Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index Predicts Newly Diagnosed Diabetes in Chinese Rural Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
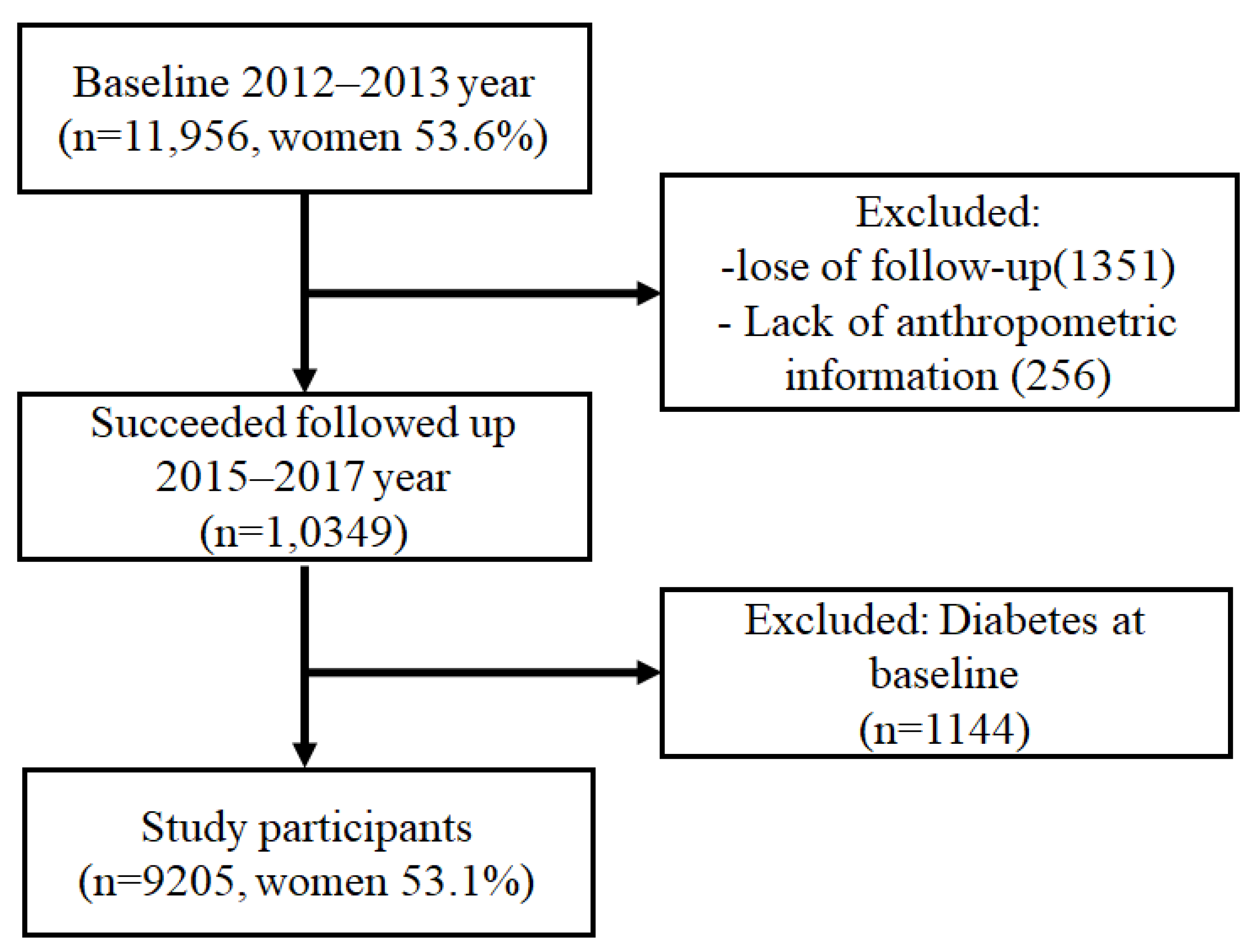
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Study Variables
2.3. Definition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Association between WWI and Newly Diagnosed T2D
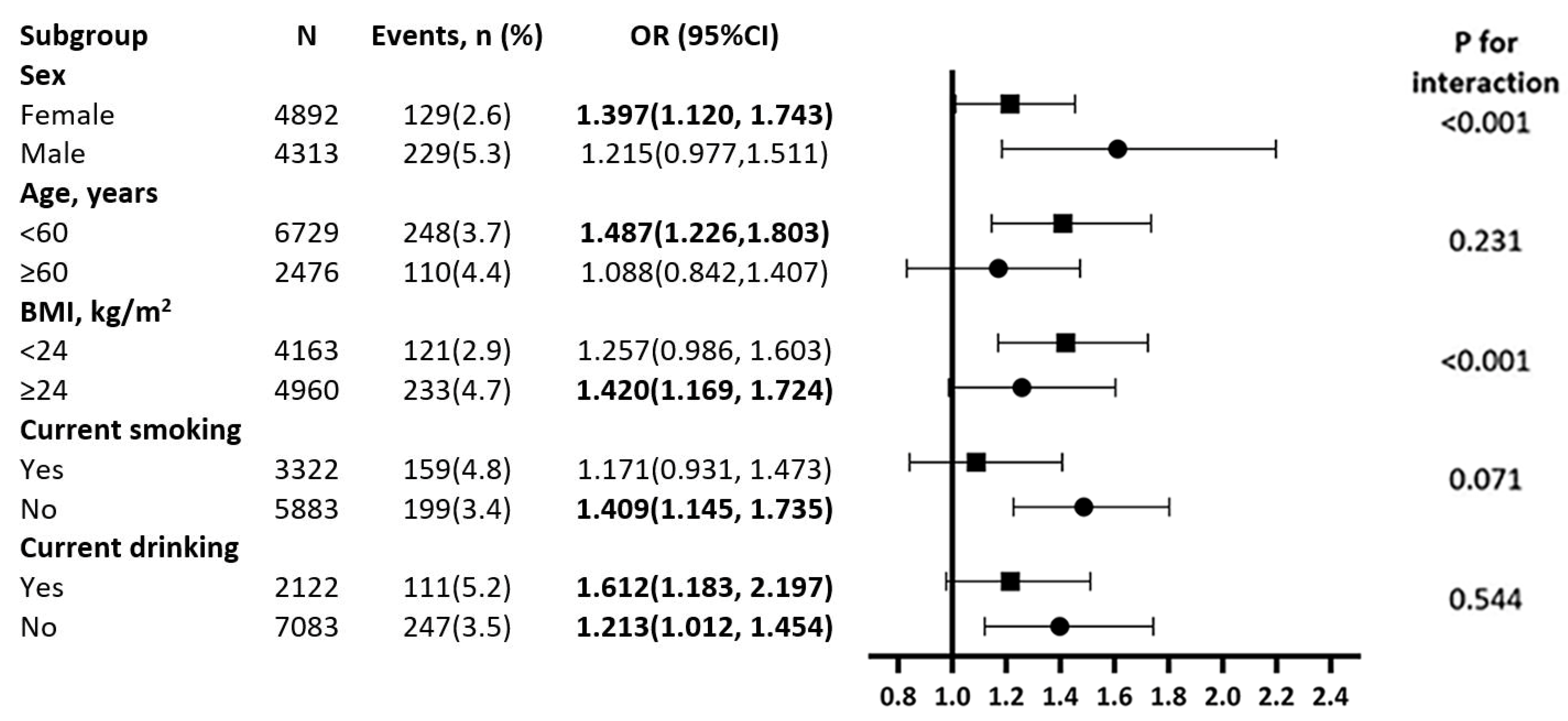
3.3. Subgroup Analyses for Association between WWI and T2D
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Gregg, E. Global economic burden of diabetes and its implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, S.W.; Wang, L.J.; Bai, Y.M.; Zeng, X.Y.; Guo, H.B.; Liu, Y.N.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Dong, W.L.; He, G.X.; et al. Burden of diabetes, hyperglycaemia in China from to 2016: Findings from the 1990 to 2016, global burden of disease study. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, F. Prevalence, awareness and control of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk factors in Chinese elderly population. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhou, Z.; Lai, S.; Tao, X.; Zhao, D.; Dong, W.; Li, D.; Lan, X.; Gao, J. Urban-rural-specific trend in prevalence of general and central obesity, and association with hypertension in Chinese adults, aged 18–65 years. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, D.; Qian, X.; Li, L.; Wu, W. Combined Effects of Obesity and Dyslipidaemia on the Prevalence of Diabetes Amongst Adults Aged ≥ 45 Years: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Prediction of a new body shape index and body adiposity estimator for development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Rural Chinese Cohort Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, N.H.; Kwon, T.Y.; Kim, S.G. A novel adiposity index as an integrated predictor of cardiometabolic disease morbidity and mortality. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Park, Y.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, S.G. Weight-adjusted waist index reflects fat and muscle mass in the opposite direction in older adults. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Du, D.; Li, Y.; Chang, K.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, R.; Su, B. The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and abdominal aortic calcification in adults aged ≥ 40 years: Results from NHANES 2013–2014. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qie, R.; Qin, P.; Zhang, D.; Guo, C.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, G.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Association of weight-adjusted-waist index with incident hypertension: The Rural Chinese Cohort Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Chang, K.; Yang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Liao, R.; Su, B. The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and increased urinary albumin excretion in adults: A population-based study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 941926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Shi, W.; Shi, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Ding, C.; Song, X.; Qiu, G.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Yu, C.; et al. Positive association between weight-adjusted-waist index and hyperuricemia in patients with hypertension: The China H-type hypertension registry study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1007557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Guo, X.; Yang, H.; Zheng, L.; Sun, Y. An update on the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its associated factors in rural northeast China. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, G.; Stepaniak, U.; Micek, A.; Topor-Mądry, R.; Pikhart, H.; Szafraniec, K.; Pająk, A. Association of daily coffee and tea consumption and metabolic syndrome: Results from the Polish arm of the HAPIEE study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.; Na, J.K.; Han, J.H.; Yoon, D.K.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, D.S.; Choi, K.M. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Magno, C.P.; Lane, K.T.; Hinojosa, M.W.; Lane, J.S. Association of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome with obesity: Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999 to 2004. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 207, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Ko, S.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, S.; Choi, S.H.; Song, K.H.; Won, J.C.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Prevalence, awareness, and management of obesity in Korea: Data from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (1998–2011). Diabetes Metab. J. 2014, 38, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, F.X. The obesity epidemic: Pathophysiology and consequences of obesity. Obes. Res. 2002, 10 (Suppl. S2), 97s–104s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.S.; Stanforth, P.R.; Gagnon, J.; Rankinen, T.; Leon, A.S.; Rao, D.C.; Skinner, J.S.; Bouchard, C.; Wilmore, J.H. The effect of sex, age and race on estimating percentage body fat from body mass index: The Heritage Family Study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.C.; Koh, G.C.; Chen, C.; Wong, M.T.; Fallows, S.J. Comparison of Body Mass Index (BMI), Body Adiposity Index (BAI), Waist Circumference (WC), Waist-To-Hip Ratio (WHR) and Waist-To-Height Ratio (WHtR) as predictors of cardiovascular disease risk factors in an adult population in Singapore. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, N.; Baumeister, S.E.; Amann, U.; Rathmann, W.; Peters, A.; Huth, C.; Thorand, B.; Meisinger, C. Visceral adiposity index (VAI), lipid accumulation product (LAP), and product of triglycerides and glucose (TyG) to discriminate prediabetes and diabetes. Sci. Rep 2019, 9, 9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z. Comparisons of Visceral Adiposity Index, Body Shape Index, Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference and Their Associations with Diabetes Mellitus in Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Zhang, S.; An, R. Effectiveness of A Body Shape Index (ABSI) in predicting chronic diseases and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 737–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, M.B.; Justice, J.N.; Nicklas, B.J.; Kirkland, J.L. Physiological Aging: Links Among Adipose Tissue Dysfunction, Diabetes, and Frailty. Physiology 2017, 32, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Shetty, S.; Orci, L.; Unger, R.H.; Scherer, P.E. Diabetes and apoptosis: Lipotoxicity. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkan, M.C.; Hevener, A.L.; Greten, F.R.; Maeda, S.; Li, Z.W.; Long, J.M.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Poli, G.; Olefsky, J.; Karin, M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirosumi, J.; Tuncman, G.; Chang, L.; Görgün, C.Z.; Uysal, K.T.; Maeda, K.; Karin, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 2002, 420, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Furuhashi, M.; Li, P.; Cao, H.; Tuncman, G.; Sonenberg, N.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase links pathogen sensing with stress and metabolic homeostasis. Cell 2010, 140, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mu, J.; Wang, D.W.; Ouyang, N.; Xing, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, C.; Ren, G.; Ye, N.; Zhou, Y.; et al. A village doctor-led multifaceted intervention for blood pressure control in rural China: An open, cluster randomised trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 1964–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, E.; Kawai, R. Age- and gender-related differences in correlations between abdominal obesity and obesity-related metabolic risk factors in Japanese. Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulc, P.; Duboeuf, F.; Chapurlat, R. Age-Related Changes in Fat Mass and Distribution in Men-the Cross-Sectional STRAMBO Study. J. Clin. Densitom. 2017, 20, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Guo, Z.; Wu, M.; Hao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, X. Interaction of smoking and obesity on type 2 diabetes risk in a Chinese cohort. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Weight-Adjusted Waist Index (WWI) (cm/√kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (<9.79) | Q2 (9.79–10.37) | Q3 (≥10.37) | p Value | |
| N | 1419 | 1433 | 1419 | |
| Age (years) | 51.83 ± 9.87 | 53.31 ± 10.46 | 56.79 ± 11.20 | <0.001 |
| Current smoking (yes) | 888 (62.6) | 829 (57.9) | 758 (53.4) | <0.001 |
| Current drinking (No) | 615 (43.3) | 703 (49.1) | 633 (44.6) | 0.006 |
| Ethnicity a (Han) | 1347 (94.9) | 1343 (93.7) | 1327 (93.5) | 0.229 |
| Education status | 0.002 | |||
| Primary school or below | 545 (38.4) | 571 (39.8) | 642 (45.2) | |
| Middle school | 710 (50.0) | 677 (47.2) | 623 (43.9) | |
| High school or above | 164 (11.6) | 185 (12.9) | 154 (10.9) | |
| Annual income (CNY/year) | <0.001 | |||
| ≤5000 | 136 (9.6) | 157 (11.0) | 245 (17.3) | |
| 5000–20,000 | 780 (55.0) | 774 (54.1) | 769 (54.2) | |
| >20,000 | 503 (35.4) | 499 (34.9) | 405 (28.5) | |
| Sleep duration (h/d) | 0.027 | |||
| ≤7 | 676 (47.7) | 627 (43.8) | 664 (46.8) | |
| 7–8 | 429 (30.3) | 441 (30.8) | 387 (27.3) | |
| 8–9 | 202 (14.3) | 241 (16.8) | 222 (15.7) | |
| >9 | 110 (7.8) | 122 (8.5) | 145 (10.2) | |
| Physical activity | <0.001 | |||
| Low | 310 (22.0) | 365 (25.6) | 485 (34.6) | |
| Moderate | 268 (19.0) | 279 (19.6) | 247 (17.6) | |
| High | 829 (58.9) | 781 (54.8) | 670 (47.8) | |
| Pulse (times/min) | 75 ± 13 | 75 ± 12 | 76 ± 13 | 0.222 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.92 ± 2.68 | 24.90 ± 3.13 | 26.08 ± 3.79 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 74.95 ± 6.17 | 83.76 ± 6.64 | 90.97 ± 7.92 | <0.001 |
| Height (m) | 167.68 ± 5.71 | 166.77 ± 6.37 | 164.89 ± 6.68 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 136.61 ± 19.19 | 142.73 ± 21.97 | 149.34 ± 23.32 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80.90 ± 10.87 | 83.78 ± 11.89 | 85.79 ± 11.81 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.73 ± 0.74 | 2.89 ± 0.78 | 3.02 ± 0.81 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.51 ± 0.42 | 1.42 ± 0.46 | 1.36 ± 0.41 | <0.001 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.50 ± 0.53 | 5.58 ± 0.55 | 5.59 ± 0.58 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Weight-Adjusted Waist Index (WWI) (cm/√kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (<10.06) | Q2 (10.06–10.72) | Q3 (≥10.37) | p Value | |
| N | 1618 | 1622 | 1608 | |
| Age (years) | 48.83 ± 9.00 | 51.74 ± 9.13 | 57.61 ± 10.45 | <0.001 |
| Current smoking (yes) | 245 (15.1) | 270 (16.6) | 306 (19.0) | 0.012 |
| Current drinking (No) | 43 (2.7) | 45 (2.8) | 63 (3.9) | 0.075 |
| Ethnicity a (Han) | 1535 (94.9) | 1528 (94.2) | 1505 (93.6) | 0.299 |
| Education status | <0.001 | |||
| Primary school or below | 705 (43.6) | 909 (56.0) | 1099 (68.3) | |
| Middle school | 732 (45.2) | 576 (35.5) | 436 (27.1) | |
| High school or above | 181 (11.2) | 137 (8.4) | 73 (4.5) | |
| Annual income (CNY/year) | <0.001 | |||
| ≤5000 | 106 (6.6) | 144 (8.9) | 264 (16.4) | |
| 5000–20,000 | 866 (53.5) | 913 (56.2) | 935 (58.1) | |
| >20,000 | 646 (39.9) | 564 (34.8) | 409 (25.4) | |
| Sleep duration (h/d) | <0.001 | |||
| ≤7 | 857 (53.0) | 834 (51.5) | 841 (52.4) | |
| 7–8 | 485 (30.0) | 479 (29.1) | 395 (24.6) | |
| 8–9 | 175 (10.8) | 196 (12.1) | 242 (15.1) | |
| >9 | 99 (6.1) | 111 (6.9) | 128 (8.0) | |
| Physical activity | 0.001 | |||
| Low | 598 (37.4) | 618 (38.3) | 709 (44.5) | |
| Moderate | 323 (20.2) | 309 (19.2) | 285 (17.9) | |
| High | 680 (42.5) | 686 (42.5) | 601 (37.7) | |
| Pulse (times/min) | 79 ± 12 | 79 ± 13 | 79 ± 13 | 0.331 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.28 ± 3.40 | 24.95 ± 3.36 | 25.93 ± 4.12 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 72.61 ± 6.73 | 80.82 ± 6.76 | 88.06 ± 8.44 | <0.001 |
| Height (m) | 157.31 ± 5.62 | 156.12 ± 5.61 | 153.56 ± 6.48 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 132.00 ± 20.19 | 138.97 ± 22.71 | 145.82 ± 25.29 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 77.98 ± 10.44 | 80.71 ± 11.25 | 81.91 ± 11.73 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.77 ± 0.78 | 2.97 ± 0.82 | 3.13 ± 0.87 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.47 ± 0.34 | 1.41 ± 0.33 | 1.41 ± 0.36 | <0.001 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.39 ± 0.52 | 5.44 ± 0.55 | 5.53 ± 0.55 | <0.001 |
| WWI (cm/√kg) | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | OR (95%CI) | p Value | OR (95%CI) | p Value | OR (95%CI) | p Value |
| Q1 (<9.79) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Q2 (9.79–10.37) | 1.398 (0.968, 2.019) | 0.074 | 1.377 (0.952, 1.991) | 0.089 | 1.200 (0.816, 1.767) | 0.354 |
| Q3 (≥10.37) | 2.121 (1.505, 2.991) | <0.001 | 2.047 (1.442, 2.905) | <0.001 | 1.604 (1.088, 2.364) | 0.013 |
| P for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.013 | |||
| Female | ||||||
| Q1 (<10.06) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Q2 (10.06–10.72) | 1.487 (0.891, 2.482) | 0.129 | 1.468 (0.878, 2.457) | 0.144 | 1.191 (0.703, 2.018) | 0.516 |
| Q3 (≥10.72) | 2.727 (1.712, 4.344) | <0.001 | 2.642 (1.616, 4.319) | <0.001 | 1.899 (1.121, 3.218) | 0.017 |
| P for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.011 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Li, G.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y. Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index Predicts Newly Diagnosed Diabetes in Chinese Rural Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041620
Yu S, Wang B, Guo X, Li G, Yang H, Sun Y. Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index Predicts Newly Diagnosed Diabetes in Chinese Rural Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041620
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shasha, Bo Wang, Xiaofan Guo, Guangxiao Li, Hongmei Yang, and Yingxian Sun. 2023. "Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index Predicts Newly Diagnosed Diabetes in Chinese Rural Adults" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041620
APA StyleYu, S., Wang, B., Guo, X., Li, G., Yang, H., & Sun, Y. (2023). Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index Predicts Newly Diagnosed Diabetes in Chinese Rural Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041620





