Clinicopathological Features of Kidney Injury Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
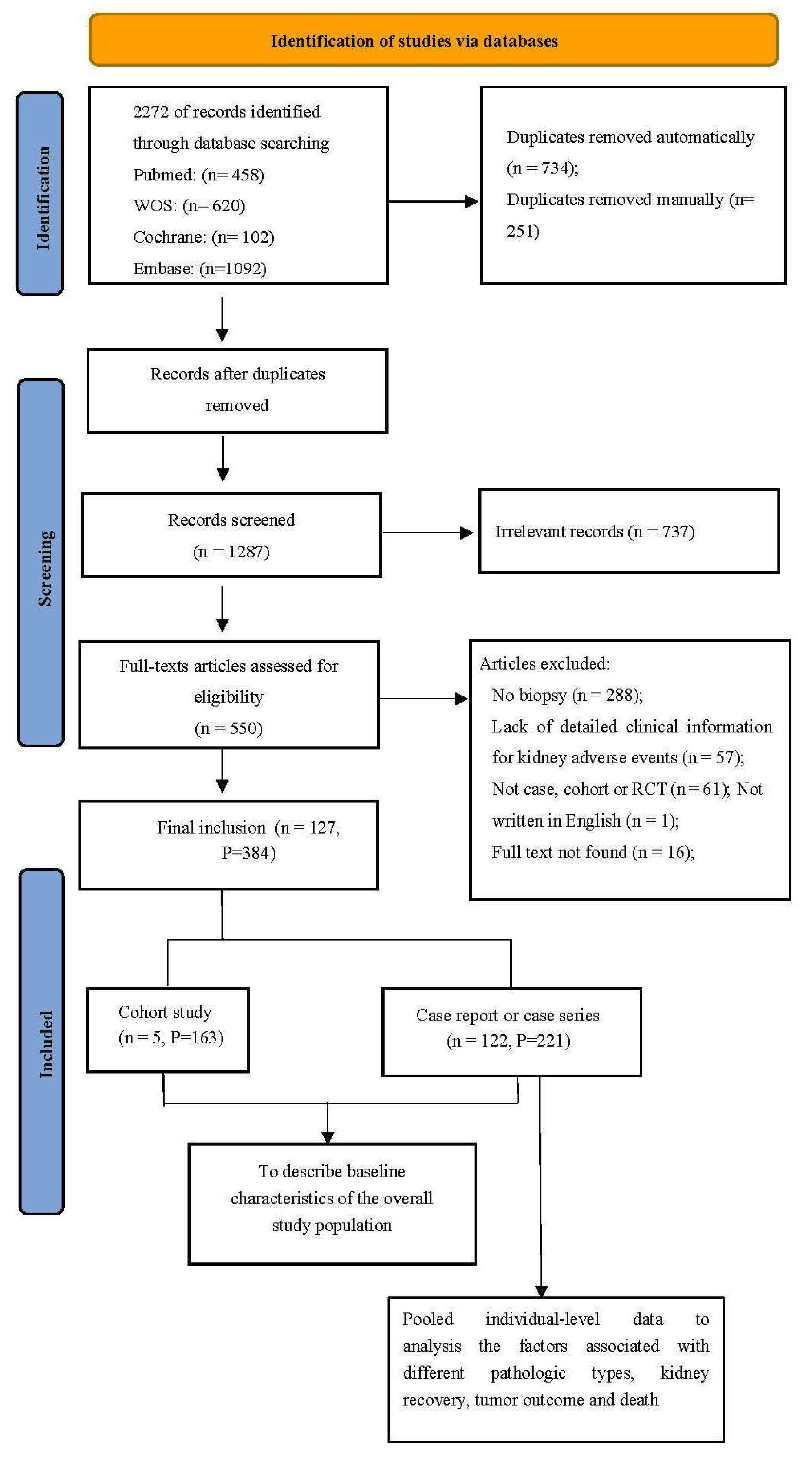
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with ICI-Kidney IRAEs
3.2. Treatment and Outcome of Patients with ICI-Kidney IRAEs
3.3. Pooled Individual Analysis of Patients with ICI-Associated Kidney IRAEs
3.4. Immunohistochemical Staining of Biopsied Kidney Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ansell, S.M.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Borrello, I.; Halwani, A.; Scott, E.C.; Gutierrez, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Millenson, M.M.; Cattry, D.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Schadendorf, D.; Dummer, R.; Smylie, M.; Rutkowski, P.; et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, K.; Turco, V.; Blobner, J.; Sonner, J.K.; Liuzzi, A.R.; Nunez, N.G.; De Feo, D.; Kickingereder, P.; Fischer, M.; Green, E.; et al. Heterogeneity of response to immune checkpoint blockade in hypermutated experimental gliomas. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, L.; Diem, S.; Larkin, J. Management of toxicities of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016, 44, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Marrone, K.A.; Troxell, M.L.; Ralto, K.M.; Hoenig, M.P.; Brahmer, J.R.; Le, D.T.; Lipson, E.J.; Glezerman, I.G.; Wolchok, J.; et al. Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koks, M.S.; Ocak, G.; Suelmann, B.B.M.; Hulsbergen-Veelken, C.A.R.; Haitjema, S.; Vianen, M.E.; Verhaar, M.C.; Kaasjager, K.A.H.; Khairoun, M. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated acute kidney injury and mortality: An observational study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.; Kompotiatis, P.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Herrmann, J.; Herrmann, S.M. Programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor treatment is associated with acute kidney injury and hypocalcemia: Meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2019, 34, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethapathy, H.; Zhao, S.; Chute, D.F.; Zubiri, L.; Oppong, Y.; Strohbehn, I.; Cortazar, F.B.; Leaf, D.E.; Mooradian, M.J.; Villani, A.C.; et al. The Incidence, Causes, and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.S.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Siew, E.D.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bittleman, D.; Cruz, D.; Endre, Z.; Fitzgerald, R.L.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Sultan, S.; Haffar, S.; Bazerbachi, F. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2018, 23, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ottawa Hospital Researh Institute Website; Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis. Available online: www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Uchida, A.; Watanabe, M.; Nawata, A.; Ikari, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Shigemoto, K.; Hisano, S.; Nakashima, H. Tubulointerstitial nephritis as adverse effect of programmed cell death 1 inhibitor, nivolumab, showed distinct histological findings. CEN Case Rep. 2017, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakil, V.; Birkenbach, M.; Woerner, K.; Bu, L. Tubulitis in a patient treated with nivolumab: Case report and literature review. J. Onco-Nephrol. 2018, 2, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabei, A.; Watanabe, M.; Ikeuchi, H.; Nakasatomi, M.; Sakairi, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Maeshima, A.; Kaira, K.; Hirato, J.; Nojima, Y.; et al. The Analysis of Renal Infiltrating Cells in Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis Induced by Anti-PD-1 Antibodies: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 3135–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Shimonishi, A.; Matsuura, H.; Ozeki, T.; Nishimura, J.; Kayatani, H.; Minami, D.; Shinno, Y.; Sato, K.; et al. Rapidly Progressive Acute Kidney Injury Associated with Nivolumab Treatment. Case Rep. Oncol. 2020, 13, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Ichikawa, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Otsuka, Y.; Mashiko, A.; Takashima, Y.; Ito, A.; Nakagawa, K.; Arima, S. Nivolumab-induced acute granulomatous tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with gastric cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Gao, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; Cui, Y.-H.; Liu, Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Ji, Y.; et al. Nivolumab-associated DRESS in a genetic susceptible individual. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messias, A.; Calado, J.; Viana, H.; Nolasco, F. Nephrotic syndrome in a patient with metastatic melanoma: Beyond the obvious. Port. J. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, R.; Watanabe, H.; Tsuchida, M.; Iino, N.; Suzuki, K.; Hasegawa, G.; Imai, N.; Narita, I. Immune checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab)-associated kidney injury and the importance of recognizing concomitant medications known to cause acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: A case report. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawhari, I.; Fenton, S.E.; Sosman, J.A.; Sustento-Reodica, N.; Kanwar, Y.S.; Aggarwal, V. Hyperacute Onset of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Related Acute Interstitial Nephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2084–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, E.; Bechtel-Walz, W.; Schell, C.; Erbel, M.; Walz, G.; Hermle, T. Development of Nivolumab/Ipilimumab-Associated Autoimmune Nephritis during Steroid Therapy. Case Rep. Nephrol. Dial. 2021, 11, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, E.C.; Clatworthy, M.R.; Lawrence, C.; Nathan, P.D.; Farrington, K. Anti-CTLA-4 (CD 152) monoclonal antibody-induced autoimmune interstitial nephritis. NDT Plus 2009, 2, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xipell, M.; Victoria, I.; Hoffmann, V.; Villarreal, J.; Garcia-Herrera, A.; Reig, O.; Rodas, L.; Blasco, M.; Poch, E.; Mellado, B.; et al. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with atezolizumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (pd-l1) antibody therapy. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1445952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irifuku, T.; Satoh, A.; Tani, H.; Mandai, K.; Masaki, T. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and IgM deposits on glomerular capillary walls after immunotherapy with nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. CEN Case Rep. 2020, 9, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.; Dokouhaki, P.; Hagel, K.; Prasad, B. Acute kidney injury from immune checkpoint inhibitor use. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e231211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulroy, M.; Ghafouri, S.; Sisk, A.; Ribas, A.; Goshtaseb, R.; Cherry, G.; Shen, J. Acute interstitial nephritis and PR3-ANCA following reintroduction of pembrolizumab: A case report. Immunotherapy 2021, 13, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmetant, X.; Teuma, C.; Lake, J.; Dijoud, F.; Frochot, V.; Deeb, A. A new expression of immune checkpoint inhibitors’ renal toxicity: When distal tubular acidosis precedes creatinine elevation. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 13, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Ikinaga, K.; Kiyohara, E.; Tanemura, A.; Wataya-Kaneda, M.; Fujimura, R.; Mizui, M.; Isaka, Y.; Katayama, I. Critical renal adverse event induced by nivolumab therapy in a stage IV melanoma patient. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escandon, J.; Peacock, S.; Trabolsi, A.; Thomas, D.B.; Layka, A.; Lutzky, J. Interstitial nephritis in melanoma patients secondary to PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryuzaki, M.; Tokuyama, H.; Uchiyama, K.; Nakaya, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Miyashita, K.; Konishi, K.; Hashiguchi, A.; Wakino, S.; Itoh, H. Acute Interstitial Nephritis With Karyomegalic Epithelial Cells After Nivolumab Treatment—Two Case Reports. Clin. Med. Insights Case Rep. 2019, 12, 1179547619853647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliere, J.; Meyer, N.; Mazieres, J.; Ollier, S.; Boulinguez, S.; Delas, A.; Ribes, D.; Faguer, S. Acute interstitial nephritis related to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassol, C.; Satoskar, A.; Lozanski, G.; Rovin, B.; Hebert, L.; Nadasdy, T.; Brodsky, S.V. Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy May Induce Interstitial Nephritis With Increased Tubular Epithelial Expression of PD-L1. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duma, N.; Abdel-Ghani, A.; Yadav, S.; Hoversten, K.P.; Reed, C.T.; Sitek, A.N.; Enninga, E.A.L.; Paludo, J.; Aguilera, J.V.; Leventakos, K.; et al. Sex Differences in Tolerability to Anti-Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Are We All Equal? Oncologist 2019, 24, e1148–e1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, A.N.; Bougrine, A.; Buchbinder, E.I.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; LeBoeuf, N.R. Female sex is associated with higher rates of dermatologic adverse events among patients with melanoma receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A retrospective cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, C.A.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Lo, S.N.; Carlino, M.S.; Tsang, V.H.M.; Menzies, A.M. Thyroid Immune-related Adverse Events Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e3704–e3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.P.; Song, H.; Ye, F.; Moslehi, J.J.; Balko, J.M.; Salem, J.E.; Johnson, D.B. Demographic Factors Associated with Toxicity in Patients Treated with Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Martin Romano, P.; Voisin, A.L.; Danlos, F.X.; Champiat, S.; Laghouati, S.; Kfoury, M.; Vincent, H.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Varga, A.; et al. Impact of aging on immune-related adverse events generated by anti-programmed death (ligand)PD-(L)1 therapies. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 129, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.; Hartshorn, K.; Rahma, O.; Lin, N.; Snyder-Cappione, J.E. Aging, immune senescence, and immunotherapy: A comprehensive review. Semin. Oncol. 2018, 45, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Lacchetti, C.; Schneider, B.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Gardner, J.M.; Ginex, P.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1714–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Kibbelaar, Z.A.; Glezerman, I.G.; Abudayyeh, A.; Mamlouk, O.; Motwani, S.S.; Murakami, N.; Herrmann, S.M.; Manohar, S.; Shirali, A.C.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated AKI: A Multicenter Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Short, S.A.P.; Sise, M.E.; Prosek, J.M.; Madhavan, S.M.; Soler, M.J.; Ostermann, M.; Herrmann, S.M.; Abudayyeh, A.; Anand, S.; et al. Acute kidney injury in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Strohbehn, I.A.; Wang, Q.; Hanna, P.E.; Seethapathy, R.; Prosek, J.M.; Herrmann, S.M.; Abudayyeh, A.; Malik, A.B.; Loew, S.; et al. Acute kidney injury in patients receiving pembrolizumab combination therapy versus pembrolizumab monotherapy for advanced lung cancer. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, R.; Netti, G.S.; Spadaccino, F.; Porta, C.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; Castellano, G.; Ranieri, E. The Use of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Oncology and the Occurrence of AKI: Where Do We Stand? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 574271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Callahan, M.K.; Flores-Chávez, A.; Keegan, N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Lambotte, O.; Mariette, X.; Prat, A.; Suárez-Almazor, M.E. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirali, A.C.; Perazella, M.A.; Gettinger, S. Association of Acute Interstitial Nephritis With Programmed Cell Death 1 Inhibitor Therapy in Lung Cancer Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, T.; Anna, P.; Annalisa, T.; Francesco, M.; Stefania, S.L.; Stella, D.; Michele, R.; Marco, T.; Loreto, G.; Franco, S. The mechanisms of acute interstitial nephritis in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919875549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Hara, S.; Okawara, M.; Teramoto, K.; Ikeda, N.; Kusunoki, Y.; Takeji, M. Nivolumab-induced membranous nephropathy in a patient with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma. CEN Case Rep. 2022, 11, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, C.; Nishino, K.; Pham, B.; Jeon, W.J.; Nguyen, M.; Cao, H. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab induced endocrinopathy and acute interstitial nephritis in metastatic sarcomatoid renal-cell carcinoma: A case report and review of literature. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 993622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abudayyeh, A.; Suo, L.; Lin, H.; Mamlouk, O.; Abdel-Wahab, N.; Tchakarov, A. Pathologic Predictors of Response to Treatment of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Kidney Injury. Cancers 2022, 14, 5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Total (n = 384) | Cohort (n = 163) | Case (n = 221) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 67 (59.73) | NA | 67 (59.73) |
| Male [n/N(%)] | 261/384 (68.0) | 108/163 (66.3) | 153/221 (69.2) |
| Hypertension [n/N(%)] | 151/305 (49.5) | 75/148 (50.7) | 76/157 (48.4) |
| Diabetics [n/N(%)] | 44/307 (14.3) | 17/148 (11.5) | 27/159 (17.0) |
| CKD [n/N(%)] | 60/219 (27.4) | 19/60 (31.7) | 41/159 (25.8) |
| CHD [n/N(%)] | 20/222 (9.0) | 5/63 (7.9) | 15/159 (9.4) |
| Tumor type | |||
| Melanoma [n/N(%)] | 150/384 (39.0) | 63/163 (38.7) e | 87/221 (39.4) |
| Lung cancer [n/N(%)] | 110/384 (28.6) | 54/163 (33.1) e | 56/221 (25.3) |
| Renal cancer [n/N(%)] | 29/324 (9.0) | 8/103 (7.8) | 21/221 (9.5) |
| Hematologic cancer a [n/N(%)] | 13/324 (4.0) | 2/103 (1.9) | 11/221 (5.0) |
| Others b [n/N(%)] | 57/324 (17.6) | 11/103 (10.7) | 46/221 (20.8) |
| ICI type | |||
| PD-1/PD-L1 [n/N(%)] | 281/372 (75.5) | 129/163 (79.1) | 152/209 (72.8) |
| CTLA-4 [n/N(%)] | 22/372 (5.9) | 6/163 (3.7) | 16/209 (7.7) |
| Combination c [n/N(%)] | 69/372 (18.5) | 28/163 (17.2) | 41/209 (19.6) |
| Other treatment | |||
| Only ICI [n/N(%)] | 249/282 (88.3) | 94/102 (92.1) | 155/180 (86.1) |
| ICI+ targeted therapy [n/N(%)] | 8/282 (2.8) | 1/102 (1.0) | 7/180 (3.9) |
| ICI+ chemotherapy [n/N(%)] | 20/282 (7.1) | 5/102 (4.9) | 15/180 (8.3) |
| ICI+VEGF [n/N(%)] | 5/282 (1.8) | 2/102 (2.0) | 3/180 (1.7) |
| Interval time (d) | 105 (59,210) | NA | 105 (59,210) |
| PPI [n/N(%)] | 123/272 (45.2) | 71/137 (51.8) | 52/135 (38.5) |
| NSAIDs [n/N(%)] | 36/213 (16.9) | 9/78 (11.5) | 27/135 (20.0) |
| Baseline SCr (mg/dl) | 1.0 (0.8,1.2) | NA | 1.0 (0.8,1.2) |
| Peak SCr (mg/dl) | 3.9 (2.5,5.9) | NA | 3.9 (2.5,5.9) |
| AKD [n/N(%)] | 363/384 (94.5) | 162/163 (99.4) | 201/221 (91.0) |
| AKD grade | |||
| 1 grade [n/N(%)] | 25/179 (14.0) | NA | 25/179 (14.0) |
| 2 grade [n/N(%)] | 31/179 (17.3) | NA | 31/179 (17.3) |
| 3 grade [n/N(%)] | 146/242 (60.3) | 23/63 (36.5) f | 123/179 (68.7) |
| Only proteinuria [n/N(%)] | 21/384 (5.5) | 1/163 (0.6) | 20/221 (9.0) |
| Extrarenal IRAE [n/N(%)] | 117/340 (34.4) | 53/134 (39.6) | 64/206 (31.1) |
| Skin [n/N(%)] | 36/340 (10.0) | 14/134 (10.4) g | 22/206 (10.7) |
| Gastrointestinal [n/N(%)] | 30/284 (10.6) | 9/78 (11.5) | 21/206 (10.2) |
| Endocrine [n/N(%)] | 22/284 (6.5) | 5/78 (6.4) | 17/206 (8.3) |
| Pneumonitis [n/N(%)] | 10/340 (2.9) | 3/134 (2.2) g | 7/206 (3.4) |
| Others d [n/N(%)] | 31/284 (4.6) | 1/78 (1.3) | 12/206 (5.8) |
| Total (n = 384) | Cohort (n = 163) | Case (n = 221) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATIN/AIN [n/N(%)] | 277 (72.3) | 134 | 143 a |
| ATIN [n/N(%)] | 191 (49.9) | 121 | 70 |
| AIN [n/N(%)] | 86 (22.5) | 13 | 73 |
| Total ATN [n/N(%)] | 29 (7.6) | 18 | 11 |
| ATN alone [n/N(%)] | 23 (6.0) | 17 | 6 |
| ATN with glomerular injury [n/N(%)] | 6 (1.6) | 1 | 5 |
| Glomerular injury [n/N(%)] | 54 (14.1) | 8 | 46 b |
| Podocyte injury [n/N(%)] | 23 (6.0) | 4 | 19 |
| FSGS [n/N(%)] | 8 (2.1) | 1 | 7 |
| MCD [n/N(%)] | 15 (3.9) | 3 | 12 |
| IgA nephropathy [n/N(%)] | 8 (2.1) | 0 | 8 |
| MN [n/N(%)] | 11 (2.9) | 1 | 10 |
| GN [n/N(%)] | 15 (3.9) | 3 | 12 |
| Crescent GN [n/N(%)] | 2 (0.5) | 0 | 2 |
| C3 GN [n/N(%)] | 3 (0.8) | 1 | 2 |
| Immune-mediated GN [n/N(%)] | 5 (1.3) | 0 | 5 |
| Unclassed GN [n/N(%)] | 5 (1.3) | 2 | 3 |
| Systematic disease [n/N(%)] | 42 (10.9) | 3 | 39 c |
| Vasculitis/ANCA vasculitis [n/N(%)] | 18 (4.7) | 2 | 16 |
| Anti-GBM disease [n/N(%)] | 4 (1.0) | 1 | 3 |
| TMA [n/N(%)] | 8 (2.1) | 0 | 8 |
| AA amyloidosis [n/N(%)] | 5 (1.3) | 0 | 5 |
| Renal graft rejection [n/N(%)] | 7 (1.8) | 0 | 7 |
| Lupus nephritis [n/N(%)] | 1 (0.3) | 0 | 1 |
| Total (n = 384) | Cohort (n = 163) | Case (n = 221) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroid [n/N(%)] | 342/384 (89.1) | 138/163 (84.7) | 204/221 (92.3) |
| Intravenous corticosteroid [n/N(%)] | 76/289 (26.3) | 18/88 (20.5) | 58/201 (28.9) |
| Dose (mg/d) | 500 (225,1000) | NA | 500 (225–1000) |
| Pulse steroid therapy [n/N(%)] | 31/43 (72.1) | NA | 31/43 (72.1) |
| Dose (mg/d) | 701 ± 262 | NA | 701 ± 262 |
| Oral corticosteroid (mg/kg/d) | 1.0 (0.8,1.0) | NA | 1.0 (0.8–1.0) |
| Low-dose (<0.5 mg/kg/d) | 18/136 (13.2) | NA | 18/136 (13.2) |
| Moderate-dose (0.5–1.0 mg/kg/d) | 99/136 (72.8) | NA | 99/136 (72.8) |
| High-dose (>1.0 mg/kg/d) | 19/136 (14.0) | NA | 19/136 (14.0) |
| Immunosuppressants [n/N(%)] | 49/351 (14.0) | 7/148 (4.7) | 42/203 (20.7) a |
| Infliximab [n/N(%)] | 12/351 (3.4) | NA | 12/203 (5.6) |
| Rituximab [n/N(%)] | 15/351 (4.3) | NA | 15/203 (7.4) |
| MMF [n/N(%)] | 11/351 (3.1) | NA | 11/203 (5.4) |
| Others [n/N(%)] | 7/351 (2.0) | NA | 7/203 (3.5) |
| Discontinued ICI [n/N(%)] | 322/336 (95.8) | 139/145 (95.9) | 183/191 (95.8) |
| RRT [n/N(%)] | 42/292 (14.4) | 7/90 (7.8) | 35/202 (17.3) |
| Disruption of RRT [n/N(%)] | 14/36 (38.9) | 1/2 (50.0) | 13/34 (38.2) |
| Recovery SCr level (mg/dl) | 1.5 (1.1,1.8) | NA | 1.5 (1.1,1.8) |
| Protein remission [n/N(%)] | 16/20 (80.0) | NA | 16/20 (80.0) |
| Renal function recovery | |||
| Complete recovery [n/N(%)] | 129/311 (41.5) | 56/143 (39.2) b | 73/168 (43.5) |
| Partial recovery [n/N(%)] | 123/287 (42.9) | 59/119 (49.6) | 64/168 (38.1) |
| No recovery [n/N(%)] | 48/287 (16.7) | 17/119 (14.3) | 31/168 (18.5) |
| Death [n/N(%)] | 36/252 (14.3) | 8/90 (8.9) | 28/162 (17.3) |
| Tumor response | |||
| DCR [n/N(%)] | 52/93 (55.9) | NA | 52/93 (55.9) |
| Complete response [n/N(%)] | 14/93 (15.1) | NA | 14/93 (15.1) |
| Partial response [n/N(%)] | 14/93 (15.1) | NA | 14/93 (15.1) |
| Stable [n/N(%)] | 24/93 (25.8) | NA | 24/93 (25.8) |
| Progression [n/N(%)] | 41/93 (44.1) | NA | 41/93 (44.1) |
| Rechallenge [n/N(%)] | 41/190 (21.7) | 18/84 (21.4) | 23/106 (21.7) |
| Flare [n/N(%)] | 10/39 (25.6) | 1/18 (5.6) | 9/21 (42.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.-Y.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yu, X.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Zheng, X.-Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S.-X.; Liu, G.; Yang, L. Clinicopathological Features of Kidney Injury Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041349
Xu L-Y, Zhao H-Y, Yu X-J, Wang J-W, Zheng X-Z, Jiang L, Wang S-X, Liu G, Yang L. Clinicopathological Features of Kidney Injury Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041349
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ling-Yi, Hai-Ya Zhao, Xiao-Juan Yu, Jin-Wei Wang, Xi-Zi Zheng, Lei Jiang, Su-Xia Wang, Gang Liu, and Li Yang. 2023. "Clinicopathological Features of Kidney Injury Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041349
APA StyleXu, L.-Y., Zhao, H.-Y., Yu, X.-J., Wang, J.-W., Zheng, X.-Z., Jiang, L., Wang, S.-X., Liu, G., & Yang, L. (2023). Clinicopathological Features of Kidney Injury Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041349






