young women. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biguzzi, E.; Merati, G.; Liaw, P.C.; Bucciarelli, P.; Oganesyan, N.; Qu, D.; Gu, J.M.; Fetiveau, R.; Esmon, C.T.; Mannucci, P.M.; et al. A 23bp insertion in the endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) gene impairs EPCR function. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medina, P.; Navarro, S.; Estelles, A.; Vaya, A.; Woodhams, B.; Mira, Y.; Villa, P.; Migaud-Fressart, M.; Ferrando, F.; Aznar, J.; et al. Contribution of polymorphisms in the endothelial protein C receptor gene to soluble endothelial protein C receptor and circulating activated protein C levels, and thrombotic risk. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitte de Willige, S.; Van Marion, V.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Vos, H.L.; de Visser, M.C.; Bertina, R.M. Haplotypes of the EPCR gene, plasma sEPCR levels and the risk of deep venous thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, P.; Navarro, S.; Bonet, E.; Martos, L.; Estellés, A.; Bertina, R.M.; Vos, H.L.; España, F. Functional analysis of two haplotypes of the human endothelial protein C receptor gene. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, L.; Oto, J.; Fernandez-Pardo, A.; Plana, E.; Solmoirago, M.J.; Cana, F.; Hervas, D.; Bonanad, S.; Ferrando, F.; Espana, F.; et al. Increase of Neutrophil Activation Markers in Venous Thrombosis-Contribution of Circulating Activated Protein C. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. The Ser219-->Gly dimorphism of the endothelial protein C receptor contributes to the higher soluble protein levels observed in individuals with the A3 haplotype. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cespedes, J.C.; Hibbert, J.; Krishna, S.; Yan, F.; Bharti, P.K.; Stiles, J.K.; Liu, M. Association of EPCR Polymorphism rs867186-GG With Severity of Human Malaria. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, K.; Cushman, M.; Heckbert, S.R.; Tsai, M.Y.; Folsom, A.R. Lack of association of soluble endothelial protein C receptor and PROCR 6936A/G polymorphism with the risk of venous thromboembolism in a prospective study. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, X.X.; Geng, H.Y.; Gong, G.; Kim, H.J. EPCR Gene Ser219Gly Polymorphism and Venous Thromboembolism: A Meta-Analysis of 9,494 Subjects. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoheir, N.; Eldanasouri, N.; Abdel-Aal, A.A.; Hosny, K.A.; Abdel-Ghany, W.M. Endothelial cell protein C receptor gene 6936A/G and 4678G/C polymorphisms as risk factors for deep venous thrombosis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2016, 27, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, S.; Medina, P.; Mira, Y.; Estelles, A.; Villa, P.; Ferrando, F.; Vaya, A.; Bertina, R.M.; Espana, F. Haplotypes of the EPCR gene, prothrombin levels, and the risk of venous thrombosis in carriers of the prothrombin G20210A mutation. Haematologica 2008, 93, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cochery-Nouvellon, E.; Chauleur, C.; Demattei, C.; Mercier, E.; Fabbro-Peray, P.; Mares, P.; Mismetti, P.; Lissalde-Lavigne, G.; Gris, J.C. The A6936G polymorphism of the endothelial protein C receptor gene is associated with the risk of unexplained foetal loss in Mediterranean European couples. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavigne-Lissalde, G.; Cochery-Nouvellon, E.; Mercier, E.; Marès, P.; Gris, J.C. High plasma levels of endothelial protein C receptor are associated with the risk of unexplained fetal death. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Basu, S.; Kong, X.; Pankow, J.S.; Aleksic, N.; Tan, A.; Cushman, M.; Boerwinkle, E.; Folsom, A.R. Genome-wide association study identifies novel loci for plasma levels of protein C: The ARIC study. Blood 2010, 116, 5032–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, A.P.; Carty, C.L.; Jenny, N.S.; Nievergelt, C.; Cushman, M.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J.; Kurosawa, S.; Kuller, L.H.; Lange, L.A. PROC, PROCR and PROS1 polymorphisms, plasma anticoagulant phenotypes, and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in older adults: The Cardiovascular Health Study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.L.; Chen, M.H.; Dehghan, A.; Strachan, D.P.; Basu, S.; Soranzo, N.; Hayward, C.; Rudan, I.; Sabater-Lleal, M.; Bis, J.C.; et al. Novel associations of multiple genetic loci with plasma levels of factor VII, factor VIII, and von Willebrand factor: The CHARGE (Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genome Epidemiology) Consortium. Circulation 2010, 121, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunke, F.; Rose-John, S. The shedding protease ADAM17: Physiology and pathophysiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J. Endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) is constitutively translocated into the nucleus and also mediates activated protein C, but not protein C, nuclear translocation. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 114, 652a. [Google Scholar]
- Gavlovsky, P.J.; Tonnerre, P.; Guitton, C.; Charreau, B. Expression of MHC class I-related molecules MICA, HLA-E and EPCR shape endothelial cells with unique functions in innate and adaptive immunity. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlback, B. Advances in understanding pathogenic mechanisms of thrombophilic disorders. Blood 2008, 112, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, J.; Johnson, C.Y.; Adediran, A.S.; de Andrade, M.; Heit, J.A.; Morange, P.E.; Tregouet, D.A.; Gagnon, F. The endothelial protein C receptor (PROCR) Ser219Gly variant and risk of common thrombotic disorders: A HuGE review and meta-analysis of evidence from observational studies. Blood 2012, 119, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J.; Kurosawa, S.; Mollica, J.S.; Ferrell, G.L.; Esmon, C.T. The endothelial cell protein C receptor augments protein C activation by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. PNAS 1996, 93, 10212–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.M.; Fukudome, K.; Esmon, C.T. Characterization and regulation of the 5’-flanking region of the murine endothelial protein C receptor gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12481–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshava, S.; Sundaram, J.; Rajulapati, A.; Esmon, C.; Pendurthi, U.; Rao, L.V.M. Factor VIIa interaction with EPCR modulates the hemostatic effect of rFVIIa in hemophilia therapy: Mode of its action. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwens, E.A.; Stavenuiter, F.; Mosnier, L.O. Mechanisms of anticoagulant and cytoprotective actions of the protein C pathway. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11 (Suppl. S1), 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, S.R. Protease-activated receptors in hemostasis, thrombosis and vascular biology. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riewald, M.; Petrovan, R.J.; Donner, A.; Mueller, B.M.; Ruf, W. Activation of endothelial cell protease activated receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1880–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.V.; Ardeshirylajimi, A.; Dinarvand, P.; Yang, L.; Rezaie, A.R. Occupancy of human EPCR by protein C induces beta-arrestin-2 biased PAR1 signaling by both APC and thrombin. Blood 2016, 128, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlback, B.; Villoutreix, B.O. Regulation of blood coagulation by the protein C anticoagulant pathway: Novel insights into structure-function relationships and molecular recognition. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosnier, L.O.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Griffin, J.H. The cytoprotective protein C pathway. Blood 2007, 109, 3161–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.H.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Mosnier, L.O. Protein C anticoagulant and cytoprotective pathways. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnier, L.; Mosnier, L.O. Novel mechanisms for activated protein C cytoprotective activities involving noncanonical activation of protease-activated receptor 3. Blood 2013, 122, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, L.D.; Puy, C.; Fernandez, J.A.; Mitrugno, A.; Keshari, R.S.; Taku, N.A.; Chu, T.T.; Xu, X.; Gruber, A.; Lupu, F.; et al. Activated protein C inhibits neutrophil extracellular trap formation in vitro and activation in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8616–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Dervish, S.; Harrison, L.C.; Fulcher, G.; Jackson, C.J. Activated protein C inhibits pancreatic islet inflammation, stimulates T regulatory cells and prevents diabetes in NOD mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16356–16364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Dervish, S.; McKelvey, K.J.; March, L.; Wang, F.; Little, C.B.; Jackson, C.J. Activated protein C targets immune cells and rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts to prevent inflammatory arthritis in mice. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtnekert, J.; Rupanagudi, K.V.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Darisipudi, M.N.; Allam, R.; Anders, H.J. Activated protein C attenuates systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sagaseta, J.; Montes, R.; Puy, C.; Diez, N.; Fukudome, K.; Hermida, J. Binding of factor VIIa to the endothelial cell protein C receptor reduces its coagulant activity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.S.; Yang, L.; Manithody, C.; Rezaie, A.R. The ligand occupancy of endothelial protein C receptor switches the protease-activated receptor 1-dependent signaling specificity of thrombin from a permeability-enhancing to a barrier-protective response in endothelial cells. Blood 2007, 110, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondreddy, V.; Wang, J.; Keshava, S.; Esmon, C.T.; Rao, L.V.M.; Pendurthi, U.R. Factor VIIa induces anti-inflammatory signaling via EPCR and PAR1. Blood 2018, 131, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Kothari, H.; Keshava, S.; Clark, C.A.; Esmon, C.T.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V. Factor VIIa bound to endothelial cell protein C receptor activates protease activated receptor-1 and mediates cell signaling and barrier protection. Blood 2011, 117, 3199–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuepbach, R.A.; Riewald, M. Coagulation factor Xa cleaves protease-activated receptor-1 and mediates signaling dependent on binding to the endothelial protein C receptor. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disse, J.; Petersen, H.H.; Larsen, K.S.; Persson, E.; Esmon, N.; Esmon, C.T.; Teyton, L.; Petersen, L.C.; Ruf, W. The endothelial protein C receptor supports tissue factor ternary coagulation initiation complex signaling through protease-activated receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5756–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.P.; Kerschen, E.J.; Hernandez, I.; Basu, S.; Zogg, M.; Botros, F.; Jia, S.; Hessner, M.J.; Griffin, J.H.; Ruf, W.; et al. EPCR-dependent PAR2 activation by the blood coagulation initiation complex regulates LPS-triggered interferon responses in mice. Blood 2015, 125, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wu, S.; Yu, J.; Yu, L.; Sun, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; et al. FVIIa prevents the progressive hemorrhaging of a brain contusion by protecting microvessels via formation of the TF-FVIIa-FXa complex. Neuroscience 2017, 348, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavenuiter, F.; Mosnier, L.O. Noncanonical PAR3 activation by factor Xa identifies a novel pathway for Tie2 activation and stabilization of vascular integrity. Blood 2014, 124, 3480–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Meyer, C.; Bonneville, M. γδ T cells: First line of defense and beyond. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 121–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.X.; Yin, S.S.; Chen, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.X.; Zhao, L.D.; Fei, Y.Y.; Yang, H.X.; Guo, J.B.; Mao, Y.J.; et al. Chemotaxis of Vdelta2 T cells to the joints contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcox, C.R.; Pitard, V.; Netzer, S.; Couzi, L.; Salim, M.; Silberzahn, T.; Moreau, J.F.; Hayday, A.C.; Willcox, B.E.; Dechanet-Merville, J. Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress surveillance by binding of a human gammadelta T cell antigen receptor to endothelial protein C receptor. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witherden, D.A.; Havran, W.L. EPCR: A stress trigger for gammadelta T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, L.; Lavstsen, T.; Berger, S.S.; Wang, C.W.; Petersen, J.E.; Avril, M.; Brazier, A.J.; Freeth, J.; Jespersen, J.S.; Nielsen, M.A.; et al. Severe malaria is associated with parasite binding to endothelial protein C receptor. Nature 2013, 498, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, E.; Hanisch, B.; Opoka, R.O.; Lavstsen, T.; John, C.C. Plasmodium falciparum EPCR-binding PfEMP1 expression increases with malaria disease severity and is elevated in retinopathy negative cerebral malaria. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait-Oufella, H.; Mallat, Z.; Tedgui, A. Lp-PLA2 and sPLA2: Cardiovascular biomarkers. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 526–531. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Sagaseta, J.; Puy, C.; Tamayo, I.; Allende, M.; Cervero, J.; Velasco, S.E.; Esmon, C.T.; Montes, R.; Hermida, J. sPLA2-V inhibits EPCR anticoagulant and antiapoptotic properties by accommodating lysophosphatidylcholine or PAF in the hydrophobic groove. Blood 2012, 119, 2914–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tamayo, I.; Velasco, S.E.; Puy, C.; Esmon, C.T.; Dichiara, M.G.; Montes, R.; Hermida, J. Group V secretory phospholipase A2 impairs endothelial protein C receptor-dependent protein C activation and accelerates thrombosis in vivo. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Shen, K.; McKelvey, K.; Li, J.; Chan, Y.K.; Hatzis, V.; March, L.; Little, C.B.; Tonkin, M.; Jackson, C.J. Endothelial protein C receptor associated invasiveness of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts is likely driven by group V secretory phospholipase A2. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, B.; Kuhl, A.; Bayat, B.; Santoso, S.; Jenne, D.E. A hydrophobic patch on proteinase 3, the target of autoantibodies in Wegener granulomatosis, mediates membrane binding via NB1 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35976–35982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, G.A.; Zarella, C.S.; Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd; Rudolph, E.H.; Yang, J.J.; Sekura, S.B.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Novel effects of neutrophil-derived proteinase 3 and elastase on the vascular endothelium involve in vivo cleavage of NF-kappaB and proapoptotic changes in JNK, ERK, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2840–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bruner, B.F.; Vista, E.S.; Wynn, D.M.; Harley, J.B.; James, J.A. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies target sequential functional proteinase 3 epitopes in the sera of patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 162, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan Rao, L.V.; Esmon, C.T.; Pendurthi, U.R. Endothelial cell protein C receptor: A multiliganded and multifunctional receptor. Blood 2014, 124, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosawa, S.; Esmon, C.T.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J. The soluble endothelial protein C receptor binds to activated neutrophils: Involvement of proteinase-3 and CD11b/CD18. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 4697–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas-Mendez, A.; Montes, R.; Ambrose, L.R.; Warrens, A.N.; Laffan, M.; Lane, D.A. Proteolysis of the endothelial cell protein C receptor by neutrophil proteinase 3. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, K.; Busch, H.J.; Bourgeois, N.; Schwarz, M.; Wolf, D.; Zirlik, A.; Peter, K.; Bode, C.; von Zur Muhlen, C. Mac-1 directly binds to the endothelial protein C-receptor: A link between the protein C anticoagulant pathway and inflammation? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.Q. The pivotal role of endothelial protein C receptor for antiphospholipid antibody-mediated pathologies. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 883–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforti, A.; Di Cola, I.; Pavlych, V.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Ursini, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Cipriani, P. Beyond the joints, the extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartok, B.; Firestein, G.S. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, L.J.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophils in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Breaking Immune Tolerance and Fueling Disease. Trends. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, S.; Hoff, M.; Brown, M.A.; Hveem, K.; Videm, V. Comparison of methods to construct a genetic risk score for prediction of rheumatoid arthritis in the population-based Nord-Trondelag Health Study, Norway. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Koeller, M.; Weisman, M.H.; Emery, P. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2007, 370, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Kwon, E.J.; Lee, J.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, F.; Maurits, M.P.; van Boheemen, L.; Verstappen, M.; Mankia, K.; Matthijssen, X.M.E.; Dorjee, A.L.; Emery, P.; Knevel, R.; van Schaardenburg, D.; et al. Determining in which pre-arthritis stage HLA-shared epitope alleles and smoking exert their effect on the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; March, L.; Sambrook, P.N.; Jackson, C.J. Differential regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and matrix metalloproteinase 9 by activated protein C: Relevance to inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis. Rheum. 2007, 56, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Liu, W.; Guo, P.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Pang, C.; Zhang, W.; Yin, F.; Wang, Y. Elevated levels of soluble Endothelial protein C receptor in rheumatoid arthritis and block the therapeutic effect of protein C in collagen-induced arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Lin, H.; Liang, H.; Bereza-Malcolm, L.; Lynch, T.; Sinnathurai, P.; Weiler, H.; Jackson, C.; March, L. EPCR deficiency ameliorates inflammatory arthritis in mice via suppressing the activation and migration of T cells and dendritic cells. Rheumatology 2023, 63, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.F.; Yang, C.Y.; Chao, S.C.; Li, J.S.; Weng, T.H.; Lei, H.Y. Distribution of double-negative (CD4- CD8-, DN) T subsets in blood and synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 1999, 18, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, J.L.; Trujillo, A.; Alonso, J.M.; Mulero, J.; Martinez, C. Selective expansion of T cells bearing the gamma/delta receptor and expressing an unusual repertoire in the synovial membrane of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis. Rheum. 1991, 34, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Yin, F.; Pang, C.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L. Endothelial cell protein C receptor regulates neutrophil extracellular trap-mediated rheumatoid arthritis disease progression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 112, 109249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chang, C.; Lu, Q. The Epigenetics of Lupus Erythematosus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1253, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koarada, S.; Tsuneyoshi, N.; Haruta, Y.; Tada, Y.; Mitamura, M.; Inoue, H.; Ohta, A.; Fukudome, K.; Nagasawa, K. Effect of disease activity and corticosteroids on serum levels of soluble endothelial cell protein C receptor in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod. Rheumatol. 2009, 19, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosawa, S.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J.; Carson, C.W.; D’Angelo, A.; Della Valle, P.; Esmon, C.T. Plasma levels of endothelial cell protein C receptor are elevated in patients with sepsis and systemic lupus erythematosus: Lack of correlation with thrombomodulin suggests involvement of different pathological processes. Blood 1998, 91, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, S.; Dai, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Li, X. Detection of soluble endothelial protein C receptor (sEPCR) in patients with CHD, DM and SLE. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2000, 21, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leibovich, S.J. Vasculopathy and renal injury in lupus erythematosus: Does shedding of the endothelial protein C receptor play a role? Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesin, C.A.; Yin, X.; Esmon, C.T.; Buyon, J.P.; Clancy, R.M. Shedding of endothelial protein C receptor contributes to vasculopathy and renal injury in lupus: In vivo and in vitro evidence. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Asmaa, A.; Nadia, A.; Hebatallah, A.; Rana, A.; Nadia, G.; Nesrine, A. Soluble and membranous endothelial protein C receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: Relation to nephritis. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2019, 41, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Saigusa, R.; Asano, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Miyagaki, T.; Sugaya, M.; et al. Fli1 deficiency contributes to the downregulation of endothelial protein C receptor in systemic sclerosis: A possible role in prothrombotic conditions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Chang, S.J.; Tsai, W.C.; Ou, T.T.; Wu, C.C.; Sung, W.Y.; Hsieh, M.C.; Yen, J.H. Increased incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in multiple sclerosis: A nationwide cohort study. Medicine 2016, 95, e3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festoff, B.W.; Li, C.; Woodhams, B.; Lynch, S. Soluble thrombomodulin levels in plasma of multiple sclerosis patients and their implication. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 323, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Hehir, Z.D.; Lynch, T.; O’Neill, S.; March, L.; Xue, M. Endothelial Protein C Receptor and Its Impact on Rheumatic Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072030
O’Hehir ZD, Lynch T, O’Neill S, March L, Xue M. Endothelial Protein C Receptor and Its Impact on Rheumatic Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(7):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072030
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Hehir, Zachary Daniel, Tom Lynch, Sean O’Neill, Lyn March, and Meilang Xue. 2024. "Endothelial Protein C Receptor and Its Impact on Rheumatic Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 7: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072030
APA StyleO’Hehir, Z. D., Lynch, T., O’Neill, S., March, L., & Xue, M. (2024). Endothelial Protein C Receptor and Its Impact on Rheumatic Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(7), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072030





