Evaluating Community-Based Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: Effectiveness, Safety, and Feasibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demography
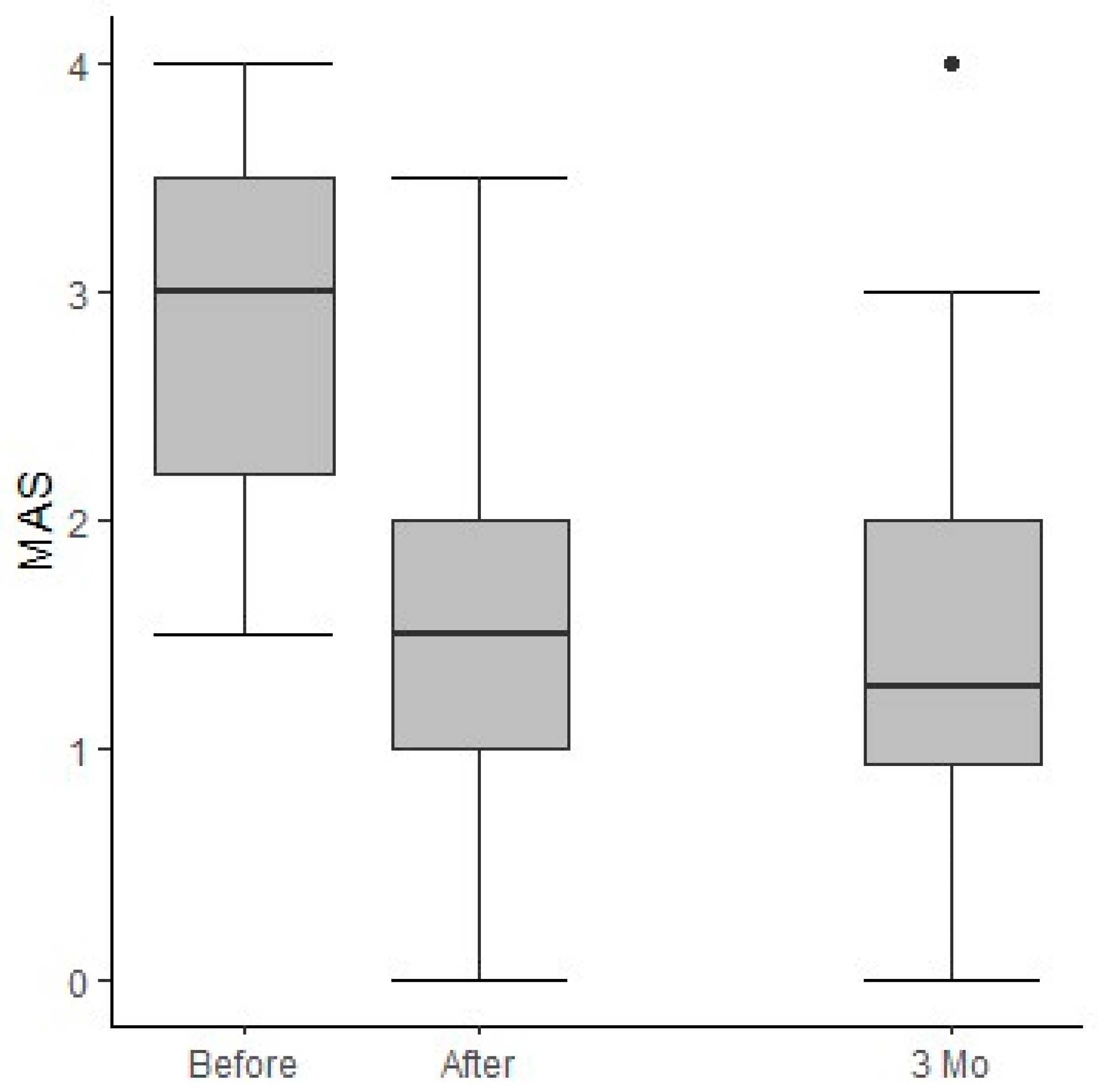
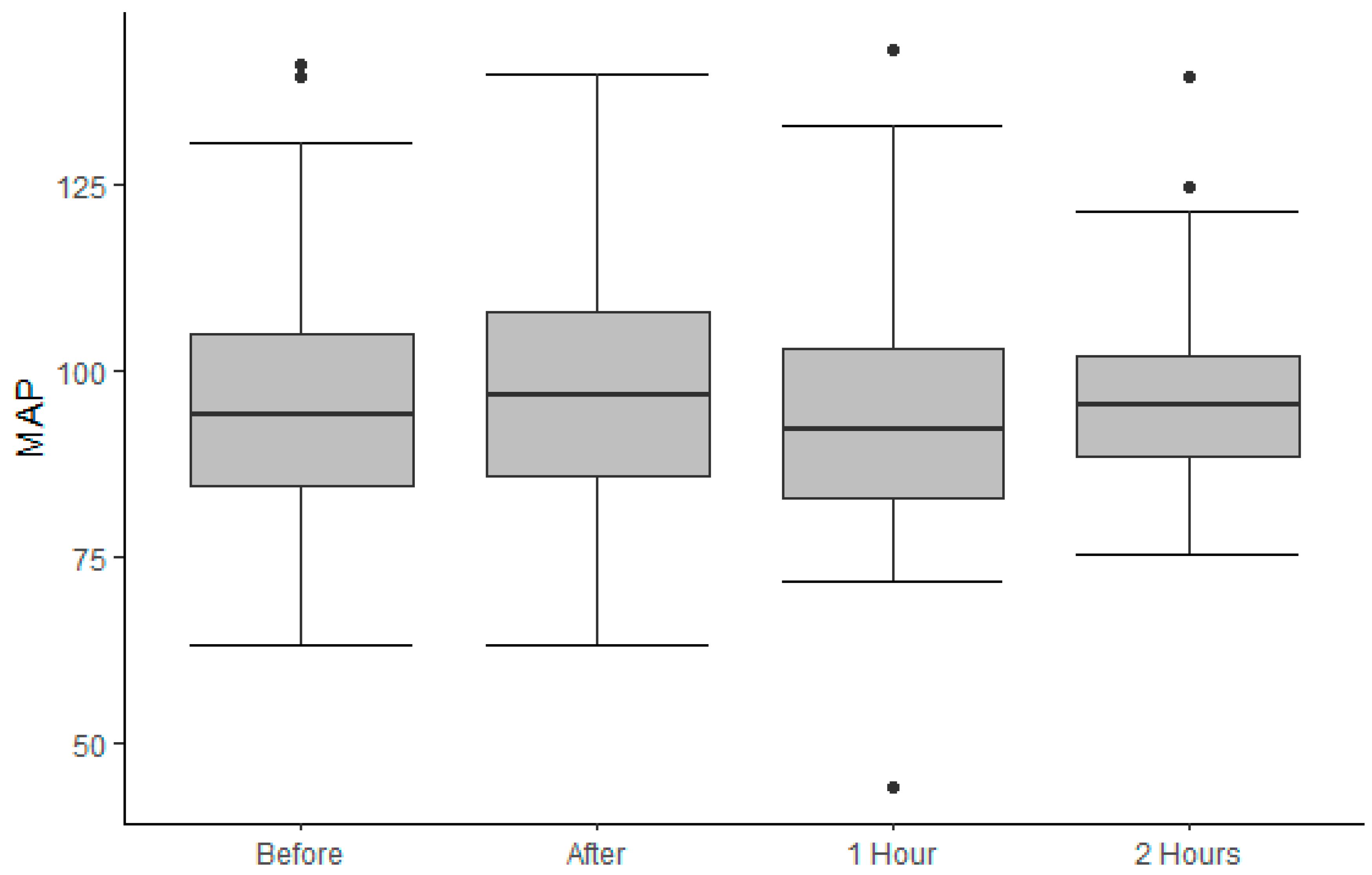
3.2. Outcomes
Feasibility
3.3. Treatment Goals
3.4. Safety
AEs and Severe AEs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Adverse event |
| BI | Traumatic brain injuries |
| CP | Cerebral palsy |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| ITB | Intrathecal baclofen |
| LP | Lumbar puncture |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| MAS | Modified Ashworth Scale |
| Mcg | Micrograms |
| mmHG | Millimeter of mercury |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| NH | Nursing home |
| NP | Nurse practitioner |
| PDPH | Post-dural puncture headache |
| SAE | Serious adverse event |
| Sec | Seconds |
References
- Martin, A.; Abogunrin, S.; Kurth, H.; Dinet, J. Epidemiological, humanistic, and economic burden of illness of lower limb spasticity in adults: A systematic review. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Opheim, A.; Danielsson, A.; Alt Murphy, M.; Persson, H.C.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Upper-limb spasticity during the first year after stroke: Stroke arm longitudinal study at the University of Gothenburg. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 93, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissel, J.; Manack, A.; Brainin, M. Toward an epidemiology of poststroke spasticity. Neurology 2013, 80, S13–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtz, K.A.; Lipson, R.; Noonan, V.K.; Kwon, B.K.; Mills, P.B. Prevalence and Effect of Problematic Spasticity After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo-Parker, F.J.; Adkinson, J.M. Common Etiologies of Upper Extremity Spasticity. Hand Clin. 2018, 34, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinares, D.M.; Gater, D.R.; Daniel, S.; Pontee, N.L. Nontraumatic Spinal Cord Injury: Epidemiology, Etiology and Management. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, R.; Wolswijk, A.; Eijsden, H.V. Prevalence, impact and treatment of spasticity in nursing home patients with central nervous system disorders: A cross-sectional study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbett, J.; Widerström-Noga, E.G.; Thomas, C.K.; Field-Fote, E.C. Impact of spasticity on transfers and activities of daily living in individuals with spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2019, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, V.L. Intrathecal baclofen in multiple sclerosis. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72 (Suppl. S1), 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.P.; Marsden, J. The management of spasticity in adults. BMJ 2014, 349, g47372014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertzgaard, P.; Campo, C.; Calabrese, A. Efficacy and safety of oral baclofen in the management of spasticity: A rationale for intrathecal baclofen. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakheit, A.M. The pharmacological management of post-stroke muscle spasticity. Drugs Aging 2012, 29, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.K.; Lee, K.C.; Cho, H.E.; Chae, M.; Chang, J.W.; Chang, W.S.; Cho, S.R. Outcomes of intrathecal baclofen therapy in patients with cerebral palsy and acquired brain injury. Medicine 2017, 96, e7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creamer, M.; Cloud, G.; Kossmehl, P.; Yochelson, M.; Francisco, G.E.; Ward, A.B.; Wissel, J.; Zampolini, M.; Abouihia, A.; Berthuy, N.; et al. Intrathecal baclofen therapy versus conventional medical management for severe poststroke spasticity: Results from a multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label trial (SISTERS). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, A.; Gudesblatt, M.; Bethoux, F.; Bennett, S.E.; Koelbel, S.; Plunkett, R.; Sadiq, S.; Stevenson, V.L.; Thomas, A.M.; Tornatore, C.; et al. Intrathecal baclofen in multiple sclerosis: Too little, too late? Mult. Scler. 2011, 17, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, S.N.; Chu, S.K.; McCormick, Z.; Chang Chien, G.C.; Marciniak, C.M. Long-term intrathecal baclofen: Outcomes after more than 10 years of treatment. PM&R 2014, 6, 506–513.e501. [Google Scholar]
- Goslinga-van der Gaag, S.M.E.; Delhaas, E.M.; Frankema, S.P.G.; Huygen, F. Efficiency and Safety of Aftercare with Intrathecal Baclofen on Location. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, A.; Mays, R.; Mehta, S.; Janzen, S.; Townson, A.; Hsieh, J.; Wolfe, D.; Teasell, R. Examining the effectiveness of intrathecal baclofen on spasticity in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury: A systematic review. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2014, 37, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, R.N.; Kurrek, M.M. Special announcement: Guidelines to the Practice of Anesthesia, Revised Edition 2014. Can. J. Anaesth. 2014, 61, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, B.C.; Morris, A.R. Modified Ashworth scale reliability for measurement of lower extremity spasticity among patients with SCI. Spinal Cord. 2010, 48, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boster, A.L.; Bennett, S.E.; Bilsky, G.S.; Gudesblatt, M.; Koelbel, S.F.; McManus, M.; Saulino, M. Best Practices for Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: Screening Test. Neuromodulation 2016, 19, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, K.B.; Cheng, N.; Hansen, R.A. Serious Adverse Drug Events Reported to the FDA: Analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System 2006-2014 Database. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2018, 24, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, M.; D’Oria, S.; Nero, V.V.; Squillante, E.; Gentile, M.; Rotondo, M. Long-term effects of intrathecal baclofen in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 143, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulino, M.; Anderson, D.J.; Doble, J.; Farid, R.; Gul, F.; Konrad, P.; Boster, A.L. Best Practices for Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: Troubleshooting. Neuromodulation 2016, 19, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulino, M.; Guillemette, S.; Leier, J.; Hinnenthal, J. Medical cost impact of intrathecal baclofen therapy for severe spasticity. Neuromodulation 2015, 18, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendran, R.C.; Duarte, R.V.; Valyi, A.; Eldabe, S. The need for and provision of intrathecal baclofen therapy for the management of spasticity in England: An assessment of the Hospital Episode Statistics database. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e0075172015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Referred Population | Eligible for ITB Trial | |
|---|---|---|
| n = 102 | n = 89 | |
| Gender | ||
| Sex, male n (%) | 64 (63.0%) | 59 (66.3%) |
| Age, median (IQR) | 51 (39–60) | 51 (39–59) |
| Care institution | ||
| Nursing home | 76 (77.2%) | |
| Disability communities | 26 (26.5%) | |
| Disease | ||
| Multiple sclerosis | 36 (35.3%) | 31 (34.8%) |
| Cerebral palsy | 20 (19.6%) | 16 (18.0%) |
| Brain injury | 19 (18.6%) | 19 (21.3%) |
| Spinal cord lesion | 9 (8.8%) | 6 (6.7%) |
| Stroke | 9 (8.8%) | 8 (9.0%) |
| Others | 9 (8.8%) | 9 (10.0%) |
| ITB Trial | Post-Operation | 3-Month Follow-Up | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient total | n = 80 | n = 67 | n = 55 |
| Patients with (S)AEs | n = 4 (5%) | n = 26 (38.8%) | n = 8 (14.5%) |
| Number of complications | 4 | 32 | 8 |
| Procedure-related | 2/4 | 15/32 | 3/8 |
| PDPH | 1 | 6 | |
| Constipation | 3 | ||
| Pocket pain | 1 | ||
| Radiating pain | 1 | ||
| Hematoma pocket | 1 | ||
| Perforation of intrathecal catheter skin | 1 | ||
| Blisters due to band aid | 1 | ||
| Pressure ulcers | 2 | ||
| No effect on spasticity | 2 | ||
| Incorrect programming (concentration of baclofen) | 1 | ||
| Drug-related | 2/4 | 11/32 | 1/8 |
| Cotton-ball feeling in head | 1 | ||
| Loss of strength | 2 | 1 | |
| Urinary retention | 2 | ||
| Somnolence | 5 | ||
| Nausea/emesis | 1 | 2 | |
| Patient-related | 0/4 | 6/32 | 4/8 |
| Autonomic dysregulation | 1 | ||
| Urinary catheter blockage | 1 | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 1 | ||
| Hypercalcemia | 1 | ||
| Urinary tract infection | 1 | ||
| SARS-CoV-2 infection | 2 | ||
| Pneumonia | 2 | ||
| Unclarified increased C-reactive protein (CRP) level | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van der Gaag, S.M.E.; Frankema, S.P.G.; van der Ploeg, E.S.; Baart, S.J.; Huygen, F.J.M.P. Evaluating Community-Based Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: Effectiveness, Safety, and Feasibility. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071840
van der Gaag SME, Frankema SPG, van der Ploeg ES, Baart SJ, Huygen FJMP. Evaluating Community-Based Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: Effectiveness, Safety, and Feasibility. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(7):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071840
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan der Gaag, Simone M. E., Sander P. G. Frankema, Eva S. van der Ploeg, Sara J. Baart, and Frank J. M. P. Huygen. 2024. "Evaluating Community-Based Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: Effectiveness, Safety, and Feasibility" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 7: 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071840
APA Stylevan der Gaag, S. M. E., Frankema, S. P. G., van der Ploeg, E. S., Baart, S. J., & Huygen, F. J. M. P. (2024). Evaluating Community-Based Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: Effectiveness, Safety, and Feasibility. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(7), 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071840





