Dysfunction of Biliary Sphincter of Oddi—Clinical, Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Anatomy and Pathophysiology
3. Clinical Manifestations, Classifications, and Laboratory Findings
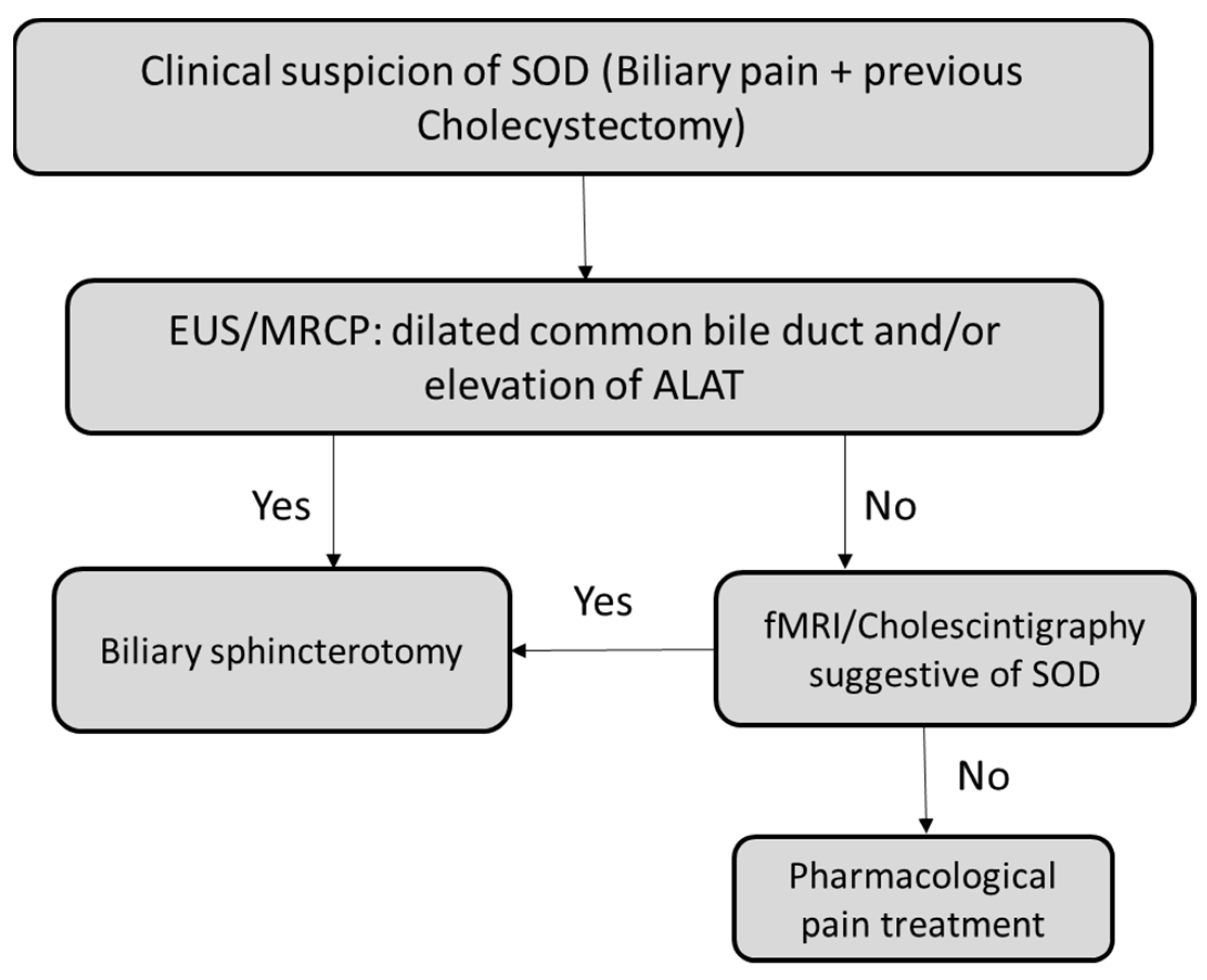
4. Diagnostic Challenges
5. Treatment Options
5.1. Non-Pharmacologic Treatment
5.2. Pharmacologic Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ziessman, H.A. Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy in 2014. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2014, 42, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toouli, J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Kellow, J.; Dowsett, J.; Saccone, G.T.; Evans, P.; Jeans, P.; Cox, M.; Anderson, P.; Worthley, C.; et al. Manometry Based Randomised Trial of Endoscopic Sphincterotomy for Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction. Gut 2000, 46, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, N.A.; Thompson, E.; Sanderson, C.F. Symptoms and Health Status before and Six Weeks after Open Cholecystectomy: A European Cohort Study.ECHSS Group. European Collaborative Health Services Study Group. Gut 1994, 35, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latenstein, C.S.S.; Wennmacker, S.Z.; De Jong, J.J.; Van Laarhoven, C.J.H.M.; Drenth, J.P.H.; De Reuver, P.R. Etiologies of Long-Term Postcholecystectomy Symptoms: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziessman, H.A. CHOLECYSTOKININ CHOLESCINTIGRAPHY. Radiol. Clin. North. Am. 2001, 39, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashdan, A.; Fogel, E.; McHenry, L.; Lehman, G.; Sherman, S. Frequency of Biliary Crystals in Patients with Suspected Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2003, 58, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanzadeh, D.M. The Symptomatic Outcomes of Cholecystectomy for Gallstones. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.M. Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction Type III: New Studies Suggest New Approaches Are Needed. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5755–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazziari, E.S.; Cotton, P.B. Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.V.; Wu, G.Y. Update on Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: A Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 515–521. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, S.; Lehman, G.A. Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Diagnosis and Treatment. JOP 2001, 2, 382–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toouli, J. What Is Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction? Gut 1989, 30, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behar, J.; Corazziari, E.; Guelrud, M.; Hogan, W.; Sherman, S.; Toouli, J. Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afghani, E.; Lo, S.K.; Covington, P.S.; Cash, B.D.; Pandol, S.J. Sphincter of Oddi Function and Risk Factors for Dysfunction. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazziari, E.; Shaffer, E.A.; Hogan, W.J.; Sherman, S.; Toouli, J. Functional Disorders of the Biliary Tract and Pancreas. Gut 1999, 45 (Suppl. S2), II48–II54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, P.B.; Durkalski, V.; Romagnuolo, J.; Pauls, Q.; Fogel, E.; Tarnasky, P.; Aliperti, G.; Freeman, M.; Kozarek, R.; Jamidar, P.; et al. Effect of Endoscopic Sphincterotomy for Suspected Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction on Pain-Related Disability Following Cholecystectomy: The EPISOD Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geenen, J.E.; Hogan, W.J.; Dodds, W.J.; Toouli, J.; Venu, R.P. The Efficacy of Endoscopic Sphincterotomy after Cholecystectomy in Patients with Sphincter-of-Oddi Dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, P.B.; Pauls, Q.; Keith, J.; Thornhill, A.; Drossman, D.; Williams, A.; Durkalski-Mauldin, V. The EPISOD Study: Long-Term Outcomes. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanzadeh, D.M.; Martinussen, T.; Sørensen, L.T. Development of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer in Patients with Symptomatic Gallstones, Cholecystectomy, and Sphincterotomy: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Scand. J. Surg. 2022, 111, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, G.L.; Hudson, S.V.; Roy, J.A.; Gracias, V.H.; Strom, B.L. Use of a New Prevention Model in Acute Care Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2022, 3, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.F.; Howell, D.A. Grover Shilpa Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction. UpToDate 2021. Available online: https://publishingimages.s3.amazonaws.com/eZineImages/PracticePerfect/726/Clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2023).
- Rosenblatt, M.L.; Catalano, M.F.; Alcocer, E.; Geenen, J.E. Comparison of Sphincter of Oddi Manometry, Fatty Meal Sonography, and Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 54, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M. Function and Dysfunction of the Sphincter of Oddi. Dig. Surg. 2010, 27, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauge, C.W.; Mark, J.B. Common Bile Duct Motility and Sphincter Mechanism. I. Pressure Measurements with Multiple-Lumen Catheter in Dogs. Ann. Surg. 1965, 162, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedner, P.; Rorsman, G. On the Mechanism of Action for the Effect of Cholecystokinin on the Choledochoduodenal Junction in the Cat. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 1969, 76, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMorte, W.W.; Gaca, J.M.; Wise, W.E.; Birkett, D.H.; Williams, L.F. Choledochal Sphincter Relaxation in Response to Histamine in the Primate. J. Surg. Res. 1980, 28, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K. The Discharge of Bile into the Duodenum and Electrical Activities of the Muscle of Oddi and Duodenum. Nihon. Heikatsukin. Gakkai. Zasshi. 1970, 6, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Devereaux, B.M.; Sherman, S.; Lehman, G.A. Sphincter of Oddi (Pancreatic) Hypertension and Recurrent Pancreatitis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2002, 4, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassiliou, M.C.; Laycock, W.S. Biliary Dyskinesia. Surg. Clin. North. Am. 2008, 88, 1253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.J.; Kozarek, R.A. Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction or Discordance? What Is the State of the Art in 2018? Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 34, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, P.B.; Elta, G.H.; Carter, C.R.; Pasricha, P.J.; Corazziari, E.S. Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Simon, A.; Sendino, O.; Chavez-Rivera, K.; Córdova, H.; Colmenero, J.; Crespo, G.; Fundora, Y.; Samaniego, F.; Ruiz, P.; Fondevila, C.; et al. The Presence and Outcome of Biliary Sphincter Disorders in Liver-Transplant Recipients According to the Rome IV Classification. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2021, 9, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Baillie, J. Biliary and Gallbladder Dyskinesia. Curr. Treatm. Opt. Gastroenterol. 2007, 10, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, W.J.; Geenen, J.E. Biliary Dyskinesia. Endoscopy 1988, 20, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.B. Biliary Dyskinesia: Does It Exist? If So, How Do We Diagnose It? Is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Effective or a Sham Operation? J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrmann, T. Long-Term Results (≥10 Years) of Endoscopic Therapy for Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction in Patients with Acute Recurrent Pancreatitis. Endoscopy 2011, 43, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoobi, M.; Romagnuolo, J. Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Updates from the Recent Literature. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicala, M.; Habib, F.I.; Vavassori, P.; Pallotta, N.; Schillaci, O.; Costamagna, G.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Scopinaro, F.; Fiocca, F.; Torsoli, A.; et al. Outcome of Endoscopic Sphincterotomy in Post Cholecystectomy Patients with Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction as Predicted by Manometry and Quantitative Choledochoscintigraphy. Gut 2002, 50, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazziari, E.; Habib, F.; Biliotti, D.; Primerano, L.; Pallotta, N.; DeMasi, E.; Bolognese, A. Reading Error and Time Variability of Sphincter of Oddi (SO) Recordings. Ital. J. Gastroenterol. 1985, 17, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Smithline, A.; Hawes, R.; Lehman, G. Sphincter of Oddi Manometry: Interobserver Variability. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1993, 39, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thune, A.; Scicchitano, J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.; Toouli, J. Reproducibility of Endoscopic Sphincter of Oddi Manometry. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1991, 36, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.L.; DiSario, J.A.; Nelson, D.B.; Fennerty, M.B.; Lee, J.G.; Bjorkman, D.J.; Overby, C.S.; Aas, J.; Ryan, M.E.; Bochna, G.S.; et al. Risk Factors for Post-Ercp Pancreatitis: A Prospective, Multicenter Study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 54, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaitzakis, E.; Ambrose, T.; Phillips-Hughes, J.; Collier, J.; Chapman, R.W. Management of Patients with Biliary Sphincter of Oddi Disorder without Sphincter of Oddi Manometry. BMC. Gastroenterol. 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.J. An Update on Biliary Dyskinesia. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2019, 99, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testoni, P.A.; Mangiavillano, B.; Mariani, A.; Carrara, S.; Notaristefano, C.; Arcidiacono, P.G. Investigation of Oddi Sphincter Structure by Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Biliary-Type 1 Dysfunction: A Pilot in Vivo Study. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2009, 41, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, M.T.; Lamba, R.; McGahan, J.P. Functional MR Cholangiography of the Cystic Duct and Sphincter of Oddi Using Gadoxetate Disodium: Is a 30-Minute Delay Long Enough? JMRI 2013, 37, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, B.K.; Dibaise, J.; Ziessman, H. Utilization of Cholecystokinin Cholescintigraphy in Clinical Practice. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 217, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toouli, J. Sphincter of Oddi: Function, Dysfunction, and Its Management. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24 Suppl 3, S57–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitton, V.; Ezzedine, S.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Gasmi, M.; Grimaud, J.C.; Barthet, M. Medical Treatment for Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Can It Replace Endoscopic Sphincterotomy? World. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakeeb, A. Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: How Is It Diagnosed? How Is It Classified? How Do We Treat It Medically, Endoscopically, and Surgically? J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 1557–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pier Michele Guarino, L.; Cocca, S.; Altomare, A.; Emerenziani, S.; Cicala, M.; Alto-Mare, A. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Therapy in Gallbladder Disease, a Story Not yet Completed. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5029–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, N.; Patel, A.; Goldstein, M.; Narahari, N.; Cai, Q. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Treatment for Patients with Postcholecystectomy Pain and Bile Microlithiasis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 68, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuroo, M.; Zargar, S.; Yattoo, G. Efficacy of Nifedipine Therapy in Patients with Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo- Controlled, Cross over Trial. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 33, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staritz, M.; Poralla, T.; Ewe, K.; Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K.H. Effect of Glyceryl Trinitrate on the Sphincter of Oddi Motility and Baseline Pressure. Gut 1985, 26, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.I.; Lee, T.H.; Jeong, S.; Kwon, C.I.; Koh, D.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Do, M.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, D.K. Efficacy of Chenodeoxycholic Acid and Ursodeoxycholic Acid Treatments for Refractory Functional Dyspepsia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, T.; Zfass, A.; Schubert, M.L. Management of Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Teaching an Old SOD New Tricks? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2459–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, J.; Nordback, I.; Koskinen, M.; Matikainen, M.; Lindholm, T.S. Nifedipine for Suspected Type II Sphincter of Oddi Dyskinesia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 88, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wehrmann, T.; Seifert, H.; Seipp, M.; Lembcke, B.; Caspary, W.F. Endoscopic Injection of Botulinum Toxin for Biliary Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction. Endoscopy 1998, 30, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, Q.; Durkalski-Mauldin, V.; Brawman-Mintzer, O.; Lawrence, C.; Whichard, R.; Cotton, P.B. Duloxetine for the Treatment of Patients with Suspected Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: A Pilot Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2704–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Holt, A.; Farmer, A.D. Intra-Sphincteric Botulinum Toxin in the Management of Functional Biliary Pain. Endosc. Int. Open. 2022, 10, E521–E527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, J.; Arvola, P.; Nordback, I. Calcium Channel Antagonists and Inhibition of Human Sphincter of Oddi Contractions. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type 1 | Biliary pain and all 3 of the following: |
| -Serum aminotransferases: elevation of serum-aminotransferases above 2 times the upper limit on 2 or more occasions. | |
| -CBD* dilation: above 10 mm on US ** or above 12 mm on ERCP ***. | |
| -Delayed drainage of contrast from the CBD * on ERCP ***. | |
| Type 2 | Biliary pain and 1 or 2 out of the 3 above criteria. |
| Type 3 | Biliary pain. |
| Biliary SOD |
|---|
| Biliary pain. Absence of bile duct stones or other structural abnormalities. Elevated liver enzymes or dilated bile duct (but not both). Supportive criteria: Normal amylase/lipase. Abnormal Sphincter of Oddi manometry. Abnormal hepatobiliary scintigraphy. |
| Diagnostic Tools | Short Description of the Method | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sphincter of Oddi manometry [2,5,36,37] | Performed during ERCP *. A catheter is inserted into the bile duct. | Can directly assess SO ** motor activity. | Risk of post-ERCP * pancreatitis. Rare availability due to need for highly trained expertise. |
| Functional MRI *** [37,46] | Measurement of biliary contrast agent excretion to the duodenum. | Non-invasive. | Cannot be used on patients with metal devices, claustrophobia or intolerance of contrast. |
| Optical Coherence Tomography [37,45] | A probe is inserted into the CBD **** through an ERCP * catheter. Low-power infra-red light allows for visualization of the SO ** microstructure, which is thickened in patients with SOD. | High-resolution, real-time imaging. | Risk of post-ERCP * pancreatitis. |
| Functional Lumen Imaging Probe technique [37] | Performed during ERCP* | Analyzes the sphincter profile and motility patterns. | Risk of post-ERCP * pancreatitis. Need for highly trained expertise. |
| Hepatobiliary scintigraphy (cholescintigraphy) [1,13,23,38,44,47] | Measurement of time–activity curve for excretion of a radio nucleotide (injected IV) via the hepatobiliary system. | Assesses the rate of bile flow into the duodenum. | Quite challenging to interpret due to lack of consensus on its diagnostic use. |
| Treatment: Non-P */P ** | SOD Type/Level of Evidence *** | Short Description of the Method | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-P *: Biliary sphincterotomy [2,17] | Biliary-type pain/biliary obstruction /Level 2 | Performed during ERCP. | Most definite treatment option. | Risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Need for highly trained expertise. No clinical effect for type 3 SOD. |
| Non-P *: Biliary sphincterotomy [16] | SOD type 3 /Level 2 | |||
| P **: Calcium-channel blockers [53,57] | SOD type 2 /Level 2 | Inhibit SO contractions and decrease basal pressure of the SO. | Non-invasive | Only short-term effects were explored. |
| P **: Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) [59] | SOD type 3 /Level 4 | 5-HT-receptor-mediated pain relief. | Non-invasive | Usual precausions (allergies, intolerance, side effects, etc.). |
| P **: Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline) [43] | SOD type 1, 2 and 3 /Level 5 | Relax the SO. | Non-invasive | Only short-term effects were explored. |
| P **: Glyceryl trinitrate [43,54] | SOD type 1, 2 and 3 /Level 5 | Relaxes the SO musculature. | Non-invasive | Only short-term effects were explored. |
| P **: Injection of botulinum toxin into SO [58,60] | SOD type 3 /Level 4 | Decreases basal pressure of the SO. | Temporary pain relief (about 4 months) | Invasive method. |
| P **: Ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk) [52] | SOD type 3 /Level 4 | Dissolves biliary crystals that can cause a biliary pain. | Non-invasive | Usual precausions (allergies, intolerance, side effects, etc.). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kegnæs, M.; Novovic, S.; Shabanzadeh, D.M. Dysfunction of Biliary Sphincter of Oddi—Clinical, Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144802
Kegnæs M, Novovic S, Shabanzadeh DM. Dysfunction of Biliary Sphincter of Oddi—Clinical, Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(14):4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144802
Chicago/Turabian StyleKegnæs, Marina, Srdan Novovic, and Daniel Mønsted Shabanzadeh. 2023. "Dysfunction of Biliary Sphincter of Oddi—Clinical, Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 14: 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144802
APA StyleKegnæs, M., Novovic, S., & Shabanzadeh, D. M. (2023). Dysfunction of Biliary Sphincter of Oddi—Clinical, Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(14), 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144802






