No Harmful Effect of Endovascular Treatment before Decompressive Surgery—Implications for Handling Patients with Space-Occupying Brain Infarction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
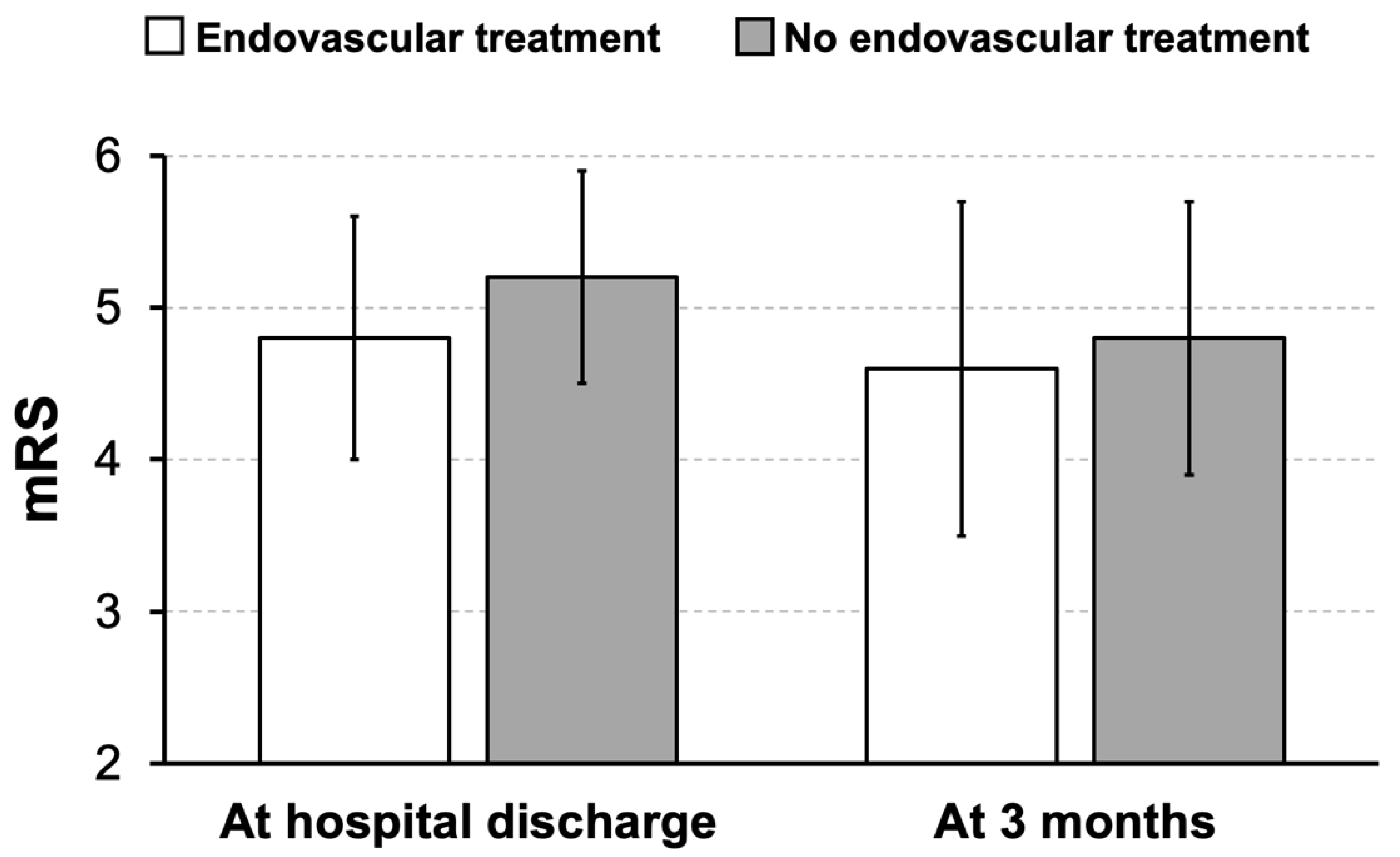
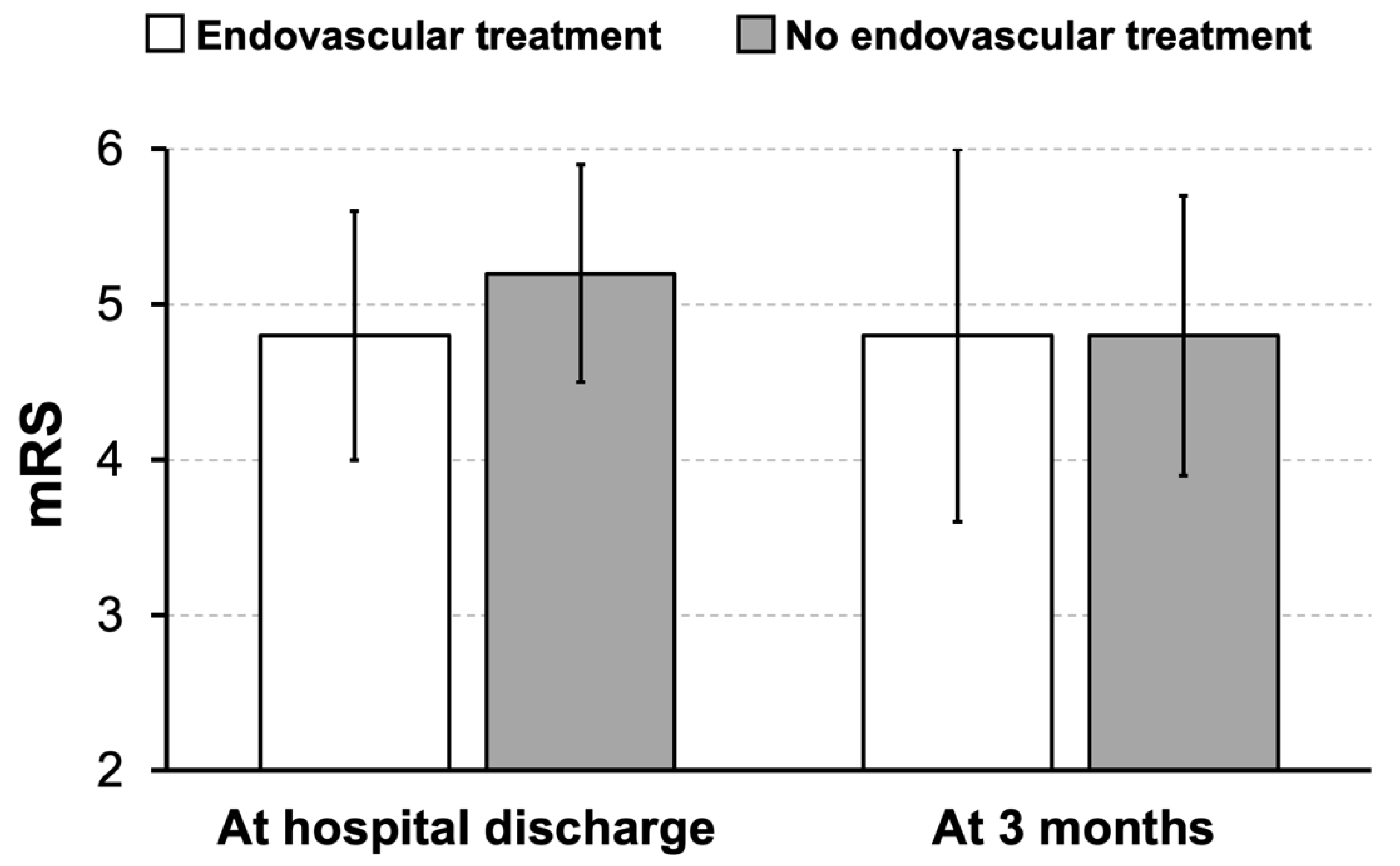
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hacke, W.; Schwab, S.; Horn, M.; Spranger, M.; De Georgia, M.; Von Kummer, R. ‘Malignant’ middle cerebral artery territory infarction: Clinical course and prognostic signs. Arch. Neurol. 1996, 53, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, H.B.; Schwab, S. Malignant middle cerebral artery infarction: Clinical characteristics, treatment strategies, and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, H.; Jüttler, E. Hemicraniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction: Current status and future directions. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, K.; Hofmeijer, J.; Juettler, E.; Vicaut, E.; George, B.; Algra, A.; Amelink, G.J.; Schmiedeck, P.; Schwab, S.; Rothwell, P.M.; et al. Early decompressive surgery in malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery: A pooled analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badhiwala, J.H.; Nassiri, F.; Alhazzani, W.; Selim, M.H.; Farrokhyar, F.; Spears, J.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Singh, S.; Alqahtani, A.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. Endovascular Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-analysis. JAMA 2015, 314, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; Van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dávalos, A.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; Van Der Lugt, A.; De Miquel, M.A.; et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016, 387, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Sakai, N.; Yamagami, H.; Uchida, K.; Beppu, M.; Toyoda, K.; Matsumaru, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kimura, K.; Takeuchi, M.; et al. Endovascular Therapy for Acute Stroke with a Large Ischemic Region. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Ma, G.; Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Nguyen, T.N.; Yuan, G.; Han, H.; Chen, W.; Wei, M.; et al. Trial of Endovascular Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke with Large Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarraj, A.; Hassan, A.E.; Abraham, M.G.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Kasner, S.E.; Hussain, M.S.; Chen, M.; Blackburn, S.; Sitton, C.W.; Churilov, L.; et al. Trial of Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large Ischemic Strokes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, H.; For the IGNITE-study group; Schönenberger, S.; Niesen, W.-D.; Seide, S.; Meyne, J.; Gerner, S.T.; Vollmuth, C.; Beck, C.; Meckel, S.; et al. Endovascular stroke treatment’s impact on malignant type of edema (ESTIMATE). J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabben, C.; Desilles, J.; Charbonneau, F.; Savatovsky, J.; Morvan, E.; Obadia, A.; Raynouard, I.; Fela, F.; Escalard, S.; Redjem, H.; et al. Early successful reperfusion after endovascular therapy reduces malignant middle cerebral artery infarction occurrence in young patients with large diffusion-weighted imaging lesions. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Haussen, D.C.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Jovin, T.G.; Gupta, R.; Saver, J.L.; Jadhav, A.P.; Budzik, R.F.; Baxter, B.; Krajina, A.; et al. Clinical effectiveness of endovascular stroke treatment in the early and extended time windows. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchtouris, N.; Al Saiegh, F.; Baldassari, M.P.; Velagapudi, L.; Khanna, O.; Hafazalla, K.; Nauheim, D.; Sweid, A.; Romo, V.; Gooch, M.R.; et al. Decompressive Hemicraniectomy in the Modern Era of Mechanical Thrombectomy. World Neurosurg. 2021, 156, e77–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, P.B.; Minnerup, J.; Warneke, N.; Dziewas, R.; Hanning, U.; Berkemeyer, S.; Zoubi, T.; Heindel, W.; Schwindt, W.; Niederstadt, T. Impact of the Implementation of Thrombectomy with Stent Retrievers on the Frequency of Hemicraniectomy in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2017, 27, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttsche, J.; Flottmann, F.; Jank, L.; Thomalla, G.; Rimmele, D.L.; Czorlich, P.; Westphal, M.; Regelsberger, J. Decompressive craniectomy in malignant MCA infarction in times of mechanical thrombectomy. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 3147–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurland, D.B.; Khaladj-Ghom, A.; Stokum, J.A.; Carusillo, B.; Karimy, J.K.; Gerzanich, V.; Sahuquillo, J.; Simard, J.M. Complications Associated with Decompressive Craniectomy: A Systematic Review. Neurocrit. Care 2015, 23, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arba, F.; Rinaldi, C.; Caimano, D.; Vit, F.; Busto, G.; Fainardi, E. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 594613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.M.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, M. Hemorrhagic Transformation After Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms and Management. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 703258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttler, E.; Schwab, S.; Schmiedek, P.; Unterberg, A.; Hennerici, M.; Woitzik, J.; Witte, S.; Jenetzky, E.; Hacke, W. Decompressive Surgery for the Treatment of Malignant Infarction of the Middle Cerebral Artery (DESTINY): A randomized, controlled trial. Stroke 2007, 38, 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttler, E.; Unterberg, A.; Woitzik, J.; Bösel, J.; Amiri, H.; Sakowitz, O.W.; Gondan, M.; Schiller, P.; Limprecht, R.; Luntz, S.; et al. Hemicraniectomy in older patients with extensive middle-cerebral-artery stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, P.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Buchan, A.M. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. Lancet 2000, 355, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebeskind, D.S.; Bracard, S.; Guillemin, F.; Jahan, R.; Jovin, T.G.; Majoie, C.B.; Mitchell, P.J.; van der Lugt, A.; Menon, B.K.; Román, L.S.; et al. eTICI reperfusion: Defining success in endovascular stroke therapy. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Alhalabi, O.T.; Schönenberger, S.; Ringleb, P.; Vollherbst, D.F.; Möhlenbruch, M.; Unterberg, A.; Neumann, J.-O. Prior Thrombectomy Does Not Affect the Surgical Complication Rate of Decompressive Hemicraniectomy in Patients with Malignant Ischemic Stroke. Neurocrit. Care 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzayiani, M.; Schmidt, T.; Veldeman, M.; Riabikin, A.; Brockmann, M.A.; Schiefer, J.; Clusmann, H.; Schubert, G.A.; Albanna, W. Risk profile of decompressive hemicraniectomy for malignant stroke after revascularization treatment. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 420, 117275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrieder, D.; Layer, K.; Müller, H.-P.; Rücker, V.; Kassubek, J.; Juettler, E.; Neugebauer, H.; Althaus, K.; Aral-Becher, B.; Bardutzky, J.; et al. Association of Infarct Volume Before Hemicraniectomy and Outcome After Malignant Infarction. Neurology 2021, 96, e2704–e2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, Q.; Shi, X.; Xu, X.; Ge, L.; Ding, X.; Zhou, Z. Predictors of malignant brain edema after mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Huang, C.; Chen, W.; Xu, C.; Liu, M.; Xu, H.; Cai, C. Risk factors for decompressive craniectomy after endovascular treatment in acute ischemic stroke. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 1357–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.F.; Pahwa, S.; Maniskas, M.; Michas, C.; Martinez, M.; Pennypacker, K.R.; Dornbos, D. Now that the door is open: An update on ischemic stroke pharmacotherapeutics for the neurointerventionalist. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W. Late Window Paradox. Stroke 2018, 49, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoene, D.; Hartmann, C.; Winzer, S.; Moustafa, H.; Günther, A.; Puetz, V.; Barlinn, K.; IGNITE study group. Postoperative management following decompressive hemicraniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction-A German nationwide survey study. Nervenarzt 2023, 94, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelz, J.O.; Fischer, M.M.; Bungert-Kahl, P.; Lindner, D.; Fricke, C.; Michalski, D. Fluid Balance Variations During the Early Phase of Large Hemispheric Stroke Are Associated with Patients’ Functional Outcome. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall Sample | Endovascular Treatment | No Endovascular Treatment | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 65 | 39 | 26 | |
| Age in years (M ± SD) | 59 ± 11 | 58 ± 12 | 61 ± 9 | 0.088 + |
| Sex (% female) (f/m) | 30.8 (20/45) | 28.2 (11/28) | 34.6 (9/17) | 0.583 # |
| ASPECTS of the first non-contrast CT (M ± SD) | 5.0 ± 2.9 | 6.4 ± 2.6 | 2.7 ± 1.6 | <0.001 * |
| Intravenous thrombolysis (% (n/n)) | 32.3 (21/65) | 41.0 (16/39) | 17.9 (5/26) | 0.066 # |
| eTICI (n) | 0 = 3 | - | - | |
| 1 = 6 | ||||
| 2a = 5 | ||||
| 2b = 10 | ||||
| 2c = 2 | ||||
| 3 = 13 | ||||
| Volume (in mL, M ± SD) and proportion (%, M ± SD) of edema/infarction referring to whole brain volume on CT prior to hemicraniectomy 1 | 276 ± 83 22.1 ± 6.3 | 280 ± 90 22.1 ± 6.5 | 269 ± 73 22.1 ± 6.1 | 0.633 + 0.989 + |
| Overall Sample | Endovascular Treatment | No Endovascular Treatment | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 41 | 16 | 25 | |
| Age in years (M ± SD) | 60 ± 10 | 57 ± 11 | 61 ± 9 | 0.150 + |
| Sex (% female) (f/m) | 29.3 (12/29) | 18.8 (3/13) | 36.0 (9/16) | 0.236 # |
| ASPECTS of the first non-contrast CT (M ± SD) | 3.2 ± 1.6 | 3.9 ± 1.5 | 2.7 ± 1.6 | 0.021 * |
| Patients with an ASPECTS between 3 and 5 (% (n/n)) on the first non-contrast CT | 68.3 (28/41) | 87.5 (14/16) | 60.0 (15/25) | 0.059 # |
| Intravenous thrombolysis (% (n/n)) | 19.5 (8/41) | 18.8 (3/16) | 20.0 (5/25) | 0.921 # |
| eTICI (n) | 0 = 1 | - | - | |
| 1 = 2 | ||||
| 2a = 2 | ||||
| 2b = 3 | ||||
| 2c = 2 | ||||
| 3 = 6 | ||||
| Volume (in mL, M ± SD) and proportion (%, M ± SD) of edema/infarction referring to whole brain volume on CT prior to hemicraniectomy 1 | 283 ± 89 22.8 ± 6.6 | 297 ± 110 23.4 ± 7.6 | 273 ± 72 22.4 ± 6.0 | 0.421 + 0.655 + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelz, J.O.; Engelmann, S.; Scherlach, C.; Bungert-Kahl, P.; Dabbagh, A.; Lindner, D.; Michalski, D. No Harmful Effect of Endovascular Treatment before Decompressive Surgery—Implications for Handling Patients with Space-Occupying Brain Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030918
Pelz JO, Engelmann S, Scherlach C, Bungert-Kahl P, Dabbagh A, Lindner D, Michalski D. No Harmful Effect of Endovascular Treatment before Decompressive Surgery—Implications for Handling Patients with Space-Occupying Brain Infarction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(3):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030918
Chicago/Turabian StylePelz, Johann Otto, Simone Engelmann, Cordula Scherlach, Peggy Bungert-Kahl, Alhuda Dabbagh, Dirk Lindner, and Dominik Michalski. 2024. "No Harmful Effect of Endovascular Treatment before Decompressive Surgery—Implications for Handling Patients with Space-Occupying Brain Infarction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 3: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030918
APA StylePelz, J. O., Engelmann, S., Scherlach, C., Bungert-Kahl, P., Dabbagh, A., Lindner, D., & Michalski, D. (2024). No Harmful Effect of Endovascular Treatment before Decompressive Surgery—Implications for Handling Patients with Space-Occupying Brain Infarction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(3), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030918






