Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
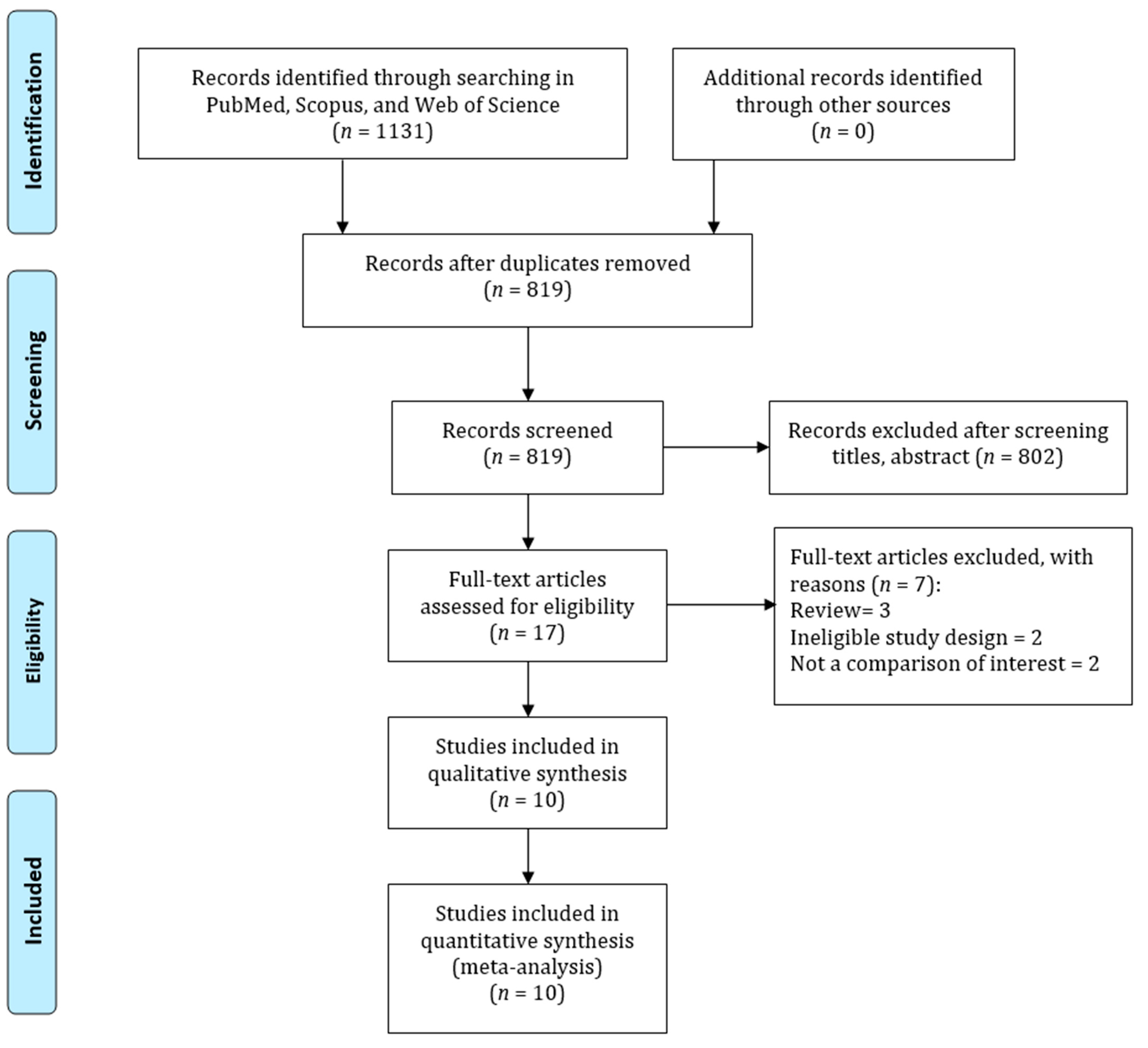
2. Methods
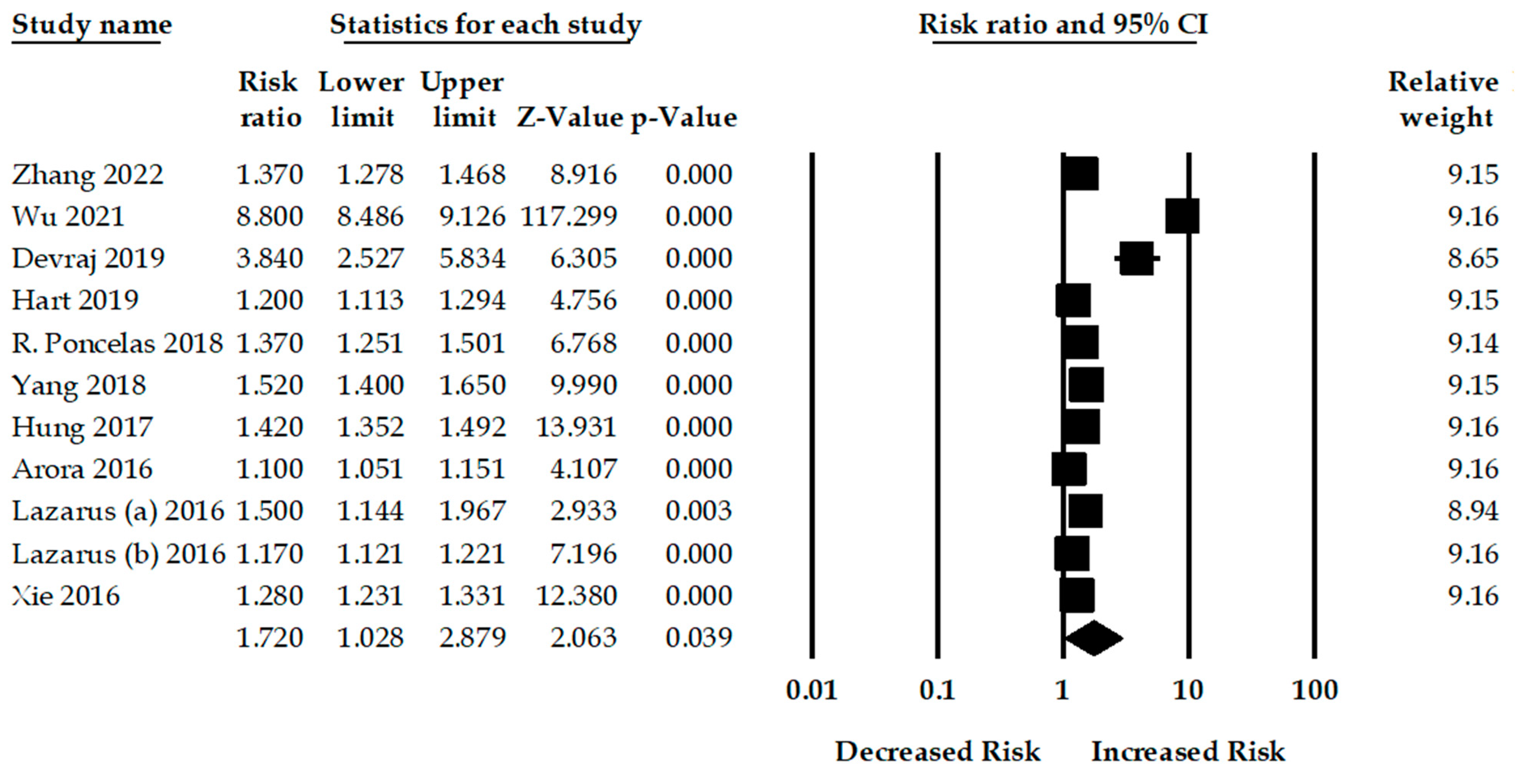
3. Results
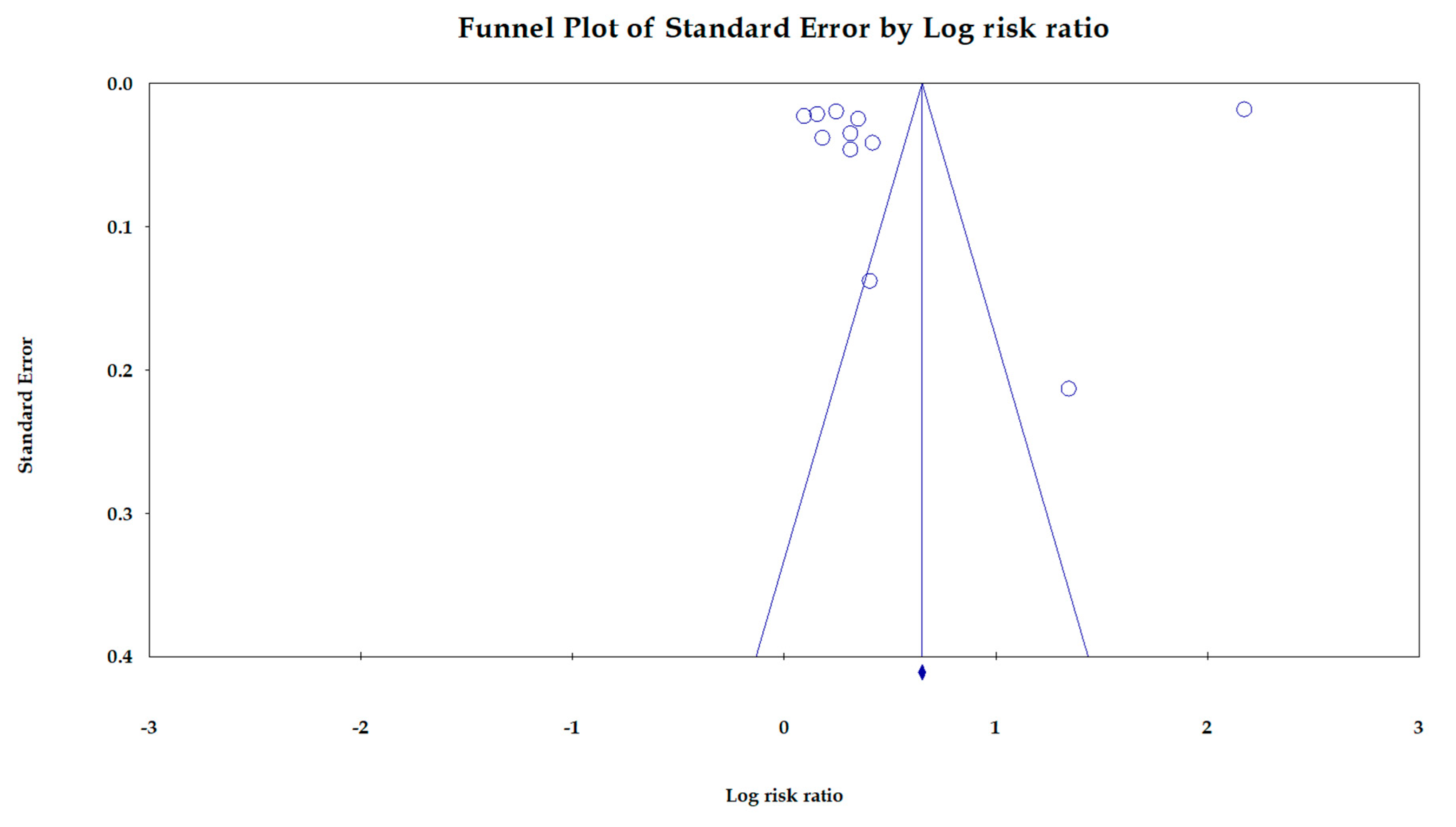
4. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Strengths and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Lui, S.-F.; Andreoli, S.; Fung, W.; Hradsky, A.; Kumaraswami, L.; Liakopoulos, V.; Rakhimova, Z.; Saadi, G. Kidney health for everyone everywhere–from prevention to detection and equitable access to care. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.P.; Goyder, E.C.; Rigby, J.E.; El Nahas, M. CKD and poverty: A growing global challenge. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; Yang, C.-W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poly, T.N.; Islam, M.M.; Walther, B.A.; Lin, M.-C.; Li, Y.-C. Proton Pump Inhibitors Use and the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: Evidence from Eleven Epidemiological Studies, Comprising 1.5 Million Individuals. Cancers 2022, 14, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fass, R.; Sifrim, D. Management of heartburn not responding to proton pump inhibitors. Gut 2009, 58, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, E.; Triadafilopoulos, G. Adverse effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 931–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Hansen, R.A.; Morgan, D.R.; Gangarosa, L.M.; Ringel, Y.; Thiny, M.T.; Russo, M.W.; Sandler, R.S. The burden of gastrointestinal and liver diseases, 2006. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2006, 101, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgacs, I.; Loganayagam, A. Overprescribing proton pump inhibitors. BMJ 2008, 336, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, S.R.; Bishop, T.F. Proton pump inhibitor use in the US ambulatory setting, 2002–2009. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, C.T.W.; Lim, W.P.; Vu, C.K.F. Inappropriate use of proton pump inhibitors in a local setting. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poly, T.; Islam, M.; Yang, H.-C.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.-C. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of hip fracture: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Poly, T.N.; Walther, B.A.; Dubey, N.K.; Anggraini Ningrum, D.N.; Shabbir, S.-A. Adverse outcomes of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poly, T.N.; Lin, M.-C.; Syed-Abdul, S.; Huang, C.-W.; Yang, H.-C.; Li, Y.-C. Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and Risk of Gastric Cancer: Current Evidence from Epidemiological Studies and Critical Appraisal. Cancers 2022, 14, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, B.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, F.P.; Sang, Y.; Chang, A.R.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E. Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of chronic kidney disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatte, D.C.; Gasparini, A.; Xu, H.; de Deco, P.; Trevisan, M.; Johansson, A.L.; Wettermark, B.; Ärnlöv, J.; Janmaat, C.J.; Lindholm, B. Association between proton pump inhibitor use and risk of progression of chronic kidney disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Maddukuri, G.; Xie, Y. Proton pump inhibitors and the kidney: Implications of current evidence for clinical practice and when and how to deprescribe. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheloufi, F.; Frankel, D.; Kaspi, E.; Lepelley, M.; Mallaret, M.; Boucherie, Q.; Roll, P.; Micallef, J. Chronic use of proton pump inhibitors, adverse events and potential biological mechanisms: A translational analysis. Therapies 2018, 73, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H. Proton pump inhibitor-induced risk of chronic kidney disease is associated with increase of indoxyl sulfate synthesis via inhibition of CYP2E1 protein degradation. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haastrup, P.F.; Thompson, W.; Søndergaard, J.; Jarbøl, D.E. Side effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor use: A review. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Islam, M.M.; Lee, A.-J.; Su, C.-H.; Weng, Y.-C.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-H.; Lin, M.-C. Association between Statin Use and Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: Evidence from 18 Observational Studies Comprising 3.7 Million Individuals. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; He, Q.-S.; Jing, Z.; He, J.-X.; Yuan, J.-Q.; Dai, X.-Y. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on the risk of chronic kidney disease: A propensity score-based overlap weight analysis using the United Kingdom Biobank. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 949699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, D.; Xu, T.; Luo, M.; He, Z.; Li, Y. Proton pump inhibitors associated acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: Data mining of US FDA adverse event reporting system. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devraj, R.; Deshpande, M. Demographic and health-related predictors of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use and association with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage in NHANES population. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2020, 16, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, E.; Dunn, T.E.; Feuerstein, S.; Jacobs, D.M. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of acute and chronic kidney disease: A retrospective cohort study. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2019, 39, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Poncelas, A.; Barcelo, M.A.; Saez, M.; Coll-de-Tuero, G. Duration and dosing of proton pump inhibitors associated with high incidence of chronic kidney disease in population-based cohort. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Juang, S.-Y.; Liao, K.-F. Proton pump inhibitors use and risk of chronic kidney disease in diabetic patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 147, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Gupta, A.; Golzy, M.; Patel, N.; Carter, R.L.; Jalal, K.; Lohr, J.W. Proton pump inhibitors are associated with increased risk of development of chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Bowe, B.; Li, T.; Xian, H.; Balasubramanian, S.; Al-Aly, Z. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of incident CKD and progression to ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2016, 27, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.-C.; Liao, K.-F.; Hung, H.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Lai, S.-W.; Lee, P.-C.; Hung, S.-R. Using proton pump inhibitors correlates with an increased risk of chronic kidney disease: A nationwide database-derived case-controlled study. Fam. Pract. 2018, 35, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Thongprayoon, C.; Chesdachai, S.; Panjawatanana, P.; Ungprasert, P.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Associations of proton-pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists with chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, H.; Cui, M.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Wei, J.; Zhou, S. The use of anti-ulcer agents and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C. Acid-suppressive drugs and risk of kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Singh, A.; Habib, A.; Najmi, A.K. Proton pump inhibitors use and risk of chronic kidney disease: Evidence-based meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 7, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.I.; Hoang, D.M.; Vandenplas, Y. The effects of proton pump inhibitors on the microbiome in young children. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minalyan, A.; Gabrielyan, L.; Scott, D.; Jacobs, J.; Pisegna, J.R. The gastric and intestinal microbiome: Role of proton pump inhibitors. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Franceschi, F.; Gasbarrini, A. The gastrointestinal microbiome–functional interference between stomach and intestine. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhann, F.; Bonder, M.J.; Vila, A.V.; Fu, J.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Cenit, M.C.; Harmsen, H.J. Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 2016, 65, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Maxan, M.-E.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Welter, D.; Ley, R.E.; Bell, J.T. Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota. Gut 2016, 65, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, P.; DeRiso, A.; Patel, M.; Battepati, D.; Khatib-Shahidi, B.; Sharma, H.; Gupta, R.; Malhotra, D.; Dworkin, L.; Haller, S. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: Diversity in the vessel wall. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieboom, B.C.; Kiefte–de Jong, J.C.; Eijgelsheim, M.; Franco, O.H.; Kuipers, E.J.; Hofman, A.; Zietse, R.; Stricker, B.H.; Hoorn, E.J. Proton pump inhibitors and hypomagnesemia in the general population: A population-based cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinutta, T.; Chewcharat, A.; Takkavatakarn, K.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Jaber, B.L.; Susantitaphong, P. Proton pump inhibitors and hypomagnesemia: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Medicine 2019, 98, e17788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moledina, D.G.; Perazella, M.A. PPIs and kidney disease: From AIN to CKD. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontecha-Barriuso, M.; Martín-Sanchez, D.; Martinez-Moreno, J.M.; Cardenas-Villacres, D.; Carrasco, S.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Ortiz, A.; Sanz, A.B. Molecular pathways driving omeprazole nephrotoxicity. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.-C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.-T.; Liu, T.; Tao, M.-M.; You, Q.-D.; Jiang, Z.-Y. CPUY192018, a potent inhibitor of the Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction, alleviates renal inflammation in mice by restricting oxidative stress and NF-κB activation. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanayagam, C.; Lim, S.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Lee, J.; Shankar, A.; Tai, E.S. Ethnic disparities in prevalence and impact of risk factors of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2564–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Kim, I.-H.; Ju, E.Y.; Ahn, S.J.; Kim, D.-K.; Lee, S.W. Chronic kidney disease and metabolic syndrome in a general Korean population: The Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III) Study. J. Public Health 2010, 32, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Luo, D.; Wu, X. The prevalence and associated factors of metabolic syndrome in Chinese aging population. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheith, O.; Farouk, N.; Nampoory, N.; Halim, M.A.; Al-Otaibi, T. Diabetic kidney disease: World wide difference of prevalence and risk factors. J. Nephropharmacol. 2016, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakris, G.L.; Ritz, E. The message for World Kidney Day 2009: Hypertension and kidney disease—A marriage that should be prevented. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2009, 23, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, J.W.T.; Ong, E.; Wilson, R. Hypomagnesaemia associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitors. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 3, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Country | Study Design | Study Participant | Age (Year) | Gender (Male) | Inclusion Criteria for CKD | Adjustment | NOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. [15] | 2022 | China | Cohort | 462,421 | 58.89 | 45.3 | ICD | Age, sex, smoking, alcohol consumption, BMI, physical activity, diabetes hypertension, hyperlipidemia, GORD, NSAIDs | 9 |
| Wu et al. [16] | 2021 | China | Cohort | 5,414,695 | Range | N/A | ICD | Age, sex | 7 |
| Devraj et al. [17] | 2019 | USA | C-C | 18,504 | 46.3 | 48.2 | ICD | Age, sex, BMI, race, smoking, alcohol, comorbidities | 7 |
| Hart et al. [18] | 2020 | USA | Cohort | 177,935 | 51.1 | 38.7 | ICD | Age, sex, BMI, smoking, alcohol, hypertension | 9 |
| Rodríguez-Poncelas et al. [19] | 2018 | Spain | Cohort | 46,541 | 41.23 | 51.2 | ICD | Age, gender, diabetes, obesity, blood pressure, hypertension, cholesterol, chronic disease | 9 |
| Yang et al. [20] | 2018 | UK | Cohort | 29,970 | 59.1 | 59.5 | ICD | Age, sex, hypertension, gout, IHD CVA, CHF, PAD, region | 9 |
| Hung et al. [24] | 2017 | Taiwan | C-C | 33,408 | Range | 58.6 | ICD | Age, sex, diabetes, hypertension | 7 |
| Arora et al. [21] | 2016 | USA | C-C | 99,269 | N/A | N/A | ICD | Age, sex, COPD, diabetes, hypertension | 7 |
| Lazarus (a) et al. [22] | 2016 | USA | Cohort | 104,820 | 62.8 | 42.5 | ICD | Age, sex, diabetes, diuretic use | 8 |
| Lazarus (b) et al. [22] | 2016 | USA | Cohort | 248,751 | 50.0 | 43.2 | ICD | Age, sex, CCI, DM, other lipid-lowering agents | 8 |
| Xie et al. [23] | 2016 | USA | Cohort | 193,591 | 56.85 | 93.4 | ICD | Age, sex, race, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, GORD, chronic lung disease, ulcer disease | 8 |
| Study | No. of Studies | Pooled Estimates | Test of Heterogeneity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95% CI) | p-Value | Q Value | p-Value | I2 (%) | ||
| All Studies | 10 | 1.72 (1.02–2.87) | 0.03 | 8730.48 | <0.001 | 99.88 |
| Study Design | ||||||
| Cohort | 7 | 1.69 (0.85–3.35) | 0.13 | 7784.31 | <0.001 | 99.91 |
| Case-control | 3 | 1.57 (1.20–2.05) | 0.001 | 83.62 | <0.001 | 97.60 |
| Region | ||||||
| Western | 6 | 1.28 (1.17–1.40) | <0.001 | 66.03 | <0.001 | 90.91 |
| Asian | 4 | 2.25 (0.74–6.81) | 0.14 | 4858.83 | 0.001 | 99.93 |
| Methodological Quality | ||||||
| High | 4 | 1.35 (1.23–1.49) | <0.001 | 17.70 | <0.001 | 83.05 |
| Moderate | 6 | 1.97 (0.95–4.07) | 0.06 | 8337.98 | <0.001 | 99.92 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 3 | 1.14 (1.01–1.28) | 0.03 | 21.73 | <0.001 | 90.80 |
| Female | 4 | 0.95 (0.63–1.42) | 0.80 | 111.94 | <0.001 | 97.32 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Hypertension | 5 | 1.38 (0.95–1.99) | 0.08 | 555.15 | <0.001 | 99.27 |
| Diabetes | 4 | 1.45 (1.27–1.65) | <0.001 | 18.02 | <0.001 | 83.35 |
| Comedication | ||||||
| NSAIDs | 3 | 0.82 (0.45–1.51) | 0.54 | 317.00 | <0.001 | 99.36 |
| Type of PPIs | ||||||
| Lansoprazole | 3 | 3.82 (0.40–36.46) | 0.24 | 2953.10 | <0.001 | 99.93 |
| Omeprazole | 3 | 1.32 (1.23–1.42) | <0.001 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0 |
| Pantoprazole | 2 | 4.13 (0.49–34.21) | 0.18 | 314.54 | <0.001 | 99.68 |
| Rabeprazole | 2 | 1.50 (1.20–1.87) | <0.001 | 0.02 | 0.86 | 0 |
| Esomeprazole | 2 | 1.53 (1.24–1.89) | <0.001 | 4.31 | 0.03 | 76.83 |
| Excluded Study | Pooled Estimates | Test of Heterogeneity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95% CI) | p-Value | Q Value | p-Value | I2 (%) | |
| All Studies | 1.72 (1.02–2.87) | 0.03 | 8730.42 | <0.001 | 99.88 |
| Arora et al. [30] | 1.80 (1.02–3.17) | 0.04 | 8066.26 | <0.001 | 99.88 |
| Devraj et al. [26] | 1.59 (0.93–2.73) | 0.09 | 8719.87 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
| Hart et al. [27] | 1.78 (1.02–3.10) | 0.04 | 8573.17 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
| Huang et al. [32] | 1.75 (0.98–3.12) | 0.05 | 8569.41 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
| Lazarus (a) et al. [15] | 1.74 (1.01–2.99) | 0.04 | 8727.31 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
| Lazarus (b) et al. [15] | 1.78 (1.00–3.18) | 0.04 | 8123.88 | <0.001 | 99.88 |
| R. Poncelas et al. [28] | 1.76 (1.01–3.05) | 0.04 | 8676.41 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
| Wu et al. [25] | 1.34 (1.24–1.45) | <0.001 | 128.22 | <0.001 | 92.98 |
| Xie et al. [31] | 1.77 (0.98–3.19) | 0.05 | 8226.78 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
| Yang et al. [29] | 1.74 (1.00–3.03) | 0.05 | 8698.44 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
| Zhang et al. [24] | 1.76 (1.00–3.07) | 0.04 | 8634.15 | <0.001 | 99.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.-C.; Liao, M.-H.; Kung, W.-M.; Wang, Y.-C. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062262
Wu C-C, Liao M-H, Kung W-M, Wang Y-C. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(6):2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062262
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chieh-Chen, Mao-Hung Liao, Woon-Man Kung, and Yao-Chin Wang. 2023. "Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 6: 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062262
APA StyleWu, C.-C., Liao, M.-H., Kung, W.-M., & Wang, Y.-C. (2023). Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(6), 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062262








