Local Tendon Transfers for Chronic Ruptures of the Achilles Tendon: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- P (Problem): Chronic rupture of the mid-portion Achilles tendon;
- I (Intervention): Transfer;
- C (Comparison): FHL, PB, FDL, and PL tendon transfers;
- O (Outcomes): Clinical outcomes, complications, and return to sport;
- T (Timing): ≥6 months of follow-up.
2.3. Selection and Data Collection
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.5. Data items
2.6. Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
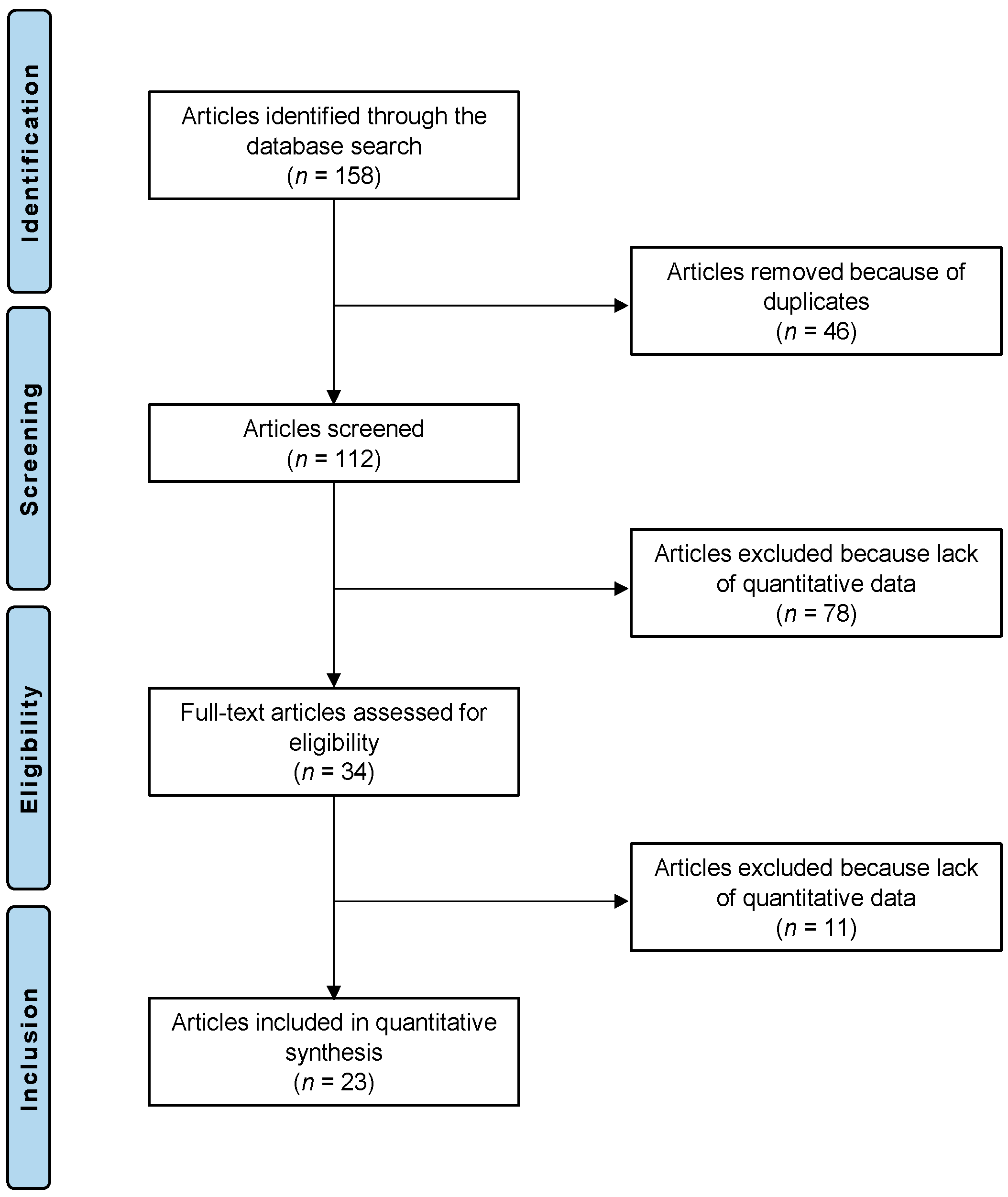
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. Study Characteristics and Results of Individual Studies
3.4. Results of Syntheses
4. Discussion
- The FHL is the second strongest plantar flexor muscle of the ankle;
- Its axis of action is in line with that of the AT;
- It maintains normal ankle muscle balance;
- Its harvest carries a low risk of iatrogenic neurovascular injury;
- It increases the vascularity of the reconstruction given its low-lying muscle belly [32].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOFAS | American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society |
| AT | Achilles tendon |
| ATRS | Achilles tendon Total Rupture Score |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CMS | Coleman Methodology Score |
| FDL | flexor digitorum longus |
| FHL | flexor hallucis longus |
| IBM SPSS | International Business Machines Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| PB | peroneus brevis |
| PICOT | Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, Timing |
| PL | peroneous longus |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PROMs | patient-reported outcome measures |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
References
- Maffulli, N. Rupture of the Achilles tendon. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1999, 81, 1019–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viidik, A. Tensile strength properties of Achilles tendon systems in trained and untrained rabbits. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1969, 40, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, F.; Meyer, P.; Maiwald, C.; Zanetti, M.; Vienne, P. Treatment of chronic achilles tendinopathy and ruptures with flexor hallucis tendon transfer: Clinical outcome and MRI findings. Foot Ankle Int. 2008, 29, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, M.; Gupta, V.; Martins, A.; Mahadevan, D.; Bhatia, M. Patient reported outcomes and satisfaction following single incision Flexor Hallucis Longus (FHL) augmentation for chronic Achilles tendon pathologies. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 23, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegrzyn, J.; Luciani, J.F.; Philippot, R.; Brunet-Guedj, E.; Moyen, B.; Besse, J.L. Chronic Achilles tendon rupture reconstruction using a modified flexor hallucis longus transfer. Int. Orthop. 2010, 34, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.T. Trauma to the heel cord. Disorders of the Foot and Ankle. Med. Surg. Manag. 1991, 2, 2355–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Perez Teuffer, A. Traumatic rupture of the Achilles Tendon. Reconstruction by transplant and graft using the lateral peroneus brevis. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1974, 5, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Maffulli, N.; Spiezia, F.; Longo, U.G.; Denaro, V. Less-invasive reconstruction of chronic achilles tendon ruptures using a peroneus brevis tendon transfer. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.A.; Holmes, G.B., Jr.; Seale, K.S.; Collins, D.N. Chronic rupture of the Achilles tendon: A new technique of repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1991, 73, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cesar Netto, C.; Chinanuvathana, A.; Fonseca, L.F.D.; Dein, E.J.; Tan, E.W.; Schon, L.C. Outcomes of flexor digitorum longus (FDL) tendon transfer in the treatment of Achilles tendon disorders. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Lin, L.C.; Hsu, C.K.; Shen, P.H.; Lien, S.B.; Hwa, S.Y.; Pan, R.Y.; Lee, C.H. Anatomic reconstruction of neglected Achilles tendon rupture with autogenous peroneal longus tendon by EndoButton fixation. J. Trauma 2009, 67, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, B.D.; Khan, K.M.; Maffulli, N.; Cook, J.L.; Wark, J.D. Studies of surgical outcome after patellar tendinopathy: Clinical significance of methodological deficiencies and guidelines for future studies. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. Rev. Artic. 2000, 10, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubeih, H.; Khaled, M.; Saleh, W.R.; Said, G.Z. Flexor hallucis longus transfer clinical outcome through a single incision for chronic Achilles tendon rupture. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Jeong, B.O. Return to Sports Activities after Flexor Hallucis Longus Transfer for Neglected Achilles Tendon Rupture. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022, 61, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alauddin, M.; Hossain, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M.; Roy, M.K.; Minto, M.R.; Islam, M.A.; Islam, M.K.; Islam, M.S.; Saha, M.K.; Mahmud, A.A.; et al. Management of Neglected Rupture of Tendoachilles with Long Gap by Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Transfer. Mymensingh Med. J. 2022, 31, 861–868. [Google Scholar]
- Alhaug, O.K.; Berdal, G.; Husebye, E.E.; Hvaal, K. Flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer for chronic Achilles tendon rupture. A retrospective study. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, I.; Besser, M.; Nazarian, L.N.; Raikin, S.M. Reconstruction for missed or neglected Achilles tendon rupture with V-Y lengthening and flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer through one incision. Foot Ankle Int. 2007, 28, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.A.; Weiss, W.M.; Iloanya, M.; Panchbhavi, V.K. Dual Purpose Use of Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon for Management of Chronic Achilles Tendon Ruptures. Foot Ankle Spec. 2019, 12, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.; Lim, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Singh, I.R.; Koo, K. Flexor hallucis longus transfer versus turndown flaps augmented with flexor hallucis longus transfer in the repair of chronic Achilles tendon rupture. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, C.J.; Bosman, H.A.; Robinson, A.H.N. The functional and dynamometer-tested results of transtendinous flexor hallucis longus transfer for neglected ruptures of the Achilles tendon at six years’ follow-up. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, T.H. Treatment of chronic noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy with endoscopic Achilles tendon debridement and flexor hallucis longus transfer. Foot Ankle Spec. 2012, 5, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffulli, N.; Spiezia, F.; Pintore, E.; Longo, U.G.; Testa, V.; Capasso, G.; Denaro, V. Peroneus brevis tendon transfer for reconstruction of chronic tears of the Achilles tendon: A long-term follow-up study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffulli, N.; Oliva, F.; Costa, V.; Del Buono, A. The management of chronic rupture of the Achilles tendon: Minimally invasive peroneus brevis tendon transfer. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffulli, N.; Oliva, F.; Maffulli, G.D.; Buono, A.D.; Gougoulias, N. Surgical management of chronic Achilles tendon ruptures using less invasive techniques. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 24, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.H.; Dalal, R.B. Flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer for reconstruction of chronically ruptured Achilles tendons. J. Orthop. Surg. 2009, 17, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Wu, Y.; Tao, H.; Yang, D.; Huang, L. Reconstruction of Kuwada grade IV chronic achilles tendon rupture by minimally invasive technique. Indian J. Orthop. 2016, 50, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, M.M.; Haapasalo, H.H.; Elo, P.P.; Laine, H.J. Hypertrophy of the flexor hallucis longus muscle after tendon transfer in patients with chronic Achilles tendon rupture. Foot Ankle Surg. 2014, 20, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, H.; Ergisi, Y.; Harput, G.; Senol, M.S.; Baltaci, G. Short-Term Results of Flexor Hallucis Longus Transfer in Delayed and Neglected Achilles Tendon Repair. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintore, E.; Barra, V.; Pintore, R.; Maffulli, N. Peroneus brevis tendon transfer in neglected tears of the Achilles tendon. J. Trauma 2001, 50, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Nag, K.; Roy, S.P.; Gupta, R.C.; Gulati, V.; Agrawal, N. Repair of Achilles tendon ruptures with peroneus brevis tendon augmentation. J. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 22, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, D.; Lin, H.A.; Tan, B.S.; Chong, K.W.; Rikhraj, I.S. Chronic Achilles tendon rupture treated with two turndown flaps and flexor hallucis longus augmentation—Two-year clinical outcome. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2010, 39, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, J.; Vilá, J.; Batista, J.; Malagelada, F.; Dalmau-Pastor, M. Endoscopic Flexor Hallucis Longus Transfer for Chronic Noninsertional Achilles Tendon Rupture. Foot Ankle Int. 2018, 39, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoman, T.F.; Brown, M.J.; Pillai, A. Early post-operative results of neglected tendo-Achilles rupture reconstruction using short flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer: A prospective review. Foot 2012, 22, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, D.A.; Lambert, B.S.; Boutris, N.; McCulloch, P.C.; Robbins, A.B.; Moreno, M.R.; Harris, J.D. Validation of Digital Visual Analog Scale Pain Scoring with a Traditional Paper-based Visual Analog Scale in Adults. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Glob. Res. Rev. 2018, 2, e088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaoka, H.B.; Alexander, I.J.; Adelaar, R.S.; Nunley, J.A.; Myerson, M.S.; Sanders, M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 1994, 15, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson-Helander, K.; Thomeé, R.; Silbernagel, K.G.; Thomeé, P.; Faxén, E.; Eriksson, B.I.; Karlsson, J. The Achilles tendon Total Rupture Score (ATRS): Development and validation. Am. J. Sports Med. 2007, 35, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.D.; Kitaoka, H.B.; Ehman, R.L. Peroneal tendon injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 1998, 19, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, G.G.; Massie, C.; Turco, V.J. Assessment of eversion and plantar flexion strength after repair of Achilles tendon rupture using peroneus brevis tendon transfer. Am. J. Orthop. 1995, 24, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, H.; Datta, B.; Maffulli, N.; Neil, M.; Walsh, W.R. Mechanical properties of reconstructed achilles tendon with transfer of peroneus brevis or flexor hallucis longus tendon. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2007, 46, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors, Years | Part A: Only One Score to Be Given for Each of the 7 Sections | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Size | Mean Follow-Up | Surgical Approach | Type of Study | Description of Diagnosis | Descriptions of Surgical Technique | Description of Postoperative Rehabilitation | |
| Abubeih et al., 2018 [14] | 4 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Ahn et al., 2022 [15] | 4 | 7 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Alauddinet al., 2022 [16] | 4 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| Alhaug et al., 2019 [17] | 4 | 7 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Elias et al., 2007 [18] | 4 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Khalid et al., 2019 [19] | 0 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Koh et al., 2019 [20] | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Lever et al., 2018 [21] | 4 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Lui et al., 2012 [22] | 0 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 0 |
| Maffulli et al., 2010 [8] | 4 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Maffulli et al., 2012 [23] | 4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Maffulli et al., 2015 [24] | 4 | 7 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Maffulli et al., 2018 [25] | 4 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Mahajan et al., 2009 [26] | 4 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Miao et al., 2016 [27] | 4 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Oksanen et al., 2014 [28] | 0 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Ozer et al., 2018 [29] | 4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Pintore et al., 2001 [30] | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Singh et al., 2014 [31] | 4 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Tay et al., 2010 [32] | 0 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Vega et al., 2018 [33] | 4 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Wegrzyn et al., 2010 [5] | 0 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Yeoman et al., 2012 [34] | 0 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| Authors, Years | Part B: Scores May Be Given for Each Option in Each of the Three Sections If Applicable | Total | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Criteria | Procedure Used to Assess Outcomes | Description of the Subject Selection Process | ||||||||||
| Outcome Measures Clearly Defined | Timing of Outcome Assessment Clearly Stated | Use of Outcome Criteria That Have Reported Reliability | General Health Measure Included | Participants Recruited | Investigator Independent of Surgeon | Written Assessment | Completion of Assessment by Patients Themselves with Minimal Investigator Assistance | Selection Criteria Reported and Unbiased | Recruitment Rate Reported > 80% | Recruitment Rate Reported < 80% | ||
| Abubeih et al., 2018 [14] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 80 |
| Ahn et al., 2022 [15] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 76 |
| Alauddin et al., 2022 [16] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 59 |
| Alhaug et al., 2019 [17] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 73 |
| Elias et al., 2007 [18] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 70 |
| Khalid et al., 2019 [19] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 66 |
| Koh et al., 2019 [20] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 60 |
| Lever et al., 2018 [21] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 76 |
| Lui et al., 2012 [22] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 74 |
| Maffulli et al., 2010 [8] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 79 |
| Maffulli et al., 2012 [23] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 82 |
| Maffulli et al., 2015 [24] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 76 |
| Maffulli et al., 2018 [25] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 76 |
| Mahajan et al., 2009 [26] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 73 |
| Miao et al., 2016 [27] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 73 |
| Oksanen et al., 2014 [28] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 64 |
| Ozer et al., 2018 [29] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 85 |
| Pintore et al., 2001 [30] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 82 |
| Singh et al., 2014 [31] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 73 |
| Tay et al., 2010 [32] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 79 |
| Vega et al., 2018 [33] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 73 |
| Wegrzyn et al., 2010 [5] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 75 |
| Yeoman et al., 2012 [34] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 75 |
| Author et al., Year | Journal Name | Design | Technique | Follow-Up (Months) | Patients (n) | Age (Mean) | Female (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abubeih et al., 2018 [14] | Int Orthop | Prospective | open FHL | 15 | 21 | 40.3 | 6 |
| Ahn et al., 2022 [15] | J Foot Ankle Surg | Retrospective | open FHL | 57 | 28 | 51 | 11 |
| Alauddin et al., 2022 [16] | Mymensingh Med J | Prospective | open FHL | 6 | 21 | 39.5 | |
| Alhaug et al., 2019 [17] | Foot Ankle Surg | Retrospective | open FHL | 54 | 21 | 54.5 | 6 |
| Elias et al., 2007 [18] | Foot Ankle Int | Retrospective | open FHL | 24.4 | 15 | 55.8 | 5 |
| Khalid et al., 2019 [19] | Foot Ankle Spec | Retrospective | endoscopic FHL | 30.9 | 10 | 58.4 | 5 |
| Koh et al., 2019 [20] | Foot Ankle Surg | Retrospective | open FHL | 12 | 29 | 56 | 13 |
| Lever et al., 2018 [21] | Bone Joint J | Retrospective | open FHL | 73 | 20 | 53 | 4 |
| Lui et al., 2012 [22] | Foot Ankle Spec | Prospective | endoscopic FHL | 37 | 5 | 46 | 2 |
| Maffulli et al., 2010 [8] | Am J Sports Med | Prospective | open PB | 48.4 | 32 | 47.13 | 4 |
| Maffulli et al., 2012 [23] | J Bone Joint Surg Am | Prospective | open PB | 186 | 16 | 55.6 | 0 |
| Maffulli et al., 2015 [24] | Bone Joint J | Retrospective | mini-open PB | 55.2 | 17 | 39 | 3 |
| Maffulli et al., 2018 [25] | Foot Ankle Surg | Prospective | mini-open FHL | 35.8 | 21 | 42.7 | 9 |
| mini-open PB | 36.4 | 20 | 45.8 | 6 | |||
| Mahajan et al., 2009 [26] | J Orthop Surg | Retrospective | open FHL | 12 | 36 | 70 | 12 |
| Miao et al., 2016 [27] | Indian J Orthop | Retrospective | mini-open FHL | 32.2 | 32 | 42.1 | 14 |
| Oksanen et al., 2014 [28] | Foot Ankle Surg | Retrospective | open FHL | 27 | 7 | 53 | 3 |
| Ozer et al., 2018 [29] | J Foot Ankle Surg | Prospective | open FHL | 280 | 19 | 47.4 | 1 |
| Pintore et al., 2001 [30] | J Trauma | Prospective | open PB | 53 | 21 | 43.3 | 1 |
| Singh et al., 2014 [31] | J Orthop Surg | Retrospective | mini-open PB | 12 | 22 | 28 | |
| Tay et al., 2010 [32] | Ann Acad Med Singap | Prospective | open FHL | 24 | 6 | 59.5 | |
| Vega et al., 2018 [33] | Foot Ankle Int | Retrospective | endoscopic FHL | 30.5 | 22 | 69 | 6 |
| Wegrzyn et al., 2010 [5] | Int Orthop | Retrospective | open FHL | 79 | 11 | 44 | 4 |
| Yeoman et al., 2012 [34] | Foot (Edinb) | Prospective | open FHL | 6 | 11 | 52.6 | 5 |
| Endpoint | Baseline | Last Follow-Up | Mean Deviation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 0.8 ± 0.8 | −1.8 | 0.04 |
| AOFAS hindfoot | 57.1 ± 8.5 | 91.4 ± 4.7 | 34.3 | <0.0001 |
| ATRS | 44.4 ± 19.2 | 85.7 ± 7.5 | 41.3 | <0.0001 |
| Complications | FHL (338 Procedures) | PB (128 Procedures) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open | Mini-Open | Endoscopic | Open | Mini-Open | |
| Pain | 2 | ||||
| Superficial infection | 11 | 5 | |||
| Deep infection | 4 | ||||
| Deep venous thrombosis | 1 | ||||
| Focal numbness | 4 | ||||
| Wound complications | 9 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Scar adhesion | 1 | ||||
| Weak push-off | 3 | ||||
| Hypertrophic scarring of the incision | 2 | ||||
| Re-rupture | 1 | ||||
| Claw toes | 2 | ||||
| Reduced skin sensation | 6 | ||||
| Neurological complications | 4 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maffulli, N.; Ziello, S.; Maisto, G.; Migliorini, F.; Oliva, F. Local Tendon Transfers for Chronic Ruptures of the Achilles Tendon: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020707
Maffulli N, Ziello S, Maisto G, Migliorini F, Oliva F. Local Tendon Transfers for Chronic Ruptures of the Achilles Tendon: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(2):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020707
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaffulli, Nicola, Salvatore Ziello, Gianluca Maisto, Filippo Migliorini, and Francesco Oliva. 2023. "Local Tendon Transfers for Chronic Ruptures of the Achilles Tendon: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 2: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020707
APA StyleMaffulli, N., Ziello, S., Maisto, G., Migliorini, F., & Oliva, F. (2023). Local Tendon Transfers for Chronic Ruptures of the Achilles Tendon: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(2), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020707









