Impact of Intra-Retinal Fluids on Changes in Retinal Ganglion Cell and Nerve Fiber Layers in Neovascular AMD under Anti-VEGF Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. RGCL Thickness
3.2. RNFL Thickness Development
3.3. BCVA
3.4. Intraretinal Fluids
3.5. Number of IVIs
3.6. Results of the Sub-Analysis of the IRF Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, P.; Liew, G.; Gopinath, B.; Wong, T.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2018, 392, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, D.J.; Kaiser, P.K.; Rosenfeld, P.J.; Stewart, M.W. Aflibercept for age-related macular degeneration: A game-changer or quiet addition? Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.L.; Oh, L.J.; Wong, E.; Wei, J.; Chilov, M. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; Lindsley, K.; Vedula, S.S.; Krzystolik, M.G.; Hawkins, B.S. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for neovascular agerelated macular degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD005139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.F.; Maguire, M.G.; Fine, S.L.; Ying, G.S.; Jaffe, G.J.; Grunwald, J.E.; Toth, C.; Redford, M.; Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials (CATT) Research Group. Ranibizumab and bevacizumab for treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration: Two-year results. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Michels, M.; Kaiser, P.K.; Heier, J.S.; Sy, J.P.; Ianchulev, T. Ranibizumab versus verteporfin photodynamic therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: Two-year results of the ANCHOR study. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 57–65.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, J.S.; Brown, D.M.; Chong, V.; Korobelnik, J.F.; Kaiser, P.K.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Kirchhof, B.; Ho, A.; Ogura, Y.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; et al. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Dail, Y.; Seitz, B.; Sideroudi, H.; Abdin, A.D. Impact of intravitreal ranibizumab, aflibercept and bevacizumab on retinal ganglion cell and nerve fibre layer thickness in Neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Acta Ophthalmol. 2023, 101, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, O.E.; Vavvas, D.; Plotas, P.; Pallikari, A.; Georgakopoulos, C.D. The effect of ranibizumab on normal neurosensory retina in the eyes of patients with exudative age related macular degeneration. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2017, 11, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.; Munk, M.R.; Ebneter, A.; Wolf, S.; Zinkernagel, M.S. Retinal ganglion cell layer change in patients treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 167, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Sim, H.E.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Chang, I.B.; Park, Y.S.; Hwang, J.H. Changes in inner retinal layer thickness in patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration during treatment with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor. Medicine 2020, 99, e19955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, M.H.; Chin, H.S. Changes in the ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer after consecutive intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor in age-related macular degeneration patients. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 34, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, Ü.Ü.; Baysal, Z.; Inan, S. Long-term changes in retinal layers in patients undergoing intravitreal ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: Retinal layers after anti-VEGF therapy. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aşikgarip, N.; Temel, E.; Örnek, K. Macular ganglion cell complex changes in eyes treated with aflibercept for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 35, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, N.; Sevincli, S.; Kayhan, B.; Sonmez, M. Anatomical effects of intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injections on inner layers of the lesion-free retina. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolrahimzadeh, S.; Gharbiya, M.; Formisano, M.; Bertini, F.; Cerini, A.; Pacella, E. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor intravitreal therapy and macular ganglion cell layer thickness in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Eye Res. 2019, 44, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Woo, J.E.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Woo, J.M.; Min, J.K. Retinal and Choroidal Changes after Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy for Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, V.A.; Bassil, F.L.; Ramdas, W.D. The effects of intravitreal injections on intraocular pressure and retinal nerve fiber layer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.N.; Chung, H.; Kim, T.E.; Kim, H.C. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy and retinal nerve fiber layer loss in eyes with age-related macular degeneration: A meta-analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1798–1806.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.Y.; Hwang, D.D.J. Short-term effect of intravitreal brolucizumab injections in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljundi, W.; Daas, L.; Suffo, S.; Seitz, B.; Abdin, A.D. First-year real-life experience with intravitreal faricimab for refractory neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, A.D.; Aljundi, W.; El Jawhari, K.; Suffo, S.; Weinstein, I.; Seitz, B. First year real life experience with intravitreal brolucizumab for treatment of refractory neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 860784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdin, A.D.; Suffo, S.; Bischoff-Jung, M.; Daas, L.; Pattmöller, M.; Seitz, B. Advantages of a designated IVI center for a German university eye hospital. Der Ophthalmol. 2020, 117, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gangaputra, S.; Lee, K.E.; Narkar, A.R.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Meuer, S.M.; Danis, R.P. Signal quality assessment of retinal optical coherence tomography images. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Azevedo, A.G.B.; Takitani, G.E.d.S.; Godoy, B.R.; Marianelli, B.F.; Saraiva, V.; Tavares, I.M.; Roisman, L. Impact of manual correction over automated segmentation of spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2020, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Yoo, Y.J.; Han, S.B. Age-related changes of macular ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer thickness in Korean elderly subjects. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 34, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Francis, B.A.; Dastiridou, A.; Chopra, V.; Tan, O.; Varma, R.; Greenfield, D.S.; Schuman, J.S.; Huang, D.; Advanced Imaging for Glaucoma Study Group; et al. Longitudinal and cross-sectional analyses of age effects on retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell complex thickness by fourier-domain OCT. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2016, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Q.N.; Gray, I.N.; Yu, Y.; VanderBeek, B.L. Repeated intravitreal injections of antivascular endothelial growth factors and risk of intraocular pressure medication use. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.M.; Chaya, C.J.; Kahook, M.Y.; Wirostko, B.M. Intraocular pressure elevation following intravitreal anti-VEGF injections: Short- and long-term considerations. J. Glaucoma 2021, 30, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsley, M.B.; Mandava, N.; Maycotte, M.A.; Kahook, M.Y. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients receiving chronic anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 150, 558–561.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; Ruiz-Calvo, A.; Saenz-Frances, F.; Reche-Frutos, J.; Calvo-Gonzalez, C.; Donate-Lopez, J.; Garcia-Feijoo, J. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness changes in patients with age-related macular degeneration treated with intravitreal ranibizumab. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6214–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobacı, G.; Güngör, R.; Ozge, G. Effects of multiple intravitreal anti-VEGF injections on retinal nerve fiber layer and intraocular pressure: A comparative clinical study. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 6, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Shin, K.C.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Change of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in various retinal diseases treated with multiple intravitreal antivascular endothelial growth factor. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, M.; Oner, F.H.; Saatci, A.O. The long-term effect of intravitreal ranibizumab on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Int. Ophthalmol. 2015, 35, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, S.; Batioğlu, F.; Özmert, E.; Erenler, F. The effect of multiple injections of ranibizumab on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Eye Res. 2015, 40, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.J.; Kim, W.J.; Shin, I.H.; Kim, J.Y. Longitudinal changes in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness after intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 30, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul, E.A.; Artunay, O.; Kumral, E.T.; Yenerel, M.; Rasier, R.; Kockar, A.; Yuzbasioglu, E. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness changes in age-related macular degeneration treated with multiple intravitreal ranibizumab. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 32, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Megías, A.; Ruiz-Calvo, A.; Murciano-Cespedosa, A.; Hernández-Ruiz, S.; Martínez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; García-Feijoo, J. Long-term effect of intravitreal ranibizumab therapy on retinal nerve fiber layer in eyes with exudative age-related macular degeneration. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammel, N.; Belghith, A.; Weinreb, R.N.; Medeiros, F.A.; Mendoza, N.; Zangwill, L.M. Comparing the rates of retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer loss in healthy eyes and in glaucoma eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 178, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hougaard, J.L.; Ostenfeld, C.; Heijl, A.; Bengtsson, B. Modelling the normal retinal nerve fibre layer thickness as measured by Stratus optical coherence tomography. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2006, 244, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendschneider, D.; Tornow, R.P.; Horn, F.K.; Laemmer, R.; Roessler, C.W.; Juenemann, A.G.; Kruse, F.E.; Mardin, C.Y. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normals measured by spectral domain OCT. J. Glaucoma 2010, 19, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, R.S.; Parikh, S.R.; Sekhar, G.C.; Prabakaran, S.; Babu, J.G.; Thomas, R. Normal age-related decay of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezari, M.; Ramezani, A.; Yaseri, M. Changes in Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness after Two Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injections for Wet Type Age-related Macular Degeneration. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2014, 9, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Swaminathan, S.S.; Yang, J.; Barikian, A.; Shi, Y.; Shen, M.; Jiang, X.; Feuer, W.; Gregori, G.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Dose-response relationship between intravitreal injections and retinal nerve fiber layer thinning in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2021, 5, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldstein, S.M.; Simader, C.; Staurenghi, G.; Chong, N.V.; Mitchell, P.; Jaffe, G.J.; Lu, C.; Katz, T.A.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Morphology and visual acuity in aflibercept and ranibizumab therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration in the VIEW trials. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Jang, K.; Sohn, J.; Park, J.I.; Hwang, D.D.J. Effect of intravitreal ranibizumab and aflibercept injections on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total Group N = 97 | IRF b N = 51 | No-IRF b N = 46 | p-Value c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age a (yrs) Mean ± SD b | 78.6 ± 7.0 | 79.2 ± 6.4 | 77.8 ± 7.7 | 0.326 d |
| Gender % Male:Female | 56:44 | 49:51 | 52:48 | 0.684 e |
| Lens status % Pseudophakic:Phakic | 58:42 | 75:25 | 48:52 | 0.012 e,f |
| Number of injections–12 months Mean ± SD | 7.4 ± 1.5 | 7.0 ± 1.8 | 8.2 ± 1.8 | 0.002 d,f |
| Number of injections–24 months Mean ± SD | 12.7 ± 3.6 | 12.2 ± 3.4 | 14.3 ± 4.3 | 0.013 d,f |
| Total Group N = 97 | p-Value a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1-Year Follow-Up | 2-Year Follow-Up | Baseline–1-Year | Baseline–2-Year | 1-Year– 2-Year | |
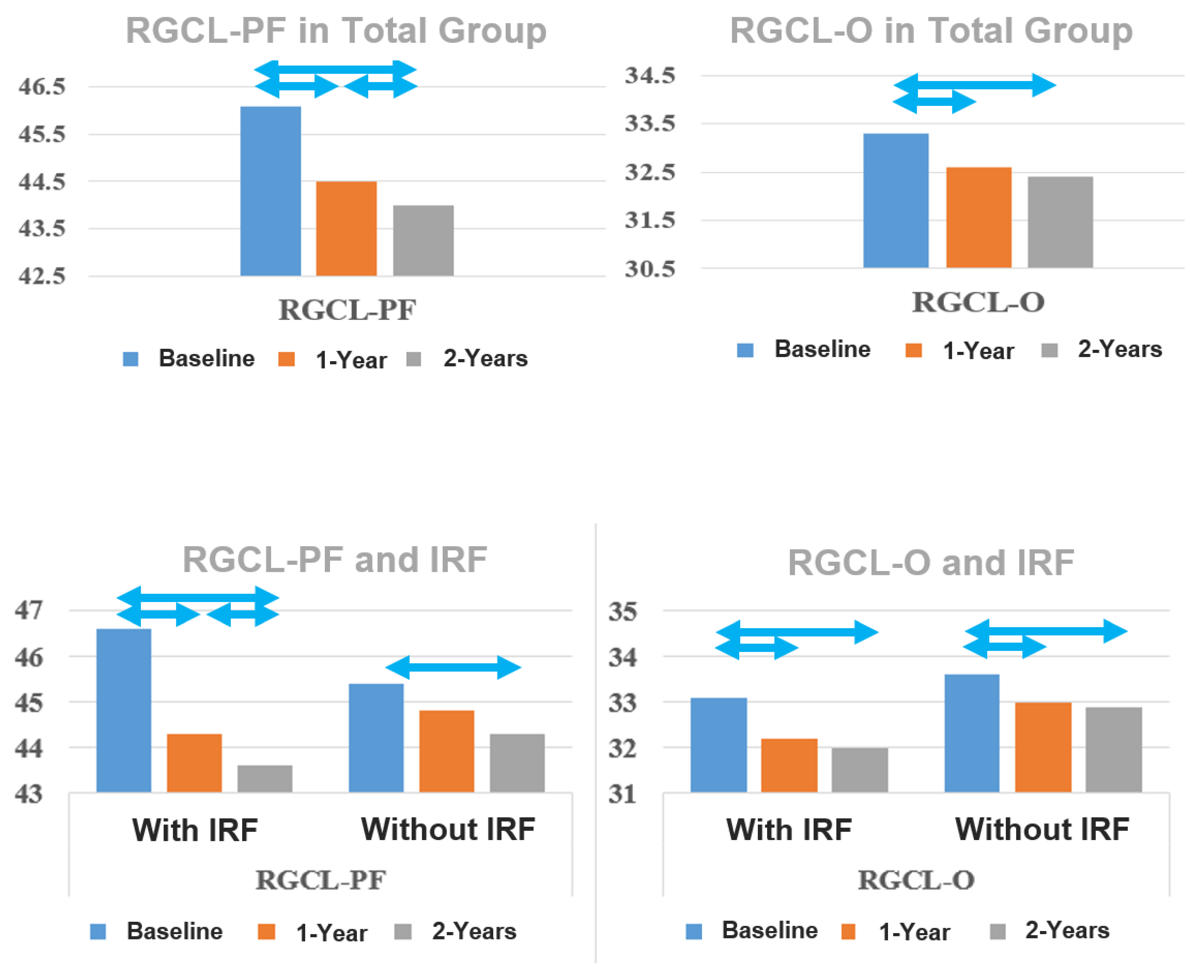
| RGCL-PF (µm) Mean ± SE | 46.1 ± 0.6 | 44.5 ± 0.6 | 44.0 ± 0.6 | <0.001 b | <0.001 | 0.012 |
| RGCL-O (µm) Mean ± SE | 33.3 ± 0.4 | 32.6 ± 0.4 | 32.4 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.180 |
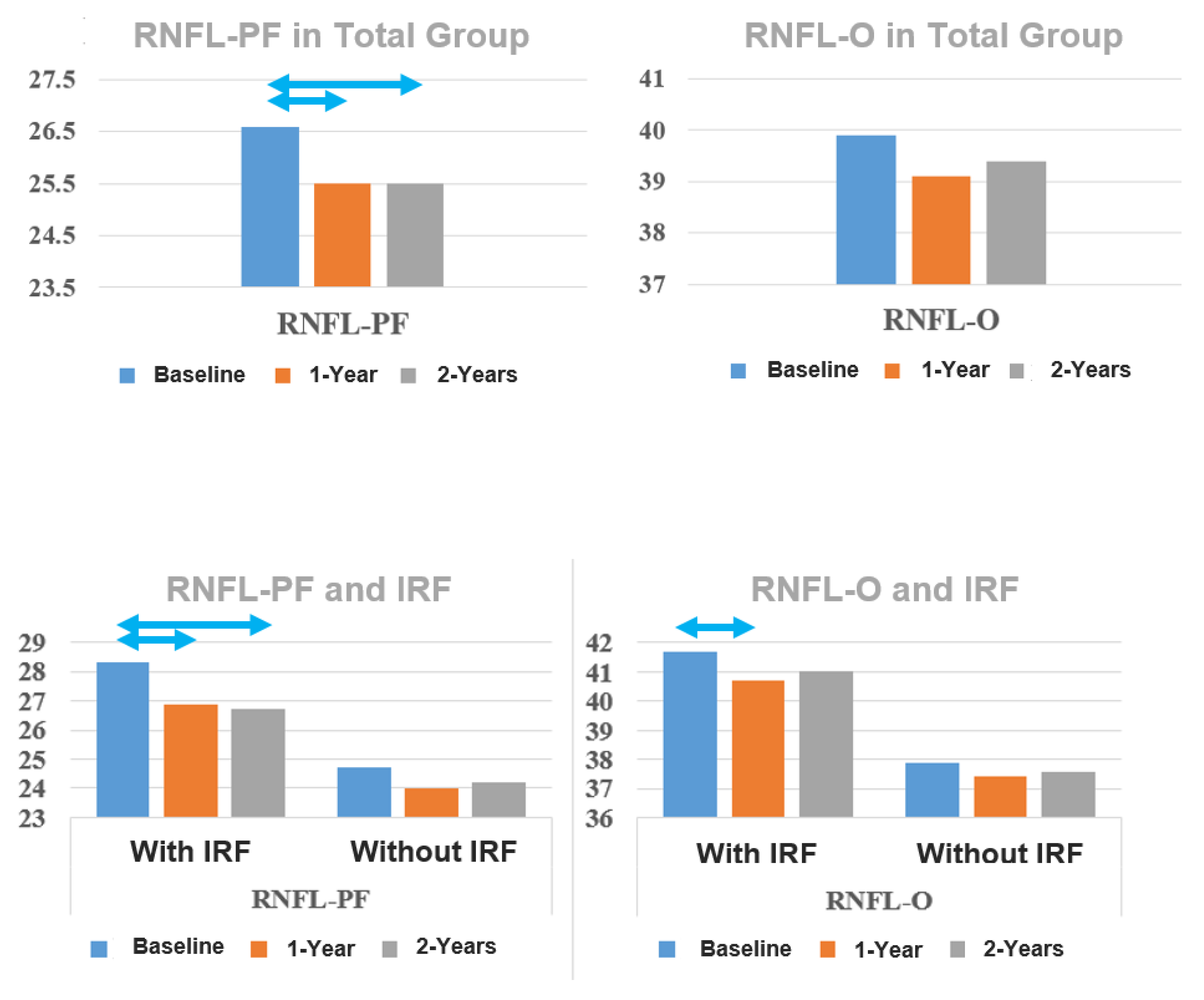
| RNFL-PF (µm) Mean ± SE | 26.6 ± 0.4 | 25.5 ± 0.4 | 25.5 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 |
| RNFL-O (µm) Mean ± SE | 39.9 ± 0.7 | 39.1 ± 0.7 | 39.4 ± 0.7 | 0.249 | 0.299 | 0.193 |
| RNFL-Nasal (µm) Mean ± SE | 55.3 ± 1.1 | 54.8 ± 1.1 | 54.7 ± 1.1 | 0.249 | 0.299 | 0.193 |
| BCVA logMAR Mean ± SE | 0.47 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.053 | 0.449 |
| Percentage of IRF | 53% | 21% | 11% | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.290 |
| Intraretinal Fluids | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes N = 51 | No N = 46 | p-Value a | |
| RGCL-PF b (um) Mean ± SE b | |||
| Baseline | 46.6 ± 0.8 | 45.4 ± 0.9 | 0.317 |
| 1-year follow-up | 44.3 ± 0.8 | 44.8 ± 0.9 | 0.746 |
| 2-year follow-up | 43.6 ± 0.9 | 44.3 ± 0.9 | 0.582 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | <0.001 c | 0.243 | |
| Baseline–2-year | <0.001 | 0.013 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 0.026 | 0.454 | |
| RGCL-O b (um) Mean ± SE | |||
| Baseline | 33.1 ± 0.5 | 33.6 ± 0.5 | 0.544 |
| 1-year follow-up | 32.2 ± 0.5 | 33.0 ± 0.6 | 0.367 |
| 2-year follow-up | 32.0 ± 0.6 | 32.9 ± 0.6 | 0.253 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | <0.001 | 0.002 | |
| Baseline–2-year | <0.001 | 0.004 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 0.104 | 1.000 | |
| Intraretinal Fluids | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes N = 51 | No N = 46 | p-Value a | |
| RNFL-PF (um) Mean ± SE | |||
| Baseline | 28.3 ± 0.6 | 24.7 ± 0.6 | <0.001 b |
| 1-year follow-up | 26.9 ±0.5 | 24.0 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| 2-year follow-up | 26.7 ± 0.6 | 24.2 ± 0.6 | 0.003 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | <0.001 | 0.304 | |
| Baseline–2-year | <0.001 | 0.882 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| RNFL-O (um) Mean ± SE | |||
| Baseline | 41.7 ± 0.9 | 37.9 ± 1.0 | 0.006 |
| 1-year follow-up | 40.7 ± 0.9 | 37.4 ± 0.9 | 0.012 |
| 2-year follow-up | 41.0 ± 0.9 | 37.6 ± 1.0 | 0.012 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | 0.013 | 0.495 | |
| Baseline–2-year | 0.261 | 1.000 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 0.868 | 1.000 | |
| RNFL-Nasal (um) Mean ± SE | |||
| Baseline | 57.7 ± 1.5 | 52.7 ± 1.6 | 0.027 |
| 1-year follow-up | 56.7 ± 1.5 | 52.7 ± 1.6 | 0.070 |
| 2-year follow-up | 57.0 ± 1.6 | 52.1 ± 1.6 | 0.035 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | 0.088 | 1.000 | |
| Baseline–2-year | 0.659 | 1.000 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 1.000 | 0.576 | |
| Intraretinal Fluids | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes N = 51 | No N = 46 | p-Value a | |
| BCVA logMAR Mean ± SE | N = 44 | N= 42 | |
| Baseline | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.041 b |
| 1-year follow-up | 0.45 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 0.009 |
| 2-year follow-up | 0.47 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | 0.014 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | 0.067 | 0.012 | |
| Baseline–2-year | 0.441 | 0.181 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 1.000 | 0.751 | |
| RGCL-PF | RGCL-O | RNFL-PF | RNFL-O | RNFL-Nasal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of injections−24 Months R (p-value a) | 0.110 (0.284) | 0.179 (0.079) | −0.222 (0.029) b | 0.020 (0.846) | 0.043 (0.675) |
| Intraretinal Fluids | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolved N = 41 | Persistent N = 10 | p-Value a | |
| RGCL-PF b (um) Mean ± SD b | |||
| Baseline | 46.3 ± 5.7 | 47.6 ± 4.5 | 0451 |
| 1-year follow-up | 43.8 ± 5.9 | 46.7 ± 3.8 | 0.070 |
| 2-year follow-up | 42.8 ± 6.2 | 47.0 ± 5.3 | 0.048 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | <0.001 c | 0.559 | |
| Baseline–2-year | <0.001 | 1.000 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 0.05 | 1.000 | |
| RGCL-O b (um) Mean ± SD | |||
| Baseline | 33.2 ± 3.8 | 32.8 ± 2.6 | 0.686 |
| 1-year follow-up | 32.3 ± 3.7 | 32.1 ± 2.9 | 0.869 |
| 2-year follow-up | 31.7 ± 3.9 | 32.9 ± 3.0 | 0.324 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | <0.001 | 0.295 | |
| Baseline–2-year | <0.001 | 1.000 | |
| 1-year–2-year | <0.001 | 0.179 | |
| RNFL-PF b (um) Mean ± SD | |||
| Baseline | 27.9 ± 4.0 | 29.9 ± 5.2 | 0.298 |
| 1-year follow-up | 26.4 ± 3.4 | 28.6 ± 4.9 | 0.212 |
| 2-year follow-up | 26.0 ± 3.6 | 29.5 ± 5.7 | 0.093 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | 0.014 | 0.376 | |
| Baseline–2-year | 0.002 | 1.000 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 0.559 | 1.000 | |
| RNFL-O b (um) Mean ± SD | |||
| Baseline | 40.8 ± 6.5 | 45.0 ± 8.7 | 0.190 |
| 1-year follow-up | 39.7 ± 6.1 | 44.3 ± 7.7 | 0.108 |
| 2-year follow-up | 39.9 ± 6.2 | 45.3 ± 8.7 | 0.088 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | 0.082 | 1.000 | |
| Baseline–2-year | 0.287 | 1.000 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| RNFL-Nasal (um) Mean ± SD | |||
| Baseline | 56.2 ± 9.7 | 63.4 ± 18.7 | 0.279 |
| 1-year follow-up | 55.1 ± 9.6 | 63.0 ± 15.9 | 0.164 |
| 2-year follow-up | 55.0 ± 9.9 | 65.0 ± 17.2 | 0.109 |
| p-value a | |||
| Baseline–1-year | 0.083 | 1.000 | |
| Baseline–2-year | 0.140 | 1.000 | |
| 1-year–2-year | 1.000 | 0.545 | |
| Baseline | First Control Thickness Change (%) (Months) | Last Control Thickness Change (%) (Months) | p-Value a | p-Value b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee et al., 2020 [11] (n = 52) | 56.6 ± 10.7 | 53.0 ± 11.1 (−6%) (3 mo) | 52.4 ± 10.9 (−7%) (19 mo) | 0.098 | 0.048 |
| Kim et al., 2020 [12] (n = 96) | 70.5 ± 14.1 | 66.0 ± 13.9 (−6%) (3 mo) | 62.6 ± 16.3 (−11%) (24 mo) | 0.004 c | <0.001 |
| Inan et al., 2019 [13] (n = 37) | 44.5 ± 12.6 | 42.1 ± 12.7 (−5%) (3 mo) | 39.6 ± 10.6 (−11%) (12 mo) | 0.005 | |
| Aşikgarip et al., 2021 [14] (n = 36) | 48.1 ± 7.1 | 46.1 ± 6.7 (−4%) (3 mo) | 43.8 ± 6.1 (−9%) (12 mo) | 0.223 | 0.041 |
| Abdolrahimzadeh et al., 2019 [16] (n = 48) | 49.4 ± 5.9 | −2.1 ± 3.7 (−4%) (12 mo) | −3.0 ± 2.6 (−6%) (24 mo) | 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Baseline | First Control Thickness Change (%) (Months) | First Control Thickness Change (%) (Months) | p-Value a | p-Value b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee et al., 2020 [11] (n = 52) | 41.6 ± 14.4 | 35.7 ± 14.3 (−14%) (3 mo) | 35.6 ± 13.6 (−14%) (19 mo) | 0.039 c | 0.044 |
| Martinez-de-la-Casa et al., 2012 [31] (n = 49) | 105.7 ± 12.2 | 101.4 ± 10.4 (−4%) (3 mo) | 100.2 ± 11.0 (−5%) (12 mo) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Inan et al., 2019 [13] (n = 39) | 29.3 ± 12.1 | 26.1 ± 8.9 (−11%) (3 mo) | 26.9 ± 10.1 (−8%) (12 mo) | - | 0.432 |
| Aşikgarip et al., 2021 [14] (n = 36) | 21.1 ± 2.7 | 20.7 ± 2.5 (−2%) (3 mo) | 19.8 ± 2.4 (−6%) (12 mo) | 0.515 | 0.037 |
| Entezari et al., 2014 [43] (n = 18) | 89 ± 21 | 82 ± 15 (−8%) (3 mo) | 87 ± 23 (−2%) (6 mo) | 0.021 | 0.356 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Dail, Y.; Seitz, B.; Sideroudi, H.; Abdin, A.D. Impact of Intra-Retinal Fluids on Changes in Retinal Ganglion Cell and Nerve Fiber Layers in Neovascular AMD under Anti-VEGF Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175318
Abu Dail Y, Seitz B, Sideroudi H, Abdin AD. Impact of Intra-Retinal Fluids on Changes in Retinal Ganglion Cell and Nerve Fiber Layers in Neovascular AMD under Anti-VEGF Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(17):5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175318
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Dail, Yaser, Berthold Seitz, Haris Sideroudi, and Alaa Din Abdin. 2024. "Impact of Intra-Retinal Fluids on Changes in Retinal Ganglion Cell and Nerve Fiber Layers in Neovascular AMD under Anti-VEGF Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 17: 5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175318
APA StyleAbu Dail, Y., Seitz, B., Sideroudi, H., & Abdin, A. D. (2024). Impact of Intra-Retinal Fluids on Changes in Retinal Ganglion Cell and Nerve Fiber Layers in Neovascular AMD under Anti-VEGF Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(17), 5318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175318









