Not Every Size Fits All: Surgical Corridors for Clival and Cervical Chordomas—A Systematic Review of the Literature and Illustrative Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Full article in English;
- Studies analyzing more than 5 patients;
- Case series, retrospective studies, and prospective studies;
- Patients affected by skull base and/or cervical chordomas treated with a transoral, endonasal, or retropharyngeal approach;
- Studies evaluating EOR and complication rate;
- Articles not in English;
- Editorials, books, case reports, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses;
- Anatomical studies:
- Studies focusing on other surgical approaches.
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics and Data Analysis
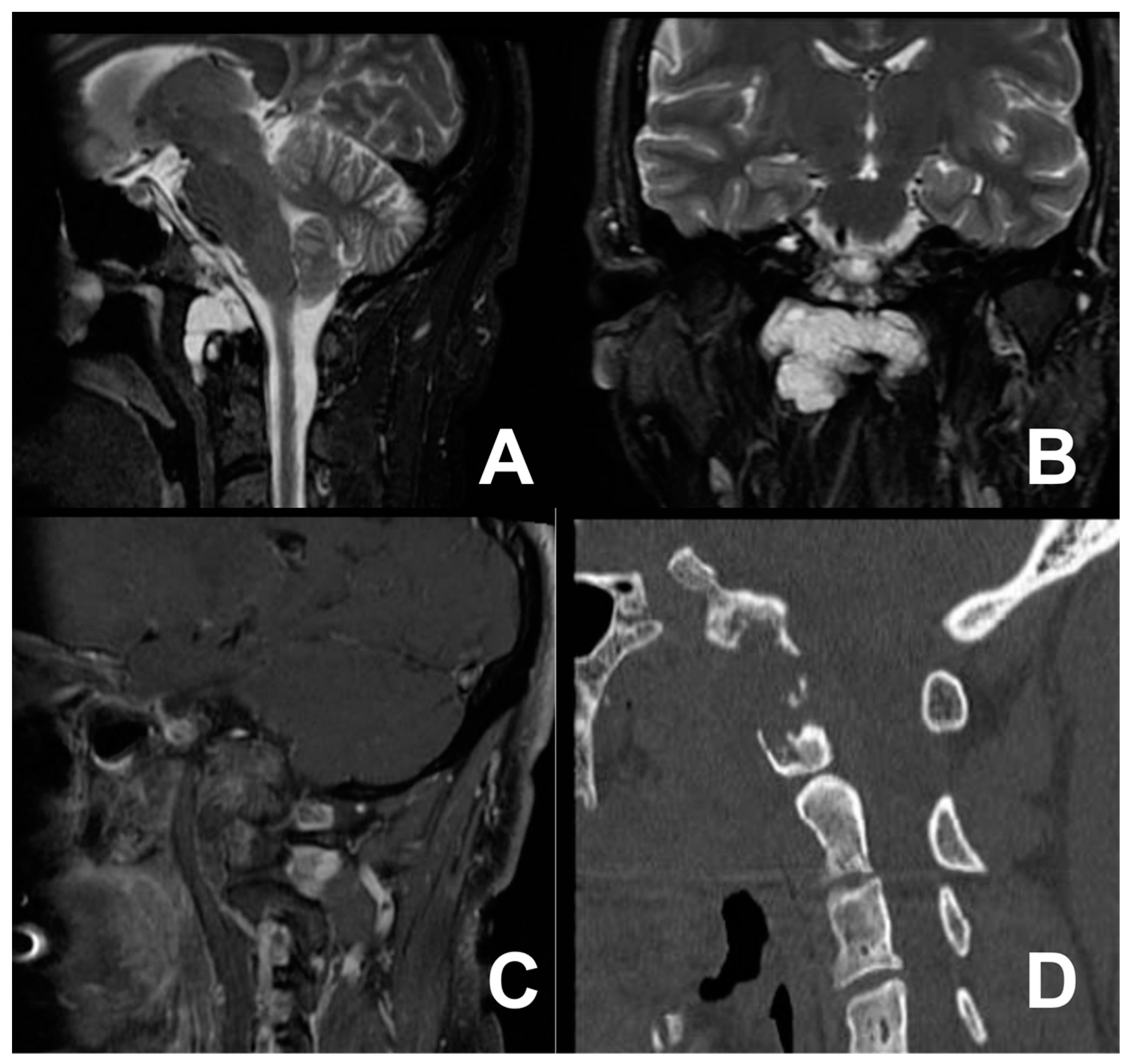
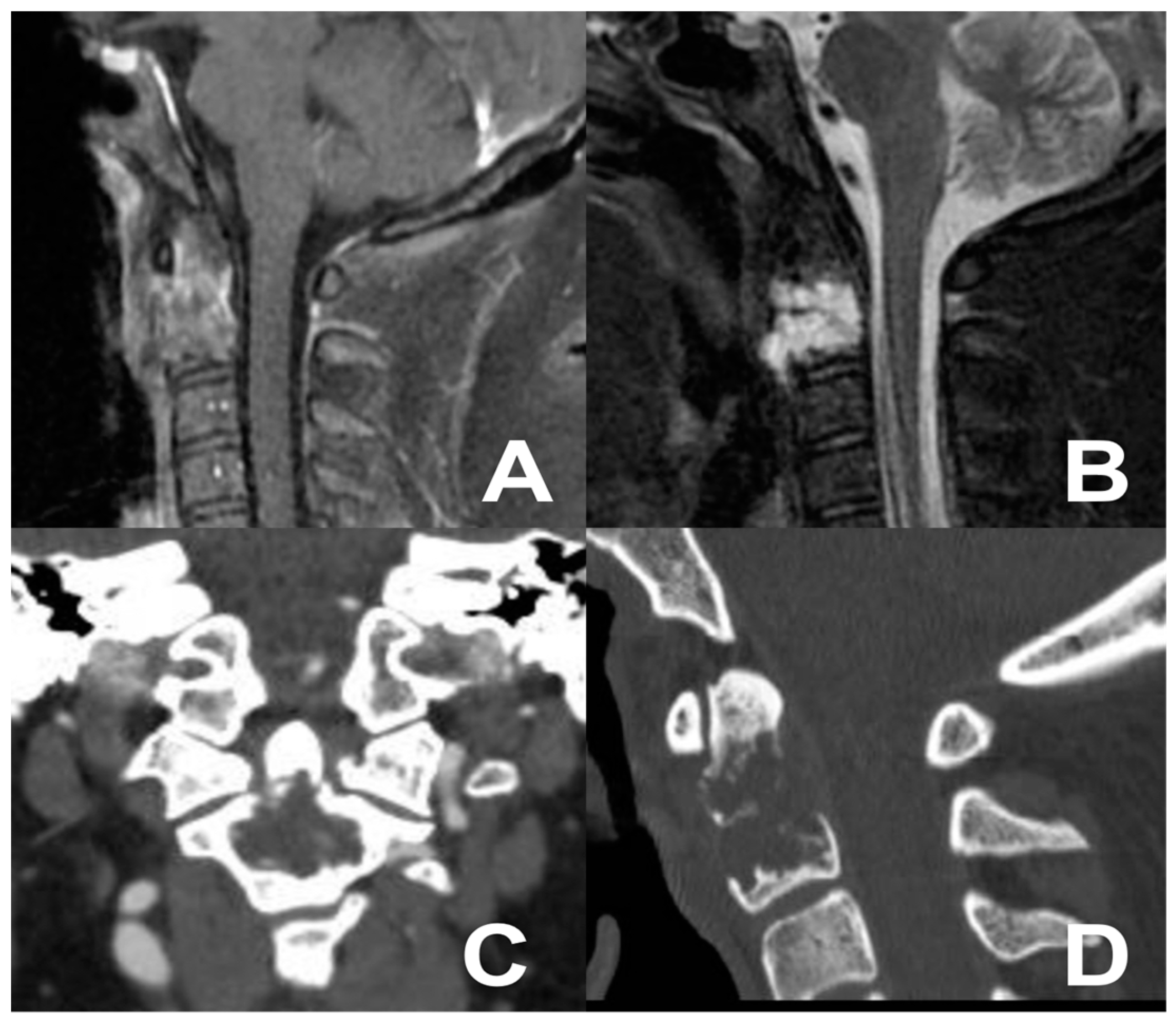
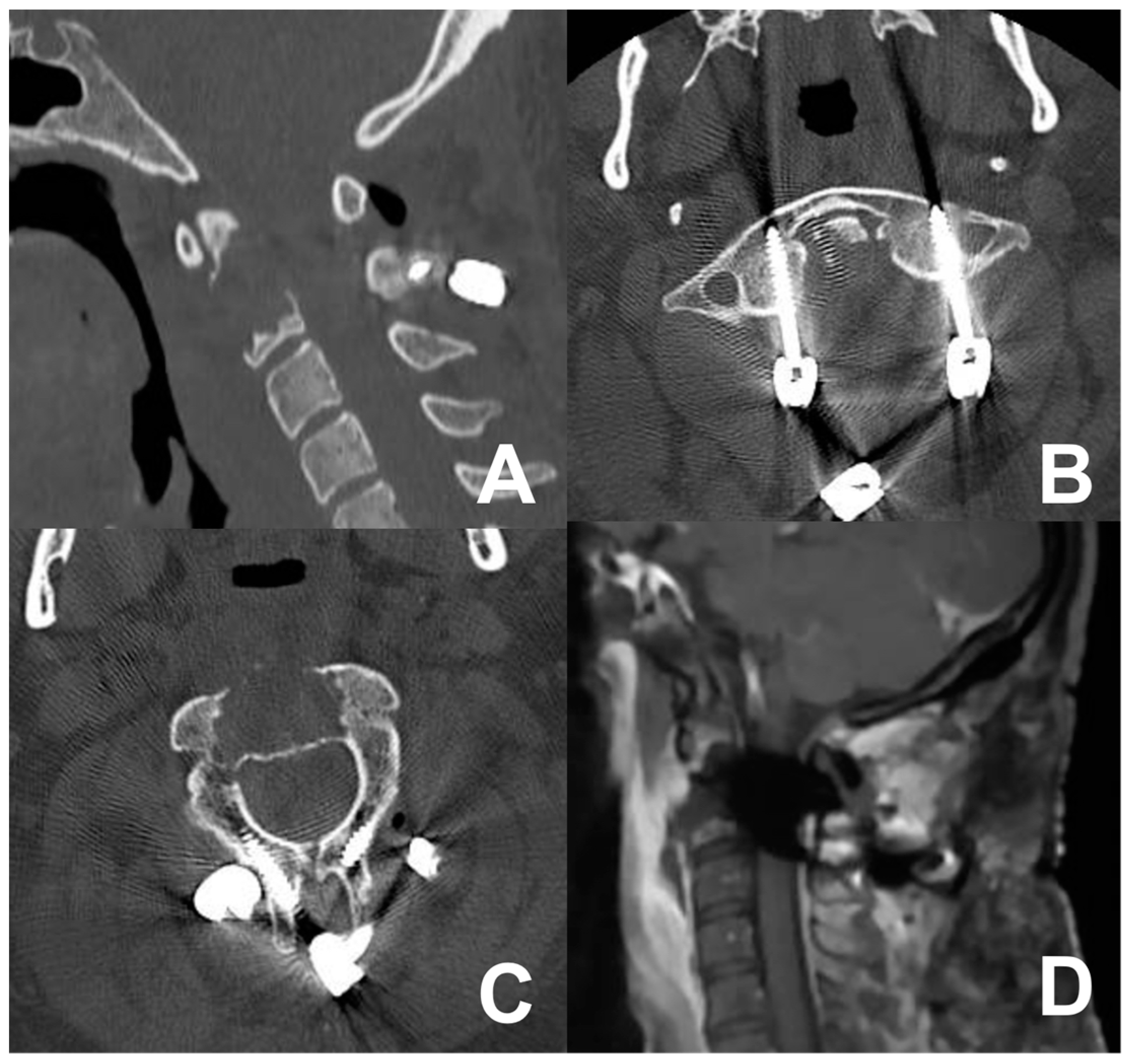
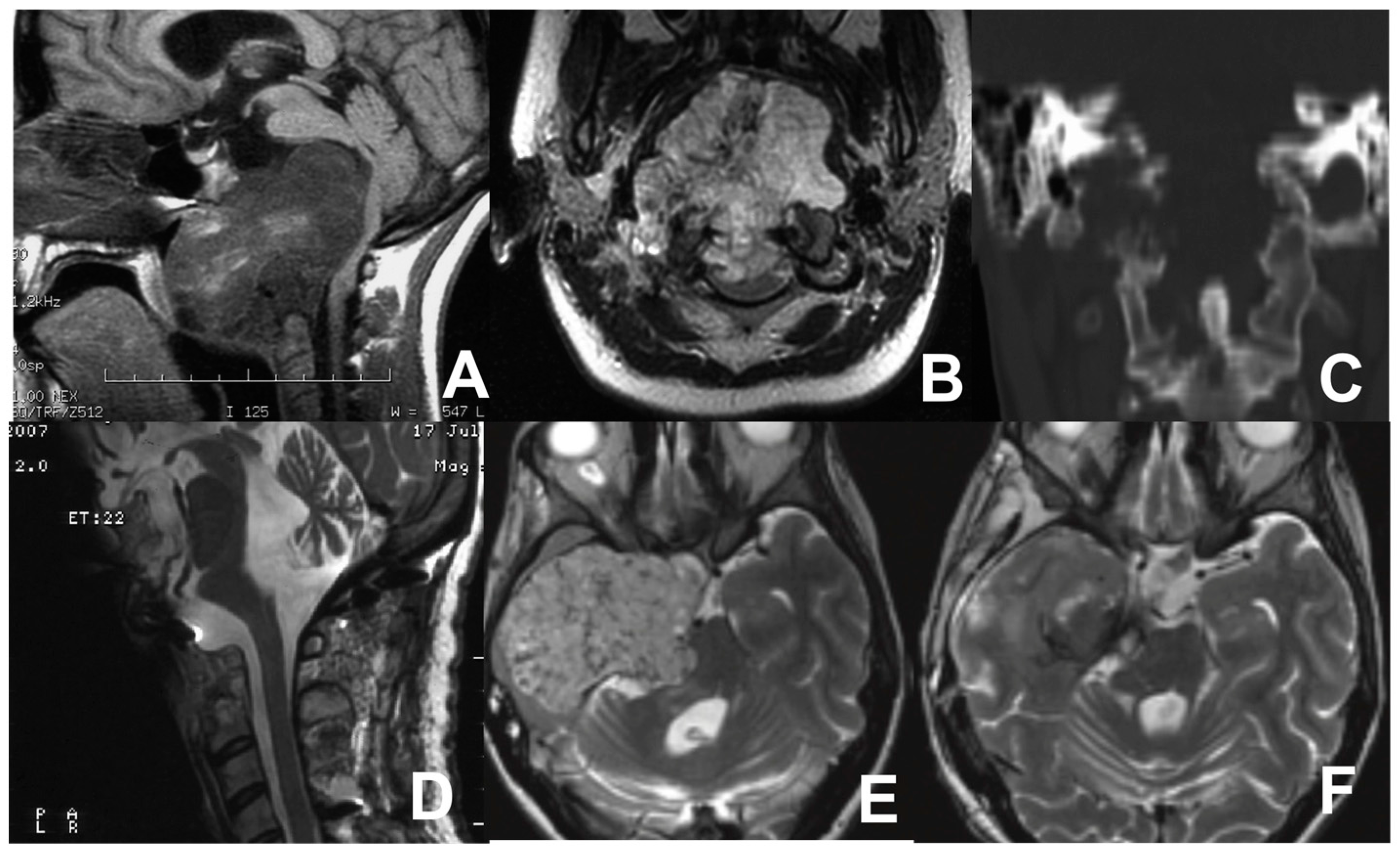
3.2. First Case: Two-Staged Submandibular Retropharyngeal and Endoscopic Endonasal Approach
3.3. Second Case: One-Stage Combined Submandibular Retropharyngeal Approach and Posterior Midline C1-C2 Fusion
3.4. Third Case: Two-Staged Transoral Approach and Posterior Midline Occipitocervical Fusion—Subtemporal/Infratemporal and Retrosigmoid Approaches for Tumor Relapse
4. Discussion
4.1. Transoral Approach
4.2. Anterior Retropharyngeal Approach
4.3. Endoscopic Endonasal Approach
- Extradural–Upper Clivus: These clival chordomas are typically in the sellar region and confined by the cavernous sinus. In cases of retrosellar invasion, the extradural transposition of the pituitary gland is employed. Additionally, the resection of the posterior clinoid is usually performed. Tumors in the upper clivus have a higher resection rate [16,69].
- Extradural–Lower Clivus: The boundaries are represented by the condyles. However, employing an EEA in this area is relatively contraindicated, especially in the case of lesions near the lower cranial nerves located posterior to the occipital condyle [22].
- Intradural: These lesions lack defined boundaries and require management through different corridors (e.g., infra-chiasmatic in the upper clivus) being careful around damage to the VI nerve [10].
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walcott, B.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Mohyeldin, A.; Coumans, J.-V.; Kahle, K.T.; Ferreira, M.J. Chordoma: Current concepts, management, and future directions. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e69–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller, C.A.; Trama, A.; Serraino, D.; Rossi, S.; Navarro, C.; Chirlaque, M.D.; Casali, P.G.; RARECARE Working Group. Descriptive epidemiology of sarcomas in Europe: Report from the RARECARE project. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacchiotti, S.; Sommer, J. Building a global consensus approach to chordoma: A position paper from the medical and patient community. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e71–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohman, L.-E.; Koch, M.; Bailey, R.L.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Lee, J.Y. Skull Base Chordoma and Chondrosarcoma: Influence of Clinical and Demographic Factors on Prognosis: A SEER Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2014, 82, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visocchi, M.; Iacopino, D.G.; Signorelli, F.; Olivi, A.; Maugeri, R. Walk the Line. The Surgical Highways to the Craniovertebral Junction in Endoscopic Approaches: A Historical Perspective. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorelli, F.; Olivi, A.; De Giorgio, F.; Pascali, V.L.; Visocchi, M. A 360° Approach to the Craniovertebral Junction in a Cadaveric Laboratory Setting: Historical Insights, Current, and Future Perspectives in a Comparative Study. World Neurosurg. 2020, 140, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbolay, O.L.; González, J.G.; González, R.H.; Gálvez, Y.H. Extended Endoscopic Endonasal Approach to the Skull Base. Min Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2009, 52, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Perna, G.; Baldassarre, B.M.; Portonero, I.; Penner, F.; Cofano, F.; Marco, R.; Marengo, N.; Garbossa, D.; Pecorari, G.; Zenga, F. Craniovertebral junction chordomas: Case series and strategies to overcome the surgical challenge. J. Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2021, 12, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butenschoen, V.M.; Krauss, P.; Bernhardt, D.; Negwer, C.; Combs, S.; Meyer, B.; Gempt, J. The transnasal endoscopic approach for resection of clival tumors: A single-center experience. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Emengen, A.; Caklili, M.; Ergen, A.; Yılmaz, E.; Uzuner, A.; Icli, D.; Cabuk, B.; Anik, I. Operative nuances and surgical limits of the endoscopic approach to clival chordomas and chondrosarcomas: A single-center experience of 72 patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 208, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbaro, S.; Cornelius, J.F.; Froelich, S.; Tigan, L.; Kehrli, P.; Debry, C.; Romano, A.; Herman, P.; George, B.; Bresson, D. Endoscopic endonasal approach in the management of skull base chordomas—Clinical experience on a large series, technique, outcome, and pitfalls. Neurosurg. Rev. 2013, 37, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Melcher, R.; Harms, J.; Crockard, A. Outcome of 132 Operations in 97 Patients With Chordomas of the Craniocervical Junction and Upper Cervical Spine. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehdashti, A.R.; Karabatsou, K.; Ganna, A.; Witterick, I.; Gentili, F. Expanded Endoscopic Endonasal Approach for Treatment of Clival Chordomas. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, N.; Dusick, J.R.; Gorgulho, A.A.; Mattozo, C.A.; Moftakhar, P.; De Salles, A.A.; Kelly, D.F. Endonasal microscopic removal of clival chordomas. Surg. Neurol. 2008, 69, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, G.; Sciarretta, V.; Calbucci, F.; Farneti, G.; Mazzatenta, D.; Pasquini, E. The Endoscopic Transnasal Transsphenoidal Approach for the Treatment of Cranial Base Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas. Neurosurg. 2006, 59, ONS-50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.F.; Nyquist, G.G.; Moore, N.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscopic Endonasal Minimal Access Approach to the Clivus. Oper. Neurosurg. 2010, 67, ons150–ons158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzaro, M.; Zenga, F.; Raimondo, L.; Pacca, P.; Pennacchietti, V.; Riva, G.; Ducati, A.; Pecorari, G. Three-dimensional endoscopy in transnasal transsphenoidal approach to clival chordomas. Head Neck 2015, 38, E1814–E1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzmann, D.; Reisch, R.; Krayenbühl, N.; Hug, E.; Bernays, R.L. The Transnasal Transclival Approach for Clivus Chordoma. Min Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2010, 53, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassam, A.B.; Prevedello, D.M.; Thomas, A.; Gardner, P.; Mintz, A.; Snyderman, C.; Carrau, R. ENDOSCOPIC ENDONASAL PITUITARY TRANSPOSITION FOR A TRANSDORSUM SELLAE APPROACH TO THE INTERPEDUNCULAR CISTERN. Neurosurg. 2008, 62, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Jeon, C.; Se, Y.-B.; Hong, S.D.; Seol, H.J.; Lee, J.-I.; Park, C.-K.; Kim, D.G.; Jung, H.-W.; Han, D.H.; et al. Clinical outcomes of an endoscopic transclival and transpetrosal approach for primary skull base malignancies involving the clivus. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.-S.; Hong, S.D.; Kang, H.; Seo, Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Seol, H.J.; Park, C.-K.; Nam, D.-H.; Lee, J.-I.; Kim, Y.H. Safety and Efficacy of Endoscopic Dorsum Sellar Resection for Access to Retroinfundibular or Upper Clival Tumors (Korean Society of Endoscopic Neurosurgery-008). World Neurosurg. 2021, 150, e675–e680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutourousiou, M.; Gardner, P.A.; Tormenti, M.J.; Henry, S.L.; Stefko, S.T.; Kassam, A.B.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Snyderman, C.H. Endoscopic Endonasal Approach for Resection of Cranial Base Chordomas. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlay, M.; Durmaz, A.; Özer, I.; Kural, C.; Temiz, Ç.; Kaya, S.; Solmaz, I.; Daneyemez, M.; Izci, Y. Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the ventral skull base lesions. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 167, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, H.; Zong, X.; Wang, X.; Gui, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, C.; Bai, J.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y. Application of endoscopic endonasal approach in skull base surgeries: Summary of 1886 cases in a single center for 10 consecutive years. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2020, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, M.M.; Zwagerman, N.T.; Wang, E.W.; Snyderman, C.H.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Gardner, P.A. Long-term outcomes in the treatment of pediatric skull base chordomas in the endoscopic endonasal era. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2021, 27, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.H.; Ahmed, R. Primary atlantoaxial bone tumors in children: Management strategies and long-term follow-up. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2014, 13, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerer, M.; Cossu, G.; Pasche, P.; Ikonomidis, C.; Simon, C.; Pralong, E.; George, M.; Levivier, M.; Daniel, R. Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to clival and paraclival tumors: Indications and limits. Neurochirurgie 2016, 62, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, C.; Muzaffar, J.; Kulendra, K.; Sanghera, P.; Shaw, S.; Shad, A.; Saravanappa, N.; Paluzzi, A.; Ahmed, S. Chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base: Treatment and outcome analysis in a consecutive case series of 24 patients. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupper, A.J.; Deconde, A.; Levy, M.; Nation, J. Pediatric Endoscopic Endonasal Approaches for Skull Base Lesions in the Very Young: Is It Safe and Effective? J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2018, 79, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeri, T.; Champagne, P.-O.; Giammattei, L.; Abbritti, R.; Cartailler, J.; Calugaru, V.; Feuvret, L.; Guichard, J.-P.; Polivka, M.; Adle-Biassette, H.; et al. Management strategies in clival and craniovertebral junction chordomas: A 29-year experience. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 138, 1640–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramm-Pettersen, J.; Frič, R.; Berg-Johnsen, J. Long-term follow-up after endoscopic trans-sphenoidal surgery or initial observation in clivus chordomas. Acta Neurochir. 2017, 159, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quon, J.L.; Kim, L.H.; Hwang, P.H.; Patel, Z.M.; Grant, G.A.; Cheshier, S.H.; Edwards, M.S.B. Transnasal endoscopic approach for pediatric skull base lesions: A case series. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahme, R.J.; Arnaout, O.M.; Sanusi, O.R.; Kesavabhotla, K.; Chandler, J.P. Endoscopic Approach to Clival Chordomas: The Northwestern Experience. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, e231–e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Toda, M.; Tomita, T.; Ogawa, K.; Yoshida, K. Surgical results of an endoscopic endonasal approach for clival chordomas. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Kondo, K.; Kin, T.; Suzukawa, K.; Saito, N. Endoscopic Transnasal Interseptal Approach for Invasive Clival Tumors: Development of an Approach Method Regarding Maximal Preservation of the Nasal Anatomy. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 2015, 55, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkarubo, A.N.; Koval, K.V.; Chernov, I.V.; Andreev, D.N.; Panteleyev, A.A. Endoscopic Endonasal Transclival Approach to Tumors of the Clivus and Anterior Region of the Posterior Cranial Fossa (Results of Surgical Treatment of 136 Patients). World Neurosurg. 2018, 121, e246–e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schur, S.; Passer, J.Z.; Hanna, E.Y.; Su, S.Y.; Kupferman, M.E.; DeMonte, F.; Raza, S.M. The impact of expanded endoscopic approaches on oncologic and functional outcomes for clival malignancies:a case series. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2022, 159, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solares, C.A.; Fakhri, S.; Batra, P.S.; Lee, J.; Lanza, D.C. Transnasal Endoscopic Resection of Lesions of the Clivus: A Preliminary Report. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soloperto, D.; Fabbris, C.; De Rossi, S.; Musumeci, A.; Marchioni, D. Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery of Clival Chordomas: Preliminary Results. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 71, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiessberger, A.; Dogra, S.; Golub, D.; Grueter, B.; Nasim, M.; Schneider, S.; Moriggl, B.; Dehdashti, A.R.; Schulder, M. Contemporary surgical management of skull base chordomas—Anatomical reflections on a single center experience retrospective case series. Clin. Anat. 2022, 35, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stippler, M.; Gardner, P.A.; Snyderman, C.H.; Carrau, R.L.; Prevedello, D.M.; Kassam, A.B. ENDOSCOPIC ENDONASAL APPROACH FOR CLIVAL CHORDOMAS. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.C.-W.; Naidoo, Y.; Oue, S.; Alexander, H.; Robinson, S.; Wickremesekera, A.; Floreani, S.; Vrodos, N.; Santoreneos, S.; Ooi, E.; et al. Endoscopic Surgery of Skull Base Chordomas. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2012, 73, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, M.; Kohmura, E. Endoscopic endonasal removal of laterally extended clival chordoma using side-viewing scopes. Acta Neurochir. 2011, 154, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellutini, E.d.A.S.; Balsalobre, L.; Hermann, D.R.; Stamm, A.C. The Endoscopic Endonasal Approach for Extradural and Intradural Clivus Lesions. World Neurosurg. 2014, 82, S106–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, G.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Xie, S.; Luo, H.; Xiao, L.; Wu, X.; Hong, T.; Tang, B. The use of three-dimensional endoscope in transnasal skull base surgery: A single-center experience from China. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 996290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Hide, T.; Shinojima, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kawano, T.; Kuratsu, J.-I. Endoscopic endonasal skull base approach for parasellar lesions: Initial experiences, results, efficacy, and complications. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2014, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Teng, H.; Feng, D.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Yuan, W.; Jia, L. Sequentially Staged Resection and 2-Column Reconstruction for C2 Tumors Through a Combined Anterior Retropharyngeal–Posterior Approach. Neurosurg. 2011, 69, ons184–ons194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.D.; Chung, J.C.; Park, K.S.; Chung, S.Y.; Park, M.S.; Ryu, S.; Kim, S.M. Long-Term Outcomes after Multimodal Treatment for Clival Chordoma: Efficacy of the Endonasal Transclival Approach with Early Adjuvant Radiation Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, J.; Afshari, F.T.; Ahmed, S.K.; Chavda, S.V.; Sanghera, P.; Paluzzi, A. Endoscopic endonasal surgery for Clival Chordomas—A single institution experience and short term outcomes. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 33, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, G.; Rout, K.; Dash, S. Endoscopic Resection of Clival Chordoma: A Tertiary Care Experience. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 72, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kong, F.; Yan, B.; Ni, Z.; Liu, H. Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery for Clival Chordoma and Chondrosarcoma. ORL 2008, 70, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, N.; Yang, M.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; Ye, C.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Jiao, J.; Xiao, J. Early Major Complications After Radical Resection of Primary C2-Involved Upper Cervical Chordoma Through the Combined Anterior Retropharyngeal–Posterior Approach: Incidence and Risk Factors. World Neurosurg. 2021, 154, e790–e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoli, M.; Rossi, N.; Friso, F.; Sturiale, C.; Frank, G.; Pasquini, E.; Mazzatenta, D. Limits of endoscopic endonasal approach for cranio-vertebral junction tumors. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2018, 62, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoli, M.; Milanese, L.; Bonfatti, R.; Faustini-Fustini, M.; Marucci, G.; Tallini, G.; Zenesini, C.; Sturiale, C.; Frank, G.; Pasquini, E.; et al. Clival chordomas: Considerations after 16 years of endoscopic endonasal surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweckberger, K.; Giese, H.; Haenig, B.; Federspil, P.A.; Baumann, I.; Albrecht, T.; Uhl, M.; Unterberg, A. Clivus chordomas: Heterogeneous tumor extension requires adapted surgical approaches. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 199, 106305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, C.Y.V.; Tang, I.P.; Ng, B.H.K.; Wong, A.S.I.I.H.; Liew, D.N.S. Endoscopic Endonasal Approach in Clival Chordoma Surgery: Case Series. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 73, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, A.; Chin, A.T.; Wagner, J.R.; Kunwar, S.; Ames, C.; Chou, D.; Barani, I.; Parsa, A.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Benet, A.; et al. Factors Predicting Recurrence After Resection of Clival Chordoma Using Variable Surgical Approaches and Radiation Modalities. Neurosurgery 2015, 76, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giammalva, G.R.; Ferini, G.; Torregrossa, F.; Brunasso, L.; Musso, S.; Benigno, U.E.; Gerardi, R.M.; Bonosi, L.; Costanzo, R.; Paolini, F.; et al. The Palliative Care in the Metastatic Spinal Tumors. A Systematic Review on the Radiotherapy and Surgical Perspective. Life 2022, 12, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, W.A.; Black, P.; Connor, G.H.; Uematsu, S. Transoral transpalatal approach for resection of clival chordoma. Laryngoscope 1971, 81, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Seljeskog, E.L.; Duvall, A.J.; Long, D.M. Transnasal transsphenoidal approach to the sella. Laryngoscope 1977, 87, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrabba, G.; Dehdashti, A.R.; Gentili, F. Surgery for clival lesions: Open resection versus the expanded endoscopic endonasal approach. Neurosurg. Focus 2008, 25, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visocchi, M.; Signorelli, F.; Liao, C.; Rigante, M.; Paludetti, G.; Barbagallo, G.; Olivi, A. Transoral Versus Transnasal Approach for Craniovertebral Junction Pathologies: Never Say Never. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visocchi, M.; Pappalardo, G.; Pileggi, M.; Signorelli, F.; Paludetti, G.; La Rocca, G. Experimental Endoscopic Angular Domains of Transnasal and Transoral Routes to the Craniovertebral Junction. Spine 2016, 41, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visocchi, M.; La Rocca, G.; Della Pepa, G.M.; Stigliano, E.; Costantini, A.; Di Nardo, F.; Maira, G. Anterior video-assisted approach to the craniovertebral junction: Transnasal or transoral? A cadaver study. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 156, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Harrop, J.; Schiffmacher, P.; Rosen, M.; Evans, J. Ventral Surgical Approaches to Craniovertebral Junction Chordomas. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, A96–A103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, X.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, D.; Han, S.; Xiao, J. Recurrent Upper Cervical Chordomas After Radiotherapy. Spine 2013, 38, E1141–E1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshafai, N.S.; Gunness, V.R.N. The High Cervical Anterolateral Retropharyngeal Approach. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2019, 125, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visocchi, M.; Benato, A.; Davila, M.F.; Bayati, A.A.; Zeoli, F.; Signorelli, F. A Three-Step Submandibular Retropharyngeal Approach to the Craniovertebral Junction: Is Less Always More? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappabianca, P.; Cavallo, L.M.; Esposito, F.; De Divitiis, O.; Messina, A.; De Divitiis, E. Extended endoscopic endonasal ap-proach to the midline skull base: The evolving role of transsphenoidal surgery. Adv. Tech. Stand. Neurosurg. 2008, 33, 151–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portonero, I.; Bue, E.L.; Penner, F.; Di Perna, G.; Baldassarre, B.M.; De Marco, R.; Pesaresi, A.; Garbossa, D.; Pecorari, G.; Zenga, F. Lesson learned in endoscopic endonasal dens resection for C1–C2 spinal cord decompression. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 33, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shidoh, S.; Toda, M.; Kawase, T.; Nakajima, H.; Tomita, T.; Ogawa, K.; Yoshida, K. Transoral vs. Endoscopic Endonasal Approach for Clival/Upper Cervical Chordoma. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 2014, 54, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, L.E.; Haugen, T.W.; Rassekh, C.H.; Adappa, N.D.; Weinstein, G.S.; O’Malley, B.W. A novel transpalatal-transoral robotic surgery approach to clival chordomas extending into the nasopharynx. Head Neck 2019, 41, E133–E140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrau, R.L.; Prevedello, D.M.; de Lara, D.; Durmus, K.; Ozer, E. Combined transoral robotic surgery and endoscopic endonasal approach for the resection of extensive malignancies of the skull base. Head Neck 2013, 35, E351–E358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, J.; Tateya, I.; Nakatomi, H.; Uyama, I.; Hirose, Y. Transoral Robotic-Assisted Neurosurgery for Skull Base and Upper Spine Lesions. Neurospine 2024, 21, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangal, D.J.; Cote, D.J.; Ruzevick, J.; Yarovinsky, B.; Kugener, G.; Wrobel, B.; Ference, E.H.; Swanson, M.; Hung, A.J.; Donoho, D.A.; et al. Robotic and robot-assisted skull base neurosurgery: Systematic review of current applications and future directions. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 52, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santegoeds, R.G.C.; Temel, Y.; Beckervordersandforth, J.C.; Van Overbeeke, J.J.; Hoeberigs, C.M. State-of-the-Art Imaging in Human Chordoma of the Skull Base. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Authors, Year | Country | N of Patients | Mean Age (Years) | Approach | Follow Up (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arbolay et al., 2009 [7] | Cuba | 2 | 31 | EEA | 6 |
| Baldassarre et al., 2021 [8] | Italy | 8 | 35,75 (range 14–77) | 5 EEA | 24 |
| 3 EEA + posterior approach | |||||
| Butenschoen et al., 2021 [9] | Germany | 42 | 53 (range 29–69) | EEA | 37 (range 6–60) |
| Ceylan et al., 2021 [10] | Turkey | 72 | 41.67 ± 17.785 | EEA + transmaxillar (3) EEA + transpterygoid (13) EEA + transcavernous (38) EEA + transodontoid (7) | 31 ± 0.7 (range 6–143) |
| Chibbaro et al., 2013 [11] | France | 54 | 49 | EEA | 34 |
| Choi et al., 2010 [12] | UK and Germany | 97 | Range 41–60 | 40 standard TOAs 16 TOAs + soft palate split 44 “open door” maxillotomy 9 transmandibular 4 midface degloving procedures | 50.4 (median 41; range 3–186) |
| Dehdashti et al., 2008 [13] | Canada | 12 | 49.4 | EEA | 16 |
| Fatemi et al., 2008 [14] | USA | 14 | 47 ± 15 | EEEA | 20 (2 multiple operations and 2 tumor recurrences, 9 RT) |
| Frank et al., 2006 [15] | Italy | 11 | 59.3 | EEEA | 27 (range 15–69) |
| Fraser et al., 2010 [16] | USA | 7 | 52 ± 18 | EEA | 18 |
| Garzaro et al., 2015 [17] | Italy | 9 | 57.4 | EEA | 9.27 (range 3–19) |
| Holzmann et al., 2010 [18] | Germany | 13 | 45.5 | EEA | 18 (range 2–48) |
| Kassam et al., 2008 [19] | USA | 4 | 25.75 (range 16–36) | EEEA | N/R |
| Kim et al., 2016 [20] | South Korea | 42 | 48.7 (range 10–72) | 38 EEAs 3 EEAs + transpterygoid 1 transodontoid | N/R |
| Kong et al., 2021 [21] | South Korea | 50 | N/R | EEA | 34.5 ± 8.2 |
| Koutourousiou et al., 2012 [22] | USA | 60 | 41 (range 4–84) | EEA | 17.8 (29 patients received RT postop, 9 tumor progressions, 21 disease-free) |
| Kutlay et al., 2018 [23] | Turkey | 106 | N/R | EEA | 28 (6–48) |
| Li et al., 2020 [24] | China | 1886 (217) | N/R | EEEA | 42,5 (chordoma recurred in 97 patients) |
| McDowell et al., 2021 [25] | USA | 20 | 12.2 (range 4–18) | 14 EEAs 6 EEAs + open transcervical | 59 (range 1–166) |
| Menezes et al., 2014 [26] | USA | 5 | Range 5–14 | 3 TOA resections + fusions 1 initial C2-4 laminectomy and tumor resection, then vertebral artery embolization and C2-C4 lateral fusion, and extrapharyngeal excision w/corpectomy 1 lateral extrapharyngeal approach + tumor resection | 8 ± 1.8 (range 2–16) |
| Messerer et al., 2016 [27] | Switzerland | 3 | 46.3 | EEEA | N/R (2 free of disease, 1 controlled residue) |
| Metcalfe et al., 2021 [28] | UK | 11 | 53 (23–81) | EEA | 7 years (9 patients PBT, 1 IMRT) |
| Nation et al., 2018 [29] | Malaysia | 5 | 23.2 (range 11–57) | EEA | N/R |
| Passeri et al., 2023 [30] | France | 210 | 47.6 ± 17.0 | 142 EEAs 15 TOAs 15 EEAs + open 7 MTS 31 open | 59.2 ± 51.9 (range 3.0–369.1, median 43.4) postop RT in 163 patients |
| Ramm-Pettersen et al.,2017 [31] | Norway | 6 | 61 (15–65) | EEA | 91 (48–158) |
| Quon et al., 2019 [32] | USA | 42 | 12.5 (range 4–18) | EEA | 46 (range 1–120) |
| Rahme et al., 2018 [33] | USA | 17 | 48.06 | EEA | 63,4 (tumor recurrence after RT in 5 patients) |
| Saito et al., 2012 [34] | Japan | 6 | 59 (range 42–72) | EEA | 15.83 |
| Shin et al., 2015 [35] | Japan | 32 | 55 (range 17–72) | ETISA | Range 3–6 |
| Shkarubo et al., 2018 [36] | Russia | 103 | N/R | EEA | N/R |
| Schur et al., 2022 [37] | USA | 78 | N/R | 38 EEA 40 open | 66,56 |
| Solares et al., 2005 [38] | USA | 3 | N/R | EEA | 13 |
| Soloperto et al., 2019 [39] | Italy | 9 | 61 | EEA | 24.9 (range 7–36) |
| Spiessberger et al., 2022 [40] | USA | 8 | 43,9 | EEA | N/R (4 RT + 3 stereotactic radiosurgery) |
| Stippler et al., 2008 [41] | USA | 20 | 44.35 (range 4–76) | EEA | 13 (range 1–45) postop RT in 8 patients |
| Tan et al., 2012 [42] | Australia | 14 | 48.5 | EEA | 41.5 (range 3–104) |
| Taniguchi et al., 2012 [43] | Japan | 4 | 56,75 | EEA | 21.3 (all patients symptom-free) |
| Vellutini et al., 2014 [44] | Brazil | 38(26) | 46 (range 6–79) | EEA | Range 6 mo–11 years |
| Xin et al., 2022 [45] | China | 3 | N/R | EEA | 7.59 |
| Yano et al., 2014 [46] | Japan | 6 | N/R | EEA | 23.1 |
| Yang et al., 2011 [47] | China | 2 | 49.5 | Anterior retropharyngeal | 32.5 |
| Yoo et al., 2023 [48] | South Korea | 17 | 38.7 (range 8–59) | 11 EEAs 6 EEAs + open | 66.7 (range 9–132) |
| Yousaf et al., 2019 [49] | UK | 10 | 49 | EEA | 39.5 |
| Zacharias et al., 2019 [50] | India | 7 | 51 | 6 EEAs 1 combined EEA + TOA | 24 |
| Zhang et al., 2008 [51] | China | 7 | 39.42 | EEA | 21.4 (range 3–39) |
| Zhong et al., 2021 [52] | China | 102 | 48.75 | Combined anterior retropharyngeal + posterior approach | N/R |
| Zoli et al., 2018 [53] | Italy | 6 | 46,8 | EEA | 18 ± 7.3 |
| Zoli et al., 2018 [54] | Italy | 65 | 48 (9–80) | EEA | 48 |
| Zweckberger et al., 2020 [55] | Germany | 50 | 39 | EEA: 15 primary and 9 recurrences TOA: 3 primary and 2 recurrences | N/R (20 postop RT + 1 chemotherapy on primary surgery, 15 postop RT + 6 chemotherapy for recurrent surgery) |
| Authors, Year | Symptoms | Clivus Site | Cervical Level | Intradural Extension | EOR | Postop CSF Leak | Other Complications | Time Surgery | Hospitalization (Days) | Recurrency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Messerer et al., 2016 [27] | 2 neck pain and dysphagia 1 CSF leakage and meningitis | 3 upper | No | No | 3 GTR | No | No | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Zweckberger et al., 2020 [55] | 24 double vision 17 headaches 7 vertigo 9 visual acuity deteriorations 9 dysphagia 6 insecure gait 4 ptosis 1 coordination disorder | 12 upper, 26 middle | N/R | 17 | 12 GTR 28 STR | 9 | 2 hemorrhages 3 strokes 2 hydrocephalus | 29 primary surgeries 41 surgeries upon recurrence | N/R | N/R |
| Fatemi et al., 2008 [14] | 8 diplopia (VI nerve palsy) 3 V nerve palsy 7 headaches 2 acuity visual losses 2 unsteady gait 2 spontaneous CSF leaks | 9 upper, 5 middle | No | 7 | 6 GTR 6 NTR 2 STR | 8 | 1 transient diabetes insipidus | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Vellutini et al., 2014 [44] | 16 VI nerve palsy 9 headaches | 26 lower, 2 middle | No | 12 | 13 GTR 7 STR 6 PR | 6 | 2 meningitis 1 stroke | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Rahme et al., 2018 [33] | 12 diplopia 8 headaches 3 cranial nerve palsy 2 paresthesia 1 neck pain 1 unsteady gait 1 tinnitus 1 dysphagia 1 coma 1 decreased smell 1 airway obstruction | 3 lower | 1 | 9 | 9 GTR | 6 | 5 cranial nerve palsy 3 meningitis 2 strokes | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Kassam et al., 2008 [19] | 2 headaches 1 VI nerve palsy 1 III nerve palsy | N/R | N/R | N/R | 3 GTR 1 STR | 3 | No | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Koutouroulsiou et al., 2012 [22] | 28 VI nerve palsy 17 headaches 4 nasal obstructions 5 III nerve palsy 5 trigeminal neuralgia 5 X nerve palsy 5 XII nerve palsy | 23 lower, 21 middle, 7 upper | 7 | 29 | 29 GTR + 11 GTR in previously treated patients 4 NTR + 5 NTR in previously treated patients 2 STR + 4 STR in previously treated patients 5 partial in previously treated patients | 12 | 4 cranial nerve palsy 2 ICA injuries 2 meningitis | 35 primary surgeries 25 recurrent surgeries | 4,5 | N/R |
| Kutlay et al., 2018 [23] | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | 3 GTR 2 STR | No | 2 VI nerve palsy (1 transient) | N/R | Range 3–36 (median 5) | N/R |
| Kong et al., 2021 [21] | N/R | 22 upper, 38 middle | N/R | N/R | 53 GTR 5 STR | 5 | 2 meningitis 3 VI nerve palsy | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Nation et al., 2018 [29] | 1 VI nerve palsy | 2 upper | N/R | No | N/R | No | 1 velopharyngeal insufficiency | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Yousaf et al., 2019 [49] | 3 VI nerve palsy 3 headaches 2 transient diplopia 2 III nerve palsy | 8 upper, 2 middle, 1 lower + occipitocervical junction | 1 | No | 4 GTR 4 NTR 2 STR | 2 | 1 meningitis 1 hypopituitarism 1 diabetes insipidus | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Zoli et al., 2018 [54] | 2 VI nerve palsy 4 XII nerve palsy 1 dysphagia 1 cervical pain | 6 middle | 6 | 4 | 2 GTR 4 STR | No | 1 pneumonia | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Kim et al., 2016 [20] | 20 VI nerve palsy 7 headaches 2 acuity visual impairments | 17 upper, 8 middle, 17 lower | N/R | 19 | 28 GTR 14 STR | 7 | 1 VI nerve palsy | 34 primary surgeries 8 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Shkarubo et al., 2018 [36] | 78 oculomotor disorders 35 V nerve palsy 28 dysphagia 13 acuity visual impairments 9 hemiparesis 34 headaches 11 coordination disorders | N/R | N/R | N/R | 67 GTR 22 STR 10 partial | N/R | N/R | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Zacharias et al., 2019 [50] | 4 VI nerve palsy Headache (not specified numbers) | 6 upper | 1 | 7 | N/R | 1 | No | 5 primary surgeries 2 recurrences | 5 | N/R |
| Metcalfe et al., 2021 [28] | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | 1 | 1 radiation toxicity and carotid stenosis 1 postop infection | N/R | N/R |
| Butenschoen et al., 2023 [9] | 14 VI nerve palsy 9 IX nerve palsy 19 headaches | 5 upper, 4 middle, 26 lower | No | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Li et al., 2020 [24] | N/R | No | N/R | N/R | 54 GTR 91 STR 57 partial resections (79–90%) 15 partial resections (<70%) | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Chibbaro et al., 2013 [11] | 43 VI nerve palsy 22 headaches 11 ophthalmoplegia 11 acuity visual impairments | 22 upper | 3 | 19 | 35 GTR 9 NTR 10 partial resections | 4 | 5 meningitis | 32 primary surgeries 22 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Spiessberg et al., 2022 [40] | 2 headaches 1 dysarthria 1 VI nerve palsy 1 XII nerve palsy 1 V nerve palsy | 5 upper, 2 middle | 1 | 2 | 4 GTR | 1 | 1 VI nerve palsy 1 panhypopituitarism | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Arbolay et al., 2009 [7] | 2 headaches 2 VI nerve palsy | N/R | N/R | N/R | 1 GTR 1 STR | No | No | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Ngu et al., 2021 [56] | 5 headaches 2 diplopia | 1 upper, 1 middle, 2 lower | 1 | 2 | 4 GTR 1 STR | No | 1 syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone | 4 primary surgeries 1 recurrency | 16,6 | N/R |
| Ceylan et al., 2021 [10] | 37 headaches 29 acuity visual impairments 10 nausea 15 diplopia 34 hypopituitarism | 19 upper, 9 middle, 25 lower | 4 | 21 | 47 GTR 25 STR | 7 | 2 VI nerve palsy 4 hydrocephalus | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Dehdashti et al., 2008 [13] | 5 headaches 2 unsteady gait 6 diplopia 1 VI nerve palsy 1 lower cranial nerve deficit | 8 upper, 4 middle | No | 7 | 6 GTR 6 STR | 4 | 1 IX nerve palsy 1 motor hemisyndrome 1 hydrocephalus 1 tension pneumocephalus | 9 primary surgeries 3 recurrences | Median 8 | N/R |
| Shin et al., 2015 [35] | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | 14 GTR | No | 4 transient amnesia and III nerve palsy | 11 primary surgeries 7 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Fraser et al., 2010 [16] | 2 diplopia 3 VI nerve palsy 2 III nerve palsy | 5 upper, 2 middle | No | 3 | 5 GTR 2 NTR | No | 1 pulmonary embolism | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Solares et al., 2005 [38] | 1 nasal obstruction 2 acuity visual impairments | 2 upper, 1 middle | No | N/R | N/R | N/R | No | 1 primary surgery 2 recurrences | 2 | N/R |
| Soloperto et al., 2019 [39] | N/R | 4 upper, 2 middle, 2 lower | No | N/R | 3 GTR 5 STR | No | No | 5 primary surgeries 4 recurrences | 11 | 3 |
| Stippler et al., 2008 [41] | 5 headaches 2 III nerve palsy 6 VI nerve palsy 3 ophthalmoplegia | 5 upper, 8 middle, 12 lower | 3 | 9 | 9 GTR 4 NTR 7 STR | 5 | 1 brainstem hemorrhage 2 transient neurological deficits 1 ICA rupture | 12 primary surgeries 8 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Frank et al. [15] | 9 VI nerve palsy 5 headaches 1 dysphagia | 11 upper | No | N/R | 5 GTR 5 STR 1 partial resection | No | N/R | 7 primary surgeries 4 recurrences | 5 | 1 |
| Garzaro et al., 2015 [17] | 4 headaches 6 diplopia | 4 upper, 1 middle, 4 lower | No | N/R | 6 GTR 1 NTR 2 partial resections | 2 | 1 V I nerve palsy 1 hypokaliemia | 7 primary surgeries 2 recurrences | 10 | 2 |
| Holzmann et al., 2010 [18] | 2 VI nerve palsy 2 III nerve palsy 3 V nerve deficits | N/R | N/R | N/R | 11 GTR 1 NTR 1 STR | 1 | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Xin et al., 2022 [45] | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | 3 GTR | N/R | 1 VI nerve palsy | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Zhang et al., 2008 [51] | 3 diplopia 3 headaches 2 nasal obstructions 3 VI nerve palsy | 7 upper, 6 middle, 8 lower | 2 | 4 | 6 GTR 1 STR | No | 1 subarachnoid hemorrhage | 5 primary surgeries 3 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Quon et al., 2019 [32] | 2 VI nerve palsy 2 headaches 1 diplopia | N/R | N/R | N/R | 2 GTR | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Yoo et al., 2023 [48] | 8 diplopia 2 headaches 1 dysphagia 2 trigeminal neuralgia | 4 upper, 5 middle, 6 lower | 2 | 6 | 6 GTR 9 NTR 2 STR | 1 | N/R | 12 primary surgeries 5 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Baldassarre et al., 2021 [8] | 5 neck pain 2 VI nerve palsy 1 dysphagia 1 rhinolalia | 4 lower | 4 | 1 | 6 GTR 2 partial resections | 1 | 1 XII nerve palsy 1 hydrocephalus 1 pulmonary aspergillosis | 7 primary surgeries 1 recurrency | N/R | N/R |
| Zoli et al., 2018 [54] | 12 acuity visual impairments 25 V nerve neuralgia 1 dysphagia 9 diplopia 4 hemiparesis 2 VII and VIII deficits | 45 upper, 12 middle | No | 25 | 47 GTR 28 STR 5 partial resections | 2 | 2 ICA injuries 1 hematoma 7 VII nerve palsy | 37 primary surgeries 28 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Taniguchi et al., 2012 [43] | 2 VI nerve palsy | 1 middle | No | 1 | 4 GTR | 1 | 1 VI nerve palsy | 1 primary surgery 3 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Tan et al., 2012 [42] | 5 headaches 4 VI nerve palsy 2 diplopia | N/R | N/R | N/R | 7 GTR 7 STR | 3 | 1 hydeocephalus 1 aspiration pneumonia | 7 primary surgeries 7 recurrences | 14 | N/R |
| Passeri et al., 2023 [30] | 88 diplopia 84 VI nerve palsy 64 neck pain 65 headaches 53 XII nerve palsy | 50 upper, 95 middle, 65 lower | 95 | 115 | 92 GTR 72 NTR 33 STR 13 partial resections | 32 | 47 worsening cranial nerve palsy | 166 primary surgeries 44 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Schur et al., 2022 [37] | N/R | 34 upper, 31 middle, 37 lower | 16 | 30 | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Saito et al., 2012 [34] | VI nerve palsy (not specified number) | 5 upper, 1 middle, 4 lower | No | 4 | 3 GTR 1 STR 2 partial resections | No | 1 meningitis 1 hydrocephalus | 6 primary surgeries | N/R | N/R |
| Ramm-Pettersen et al., 2017 [31] | 5 diplopia 3 headaches 1 facial hypoesthesia | 3 upper, 3 lower | N/R | 2 | 3 GTR 1 NTR 2 partial resections | 1 | No | 6 primary surgeries | N/R | N/R |
| McDowell et al., 2021 [25] | 7 diplopia 6 headaches 4 swallowing difficulties | 14 upper, 1 middle, 3 lower | 2 | 14 | 14 GTR 6 NTR | 3 | 2 VI nerve palsy 1 Horner’s syndrome 1 epidural hematoma | 15 primary surgeries 4 recurrences | N/R | N/R |
| Yano et al., 2014 [46] | 6 VI nerve palsy | N/R | N/R | N/R | 4 GTR 2 STR | 1 | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Choi et al., 2010 [12] | 86% neck pain 18.6% myelopathy | N/R | N/R | N/R | N/R | 6.2% | 25% tumor recurrence 4.1% chest infection 3.1% meningitis 3.1% velopharyngeal incompetence 2.1% new cranial nerve palsy 1% wound infection—pharyngeal 3.1% sepsis 3.1% dysphagia 2.1% fixation failure 1% vertebral artery stroke | N/R | N/R | N/R |
| Menezes et al., 2014 [26] | 100% neck pain 2 w/quadriparesis 1 w/swallowing difficulty and XI nerve palsy | 1 middle | 2 C2 1 C1 1 C2-C3 1 C1-C2 to clivus | 1 | GTR | N/R | No | Primary surgery | N/R | N/R |
| Yang et al., 2011 [47] | Neck pain Tetraparesis | No | 2 C2-C3 | N/R | GTR | 1 | 1 swallowing difficulty (liquid) | N/R | N/R | Yes (13–18 mo postop) |
| Zhong et al., 2021 [52] | N/R | No | 102 C2 | N/R | 21 en-bloc resections 81 total piecemeal resections | 8 | 9 dysphagia 8 pneumonia 7 dyspnea 5 surgical site infections 2 hematoma 2 pharyngeal dehiscence 1 neurological deficit 1 symptomatic venous thromboembolism 1 cerebral infarction | Primary surgery | 21.12 ± 6.32 | N/R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maugeri, R.; Bonosi, L.; Brunasso, L.; Costanzo, R.; Santi, S.; Signorelli, F.; Iacopino, D.G.; Visocchi, M. Not Every Size Fits All: Surgical Corridors for Clival and Cervical Chordomas—A Systematic Review of the Literature and Illustrative Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175052
Maugeri R, Bonosi L, Brunasso L, Costanzo R, Santi S, Signorelli F, Iacopino DG, Visocchi M. Not Every Size Fits All: Surgical Corridors for Clival and Cervical Chordomas—A Systematic Review of the Literature and Illustrative Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(17):5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175052
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaugeri, Rosario, Lapo Bonosi, Lara Brunasso, Roberta Costanzo, Samuele Santi, Francesco Signorelli, Domenico Gerardo Iacopino, and Massimiliano Visocchi. 2024. "Not Every Size Fits All: Surgical Corridors for Clival and Cervical Chordomas—A Systematic Review of the Literature and Illustrative Cases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 17: 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175052
APA StyleMaugeri, R., Bonosi, L., Brunasso, L., Costanzo, R., Santi, S., Signorelli, F., Iacopino, D. G., & Visocchi, M. (2024). Not Every Size Fits All: Surgical Corridors for Clival and Cervical Chordomas—A Systematic Review of the Literature and Illustrative Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(17), 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175052








