Guided SEFFI and CaHA: A Retrospective Observational Study of an Innovative Protocol for Regenerative Aesthetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
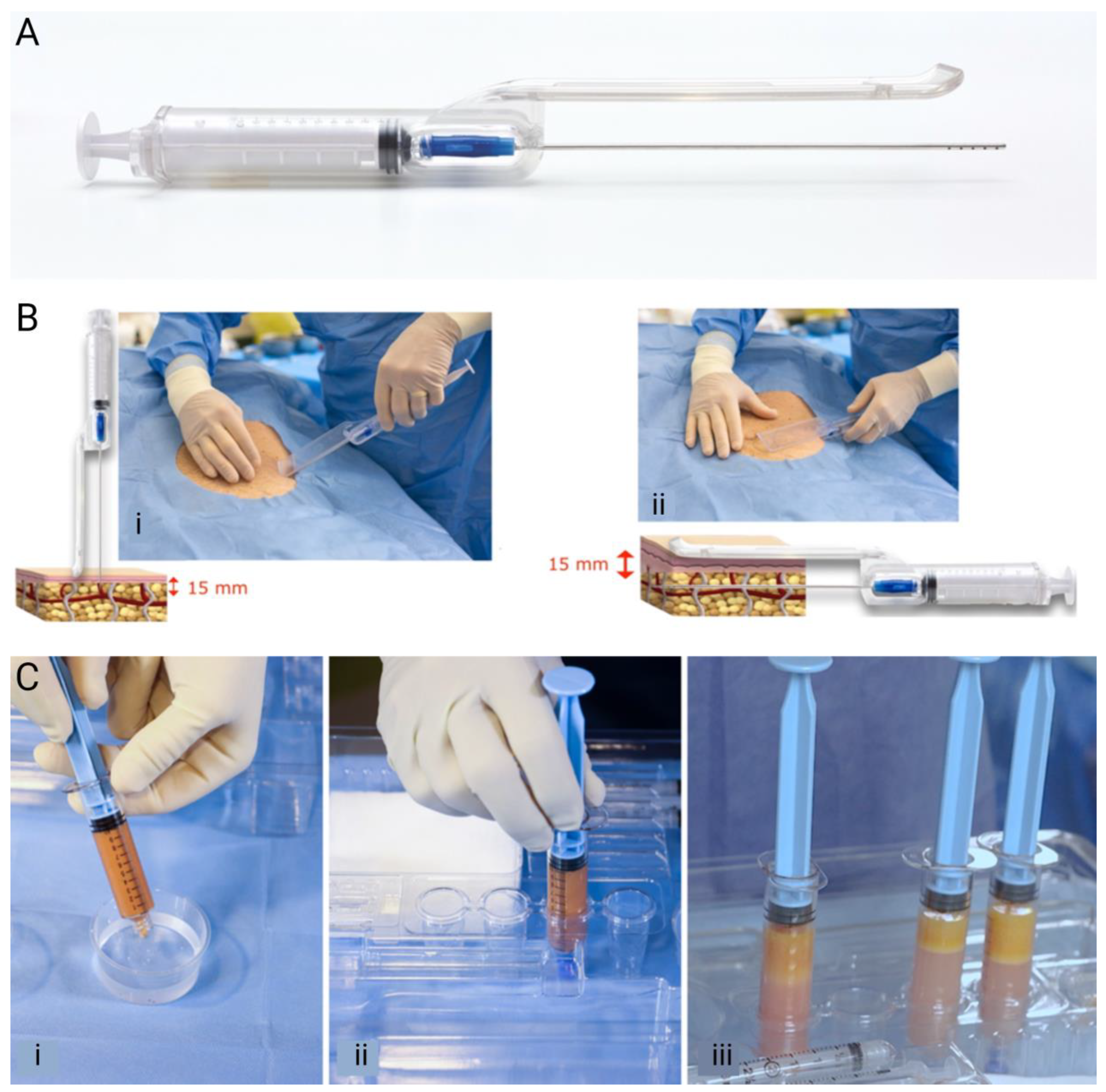
2.2. Guided SEFFI Preparation
2.3. CaHA Preparation
2.4. Facial Injection Procedure
2.5. Efficacy and Safety Measures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Injection Volumes
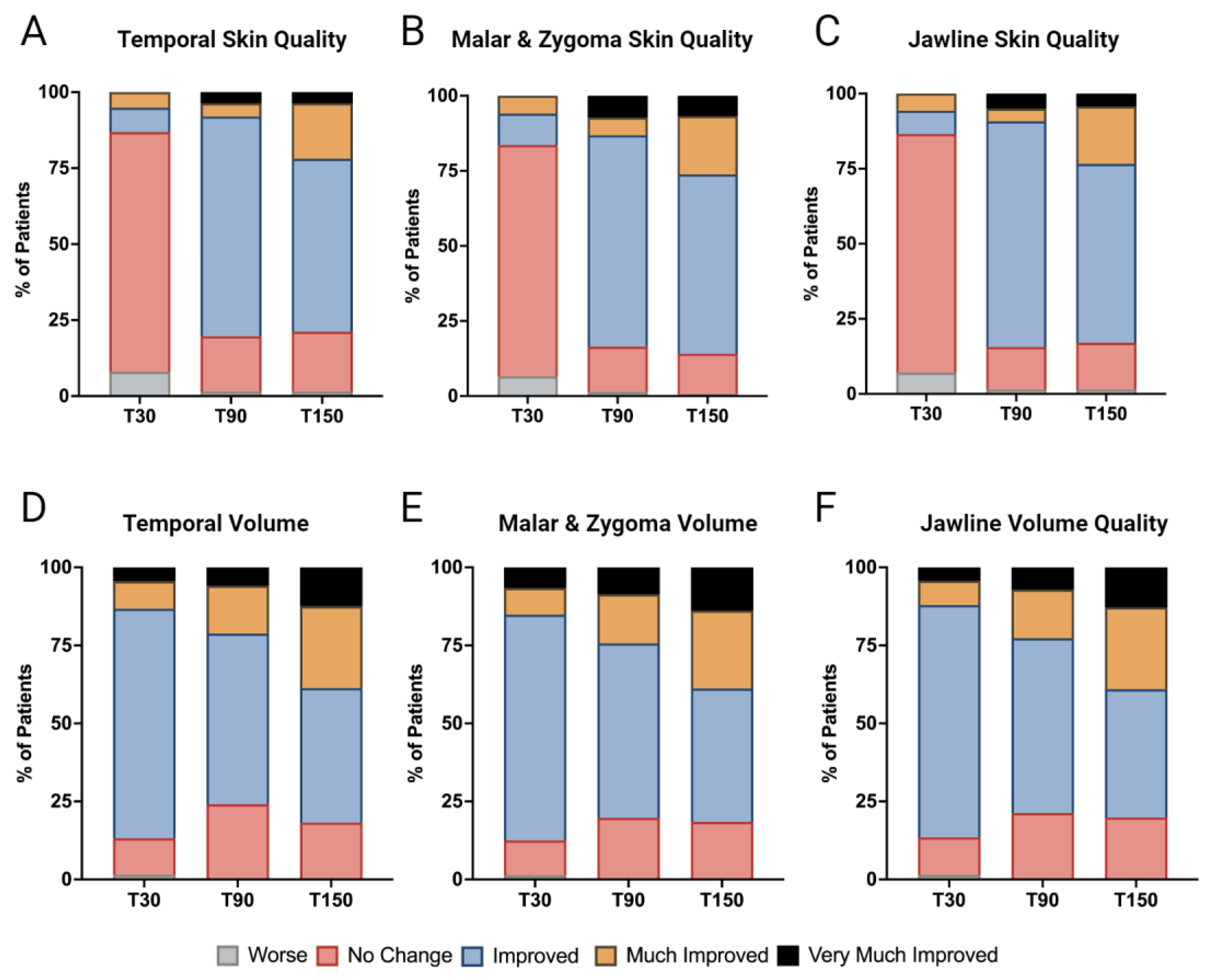
3.3. Enhancement in Skin Quality
3.4. Volume Restoration
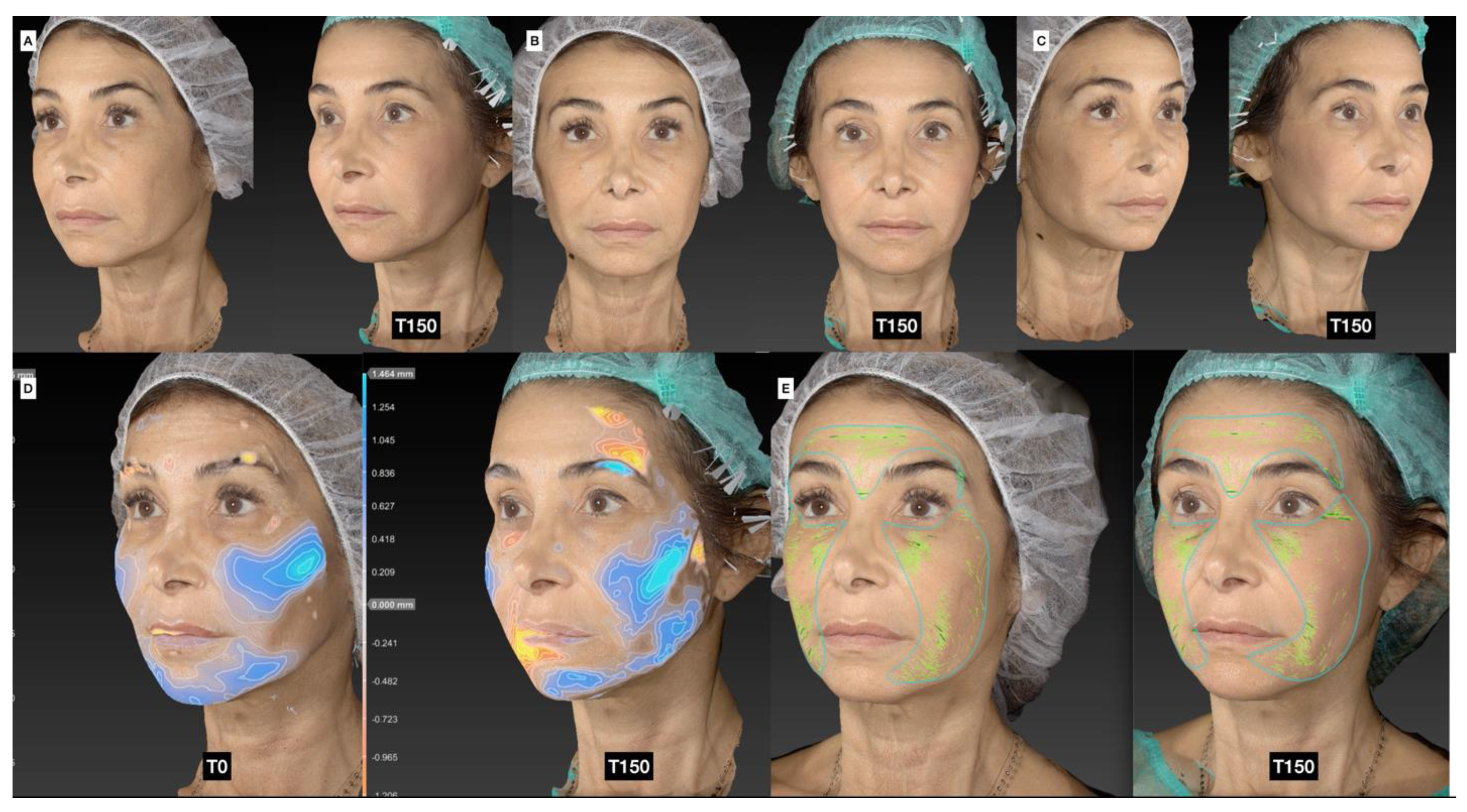
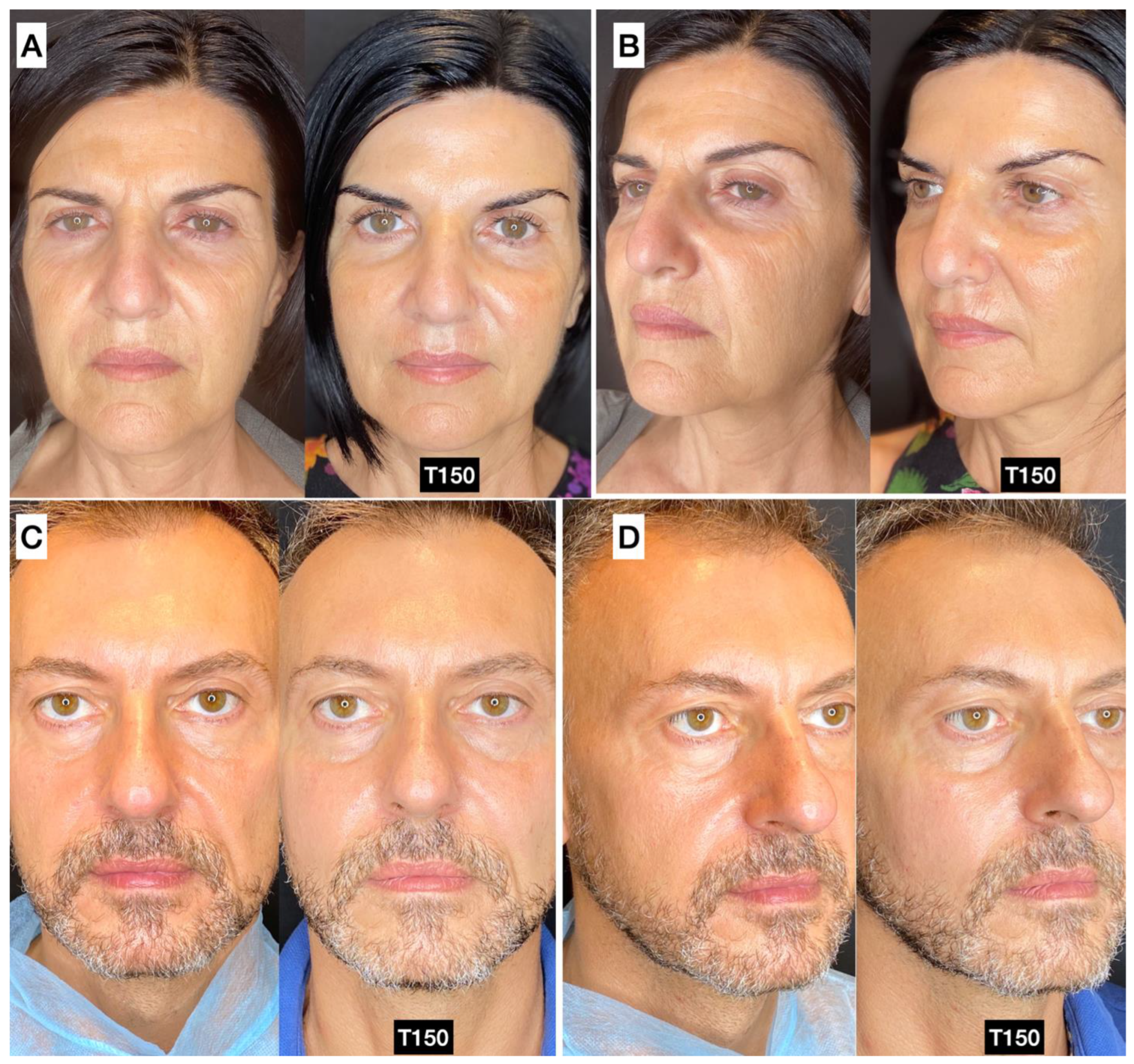
3.5. Photographic and Photogrammetric Results
3.6. Complications
3.6.1. Complications at Donor Sites
3.6.2. Complications at Injection Sites
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, J.-W.; Kwon, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Na, J.-I.; Huh, C.-H.; Choi, H.-R.; Park, K.-C. Molecular Mechanisms of Dermal Aging and Antiaging Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, Y.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of Photoaging and Chronological Skin Aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fligiel, S.E.G.; Varani, J.; Datta, S.C.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Collagen Degradation in Aged/Photodamaged Skin In Vivo and After Exposure to Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 In Vitro. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, J. Fibroblast aging: Intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Drug Discov. Today Ther. Strateg. 2010, 7, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, N.; Papismadov, N.; Solomonov, I.; Sagi, I.; Krizhanovsky, V. The ECM path of senescence in aging: Components and modifiers. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, F.M.; Fujiwara, H. Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions in Normal and Diseased Skin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, S.B.; McCarthy, A.; Khalifian, S.; Lorenc, Z.P.; Goldie, K.; Chernoff, W.G. The Role of Calcium Hydroxylapatite (Radiesse) as a Regenerative Aesthetic Treatment: A Narrative Review. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2023, 43, 1063–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, J.; Schuger, L.; Dame, M.K.; Leonard, C.; Fligiel, S.E.G.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Reduced Fibroblast Interaction with Intact Collagen as a Mechanism for Depressed Collagen Synthesis in Photodamaged Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.D.; Soares, D.J.; Chandawarkar, A.; El-Banna, R.; Hagedorn, N. Dilutional Rheology of Radiesse: Implications for Regeneration and Vascular Safety. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2024, 23, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.A.; Gorman, R.C.; Stroud, R.E.; Mukherjee, R.; Meyer, E.C.; Baker, N.L.; Morita, M.; Hamamoto, H.; Ryan, L.P.; Gorman, J.H.; et al. Targeted Regional Injection of Biocomposite Microspheres Alters Post–Myocardial Infarction Remodeling and Matrix Proteolytic Pathways. Circulation 2011, 124, S35–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowag, B.; Casabona, G.; Kippenberger, S.; Zöller, N.; Hengl, T. Calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres activate fibroblasts through direct contact to stimulate neocollagenesis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 22, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, N.; Goldberg, D.J. Evaluating the Effects of Injected Calcium Hydroxylapatite on Changes in Human Skin Elastin and Proteoglycan Formation. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovatti, P.P.; Pellacani, G.; Guida, S. Hyperdiluted Calcium Hydroxylapatite 1:2 for Mid and Lower Facial Skin Rejuvenation: Efficacy and Safety. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, e112–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellei, B.; Migliano, E.; Picardo, M. Research update of adipose tissue-based therapies in regenerative dermatology. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 1956–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, M.R.; Patel, R.A.; Adem, S.; Diaz Deleon, N.M.; Shen, A.H.; Sokol, J.; Yen, S.; Chang, E.Y.; Nazerali, R.; Nguyen, D.; et al. The antifibrotic adipose-derived stromal cell: Grafted fat enriched with CD74+ adipose-derived stromal cells reduces chronic radiation-induced skin fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, D.A.; Beeson, W.; Rachel, J.D.; Keller, G.S.; Hanke, C.W.; Waibel, J.; Leavitt, M.; Sacopulos, M. Mesothelial Stem Cells and Stromal Vascular Fraction for Skin Rejuvenation. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 26, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachura, A.; Paskal, W.; Pawlik, W.; Mazurek, M.J.; Jaworowski, J. The Use of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) in Skin Scar Treatment-A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; He, J.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Liu, H. Anti-Aging Effect of the Stromal Vascular Fraction/Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in a Mouse Model of Skin Aging Induced by UVB Irradiation. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 950967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesco, B.; Abascal, C.; Duarte, A.; Flores, R.M.; Rouaux, G.; Sampayo, R.; Bernardini, F.; Devoto, M. Autologous fat transfer with SEFFI (superficial enhanced fluid fat injection) technique in periocular reconstruction. Orbit 2018, 37, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennai, A.; Zambelli, A.; Repaci, E.; Quarto, R.; Baldelli, I.; Fraternali, G.; Bernardini, F.P. Skin Rejuvenation and Volume Enhancement with the Micro Superficial Enhanced Fluid Fat Injection (M-SEFFI) for Skin Aging of the Periocular and Perioral Regions. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2017, 37, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennai, A.; Baldessin, M.; Melfa, F.; Bovani, B.; Camporese, A.; Claysset, B.; Colli, M.; Diaspro, A.; Russo, R.; Strano, P.; et al. Guided Superficial Enhanced Fluid Fat Injection (SEFFI) Procedures for Facial Rejuvenation: An Italian Multicenter Retrospective Case Report. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 924–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, M.; Dobke, M.; Lunyak, V.V. Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue in Clinical Applications for Dermatological Indications and Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 18, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakopoulou, E.; McCarthy, A.; Perico, V.; Aguilera, S.B. Optimizing Skin Regenerative Response to Calcium Hydroxylapatite Microspheres Via Poly-Micronutrient Priming. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2023, 22, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kadouch, J.; Fakih-Gomez, N. A Hybrid Filler: Combining Calcium Hydroxylapatite and Hyaluronic Acid Fillers for Aesthetic Indications. Am. J. Cosmet. Surg. 2022, 39, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.P.M.D.; Levy, F.M.; Buzalaf, M.A.R. “RichBlend” protocol for full-face filling and collagen biostimulation. RGO Rev. Gaúch. Odontol. 2023, 71, e20230014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernoff, G. Combining topical dermal infused exosomes with injected calcium hydroxylapatite for enhanced tissue biostimulation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melfa, F.; Gennai, A.; Carfagna, G.; Bovani, B.; Piccolo, D.; Colli, M.; Baldessin, M.; Siragusa, D. Characterization of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells from tissue harvested with the guided SEFFI technique and co-cultured with calcium hydroxyapatite. J. Appl. Cosmetol. 2023, 41, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchiani, R.; Corrales, L. The Effects of Fat Harvesting and Preparation, Air Exposure, Obesity, and Stem Cell Enrichment on Adipocyte Viability Prior to Graft Transplantation. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2016, 36, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, R.Y.; Nojima, K.; Adams, W.P.; Brown, S.A. Analysis of facial skin thickness: Defining the relative thickness index. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 115, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldie, K.; Peeters, W.; Alghoul, M.; Butterwick, K.; Casabona, G.; Chao, Y.Y.Y.; Costa, J.; Eviatar, J.; Fabi, S.G.; Lupo, M.; et al. Global Consensus Guidelines for the Injection of Diluted and Hyperdiluted Calcium Hydroxylapatite for Skin Tightening. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casabona, G.; Alfertshofer, M.; Kaye, K.; Frank, K.; Moellhoff, N.; Davidovic, K.; Cotofana, S. Ex-Vivo Product Distribution of Injectable Biostimulator Substances. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2023, 43, NP348–NP356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camison, L.; Bykowski, M.; Lee, W.W.; Carlson, J.C.; Roosenboom, J.; Goldstein, J.A.; Losee, J.E.; Weinberg, S.M. Validation of the Vectra H1 portable three-dimensional photogrammetry system for facial imaging. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiraldi, L.; Sapino, G.; Meuli, J.; Maruccia, M.; Cherubino, M.; Raffoul, W.; di Summa, P.G. Facial Fat Grafting (FFG): Worth the Risk? A Systematic Review of Complications and Critical Appraisal. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, H.; Boone, D. Analyzing Likert Data. J. Ext. 2012, 50, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldie, K. The evolving field of regenerative aesthetics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22 (Suppl. S1), 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutskovskaya, Y.A.; Kogan, E.A. Improved Neocollagenesis and Skin Mechanical Properties After Injection of Diluted Calcium Hydroxylapatite in the Neck and Décolletage: A Pilot Study. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2017, 16, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fabi, S.; Alhaddad, M.; Boen, M.; Goldman, M. Prospective Clinical Trial Evaluating the Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Calcium Hydroxylapatite for Chest Rejuvenation. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, 534–537. [Google Scholar]
- Fabi, S.; Hamilton, T.; LaTowksy, B.; Kazin, R.; Marcus, K.; Mayoral, F.; Joseph, J.; Hooper, D.; Shridharani, S.; Hicks, J.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Sculptra Poly-L-Lactic Acid Injectable Implant in the Correction of Cheek Wrinkles. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2024, 23, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, L.; Davis, M.J.; Winocour, S.J. The Science of Fat Grafting. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2020, 34, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Desired Cluster Dimension (µm) | Number of Passages | Cannula or Needle Size (Gauge, Inner Diameter in mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 800 | 0 | 18, 0.83 |
| 600 | 2–3 | 20, 0.60 |
| 500 | 5–6 | 21, 0.51 |
| 400 | 10–11 | 22, 0.41 |
| 200 | 20–30 | 27, 0.21 |
| Score | GAIS Rating |
|---|---|
| 1 | Very much improved |
| 2 | Much improved |
| 3 | Improved |
| 4 | No change |
| 5 | Worse |
| 6 | Much worse |
| Region | Number Treated | Average CaHA Volume (ml/Side) | Number of Diluted (1:1) CaHA Treatments (Number, %) | Number of Hyperdiluted (1:2) CaHA Treatments (Number, %) | Average Guided SEFFI Volume (ml/side) | Number of 600 µmGuided SEFFI Treatments (Number, %) | Number of 500 µmGuided SEFFI Treatments (Number, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal | 117 | 0.8 | 89 (76.1%) | 28 (23.9%) | 2.8 | 101 (86.3%) | 16 (13.7%) |
| Malar and Zygomatic | 152 | 1.5 | 115 (75.7%) | 37 (24.3%) | 5 | 123 (80.9%) | 29 (19.1%) |
| Jawline | 113 | 0.8 | 82 (72.6%) | 31 (27.4) | 3.7 | 84 (74.3%) | 29 (25.7%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melfa, F.; McCarthy, A.; Aguilera, S.B.; van Loghem, J.; Gennai, A. Guided SEFFI and CaHA: A Retrospective Observational Study of an Innovative Protocol for Regenerative Aesthetics. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154381
Melfa F, McCarthy A, Aguilera SB, van Loghem J, Gennai A. Guided SEFFI and CaHA: A Retrospective Observational Study of an Innovative Protocol for Regenerative Aesthetics. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(15):4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154381
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelfa, Fabrizio, Alec McCarthy, Shino Bay Aguilera, Jani van Loghem, and Alessandro Gennai. 2024. "Guided SEFFI and CaHA: A Retrospective Observational Study of an Innovative Protocol for Regenerative Aesthetics" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 15: 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154381
APA StyleMelfa, F., McCarthy, A., Aguilera, S. B., van Loghem, J., & Gennai, A. (2024). Guided SEFFI and CaHA: A Retrospective Observational Study of an Innovative Protocol for Regenerative Aesthetics. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(15), 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154381







