Mid-Term Migration Pattern of a Cemented Collared Anatomical Stem—A Retrospective Study Using EBRA-FCA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pivec, R.; Johnson, A.J.; Mears, S.C.; Mont, M.A. Hip Arthroplasty. Lancet 2012, 380, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ayers, D.C.; Lewis, C.G.; Bowen, T.R.; Allison, J.J.; Franklin, P.D. Functional Gain and Pain Relief After Total Joint Replacement According to Obesity Status. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, L.; Chen, A.F. Patient Satisfaction and Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Review. Arthroplasty 2019, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärrholm, J.; Mohaddes, M.; Odin, D.; Vinblad, J.; Rogmark, C.; Rolfson, O. Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register Annual Report 2017. 2018. Available online: https://registercentrum.blob.core.windows.net/sar/r/Swedish-Hip-Arthroplasty-Register-Annual-report-2017-BylrAoP8ro.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Melvin, J.S.; Karthikeyan, T.; Cope, R.; Fehring, T.K. Early Failures in Total Hip Arthroplasty—A Changing Paradigm. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, S.P.; Sørensen, H.T.; Lucht, U.; Søballe, K.; Overgaard, S.; Pedersen, A.B. Patient-Related Predictors of Implant Failure after Primary Total Hip Replacement in the Initial, Short- and Long-Terms. A Nationwide Danish Follow-up Study Including 36,984 Patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2006, 88, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, S.D.; Seyler, T.M.; Bennett, D.; Delanois, R.E.; Saleh, K.J.; Thongtrangan, I.; Kuskowski, M.; Cheng, E.Y.; Sharkey, P.F.; Parvizi, J.; et al. Total Hip Arthroplasties: What Are the Reasons for Revision? Int. Orthop. 2008, 32, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoghi, P.; Liebensteiner, M.; Agreiter, M.; Leithner, A.; Böhler, N.; Labek, G. Revision Surgery after Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Complication-Based Analysis Using Worldwide Arthroplasty Registers. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 1329–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, J.A.; Stambough, J.B.; Sassoon, A.A.; Johnson, S.R.; Clohisy, J.C.; Nunley, R.M. Contemporary Surgical Indications and Referral Trends in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A 10-Year Review. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Gu, J.; Zhou, Y. Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Failure: Aseptic Loosening Remains the Most Common Cause of Revision. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 7080–7089. [Google Scholar]
- Anil, U.; Singh, V.; Schwarzkopf, R. Diagnosis and Detection of Subtle Aseptic Loosening in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzer, A.; Lœhr, J.F. Early Loosening of Hip Replacements: Causes, Course and Diagnosis. J. Orthopaed Traumatol. 2003, 4, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krismer, M.; Biedermann, R.; Stöckl, B.; Fischer, M.; Bauer, R.; Haid, C. The Prediction of Failure of the Stem in THR by Measurement of Early Migration Using EBRA-FCA. J. Bone Jt. Surg Br. 1999, 81, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.A.; Plante-Bordeneuve, P. Early Migration and Late Aseptic Failure of Proximal Femoral Prostheses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1994, 76, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroell, A.; Beaulé, P.; Krismer, M.; Behensky, H.; Stoeckl, B.; Biedermann, R. Aseptic Stem Loosening in Primary THA: Migration Analysis of Cemented and Cementless Fixation. Int. Orthop. 2009, 33, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärrholm, J.; Borssén, B.; Löwenhielm, G.; Snorrason, F. Does Early Micromotion of Femoral Stem Prostheses Matter? 4–7-Year Stereoradiographic Follow-up of 84 Cemented Prostheses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1994, 76, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijse, M.J.; Valstar, E.R.; Kaptein, B.L.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H. The Exeter Femoral Stem Continues to Migrate during Its First Decade after Implantation: 10–12 Years of Follow-up with Radiostereometric Analysis (RSA). Acta Orthop. 2012, 83, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, R.; Krismer, M.; Stöckl, B.; Mayrhofer, P.; Ornstein, E.; Franzén, H. Accuracy of EBRA-FCA in the Measurement of Migration of Femoral Components of Total Hip Replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1999, 81, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylde, V.; Blom, A.W. Assessment of Outcomes after Hip Arthroplasty. HIP Int. 2009, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, M.J.; Kernohan, W.G.; Nixon, J.R.; Mollan, R.A. A Statistical Analysis of Hip Scores. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1993, 75, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.E.; Ritter, M.A.; Berend, M.E.; Meding, J.B. The Importance of Range of Motion after Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 465, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubinus SP II Anatomically Adapted Cemented Hip System—Surgical Technique 2020. Available online: https://www.link-ortho.com/fileadmin/user_upload/Fuer_den_Arzt/Produkte/Downloads/EN/6431_SP_II_OP-Impl-Instr_en_2020-03_001_MAR-02619_1-0.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Noble, P.C.; Alexander, J.W.; Lindahl, L.J.; Yew, D.T.; Granberry, W.M.; Tullos, H.S. The Anatomic Basis of Femoral Component Design. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1988, 235, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, L.D.; Faugere, M.C.; Mackel, A.M.; Gruen, T.A.; Bognar, B.; Malluche, H.H. Structural and Cellular Assessment of Bone Quality of Proximal Femur. Bone 1993, 14, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Galler, M.; Zellner, M.; Bäuml, C.; Füchtmeier, B. Total Hip Arthroplasty after Failed Osteosynthesis of Proximal Femoral Fractures: Revision and Mortality of 80 Patients. J. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 2309499017717869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.A.; Alonso, M.G.; Porro, J.G.; Rueda, D.; Larrauri, P.M.; Soler, J.J. Use of the Gamma Nail in the Treatment of Fractures of the Proximal Femur. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1998, 350, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-N.; Li, C.-T.; Peng, Y.-T.; Chang, C.-H. Role of the Compression Screw in the Dynamic Hip–Screw System: A Finite-Element Study. Med. Eng. Phys. 2015, 37, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojan, A.J.; Beimel, C.; Taglang, G.; Collin, D.; Ekholm, C.; Jönsson, A. Critical Factors in Cut-out Complication after Gamma Nail Treatment of Proximal Femoral Fractures. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, K.-K.; Fang, C.-K.; Chen, C.-M.; Su, Y.-P.; Wu, H.-F.; Chiu, F.-Y. Risk Factors in Cutout of Sliding Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fractures: An Evaluation of 937 Patients. Int. Orthop. 2010, 34, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltean-Dan, D.; Apostu, D.; Tomoaia, G.; Kerekes, K.; Păiuşan, M.G.; Bardas, C.-A.; Benea, H.R.C. Causes of Revision after Total Hip Arthroplasty in an Orthopedics and Traumatology Regional Center. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2022, 95, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar-Gheiti, A.J.; McColgan, R.; Kelly, M.; Cassar-Gheiti, T.M.; Kenny, P.; Murphy, C.G. Current Concepts and Outcomes in Cemented Femoral Stem Design and Cementation Techniques: The Argument for a New Classification System. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Arshad, N.; Habib, Y.; Shami, A.M.; Rehman, O.U.; Rehman, M.; Reyaz, M.; Mumtaz, H. Effect of Cementing Technique on Aseptic Stem Loosening in Cemented Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 2884–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvik, G. Roentgen Stereophotogrammetric Analysis. Acta Radiol. 1990, 31, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.W.; Gulati, A.; Gill, H.S. Ten-Year RSA-Measured Migration of the Exeter Femoral Stem. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95-B, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Clement, N.D.; Bardgett, M.; Merrie, K.; Furtado, S.; Bowman, R.; Langton, D.J.; Deehan, D.J.; Holland, J. Cemented Exeter Total Hip Arthroplasty with a 32 Mm Head on Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene: Does Age Influence Functional Outcome, Satisfaction, Activity, Stem Migration, and Periprosthetic Bone Mineral Density? Bone Jt. Res. 2019, 8, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, F.; Tornberg, H.; Jones, C.W.; Bucher, T.A.; Malahias, M.-A. The Exeter Cemented Stem Provides Outstanding Long-Term Fixation and Bone Load at 15 Years Follow-up: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 31, 10225536231153232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesselmann, S.; Hong, Y.; Schlemmer, F.; Wiendieck, K.; Söder, S.; Hussnaetter, I.; Müller, L.A.; Forst, R.; Wierer, T. Migration Measurement of the Cemented Lubinus SP II Hip Stem—A 10-Year Follow-up Using Radiostereometric Analysis. Biomed. Tech. 2017, 62, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Voort, P.; Pijls, B.G.; Nieuwenhuijse, M.J.; Jasper, J.; Fiocco, M.; Plevier, J.W.M.; Middeldorp, S.; Valstar, E.R.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H. Early Subsidence of Shape-Closed Hip Arthroplasty Stems Is Associated with Late Revision. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 24 RSA Studies and 56 Survival Studies. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, W.; Meijer, R.; Kollen, B.J.; Verheyen, C.C.; Ettema, H.B. Excellent Results with the Cemented Lubinus SP II 130-Mm Femoral Stem at 10 Years of Follow-up: 932 Hips Followed for 5–15 Years. Acta Orthop. 2014, 85, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, P.B.; Jakobsen, S.S.; Vainorius, D.; Homilius, M.; Hansen, T.B.; Stilling, M. Less Early Subsidence of Cemented Exeter Short Stems Compared with Cemented Exeter Standard Stems in Dorr Type A Femurs. Bone Jt. Open 2023, 4, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammerer, D.; Blum, P.; Putzer, D.; Krappinger, D.; Liebensteiner, M.C.; Nogler, M.; Thaler, M. Subsidence of a Metaphyseal-Anchored Press-Fit Stem after 4-Year Follow-up: An EBRA-FCA Analysis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2022, 142, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stihsen, C.; Radl, R.; Keshmiri, A.; Rehak, P.; Windhager, R. Subsidence of a Cementless Femoral Component Influenced by Body Weight and Body Mass Index. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsten, I.; Akesson, K.; Besjakov, J.; Obrant, K.J. Migration of the Charnley Stem in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. A Roentgen Stereophotogrammetric Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1995, 77, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
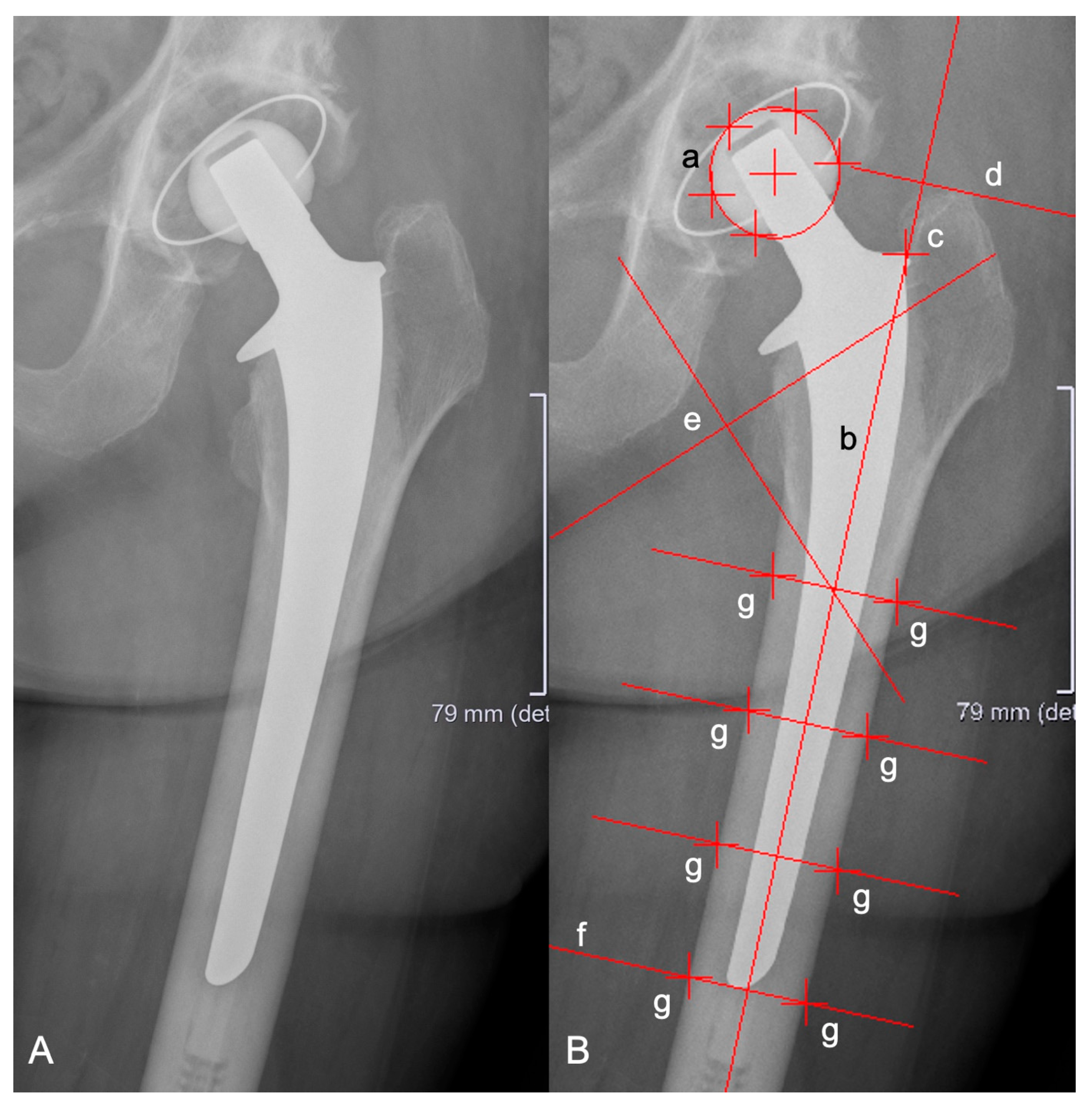
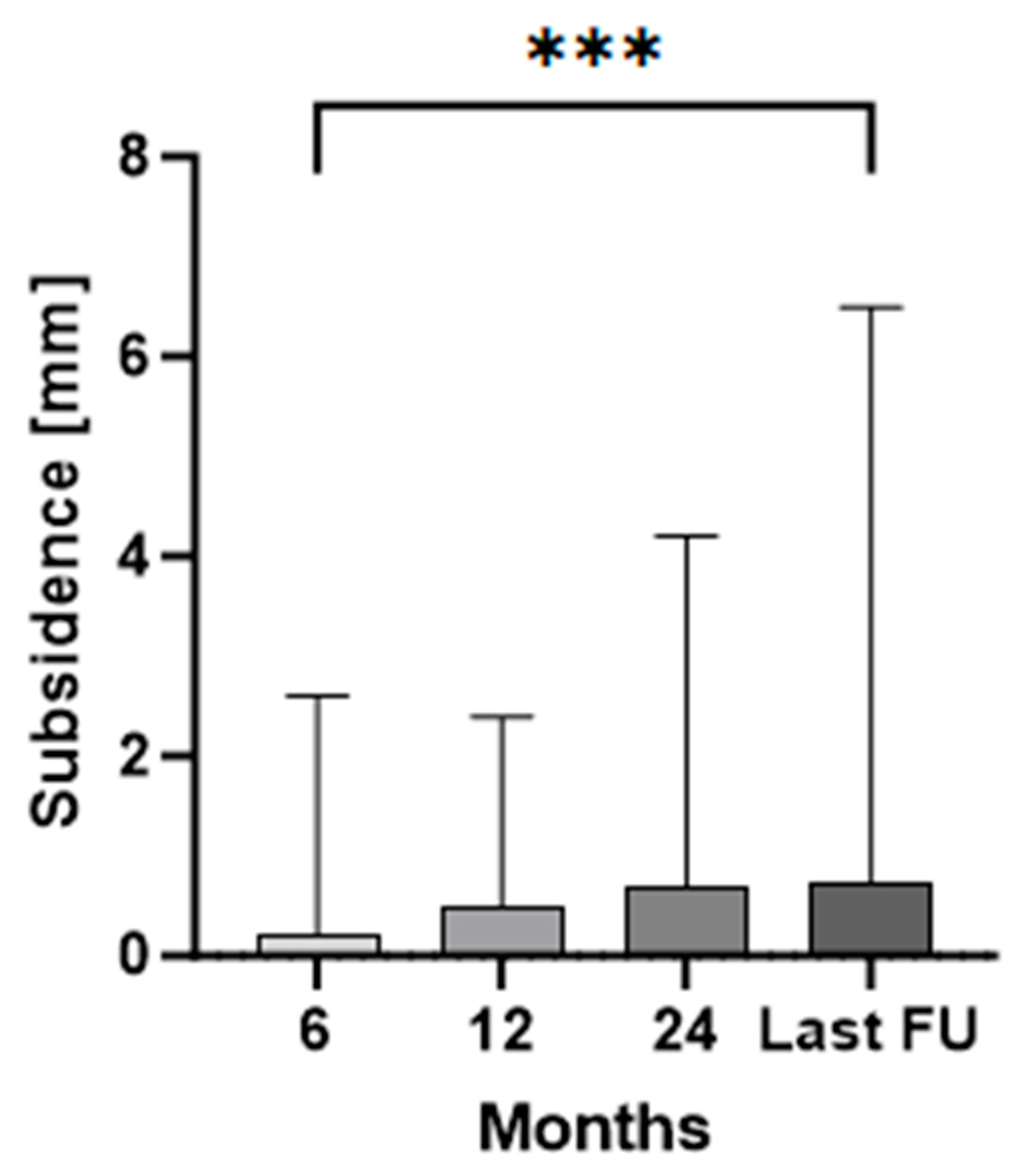
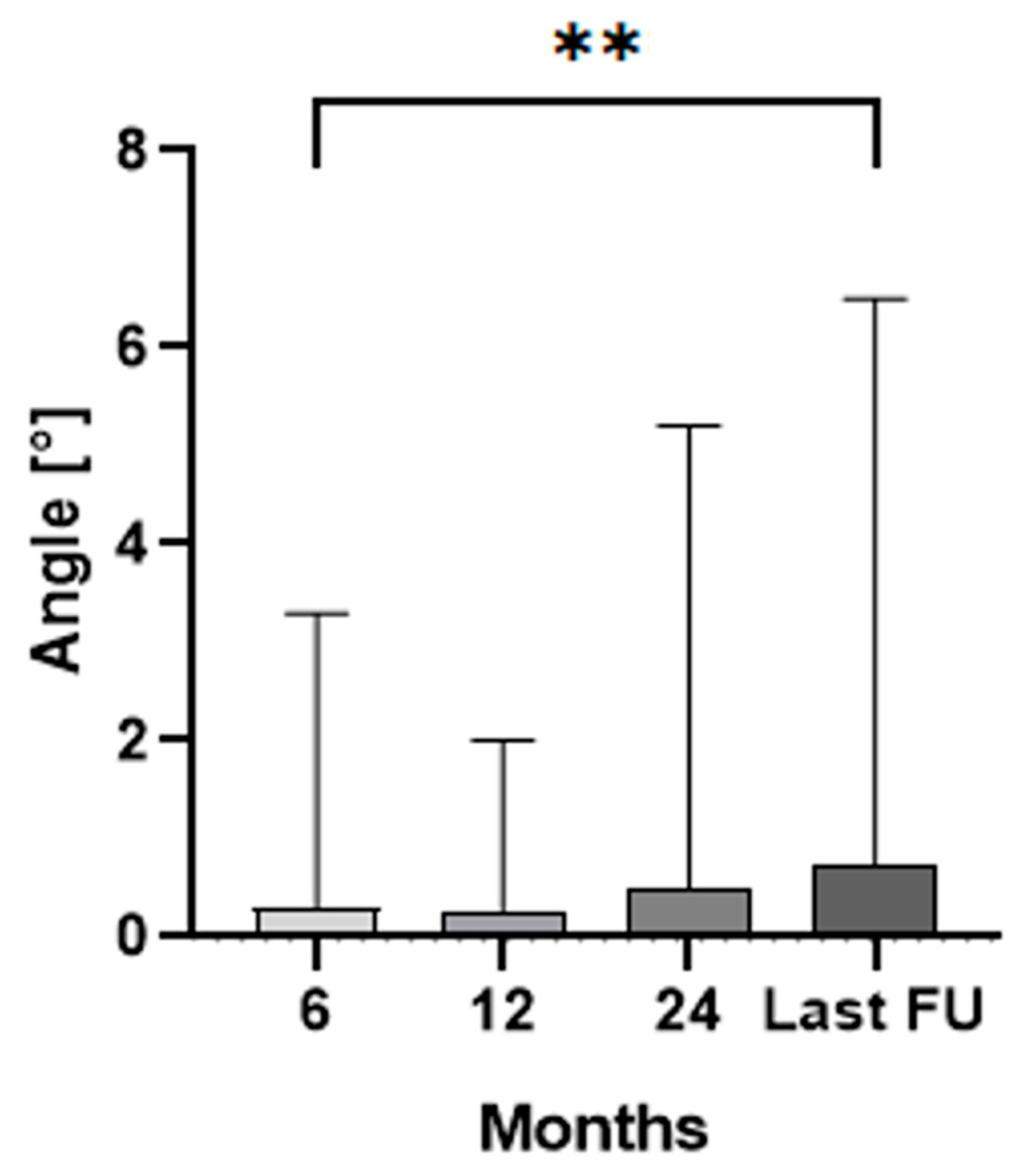
| Number of Patients | Female | 48 |
| Male | 13 | |
| Mean age (years) | 76 (30–93) | |
| Mean BMI (kg/m2) | 26 (19–34) | |
| Surgical site | Left | 27 |
| Right | 34 | |
| Median radiological follow-up (years) | 6.5 (2–16) | |
| Preoperative diagnosis | Primary osteoarthritis | 47 |
| Femoral neck fracture | 7 | |
| Avascular necrosis of femoral head | 5 | |
| Others | 2 | |
| Surgical approach | Direct anterior approach | 20 |
| Transgluteal lateral approach | 41 | |
| Surgical position | Supine | 20 |
| Lateral | 41 | |
| Mean cut-to-suture time (min) | 105 (33–282) |
| Dorr Classification | A | 15 [24.6] |
| B | 26 [42.6] | |
| C | 20 [32.8] | |
| Stem length | 130 | 0 [0.0] |
| 150 | 55 [90.2] | |
| 170 | 6 [9.8] | |
| CCD angle | 117 | 0 [0.0] |
| 126 | 26 [42.6] | |
| 135 | 35 [57.4] | |
| Head diameter (mm) | 28 | 33 [54.1] |
| 32 | 28 [45.9] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blum, P.; Neugebauer, J.; Keiler, A.; Putzer, D.; Watrinet, J.; Regenbogen, S.; Dammerer, D. Mid-Term Migration Pattern of a Cemented Collared Anatomical Stem—A Retrospective Study Using EBRA-FCA. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175187
Blum P, Neugebauer J, Keiler A, Putzer D, Watrinet J, Regenbogen S, Dammerer D. Mid-Term Migration Pattern of a Cemented Collared Anatomical Stem—A Retrospective Study Using EBRA-FCA. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(17):5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175187
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlum, Philipp, Johannes Neugebauer, Alexander Keiler, David Putzer, Julius Watrinet, Stephan Regenbogen, and Dietmar Dammerer. 2024. "Mid-Term Migration Pattern of a Cemented Collared Anatomical Stem—A Retrospective Study Using EBRA-FCA" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 17: 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175187
APA StyleBlum, P., Neugebauer, J., Keiler, A., Putzer, D., Watrinet, J., Regenbogen, S., & Dammerer, D. (2024). Mid-Term Migration Pattern of a Cemented Collared Anatomical Stem—A Retrospective Study Using EBRA-FCA. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(17), 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175187






