miR-199a-5p Reduces Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via the Indian Hedgehog Signal Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
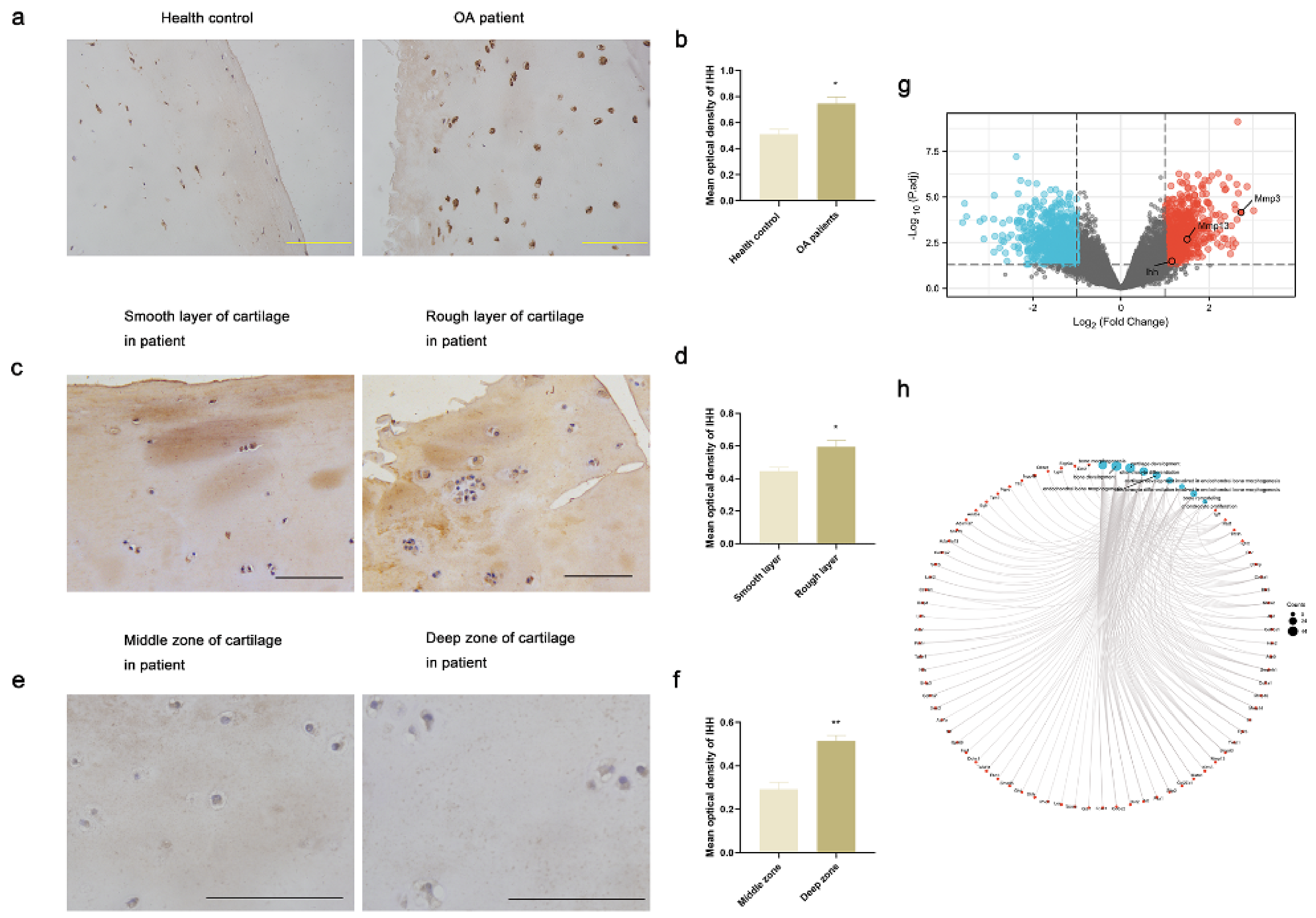
2.1. Collection of Human Articular Cartilage and Preparation of Paraffin Section
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Gene Expression Profiles in Rats
2.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
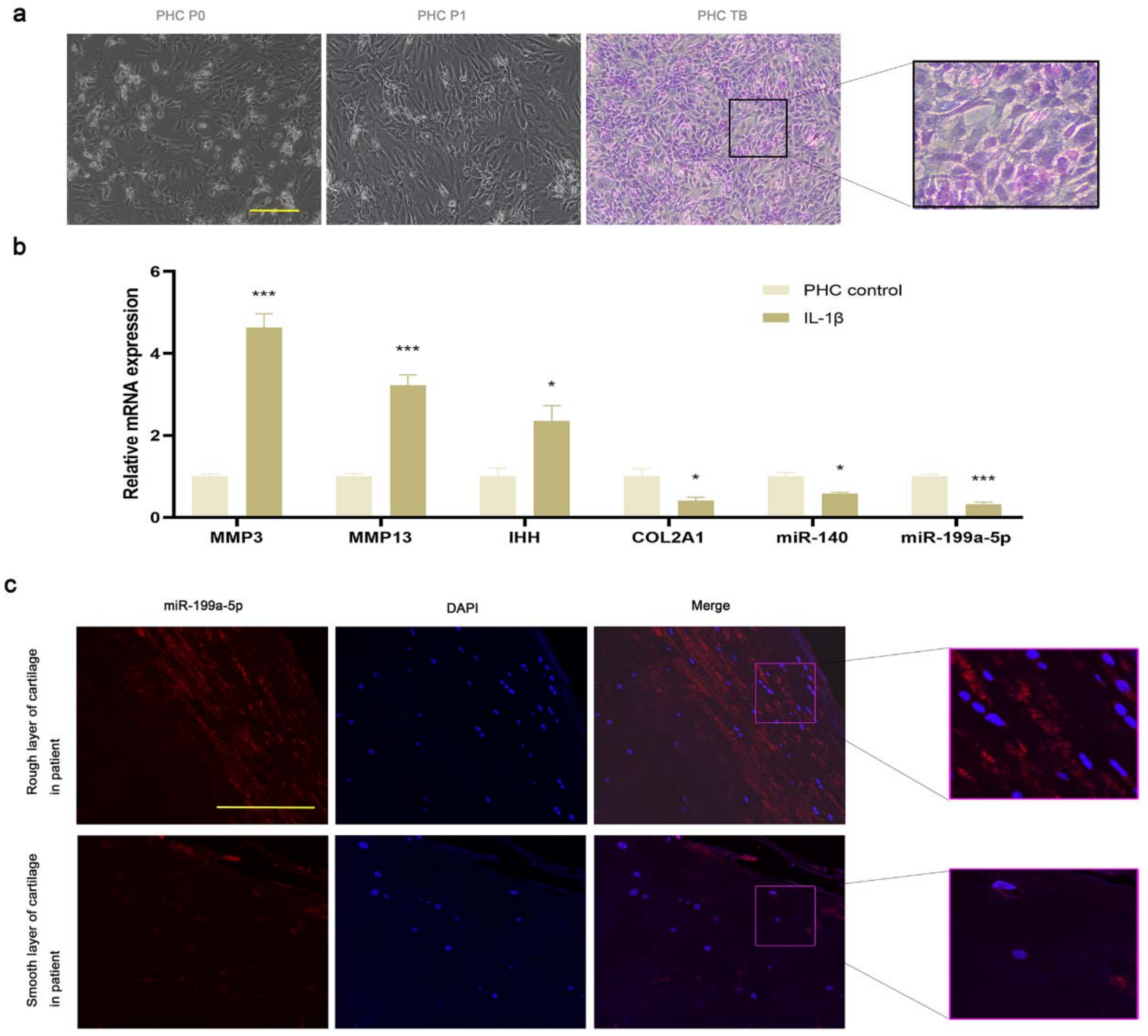
2.4. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. OA Cell Model Induction, RNA Extraction, and Quantification Analysis
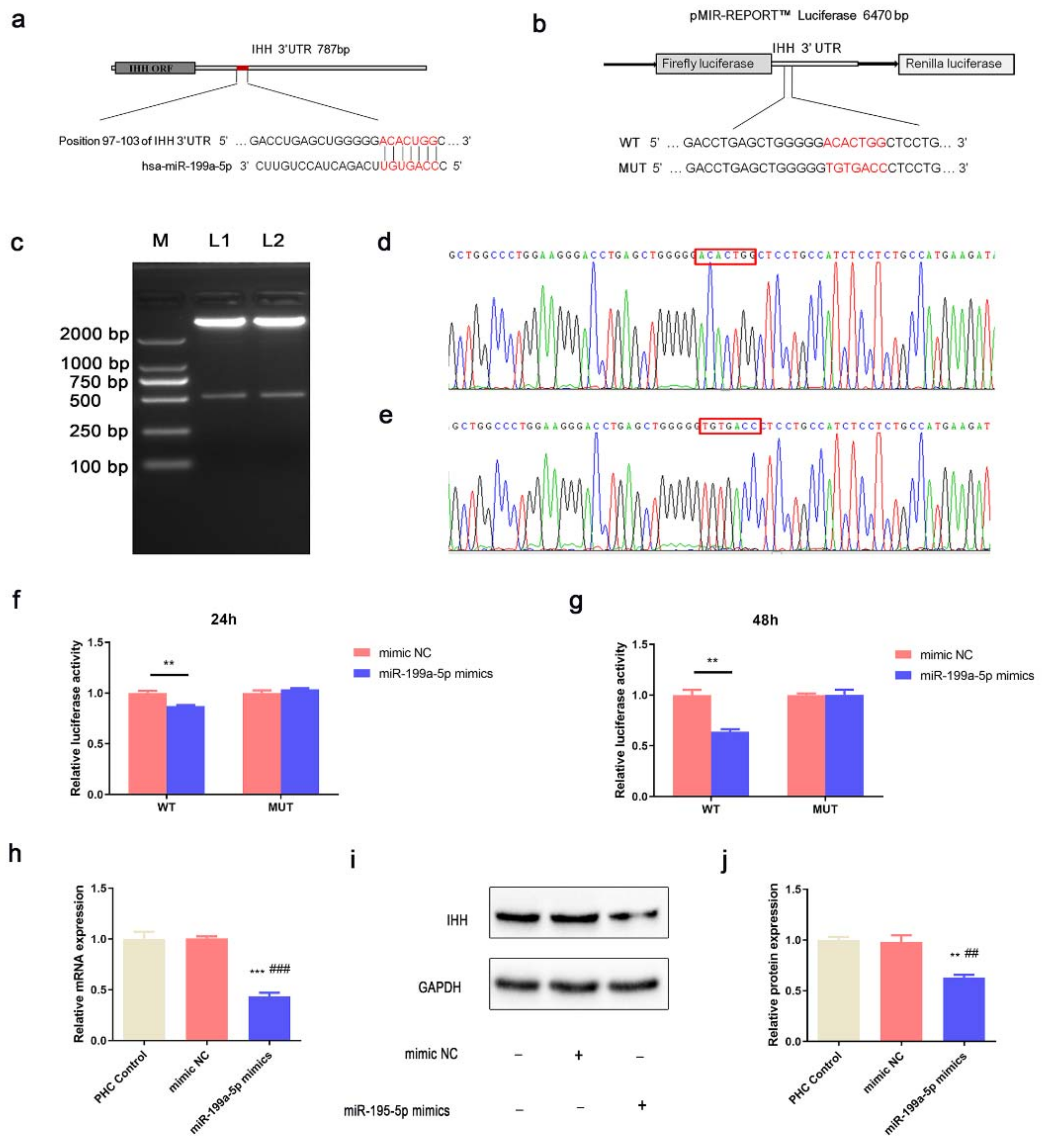
2.7. Construction of Recombinant DNA and Sequence Mutagenesis
2.8. Transfection
2.9. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
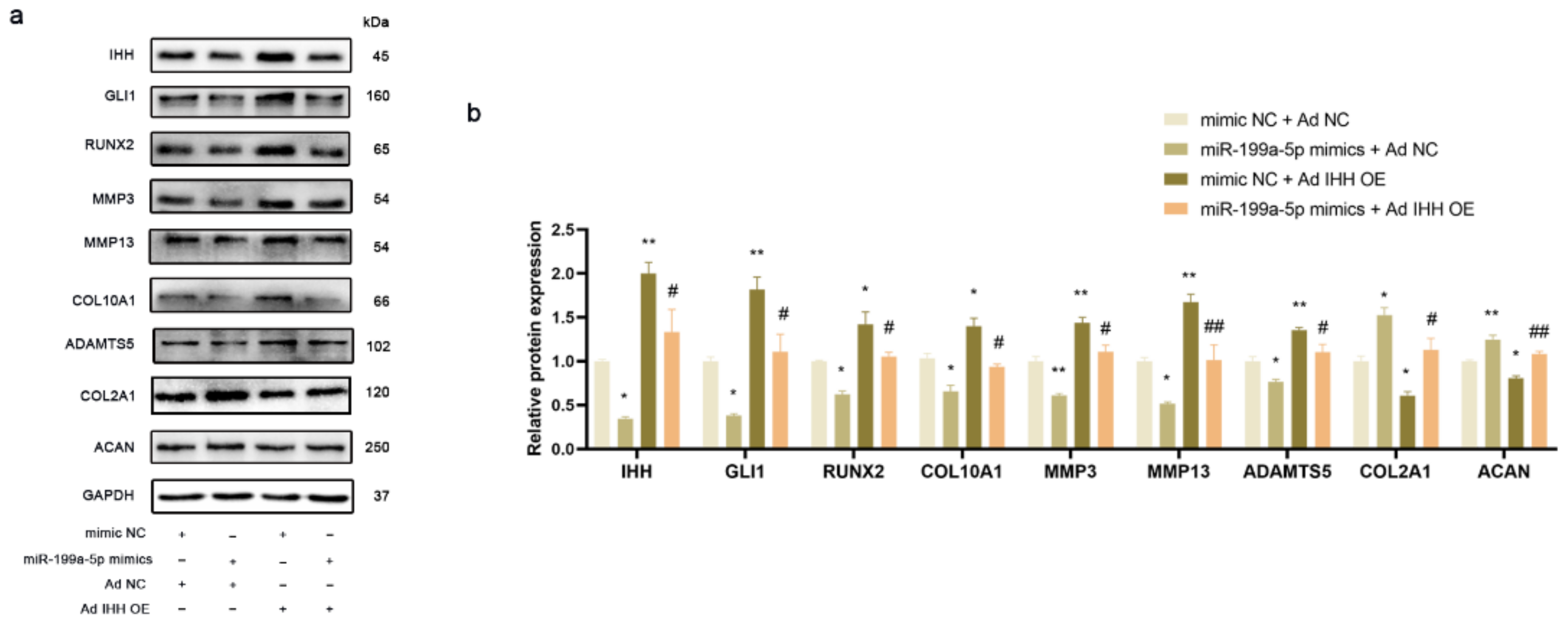
2.10. Ad-IHH Construction and Infection
2.11. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Induction of Rat Knee OA Model and Intra-Articular Injection
2.13. Histological Staining and Assessment
2.14. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. IHH Expression Was Increased in Damaged and Deep Zone Articular Cartilage in Human Samples
3.2. Ihh Expression Was Increased in Subchondral Bone in OA Rats
3.3. miR-199a-5p Expression Was Decreased in OA PHCs and Damaged Cartilage
3.4. miR-199a-5p Directly Regulated IHH in PHCs
3.5. miR-199a-5p Regulated IHH Signal Pathway to Inhibit Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Matrix Degradation in PHCs
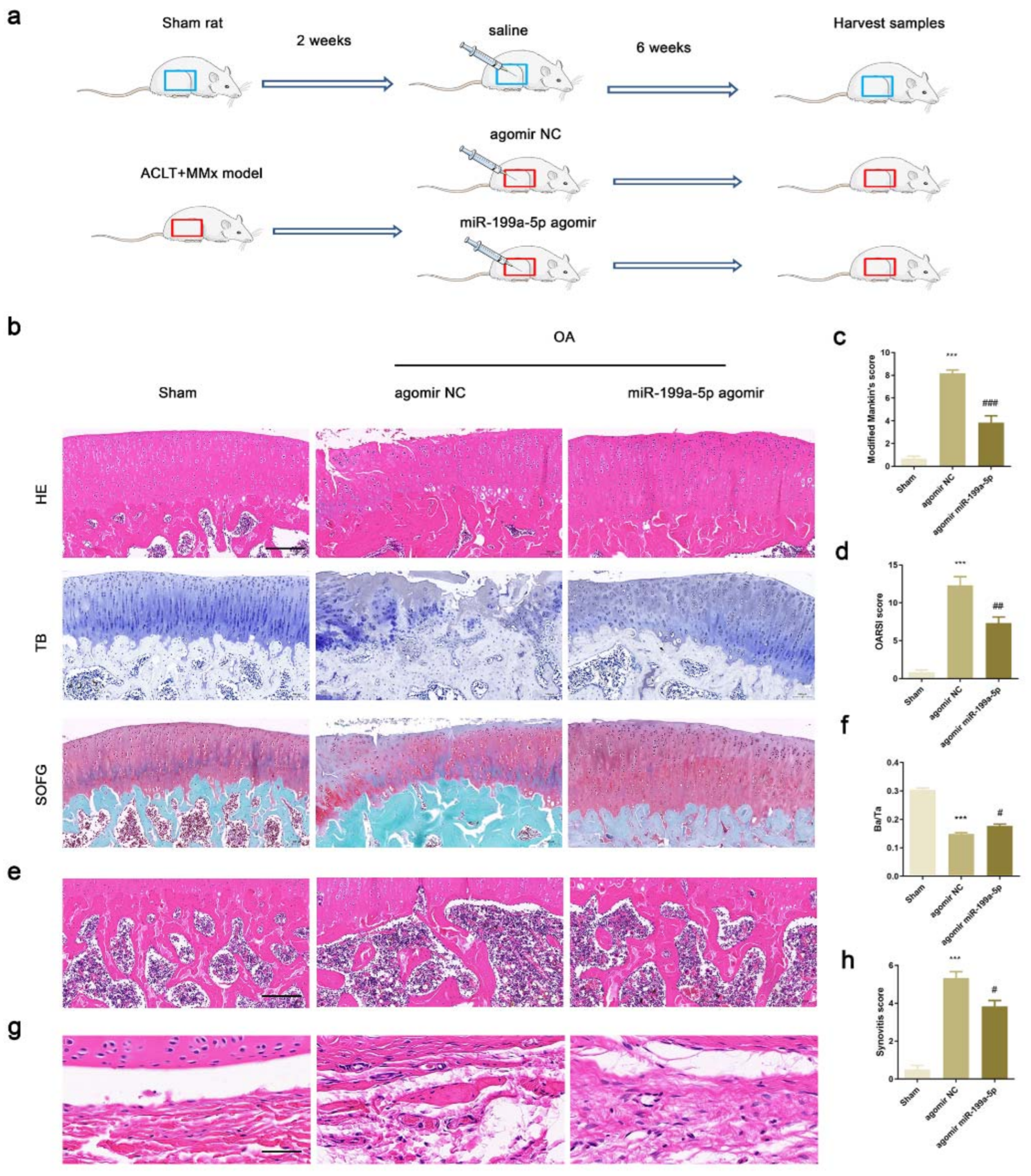
3.6. Intra-Articular Injection of miR-199a-5p Attenuated OA Progression
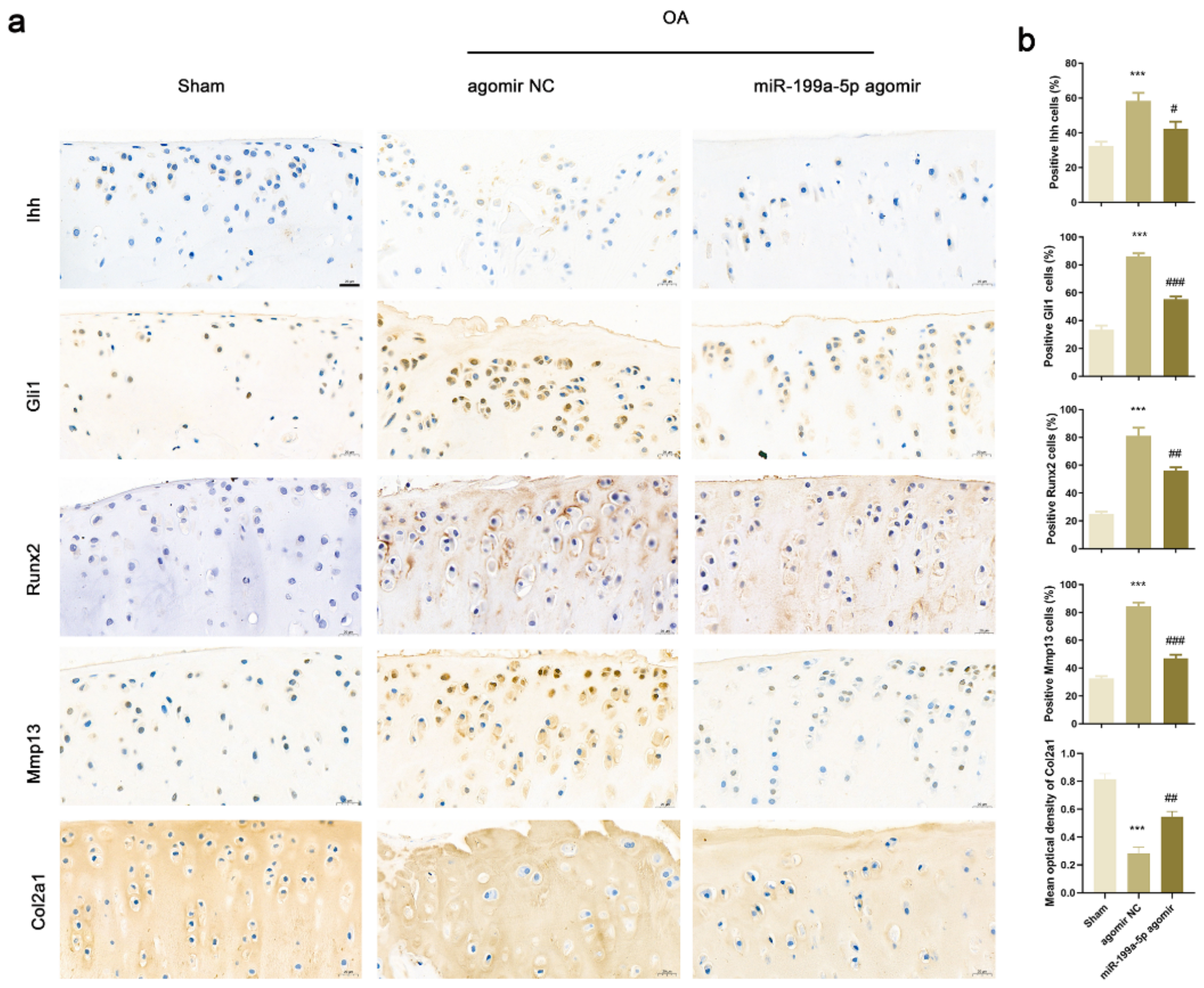
3.7. Intra-Articular Injection of miR-199a-5p Regulated Ihh Signal Pathway and Inhibited Matrix Degradation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R. Osteoarthritis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 213, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F. Aging and osteoarthritis: The role of chondrocyte senescence and aging changes in the cartilage matrix. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2009, 17, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, A.M.; Van Oene, M.; Hart, D.J.; Surdulescu, G.L.; Loughlin, J.; Doherty, M.; Spector, T.D. Reproducible genetic associations between candidate genes and clinical knee osteoarthritis in men and women. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Jacques, B.; Hammerschmidt, M.; McMahon, A.P. Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone formation. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Hu, J.; Stricker, S.; Cheung, M.; Ma, G.; Law, K.F.; Witte, F.; Briscoe, J.; Mundlos, S.; He, L.; et al. A mutation in Ihh that causes digit abnormalities alters its signalling capacity and range. Nature 2009, 458, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.K.; Kronenberg, H.M.; Chuang, P.T.; Mackem, S.; Yang, Y. Indian hedgehog signals independently of PTHrP to promote chondrocyte hypertrophy. Development 2008, 135, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.C.; Seeto, B.L.; Bartoszko, J.M.; Khoury, M.A.; Whetstone, H.; Ho, L.; Hsu, C.; Ali, S.A.; Alman, B.A. Modulating hedgehog signaling can attenuate the severity of osteoarthritis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Q.; Lanske, B.; Fleming, B.C.; Terek, R.; Wei, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Li, K.; Wei, L. Disrupting the Indian hedgehog signaling pathway in vivo attenuates surgically induced osteoarthritis progression in Col2a1-CreERT2; Ihhfl/fl mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Zhou, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Fleming, B.C.; Terek, R.; Pei, M.; Chen, Q.; Liu, T.; Wei, L. Activation of Indian hedgehog promotes chondrocyte hypertrophy and upregulation of MMP-13 in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, J.; Yao, J. Molecular mechanisms of the cartilage-specific microRNA-140 in osteoarthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, S.; Sato, T.; Inoue, A.; Otsuki, S.; Ito, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Kato, Y.; Takemoto, F.; Nakasa, T.; Yamashita, S.; et al. MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and homeostasis. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.B.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhou, Z.K.; Chen, Y.N.; Cheng, J.Q.; Lu, Y.R.; Shen, B. Intra-articular injection of microRNA-140 (miRNA-140) alleviates osteoarthritis (OA) progression by modulating extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis in rats. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Gandhi, R.; Potla, P.; Keshavarzi, S.; Espin-Garcia, O.; Shestopaloff, K.; Pastrello, C.; Bethune-Waddell, D.; Lively, S.; Perruccio, A.V.; et al. Sequencing identifies a distinct signature of circulating microRNAs in early radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Swingler, T.E.; Clark, I.M. Review: The role of microRNAs in osteoarthritis and chondrogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Huang, Y.L.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. Visfatin Promotes IL-6 and TNF-alpha Production in Human Synovial Fibroblasts by Repressing miR-199a-5p through ERK, p38 and JNK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.L.; Patel, R.; Kelly, T.A.; Wann, A.K.; Hung, C.T.; Chapple, J.P.; Knight, M.M. Hedgehog signalling does not stimulate cartilage catabolism and is inhibited by Interleukin-1beta. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhong, B.; Sun, J.; Cao, J.; Tian, J.; Zhong, N.; Zhao, W.; Tian, L.; Xu, P.; Guo, D.; et al. Down-regulated HS6ST2 in osteoarthritis and Kashin-Beck disease inhibits cell viability and influences expression of the genes relevant to aggrecan metabolism of human chondrocytes. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Fang, H.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Lu, H.; Zeng, C.; Ren, J.; Zeng, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; et al. Gene expression analyses of subchondral bone in early experimental osteoarthritis by microarray. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.; Meltzer, P.S. GEOquery: A bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1846–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Rasheed, Z.; Ramamurthy, S.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Voss, F.R.; Haqqi, T.M. MicroRNA-27b regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Min, Z.; Jiang, C.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Xu, P.; Xu, K.; Xu, J.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Downregulation of HS6ST2 by miR-23b-3p enhances matrix degradation through p38 MAPK pathway in osteoarthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thysen, S.; Luyten, F.P.; Lories, R.J. Targets, models and challenges in osteoarthritis research. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzker, K.P.; Gay, S.; Jimenez, S.A.; Ostergaard, K.; Pelletier, J.P.; Revell, P.A.; Salter, D.; van den Berg, W.B. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: Grading and staging. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulstra, S.K.; Buurman, W.A.; Walenkamp, G.H.; Van der Linden, A.J. Metabolic characteristics of in vitro cultured human chondrocytes in relation to the histopathologic grade of osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1989, 242, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.T.; Moradi, B.; Zaki, S.; Smith, M.M.; McCracken, S.; Smith, S.M.; Jackson, C.J.; Little, C.B. Depletion of protease-activated receptor 2 but not protease-activated receptor 1 may confer protection against osteoarthritis in mice through extracartilaginous mechanisms. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, A.M.; Drezner, M.K.; Glorieux, F.H.; Kanis, J.A.; Malluche, H.; Meunier, P.J.; Ott, S.M.; Recker, R.R. Bone histomorphometry: Standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. Report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1987, 2, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, N.; Hosseini, S.; Alini, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Eslaminejad, M.B. Targeted cell delivery for articular cartilage regeneration and osteoarthritis treatment. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, S.; Nakasa, T.; Otsuki, S.; Grogan, S.P.; Higashiyama, R.; Inoue, A.; Kato, Y.; Sato, T.; Lotz, M.K.; Asahara, H. MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Cho, S.W.; Shin, J.O.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, K.S.; Jung, H.S. Ihh and Runx2/Runx3 signaling interact to coordinate early chondrogenesis: A mouse model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, S. Hedgehog Signaling in Skeletal Development: Roles of Indian Hedgehog and the Mode of Its Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, K.; Densmore, M.; Nishimura, R.; Lanske, B. Indian hedgehog signaling regulates transcription and expression of collagen type X via Runx2/Smads interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24898–24910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhou, G.; Morello, R.; Chen, Y.; Garcia-Rojas, X.; Lee, B. Type X collagen gene regulation by Runx2 contributes directly to its hypertrophic chondrocyte-specific expression in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Luo, S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Intra-articular Delivery of Antago-miR-483-5p Inhibits Osteoarthritis by Modulating Matrilin 3 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 2. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ji, M.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Shi, P.L.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Im, H.J. MicroRNA-218-5p as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Human Osteoarthritis. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2676–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, Q.; Man, Z.; Huang, H.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ao, Y. Silencing of miR-101 Prevents Cartilage Degradation by Regulating Extracellular Matrix-related Genes in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Geng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J.; Zuo, B.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. MicroRNA-145 attenuates TNF-alpha-driven cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via direct suppression of MKK4. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Nakasa, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Kodama, A.; Miyaki, S.; Niimoto, T.; Okuhara, A.; Kamei, N.; Adachi, N.; Ochi, M. The effect of intra-articular injection of microRNA-210 on ligament healing in a rat model. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanishi, Y.; Nakasa, T.; Shoji, T.; Hamanishi, M.; Shimizu, R.; Kamei, N.; Usman, M.A.; Ochi, M. Intra-articular injection of synthetic microRNA-210 accelerates avascular meniscal healing in rat medial meniscal injured model. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaki, S.; Asahara, H. Macro view of microRNA function in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, J.A.; Zamore, P.D. MicroRNA therapeutics. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Jin, M.; Gu, R.; Xiao, K.; Lu, M.; Huo, X.; Sun, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. miR-199a-5p Reduces Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via the Indian Hedgehog Signal Pathway. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041313
Huang L, Jin M, Gu R, Xiao K, Lu M, Huo X, Sun M, Yang Z, Wang Z, Zhang W, et al. miR-199a-5p Reduces Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via the Indian Hedgehog Signal Pathway. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041313
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Lei, Meng Jin, Ruiying Gu, Kunlin Xiao, Mengnan Lu, Xinyu Huo, Mengyao Sun, Zhi Yang, Zhiyuan Wang, Weijie Zhang, and et al. 2023. "miR-199a-5p Reduces Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via the Indian Hedgehog Signal Pathway" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041313
APA StyleHuang, L., Jin, M., Gu, R., Xiao, K., Lu, M., Huo, X., Sun, M., Yang, Z., Wang, Z., Zhang, W., Zhi, L., Meng, Z., Ma, J., Ma, J., & Zhang, R. (2023). miR-199a-5p Reduces Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via the Indian Hedgehog Signal Pathway. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041313



