Significance as a Prognostic Factor of Eosinophil Count in Nasal Polyp Tissue in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Accompanied by Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Preoperative Evaluation
2.3. Evaluation the Eosinophil Count of Nasal Polyp Tissue
2.4. Postoperative Care and Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
| Group | Disease Status 6 Months after Surgery According to EPOS 2020 |
| Well-control | Controlled |
| Poor-control | Partly controlled or Uncontrolled |
3. Results
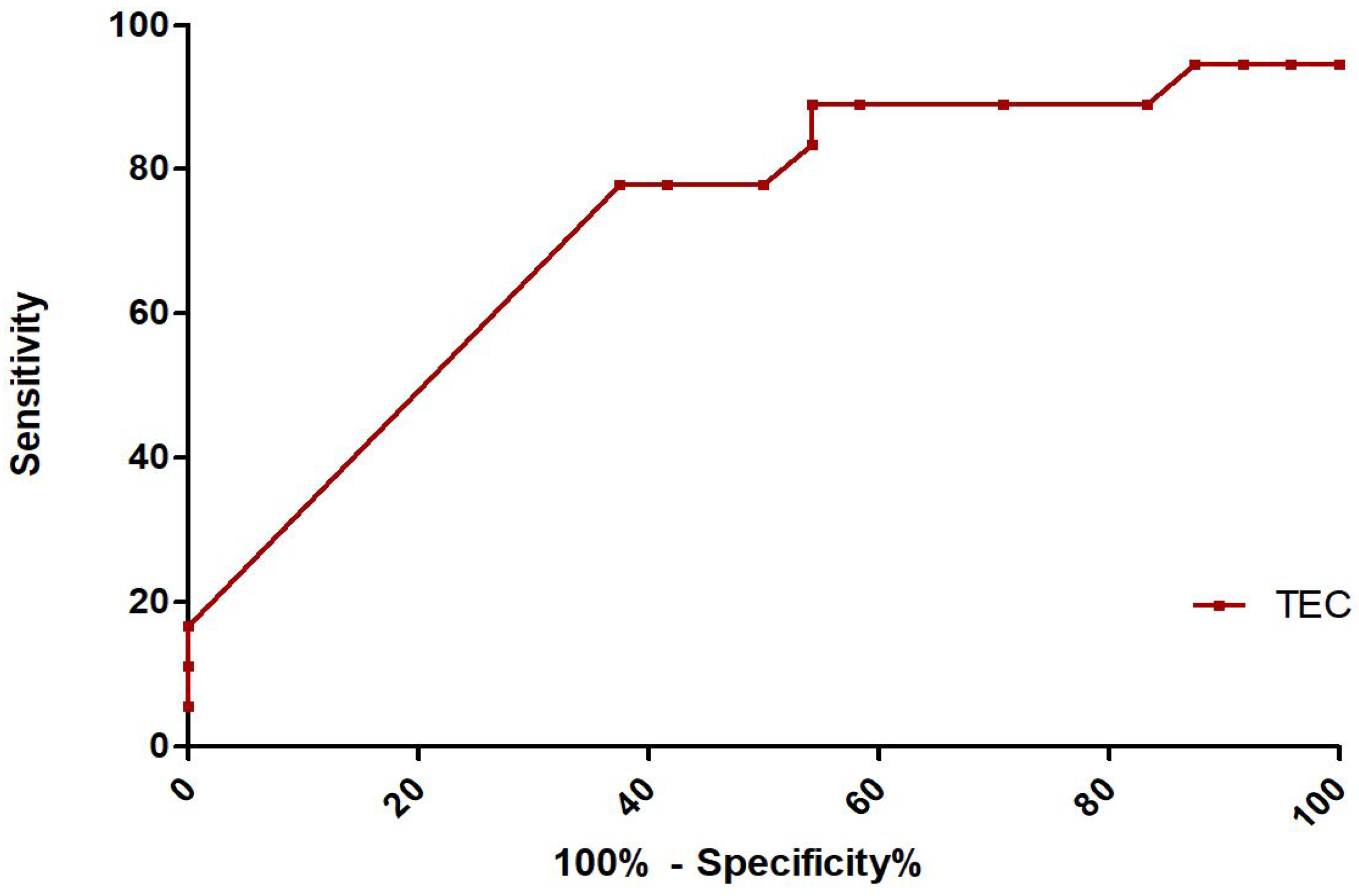
TEC as a Prognostic Factor
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Endoscopic Findings | Nasal Cavity | |
|---|---|---|
| Right | Left | |
| Polyp (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Edema (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Secretion (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Total | ||
| Paranasal Sinus CT | Right | Left |
|---|---|---|
| Maxillary (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Anterior Ethmoid (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Posterior Ethmoid (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Sphenoid (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Frontal (0, 1, 2) | ||
| Ostiomeatal Complex (0, 2) * | ||
| Total |
| Factor | Score |
|---|---|
| Disease side: both | 3 |
| Nasal polyp | 2 |
| CT shadow: ethmoid greater than or equal to maxillary | 2 |
| Eosinophils in peripheral blood | |
| >2% but ≤5% | 4 |
| >5% but ≤10% | 8 |
| >10% | 10 |
| Diagnosis | Total Score (JESREC Score) |
| ECRS | ≥11 |
| Non-ECRS | ≤10 |
| Controlled (All of the Following) | Partly Controlled (at Least 1 Present) | Uncontrolled (3 or More Present) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal blockage | Not present or not bothersome | Present on most days of the week | Present on most days of the week |
| Rhinorrhea/Postnasal drip | Little and mucous | Mucopurulent on most days of the week | Mucopurulent on most days of the week |
| Facial pain/Pressure | Not presentor not bothersome | Present on most days of the week | Present on most days of the week |
| Smell | Normal or only slightly impaired | Impaired | Impaired |
| Sleep disturbance or fatigue | Not present | Present | Present |
| Nasal endoscopy | Healthy or almost healthy mucosa | Diseased mucosa | Diseased mucosa |
| Rescue treatment(in last 6 months) | Not needed | Need of 1 course of rescue treatment | Symptoms persist despite rescue treatment(s) |
References
- Mygind, N. Nasal Allergy; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, Z.M.; Sauer, D.A.; Mace, J.; Smith, T.L. Relationship between clinical measures and histopathologic findings in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2009, 141, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassen, P.; Vandeplas, G.; Van Zele, T.; Cardell, L.O.; Arebro, J.; Olze, H.; Förster-Ruhrmann, U.; Kowalski, M.L.; Olszewska-Ziąber, A.; Holtappels, G.; et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaminck, S.; Vauterin, T.; Hellings, P.W.; Jorissen, M.; Acke, F.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P. The importance of local eosinophilia in the surgical outcome of chronic rhinosinusitis: A 3-year prospective observational study. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Zhang, N.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, L. Highlights of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in definition, prognosis, and advancement. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szucs, E.; Ravandi, S.; Goossens, A.; Beel, M.; Clement, P.A. Eosinophilia in the ethmoid mucosa and its relationship to the severity of inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. 2002, 16, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosun, F.; Arslan, H.H.; Karslioglu, Y.; Deveci, M.S.; Durmaz, A. Relationship between postoperative recurrence rate and eosinophil density of nasal polyps. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujieda, S.; Imoto, Y.; Kato, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Tsutsumiuchi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Kidoguchi, M.; Takabayashi, T. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, T.; Sakashita, M.; Haruna, T.; Asaka, D.; Takeno, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakayama, T.; Seki, N.; Ito, S.; Murata, J.; et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy 2015, 70, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Kern, R.C.; Altman, K.W. Histopathological evaluation of chronic rhinosinusitis: A critical review. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2013, 27, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snidvongs, K.; Lam, M.; Sacks, R.; Earls, P.; Kalish, L.; Phillips, P.S.; Pratt, E.; Harvey, R.J. Structured histopathology profiling of chronic rhinosinusitis in routine practice. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2012, 2, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Zhang, N.; Holtappels, G.; De Lobel, L.; van Cauwenberge, P.; Liu, S.; Lin, P.; Bousquet, J.; Van Steen, K. Presence of IL-5 protein and IgE antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins in nasal polyps is associated with comorbid asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon, C.; Mullol, J. Nasal polyps in patients with asthma: Prevalence, impact, and management challenges. J. Asthma Allergy 2016, 9, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, D.; Newson, R.; Lotvall, J.; Hastan, D.; Tomassen, P.; Keil, T.; Gjomarkaj, M.; Forsberg, B.; Gunnbjornsdottir, M.; Minov, J.; et al. Asthma in adults and its association with chronic rhinosinusitis: The GA2LEN survey in Europe. Allergy 2012, 67, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Lou, H.; Meng, Y.; Wang, C. Long-term outcomes of different endoscopic sinus surgery in recurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and asthma. Rhinology 2020, 58, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, E.; Mullol, J.; Agredo, F.; Alobid, I. Management of chronic rhinosinusitis in asthma patients: Is there still a debate? Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, A.S.; Smith, K.A.; Meeks, H.; Oakley, G.M.; Curtin, K.; LeClair, L.; Howe, H.; Orlandi, R.R.; Alt, J.A. Asthma increases long-term revision rates of endoscopic sinus surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyposis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaltis, A.J.; Li, G.; Vaezeafshar, R.; Cho, K.S.; Hwang, P.H. Modification of the Lund-Kennedy endoscopic scoring system improves its reliability and correlation with patient-reported outcome measures. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, V.J.; Kennedy, D.W. Staging for rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1997, 117, S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.L.; Hubbard, M.A.; Huyett, P.; Patrie, J.T.; Borish, L.; Payne, S.C. Sino-nasal outcome test (SNOT-22): A predictor of postsurgical improvement in patients with chronic sinusitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.C.; Yoo, Y.S.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, S.C.; Park, S.H.; Kim, J.K.; Kang, S.H. Development of KVSS Test (Korean Version of Sniffin’ Sticks Test). Korean J. Otolaryngol. 1999, 42, 855–860. [Google Scholar]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58, 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Huang, J.H.; Price, C.P.E.; Schauer, J.M.; Suh, L.A.; Harmon, R.; Conley, D.B.; Welch, K.C.; Kern, R.C.; Shintani-Smith, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for polyp recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, C.; Xu, W.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. A Nomogram Combing Peripheral Parameters for Estimation of CRSwNP Recurrence. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Meng, Y.; Piao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Bachert, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Cellular phenotyping of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Rhinology 2016, 54, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Asaka, D.; Okushi, T.; Matsuwaki, Y.; Otori, N.; Hama, T.; Moriyama, H. Mucosal eosinophilia and recurrence of nasal polyps—New classification of chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 2011, 49, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Basurrah, M.A.; Hwang, S.H. Clinical and Laboratory Features of Various Criteria of Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 15, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Meng, Y.; Piao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, A.N.; Chandra, R.K.; Chang, D.; Conley, D.B.; Tripathi-Peters, A.; Grammer, L.C.; Schleimer, R.T.; Kern, R.C. Relationships between severity of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis, asthma, and atopy. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2009, 23, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, S.; Scadding, G.K.; Lund, V.J.; Saleh, H. Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis and its effects on asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Well-Control (n = 24) | Poor-Control (n = 18) | Total (n = 42) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (M:F) | 10:14 | 9:9 | 19:23 | 0.41 |
| Age (years) | 51.54 ± 13.38 | 49.39 ± 12.35 | 50.62 ± 12.84 | 0.59 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.36 ± 3.11 | 24.80 ± 3.30 | 24.55 ± 3.16 | 0.66 |
| Alcohol (n, %) | 6 (25.0%) | 3 (16.7%) | 9 (21.4%) | 0.40 |
| Smoking (n, %) | 6 (25.0%) | 7 (38.9%) | 13 (31.0%) | 0.27 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 8 (33.3%) | 4 (22.2%) | 12 (28.6%) | 0.43 |
| DM (n, %) | 5 (20.8%) | 1 (5.6%) | 6 (14.3%) | 0.17 |
| History of sinus surgery (n, %) | 3 (12.5%) | 3 (16.7%) | 6 (14.3%) | 0.52 |
| Well-Control | Poor-Control | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC count (/mm3) | 6870.83 ± 1692.31 | 7205.56 ± 1886.63 | 0.55 |
| Eosinophil percentage (%) | 7.05 ± 3.96 | 9.11 ± 6.11 | 0.19 |
| Eosinophil count (/mm3) | 476.20 ± 290.28 | 621.23 ± 380.62 | 0.16 |
| Total IgE (IU/mL) | 328.32 ± 302.71 | 376.50 ± 341.34 | 0.63 |
| LK endoscopic score | 6.42 ± 2.50 | 5.11 ± 2.22 | 0.09 |
| LM CT score | 16.38 ± 5.41 | 17.28 ± 4.60 | 0.57 |
| SNOT-22 score | 37.67 ± 22.22 | 41.06 ± 27.20 | 0.66 |
| KVSS II score | 17.29 ± 10.61 | 13.39 ± 8.21 | 0.20 |
| JESREC score | 12.83 ± 3.63 | 14.94 ± 2.62 | 0.04 * |
| Tissue eosinophil count (/HPF) | 61.88 ± 35.11 | 124.22 ± 113.49 | 0.02 * |
| OR (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.70 (0.20–2.44) | 0.57 |
| Age | 0.98 (0.93–1.03) | 0.46 |
| BMI | 1.07 (0.86–1.32) | 0.55 |
| Smoking | 0.27 (0.03–2.15) | 0.21 |
| Alcohol | 3.59 (0.59–21.84) | 0.17 |
| DM | 0.09 (0.01–1.41) | 0.09 |
| History of sinus surgery | 3.89 (0.32–47.00) | 0.29 |
| WBC count | 1.00 (1.00–1.001) | 0.37 |
| Eosinophil ratio | 1.23 (0.76–1.99) | 0.39 |
| Eosinophil count | 0.99 (0.99–1.01) | 0.60 |
| Total IgE | 1.003 (0.99–1.01) | 0.11 |
| LK endoscopic score | 0.68 (0.99–1.001) | 0.15 |
| LM CT score | 1.11 (0.87–1.42) | 0.40 |
| SNOT-22 score | 0.98 (0.93–1.04) | 0.55 |
| JESREC score | 1.23 (0.91–1.64) | 0.09 |
| Tissue eosinophil count (/HPF) | 1.02 (1.001–1.04) | 0.03 * |
| High TEC (n = 23) | Low TEC (n = 19) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (M:F) | 7:16 | 12:7 | 0.04 * |
| Age (years) | 48.61 ± 12.74 | 53.05 ± 12.88 | 0.27 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.72 ± 3.17 | 24.35 ± 3.21 | 0.71 |
| Smoking (n, %) | 3 (13.0%) | 6 (31.6%) | 0.26 |
| Alcohol (n, %) | 6 (26.1%) | 7 (36.8%) | 0.52 |
| DM (n, %) | 3 (13.0%) | 3 (15.8%) | 1.00 |
| History of sinus surgery (n, %) | 3 (13.0%) | 3 (15.8%) | 1.00 |
| WBC count (/mm3) | 6991.30 ± 1862.53 | 7042.11 ± 1686.32 | 0.93 |
| Eosinophil percentage (%) | 9.19 ± 5.55 | 6.42 ± 3.95 | 0.08 |
| Eosinophil count (/mm3) | 608.69 ± 341.85 | 453.21 ± 348.39 | 0.14 |
| Total IgE (IU/mL) | 386.44 ± 312.02 | 303.62 ± 324.81 | 0.41 |
| LK endoscopic score | 5.74 ± 2.14 | 6.00 ± 2.83 | 0.74 |
| LM CT score | 17.83 ± 4.16 | 15.47 ± 5.79 | 0.13 |
| SNOT-22 score | 42.91 ± 26.50 | 34.53 ± 20.92 | 0.27 |
| TDI (KVSS II) score | 13.96 ± 8.35 | 17.69 ± 11.10 | 0.23 |
| JESREC score | 14.57 ± 2.74 | 12.74 ± 3.84 | 0.08 |
| High TEC | Low TEC | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LK endoscopy score (6 months after surgery) | 1.87 ± 1.84 | 0.47 ± 0.77 | 0.002 * |
| Poor control (n, %) | 14 (60.9%) | 4 (21.1%) | 0.01 * |
| Usage of steroid (n, %) | 7 (30.4%) | 4 (21.1%) | 0.73 |
| Usage of antibiotics (n, %) | 6 (26.1%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.K.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, H.N.; Jung, S.M.; Jeong, J.H. Significance as a Prognostic Factor of Eosinophil Count in Nasal Polyp Tissue in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Accompanied by Asthma. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195849
Kim MK, Cho SH, Lee HN, Jung SM, Jeong JH. Significance as a Prognostic Factor of Eosinophil Count in Nasal Polyp Tissue in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Accompanied by Asthma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(19):5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195849
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Moo Keon, Seok Hyun Cho, Ha Na Lee, Seon Min Jung, and Jin Hyeok Jeong. 2024. "Significance as a Prognostic Factor of Eosinophil Count in Nasal Polyp Tissue in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Accompanied by Asthma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 19: 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195849
APA StyleKim, M. K., Cho, S. H., Lee, H. N., Jung, S. M., & Jeong, J. H. (2024). Significance as a Prognostic Factor of Eosinophil Count in Nasal Polyp Tissue in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Accompanied by Asthma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(19), 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195849







