Association between Pericarotid Fat Density and Positive Remodeling in Patients with Carotid Artery Stenosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Ethics
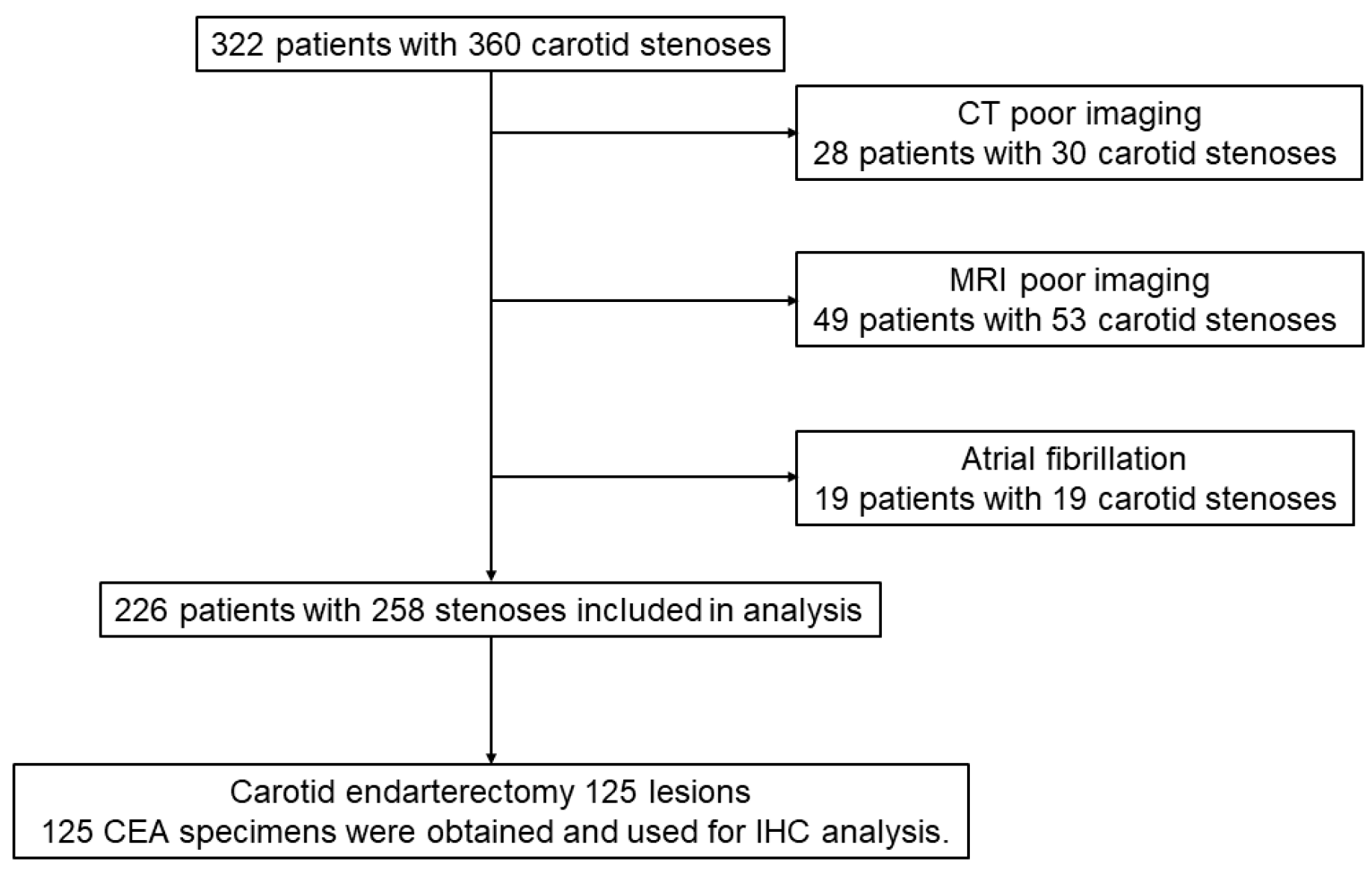
2.2. Study Population
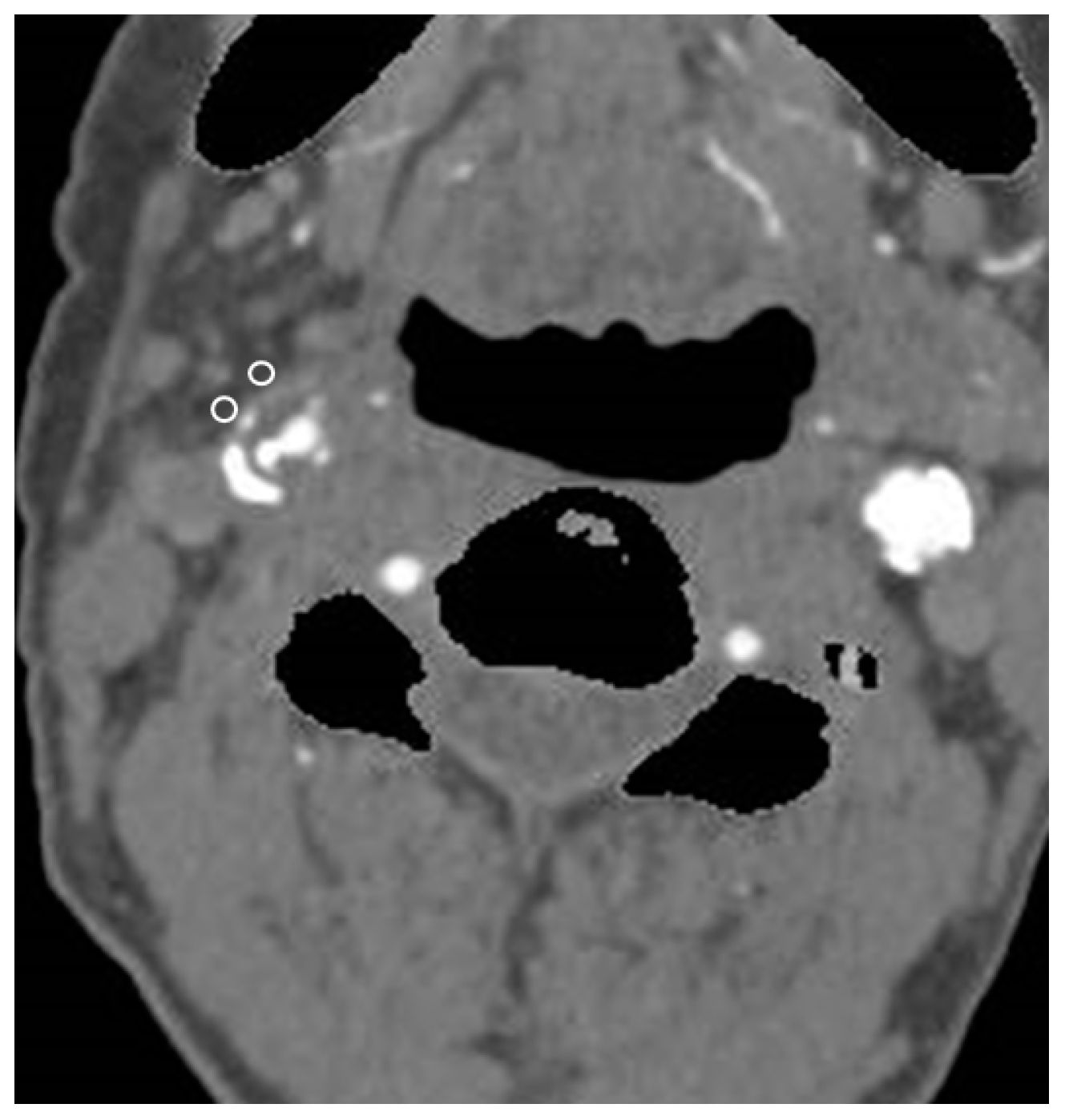
2.3. CTA and Pericarotid Fat Density Measurement
2.4. MR Plaque Imaging to Evaluate Plaque Composition
2.5. Measurement of Expansive Remodeling Rate
2.6. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
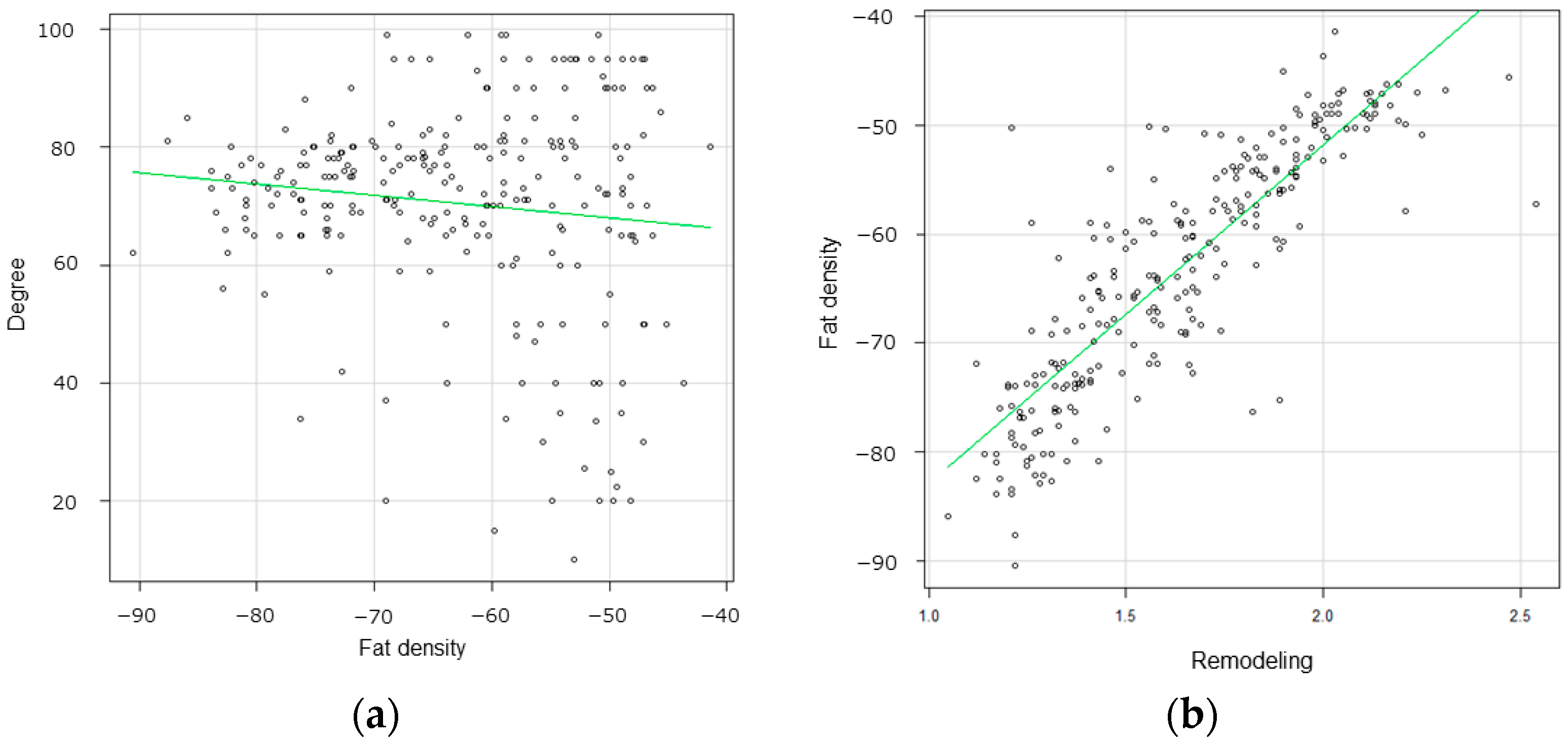
3.2. Radiological Findings
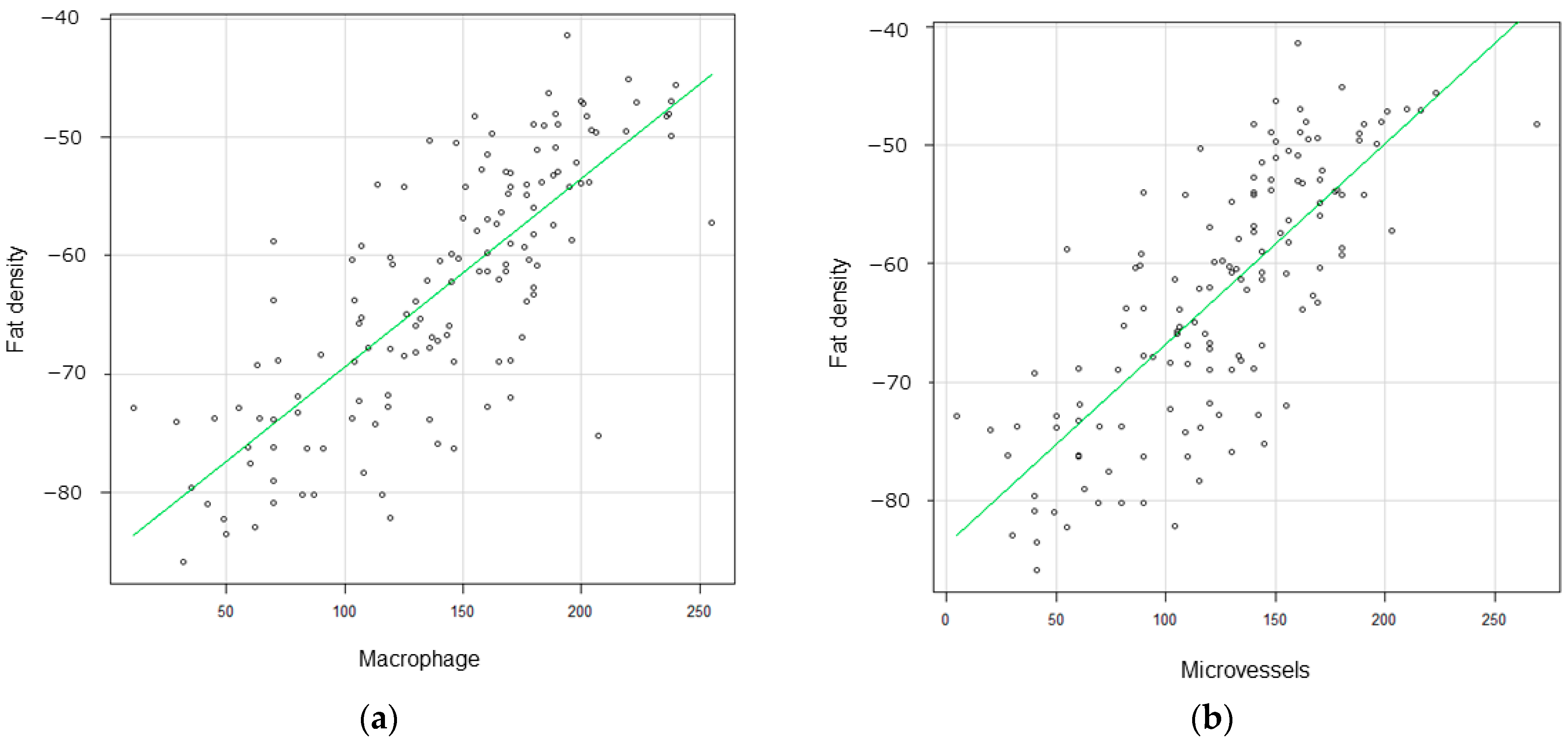
3.3. Correlation between Pericarotid Fat Density and IHC
3.4. Radiological Findings in Mild Carotid Stenosis
4. Discussion
4.1. Crosstalk between Pericarotid Fat and the Carotid Artery Wall
4.2. Usefulness of Carotid Fat Density in Clinical Practice
4.3. Pericarotid Fat Density and Positive Remodeling in Mild Carotid Stenosis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saba, L.; Saam, T.; Jager, H.R.; Yuan, C.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Saloner, D.; Wasserman, B.A.; Bonati, L.H.; Wintermark, M. Imaging biomarkers of vulnerable carotid plaques for stroke risk prediction and their potential clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H.; Cai, Y.; Rahimi, K.; Zhu, Y.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Fowkes, F.J.I.; Rudan, I. Global and regional prevalence, burden, and risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e721–e729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roopnarinesingh, R.; Leppert, M.; Mukherjee, D. Evidence and Mechanisms for Embolic Stroke in Contralateral Hemispheres From Carotid Artery Sources. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e030792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwazaki, D.; Akioka, N.; Kuwayama, N.; Noguchi, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kuroda, S. Pathophysiology of acute cerebrovascular syndrome in patients with carotid artery stenosis: A magnetic resonance imaging/single-photon emission computed tomography study. Neurosurgery 2015, 76, 427–433; discussion 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopyto, E.; Czeczelewski, M.; Mikos, E.; Stepniak, K.; Kopyto, M.; Matuszek, M.; Nieoczym, K.; Czarnecki, A.; Kuczynska, M.; Cheda, M.; et al. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Feasibility in Assessing Carotid Plaque Vulnerability-Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.; Qiu, C.; et al. Association of sdLDL-C With Incident Carotid Plaques With Stable and Vulnerable Morphology: A Prospective Cohort Study. Stroke 2024, 55, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, F.; Mi, D.; Wang, A.; Ju, Y.; Sui, B.; Geng, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X. Extracranial carotid plaque hemorrhage predicts ipsilateral stroke recurrence in patients with carotid atherosclerosis—A study based on high-resolution vessel wall imaging MRI. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, A.; Schinner, R.; Altaf, N.; Hosseini, A.A.; Simpson, R.J.; Esposito-Bauer, L.; Singh, N.; Kwee, R.M.; Kurosaki, Y.; Yamagata, S.; et al. Prediction of Stroke Risk by Detection of Hemorrhage in Carotid Plaques: Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, N.; Yuan, C.; Chu, B.; Saam, T.; Underhill, H.; Cai, J.; Tran, N.; Polissar, N.L.; Isaac, C.; Ferguson, M.S.; et al. Association between carotid plaque characteristics and subsequent ischemic cerebrovascular events: A prospective assessment with MRI--initial results. Stroke 2006, 37, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, Y.; Kinosada, M.; Ikeda, H.; Yamashita, H.; Yoshida, K.; Chin, M. Clinical features and long-term outcomes of symptomatic low-grade carotid stenosis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Yang, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kurosaki, Y.; Funaki, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Ishii, A.; Kataoka, H.; Miyamoto, S. Expansive carotid artery remodeling: Possible marker of vulnerable plaque. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, N.A.; Westra, J.; van Dam, G.M.; Teteloshvili, N.; Tio, R.A.; Breek, J.C.; Slart, R.H.; Boersma, H.; Low, P.S.; Bijl, M.; et al. Targeted folate receptor beta fluorescence imaging as a measure of inflammation to estimate vulnerability within human atherosclerotic carotid plaque. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waden, K.; Karlof, E.; Narayanan, S.; Lengquist, M.; Hansson, G.K.; Hedin, U.; Roy, J.; Matic, L. Clinical risk scores for stroke correlate with molecular signatures of vulnerability in symptomatic carotid patients. iScience 2022, 25, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agabiti-Rosei, C.; Saxton, S.N.; De Ciuceis, C.; Lorenza Muiesan, M.; Rizzoni, D.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Heagerty, A.M. Influence of Perivascular Adipose Tissue on Microcirculation: A Link Between Hypertension and Obesity. Hypertension 2024, 81, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Garcia-Barrio, M.T.; Chen, Y.E. Perivascular Adipose Tissue Regulates Vascular Function by Targeting Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1094–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, S.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; Carvalho, E. Cellular cross-talk between epicardial adipose tissue and myocardium in relation to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E937–E949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczynski, J.; Sellers, S.; Seidman, M.A.; Syed, M.; Dennis, M.; McNaught, G.; Jansen, M.; Semple, S.I.; Alcaide-Corral, C.; Tavares, A.A.S.; et al. (18)F-NaF PET/MRI for Detection of Carotid Atheroma in Acute Neurovascular Syndrome. Radiology 2022, 305, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, B.; Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, B.; Ma, Y.; Jiao, L.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Morphological feature and mapping inflammation in classified carotid plaques in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients: A hybrid (18)F-FDG PET/MR study. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1144248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, J.D.; Saver, J.L.; Albers, G.W.; Alberts, M.J.; Chaturvedi, S.; Feldmann, E.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Higashida, R.T.; Johnston, S.C.; Kidwell, C.S.; et al. Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke 2009, 40, 2276–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, H.J.; Taylor, D.W.; Eliasziw, M.; Fox, A.J.; Ferguson, G.G.; Haynes, R.B.; Rankin, R.N.; Clagett, G.P.; Hachinski, V.C.; Sackett, D.L.; et al. Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran, H.; Myneni, P.K.; Patel, P.; Askin, G.; Gialdini, G.; Al-Dasuqi, K.; Kamel, H.; Gupta, A. Association Between Carotid Artery Perivascular Fat Density and Cerebrovascular Ischemic Events. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwazaki, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Hori, E.; Akioka, N.; Noguchi, K.; Kuroda, S. Thin calcification (<2 mm) can highly predict intraplaque hemorrhage in carotid plaque: The clinical significance of calcification types. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szasz, T.; Bomfim, G.F.; Webb, R.C. The influence of perivascular adipose tissue on vascular homeostasis. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2013, 9, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulos, N.; McLean, D.S.; Janik, M.; Arepalli, C.D.; Stillman, A.E.; Raggi, P. Epicardial adipose tissue and coronary artery plaque characteristics. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.D.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Tu, Y.F.; Shen, B.Z. Relationship between epicardial adipose tissue volume measured using coronary computed tomography angiography and atherosclerotic plaque characteristics in patients with severe coronary artery stenosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 41, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Horiguchi, J.; Kitagawa, T.; Kunita, E.; Utsunomiya, H.; Oka, T.; Kohno, N.; Kihara, Y. Association between visceral adipose tissue area and coronary plaque morphology assessed by CT angiography. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Qiu, S.; Wang, B.; Bao, Y.; Du, B.; Zhu, S.; Ge, Y.; et al. Associations between pericarotid fat density and image-based risk characteristics of carotid plaque. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 153, 110364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, L.; Zucca, S.; Gupta, A.; Micheletti, G.; Suri, J.S.; Balestrieri, A.; Porcu, M.; Crivelli, P.; Lanzino, G.; Qi, Y.; et al. Perivascular Fat Density and Contrast Plaque Enhancement: Does a Correlation Exist? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Donato, G.; Pasqui, E.; Alba, G.; Giannace, G.; Panzano, C.; Cappelli, A.; Setacci, C.; Palasciano, G. Clinical considerations and recommendations for OCT-guided carotid artery stenting. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 18, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Schottlander, D.; Marwan, M.; Mathers, C.; Tomlins, P.; Siddique, M.; Kluner, L.V.; Shirodaria, C.; Mavrogiannis, M.C.; et al. Standardized measurement of coronary inflammation using cardiovascular computed tomography: Integration in clinical care as a prognostic medical device. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2677–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decano, J.L.; Maiorino, E.; Matamalas, J.T.; Chelvanambi, S.; Tiemeijer, B.M.; Yanagihara, Y.; Mukai, S.; Jha, P.K.; Pestana, D.V.S.; D’Souza, E.; et al. Cellular Heterogeneity of Activated Primary Human Macrophages and Associated Drug-Gene Networks: From Biology to Precision Therapeutics. Circulation 2023, 148, 1459–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfella, R.; Prattichizzo, F.; Sardu, C.; Paolisso, P.; D’Onofrio, N.; Scisciola, L.; La Grotta, R.; Frige, C.; Ferraraccio, F.; Panarese, I.; et al. Evidence of an anti-inflammatory effect of PCSK9 inhibitors within the human atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis 2023, 378, 117180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, S.; et al. Association between high sensitivity C-Reactive protein and prevalence of asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Atherosclerosis 2016, 246, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E.; Rifai, N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf, N.; Daniels, L.; Morgan, P.S.; Auer, D.; MacSweeney, S.T.; Moody, A.R.; Gladman, J.R. Detection of intraplaque hemorrhage by magnetic resonance imaging in symptomatic patients with mild to moderate carotid stenosis predicts recurrent neurological events. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 47, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam-Nolen, D.H.K.; Truijman, M.T.B.; van der Kolk, A.G.; Liem, M.I.; Schreuder, F.; Boersma, E.; Daemen, M.; Mess, W.H.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; et al. Carotid Plaque Characteristics Predict Recurrent Ischemic Stroke and TIA: The PARISK (Plaque At RISK) Study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, A.; Erta, M.; Suri, J.S.; Gupta, A.; Wintermark, M.; Saba, L. CT imaging features of carotid artery plaque vulnerability. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| All Lesion | CEA | CAS | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 258 lesions | 125 | 133 | ||
| Age | 74.4 ± 8.9 | 74.0 ± 8.7 | 74.8 ± 9.1 | 0.65 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 237 | 116 | 121 | 0.65 |
| Female | 21 | 9 | 12 | |
| Symptomatic | 130 | 103 | 27 | <0.01 |
| Asymptomatic | 128 | 30 | 98 | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Hypertension | 191 | 89 | 102 | 0.32 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 90 | 40 | 50 | 0.36 |
| Dyslipidemia | 122 | 60 | 62 | 0.9 |
| Coronary artery disease | 88 | 40 | 48 | 0.51 |
| Laboratory | ||||
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 109.8 ± 20.1 | 112.3 ± 22.2 | 106.1 ± 18.6 | 0.55 |
| HbA1c | 6.1 ± 1.1 | 6.0 ± 1.0 | 6.2 ± 1.2 | 0.74 |
| Drug administration | ||||
| Hypertension | 220 | 105 | 115 | 0.6 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 85 | 39 | 46 | 0.6 |
| Dyslipidemia (statin) | 128 | 60 | 68 | 0.62 |
| Antiplatelet | 165 | 82 | 83 | 0.61 |
| Anticoagulant | 22 | 10 | 12 | 0.71 |
| Radiological findings | ||||
| % Stenosis | 70.1 ± 15.2% | 64.7 ± 25.2% | 75.8 ± 9.2% | <0.01 |
| Severe (≥70%) | 163 | 55 | 108 | |
| Moderate (50–69%) | 63 | 40 | 23 | |
| Mild (<50%) | 32 | 30 | 2 | |
| Plaque composition | ||||
| Fibrous plaques | 94 | 19 | 75 | <0.01 |
| LR/NC | 62 | 34 | 28 | |
| IPH | 102 | 72 | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kashiwazaki, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Akioka, N.; Hori, E.; Noguchi, K.; Kuroda, S. Association between Pericarotid Fat Density and Positive Remodeling in Patients with Carotid Artery Stenosis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133892
Kashiwazaki D, Yamamoto S, Akioka N, Hori E, Noguchi K, Kuroda S. Association between Pericarotid Fat Density and Positive Remodeling in Patients with Carotid Artery Stenosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133892
Chicago/Turabian StyleKashiwazaki, Daina, Shusuke Yamamoto, Naoki Akioka, Emiko Hori, Kyo Noguchi, and Satoshi Kuroda. 2024. "Association between Pericarotid Fat Density and Positive Remodeling in Patients with Carotid Artery Stenosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133892
APA StyleKashiwazaki, D., Yamamoto, S., Akioka, N., Hori, E., Noguchi, K., & Kuroda, S. (2024). Association between Pericarotid Fat Density and Positive Remodeling in Patients with Carotid Artery Stenosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133892





