Emotion Regulation Is Associated with Anxiety, Depression and Stress in Adults with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Participants, Procedures and Measures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007, 109 (Suppl. S109), 8–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sigurdardottir, S.; Indredavik, M.S.; Eiriksdottir, A.; Einarsdottir, K.; Guðmundsson, H.S.; Vik, T. Behavioural and emotional symptoms of preschool children with cerebral palsy: A population-based study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, J.; White-Koning, M.; O Dickinson, H.; Thyen, U.; Arnaud, C.; Beckung, E.; Fauconnier, J.; Marcelli, M.; McManus, V.; Michelsen, S.I.; et al. Psychological problems in children with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional European study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittingham, K.; Bodimeade, H.L.; Lloyd, O.; Boyd, R.N. Everyday psychological functioning in children with unilateral cerebral palsy: Does executive functioning play a role? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brossard-Racine, M.; Hall, N.; Majnemer, A.; Shevell, M.I.; Law, M.; Poulin, C.; Rosenbaum, P. Behavioural problems in school age children with cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte-Darraz, S.; Montoro, C.I.; Andrade, N.C.; Montoya, P.; Riquelme, I. Alteration of Emotion Knowledge and Its Relationship with Emotion Regulation and Psychopathological Behavior in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.J. Emotion Regulation: Conceptual and Empirical Foundations; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- John, O.P.; Gross, J.J. Healthy and Unhealthy Emotion Regulation: Personality Processes, Individual Differences, and Life Span Development. J. Pers. 2004, 72, 1301–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L. Teaching teachers about emotion regulation in the classroom. Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2011, 36, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandey, A.A. Emotion regulation in the workplace: A new way to conceptualize emotional labor. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2000, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.J.; John, O.P. Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 85, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Etkin, A.; Büchel, C.; Gross, J.J. The neural bases of emotion regulation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, H.; Serra-Mestres, J. Neuropsychiatry of the basal ganglia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felling, R.J.; Singer, H.S. Neurobiology of Tourette syndrome: Current status and need for further investigation. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 12387–12395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monbaliu, E.; Himmelmann, K.; Lin, J.-P.; Ortibus, E.; Bonouvrié, L.; Feys, H.; Vermeulen, R.J.; Dan, B. Clinical presentation and management of dyskinetic cerebral palsy. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Badawi, N.; Blair, E.; Himmelmann, K.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; McIntyre, S.; Slee, J.; Uldall, P.; Watson, L.; Wilson, M. What constitutes cerebral palsy in the twenty-first century? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik-Parvinchi, D.; MyStory Study Group; Davis, A.; Roth, S.; Rosenbaum, P.; Hopmans, S.N.; Dudin, A.; Hall, G.; Gorter, J.W. Functional connectivity and quality of life in young adults with cerebral palsy: A feasibility study. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenbach, G. Improving the quality of Web surveys: The Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys (CHERRIES). J. Med. Internet Res. 2004, 6, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.; Rosenbaum, P.; Bartlett, D.; Livingston, M.; Walter, S.; Russell, D. GMFCS-E&R; CanChild Centre for Childhood Disability Research, McMaster University: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2007; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Hidecker, M.J.C.; Paneth, N.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Kent, R.D.; Lillie, J.; Eulenberg, J.B.; Chester, K., Jr.; Johnson, B.; Michalsen, L.; Evatt, M.; et al. Developing and validating the Communication Function Classification System for individuals with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.; Crawford, J. The short-form version of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21): Construct validity and normative data in a large non-clinical sample. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 44, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, K.; Roemer, L. Multidimensional Assessment of Emotion Regulation and Dysregulation: Development, Factor Structure, and Initial Validation of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2004, 26, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giromini, L.; Ales, F.; De Campora, G.; Zennaro, A.; Pignolo, C. Developing age and gender adjusted normative reference values for the difficulties in emotion regulation scale (DERS). J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2017, 39, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.J.; Hollenstein, T.; Mackey, A. The effect of suppressing and not accepting emotions on depressive symptoms: Is suppression different for men and women? Pers. Individ. Differ. 2010, 49, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joormann, J.; Stanton, C.H. Examining emotion regulation in depression: A review and future directions. Behav. Res. Ther. 2016, 86, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, C.; Ownsworth, T.; O’Donovan, A.; Fleming, J. A transdiagnostic investigation of emotional distress after traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2016, 26, 410–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.; Sullivan, S.; Tchanturia, K.; Treasure, J. Emotional functioning in eating disorders: Attentional bias, emotion recognition and emotion regulation. Psychol. Med. 2010, 40, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, L.; Williston, S.K.; Rollins, L.G. Mindfulness and emotion regulation. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2015, 3, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.D.; Lin, P.; Kamdar, N.; Mahmoudi, E.; Marsack-Topolewski, C.N.; Haapala, H.; Muraszko, K.; Hurvitz, E.A. Psychological morbidity among adults with cerebral palsy and spina bifida. Psychol. Med. 2020, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, D.G.; Warschausky, S.A.; Ng, S.; Hurvitz, E.A.; Kamdar, N.S.; Peterson, M.D. Prevalence of mental health disorders among adults with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Peterson, M.; O’Connell, N.E.; Victor, C.; Liverani, S.; Anokye, N.; Ryan, J. Risk of depression and anxiety in adults with cerebral palsy. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australia Bureau of Statistics. National Health Survey: First Results, Australia, 2017–2018; Australia Bureau of Statistics: Canberra, Australia, 2018.
- Lanciego, J.L.; Luquin, N.; Obeso, J.A. Functional neuroanatomy of the basal ganglia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.R.; Cano, A. Comorbid chronic pain and depression: Who is at risk? J. Pain 2009, 10, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goesling, J.; Clauw, D.J.; Hassett, A.L. Pain and depression: An integrative review of neurobiological and psychological factors. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2013, 15, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Slot, W.M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, C.; Van Den Berg-Emons, R.J.; Bergen, M.P.; Hilberink, S.R.; Stam, H.J.; Roebroeck, M.E. Chronic pain, fatigue, and depressive symptoms in adults with spastic bilateral cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, D.G.; A Hurvitz, E.; Ryan, J.M.; Devlin, M.J.; Caird, M.S.; French, Z.P.; Ellenberg, E.C.; Peterson, M.D. Noncommunicable disease and multimorbidity in young adults with cerebral palsy. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnsen, R.; Villien, L.; Aamodt, G.; Stanghelle, J.; Holm, I. Musculoskeletal pain in adults with cerebral palsy compared with the general population. J. Rehabil. Med. 2004, 36, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, T.; Danese, A.; Wertz, J.; Odgers, C.L.; Ambler, A.; Moffitt, T.E.; Arseneault, L. Social isolation, loneliness and depression in young adulthood: A behavioural genetic analysis. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2016, 51, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mann, F.; Lloyd-Evans, B.; Ma, R.; Johnson, S. Associations between loneliness and perceived social support and outcomes of mental health problems: A systematic review. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, S.; Berg, N.; Waller, A. Assessing the loneliness of older people with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, S.I.; Uldall, P.; Hansen, T.; Madsen, M. Social integration of adults with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Helber, A.; Mader, I.; Staudt, M.; Wolff, M.; Groenendaal, F.; DeVries, L. Bilateral lesions of thalamus and basal ganglia: Origin and outcome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Kim, K.M. Effect of digital divide on people with disabilities during the COVID-19 pandemic. Disabil. Health J. 2022, 15, 101214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total n = 42 |
|---|---|
| Females; n (%) | 24 (57.1) |
| Age; Mean (SD); Range | 31.50 (13.48); (18–72) |
| CP Type/topography ++ n (%) | |
| Spastic | 30 (73.2) |
| Hemiplegia | 15 (50.0) |
| Diplegia | 8 (26.7) |
| Quadriplegia | 7 (23.3) |
| Dyskinesia | 4 (9.7) |
| Ataxia | 1 (2.4) |
| Mixed | 5 (12.2) |
| Unknown | 1 (2.4) |
| Intellectual Ability n (%) | |
| No impairment | 37 (88.1) |
| Mild impairment | 5 (11.9) |
| Functional Communication Level ++ n (%) | |
| Effective communicator | 33 (80.5) |
| Slow but effective communicator | 6 (14.6) |
| Effective communicator with familiar people | 2 (4.9) |
| Inconsistent communicator | 0 |
| Seldom effective communicator | 0 |
| AAC; N (%) | |
| Use AAC | 6 (14.3) |
| GMFCS level; n (%) | |
| I | 14 (33.3) |
| II | 13 (31) |
| III | 4 (9.5) |
| IV | 6 (14.3) |
| V | 5 (11.9) |
| Gross Motor Function; n (%) | |
| Ambulant | 27 (64.3) |
| Supported mobility | 15 (35.7) |
| Employment Status + n (%) | |
| Employed | 28 (70.0) |
| Unemployed | 12 (30) |
| Living Arrangement ++ n (%) | |
| Alone | 7 (17.1) |
| Share house | 5 (12.2) |
| With spouse | 5 (12.2) |
| Other family | 24 (58.5) |
| Primary Support Person; n (%) | |
| Parent | 22 (52.4) |
| I do not have a primary support person | 13 (31.0) |
| Partner/spouse | 2 (4.8) |
| Sibling | 1 (2.4) |
| Caseworker/advocate/other | 4 (9.6) |
| Psychological Disorder; n (%) | |
| Diagnosed psychological disorder | 17 (40.5) |
| Routine Services; n (%) | |
| Receiving routine services | 18 (42.9) |
| DERS Scores | ||||||||
| Raw DERS | T-Scores | |||||||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | WNL 1 N (%) | Elevated 2 N (%) | p-Value | ||||
| Total | 81.93 (30.30) | 50.95 (14.87) | 38 (90.5) | 4 (9.5) | Not able to compute | |||
| Nonaccept | 14.69 (6.99) | 55.52 (14.64) | 32 (76.2) | 10 (23.8) | <0.001 | |||
| Goals | 13.45 (5.29) | 49.67 (12.32) | 36 (85.7) | 6 (14.3) | 0.048 | |||
| Impulse | 12.50 (6.31) | 51.28 (13.26) | 36 (85.7) | 6 (14.3) | 0.048 | |||
| Awareness | 13.45 (5.53) | 51.52 (13.51) | 36 (85.7) | 6 (14.3) | 0.048 | |||
| Strategies | 17.86 (8.26) | 52.25 (12.76) | 35 (83.3) | 7 (16.7) | 0.010 | |||
| Clarity | 9.98 (4.41) | 49.04 (11.36) | 37 (88.1) | 5 (11.9) | 0.175 | |||
| DASS-21 Scores | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | Range | n (%) Scoring in Ranges | |||||
| Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Extremely Severe | ||||
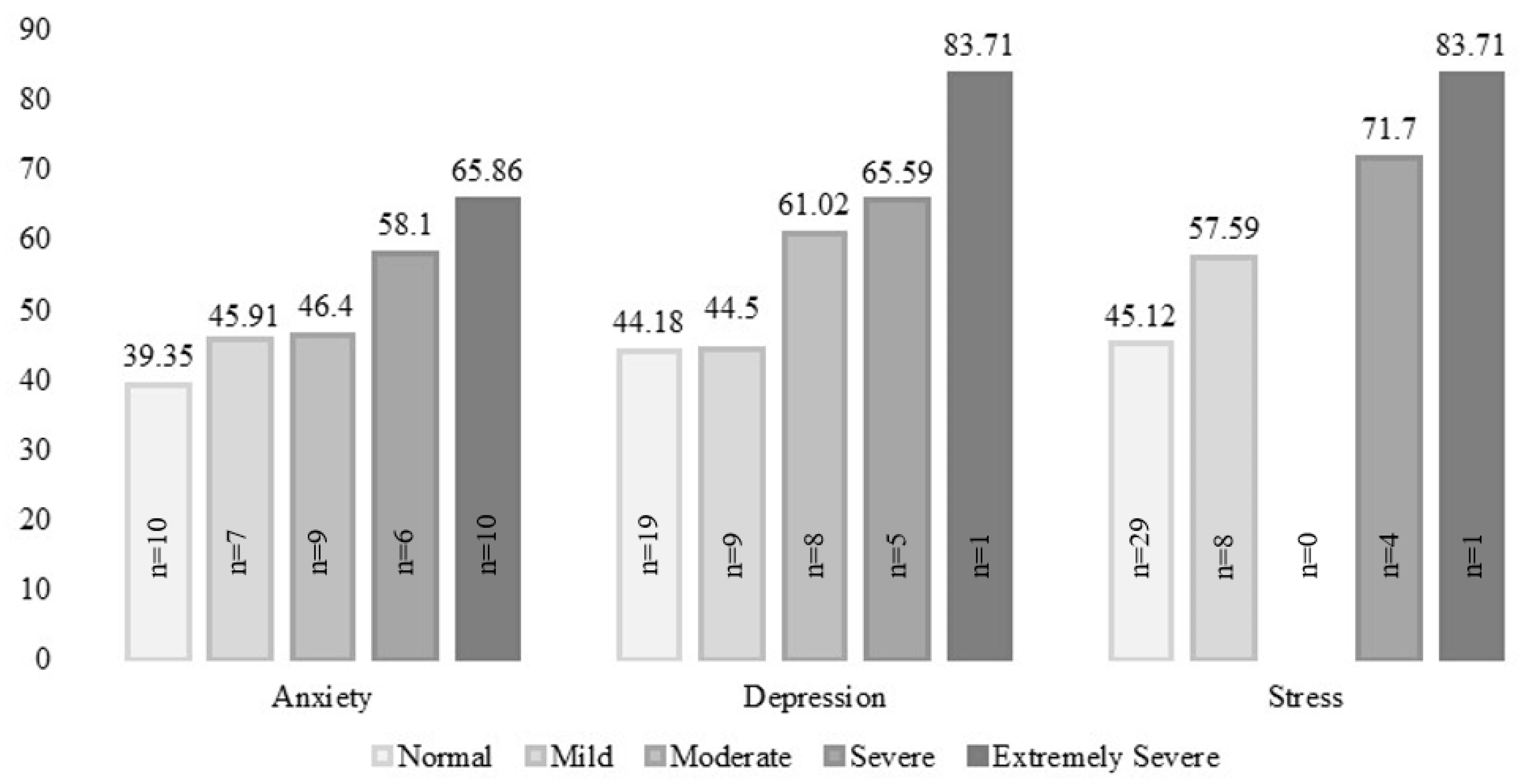
| Depression | 5.71 | 3.897 | 0–18 | 19 (45.2) | 9 (21.4) | 8 (19.0) | 5 (11.9) | 1 (2.4) |
| Anxiety | 7.10 | 4.143 | 2–19 | 10 (23.8) | 7 (16.7) | 9 (21.4) | 6 (14.3) | 10 (23.8) |
| Stress | 5.62 | 4.654 | 0–20 | 29 (69.0) | 8 (19.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (9.5) | 1 (2.4) |
| DASS Low Group | DASS Elevated Group | Change Statistic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DERS Total T-Score | DERS Total T-Score | ||||||
| N | Median | IQR | N | Median | IQR | p-Value | |
| Anxiety | 17 | 42.85 | 16.64 | 25 | 56.82 | 16.86 | 0.001 |
| Depression | 28 | 43.16 | 15.94 | 14 | 62.18 | 16.29 | <0.001 |
| Stress | 37 | 49.74 | 17.65 | 5 | 71.64 | 29.27 | 0.002 |
| DERs Total | Depression | Anxiety | Stress | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR | p-Value | Median | IQR | p-Value | Median | IQR | p-Value | Median | IQR | p-Value | |
| Gross Motor Function | ||||||||||||
| Ambulant | 52.90 | 10.65 | 0.232 | 6.00 | 5.00 | 0.225 | 7.00 | 5.00 | 0.117 | 4.00 | 5.00 | 0.518 |
| Supported mobility | 43.46 | 19.08 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 6.00 | ||||
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Male | 46.30 | 26.94 | 0.416 | 6.50 | 6.25 | 0.289 | 7.00 | 7.50 | 0.574 | 5.50 | 7.00 | 0.898 |
| Female | 52.81 | 19.91 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 6.50 | 3.75 | 4.00 | 3.75 | ||||
| CFCS | ||||||||||||
| Effective communicator | 49.97 | 20.75 | 0.224 | 5.00 | 6.25 | 0.393 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 0.368 | 4.00 | 5.25 | 0.519 |
| Reduced communication | 54.36 | 24.26 | 6.50 | 5.75 | 8.00 | 8.25 | 7.00 | 6.25 | ||||
| Employment Status + | ||||||||||||
| Employed | 52.81 | 21.18 | 0.859 | 5.00 | 6.75 | 0.711 | 6.50 | 4.75 | 0.859 | 4.00 | 4.75 | 0.801 |
| Unemployed | 48.26 | 18.81 | 5.00 | 4.75 | 7.00 | 6.50 | 5.00 | 6.50 | ||||
| Diagnosed psychologicaldisorder | ||||||||||||
| yes | 54.92 | 9.93 | 0.018 | 6.00 | 5.00 | 0.091 | 7.00 | 6.00 | 0.033 | 6.00 | 4.50 | 0.008 |
| no | 42.85 | 21.67 | 4.00 | 6.50 | 5.00 | 5.50 | 3.00 | 6.00 | ||||
| Receiving routine services | ||||||||||||
| yes | 51.46 | 21.84 | 0.722 | 4.50 | 5.50 | 0.498 | 6.00 | 6.25 | 0.601 | 4.00 | 4.75 | 0.344 |
| no | 51.97 | 20.84 | 5.00 | 5.75 | 7.00 | 5.25 | 6.00 | 5.00 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honan, I.; Waight, E.; Bratel, J.; Given, F.; Badawi, N.; McIntyre, S.; Smithers-Sheedy, H. Emotion Regulation Is Associated with Anxiety, Depression and Stress in Adults with Cerebral Palsy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072527
Honan I, Waight E, Bratel J, Given F, Badawi N, McIntyre S, Smithers-Sheedy H. Emotion Regulation Is Associated with Anxiety, Depression and Stress in Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(7):2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072527
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonan, Ingrid, Emma Waight, Joan Bratel, Fiona Given, Nadia Badawi, Sarah McIntyre, and Hayley Smithers-Sheedy. 2023. "Emotion Regulation Is Associated with Anxiety, Depression and Stress in Adults with Cerebral Palsy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 7: 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072527
APA StyleHonan, I., Waight, E., Bratel, J., Given, F., Badawi, N., McIntyre, S., & Smithers-Sheedy, H. (2023). Emotion Regulation Is Associated with Anxiety, Depression and Stress in Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(7), 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072527






