Empagliflozin Reduces Interleukin-6 Levels in Patients with Heart Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. SGLT-2-inhibitors and Follow-Up
3. Statistics
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure in Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, J.R.B.; Sossalla, S.; Hamdani, N.; Coronel, R.; Weber, N.C.; Light, P.E.; Zuurbier, C.J. Cardiac mechanisms of the beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in heart failure: Evidence for potential off-target effects. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2022, 167, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Choi, D.J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Claggett, B.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; Martinez, F.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Correa, J.I.; Correa-Rotter, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.E.; Januzzi, J.L. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors and Insights from Biomarker Measurement in Heart Failure Patients. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutka, M.; Bobiński, R.; Ulman-Włodarz, I.; Hajduga, M.; Bujok, J.; Pająk, C.; Ćwiertnia, M. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Mechanisms of action in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, N.J.; Matsumura, N.; Maayah, Z.H.; Ferdaoussi, M.; Takahara, S.; Darwesh, A.M.; Levasseur, J.L.; Jahng, J.W.S.; Vos, D.; Parajuli, N.; et al. Empagliflozin Blunts Worsening Cardiac Dysfunction Associated With Reduced NLRP3 (Nucleotide-Binding Domain-Like Receptor Protein 3) Inflammasome Activation in Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020, 13, e006277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H. Measurement of health-related quality of life in heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 22 (Suppl. A4), 185A–191A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 233–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stervbo, U.; Roch, T.; Westhoff, T.H.; Gayova, L.; Kurchenko, A.; Seibert, F.S.; Babel, N. Repeated Changes to the Gravitational Field Negatively Affect the Serum Concentration of Select Growth Factors and Cytokines. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidorf, S.M.; Fiolet, A.T.L.; Mosterd, A.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Schut, A.; Opstal, T.S.J.; The, S.H.K.; Xu, X.F.; Ireland, M.A.; Lenderink, T.; et al. Colchicine in Patients with Chronic Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, C.; Yu, A.S.; Hirayama, B.A.; Kepe, V.; Liu, J.; Scafoglio, C.; Powell, D.R.; Huang, S.C.; Satyamurthy, N.; Barrio, J.R.; et al. Dapagliflozin Binds Specifically to Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 in the Proximal Renal Tubule. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshino, A.; Schechter, M.; Sen, T.; Vart, P.; Neuen, B.L.; Neal, B.; Arnott, C.; Perkovic, V.; Ridker, P.M.; Tuttle, K.R.; et al. Interleukin-6 and Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: New Insights From CANVAS. Diabetes Care. 2022, 45, 2644–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prattichizzo, F.; De Nigris, V.; Micheloni, S.; La Sala, L.; Ceriello, A. Increases in circulating levels of ketone bodies and cardiovascular protection with SGLT2 inhibitors: Is low-grade inflammation the neglected component? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Cervantes, M.I.; Galicia, O.G.; Moreno-Jaime, B.; Zapata-Morales, J.R.; Montoya-Contreras, A.; Bautista-Perez, R.; Martinez-Morales, F. Autocrine modulation of glucose transporter SGLT2 by IL-6 and TNF-α in LLC-PK(1) cells. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 68, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.E.; Asker, M.E.; Keshawy, M.M.; Hasan, R.A.; Mahmoud, Y.K. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α enhanced the antifibrotic effect of empagliflozin in an animal model with renal insulin resistance. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020, 466, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Heo, Y.J.; Choi, S.E.; Jeon, J.Y.; Han, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.J. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Empagliflozin and Gemigliptin on LPS-Stimulated Macrophage via the IKK/NF-κB, MKK7/JNK, and JAK2/STAT1 Signalling Pathways. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9944880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, E.; Cho, W.; Rim, J.H.; Hwang, I.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity via ketones and insulin in diabetes with cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolijn, D.; Pabel, S.; Tian, Y.; Lódi, M.; Herwig, M.; Carrizzo, A.; Zhazykbayeva, S.; Kovács, Á.; Fülöp, G.Á.; Falcão-Pires, I.; et al. Empagliflozin improves endothelial and cardiomyocyte function in human heart failure with preserved ejection fraction via reduced pro-inflammatory-oxidative pathways and protein kinase Gα oxidation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena-Ibáñez, J.A.; Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Rodriguez-Cordero, A.; Vargas-Delgado, A.P.; Mancini, D.; Sartori, S.; Atallah-Lajam, F.; Giannarelli, C.; Macaluso, F.; Lala, A.; et al. Mechanistic Insights of Empagliflozin in Nondiabetic Patients With HFrEF: From the EMPA-TROPISM Study. JACC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Rane, M. Interleukin-6 Signaling and Anti-Interleukin-6 Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1728–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Luo, M.Y.; Liang, N.; Gong, S.X.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, A.P. Interleukin-6: A Novel Target for Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 745061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, D.L. Inflammatory mediators and the failing heart: Past, present, and the foreseeable future. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullestad, L.; Ueland, T.; Vinge, L.E.; Finsen, A.; Yndestad, A.; Aukrust, P. Inflammatory cytokines in heart failure: Mediators and markers. Cardiology 2012, 122, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Tsutamoto, T.; Wada, A.; Mabuchi, N.; Hayashi, M.; Tsutsui, T.; Ohnishi, M.; Sawaki, M.; Fujii, M.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. High levels of plasma brain natriuretic peptide and interleukin-6 after optimized treatment for heart failure are independent risk factors for morbidity and mortality in patients with congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Empagliflozin (n = 25) | No Empagliflozin (n = 25) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 67.9 ± 11.2 | 74.1 ± 10.4 | 0.079 |
| Women (♀), n (%) | 4 (16) | 7 (28) | 0.306 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 32.8 ± 7 | 29.7 ± 6 | 0.184 |
| NYHA functional class | 0.393 | ||
| NYHA II, n (%) | 4 (16) | 4 (16) | |
| NYHA III, n (%) | 17 (68) | 13 (52) | |
| NYHA IV, n (%) | 4 (16) | 8 (32) | |
| Medical history | |||
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 18 (72) | 12 (48) | 0.083 |
| Previous hospitalizations due to heart failure, n (%) | 19 (76) | 17 (68) | 0.682 |
| ICD, n (%) | 9 (36) | 10 (40) | 0.771 |
| CRT, n (%) | 3 (12) | 5 (20) | 0.440 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 13 (52) | 15 (60) | 0.569 |
| Peripheral artery disease, n (%) | 3 (12) | 2 (8) | 0.637 |
| Previous stroke/TIA, n (%) | 3 (12) | 5 (20) | 0.440 |
| Medication | |||
| 23 (92) | 21 (84) | 0.384 | |
| ACE-Inhibitors and ARB, n (%) | 15 (60) | 18 (72) | 0.370 |
| Sacubitril/valsartan, n (%) | 8 (33) | 5 (20) | 0.291 |
| Aldosterone antagonists, n (%) | 9 (36) | 7 (28) | 0.544 |
| Loop diuretics, n (%) | 15 (60) | 19 (76) | 0.225 |
| Insulin therapy, n (%) | 8 (32) | 4 (16) | 0.185 |
| Metformin, n (%) | 14 (56) | 9 (36) | 0.156 |
| Empagliflozin (n = 25) | No Empagliflozin (n = 25) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 125 ± 14 | 122 ± 19 | 0.432 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 80 ± 12.1 | 78 ± 10.4 | 0.586 |
| MLHFQ (points) | 44.2 ± 20.2 | 48.4 ± 23.4 | 0.264 |
| Six-minute walk test (m) * | 343 ± 145 | 321 ± 157 | 0.395 |
| ECG | |||
| Heart rate (bpm) | 85 ± 23 | 76 ± 25 | 0.226 |
| QRS (ms) | 120 ± 26 | 126 ± 36 | 0.708 |
| Left bundle branch block, n (%) | 6 (24) | 6 (24) | 1.000 |
| Laboratory | |||
| HbA1c (%) | 8.0 ± 1.8 | 7.6 ± 1.9 | 0.206 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.6 ± 2.1 | 13.1 ± 1.9 | 0.461 |
| GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 68.9 ± 19.5 | 62 ± 14 | 0.210 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | |||
| LVEF (%) | 32.5 ± 8.4 | 28.8 ± 8.9 | 0.177 |
| Left atrial diameter (mm) | 43.6 ± 7 | 44.7 ± 5.1 | 0.711 |
| Mitral regurgitation | 0.481 | ||
| None/trace, n (%) | 4 (16) | 7 (28) | |
| Mild, n (%) | 17 (68) | 13 (52) | |
| Moderate, n (%) | 4 (16) | 5 (20) | |
| PAsys (mmHg) | 39.6 ± 13.8 | 41.9 ± 13.2 | 0.573 |
| Empagliflozin (n = 25) | No Empagliflozin (n = 25) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1.1 ± 0.38 | 1.26 ± 0.29 | 0.739 |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 30.4 ± 8 | 20 ± 6.4 | 0.466 |
| IFN-α2 (pg/mL) | 13.1 ± 4 | 11.1 ± 3 | 0.682 |
| IFN-γ (pg/mL) | 21.3 ± 6.9 | 14.4 ± 5.16 | 0.600 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 49.2 ± 16.2 | 39.4 ± 11.9 | 0.737 |
| MCP-1 (pg/mL) | 562 ± 80 | 598 ± 53 | 0.580 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 21.7 ± 4.32 | 20.1± 2.91 | 0.823 |
| IL-8 (pg/mL) | 210 ± 42 | 174 ± 46.9 | 0.378 |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 22.8 ± 8.3 | 71.7 ± 52.8 | 0.351 |
| IL-12p70 (pg/mL) | 17.2 ± 6.7 | 11.6 ± 4.4 | 0.904 |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | 2.11 ± 0.85 | 1.02 ± 0.82 | 0.085 |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | 34 ± 23 | 119 ± 72.2 | 0.178 |
| IL-23 (pg/mL) | 24.2 ± 9.9 | 23.3 ± 8.4 | 0.752 |
| IL-33 (pg/mL) | 127 ± 45 | 89 ± 32 | 0.633 |
| Empagliflozin (n = 25) | No Empagliflozin (n = 25) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 3 Month Follow-Up | p Value | Baseline | 3 Month Follow-Up | p Value | |
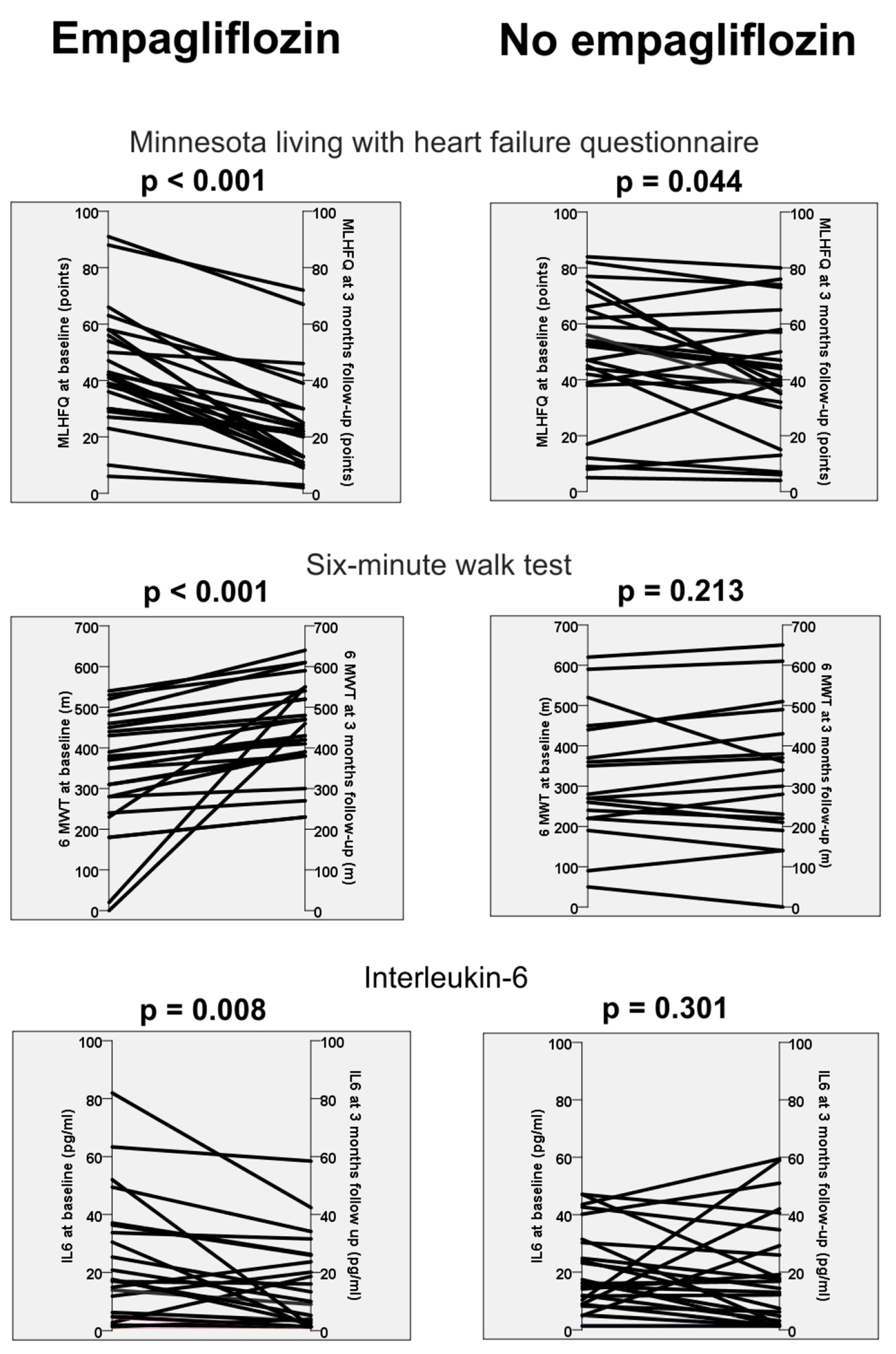
| MLHFQ (points) | 44.2 ± 20.2 | 24 ± 17.7 | <0.001 † | 48.4 ± 23.4 | 41.7 ± 22 | 0.044 |
| Six-minute walk test (m) * | 343 ± 145 | 450 ± 115 | <0.001 † | 321 ± 157 | 325 ± 170 | 0.213 |
| LVEF (%) | 32.5 ± 8.4 | 40.8 ± 13.1 | 0.001 † | 28.8 ± 8.9 | 35.9 ± 12.2 | 0.005 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1.1 ± 0.38 | 0.61 ± 0.2 | 0.050 | 1.26 ± 0.29 | 0.47 ± 0.10 | 0.022 |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 30.4 ± 8 | 27 ± 7.1 | 0.532 | 20 ± 6.4 | 27.1 ± 7.55 | 0.255 |
| IFN-α2 (pg/mL) | 13.1 ± 4 | 12.9 ± 3.5 | 0.532 | 11.1 ± 3 | 12.2 ± 2.94 | 0.070 |
| IFN-γ (pg/mL) | 21.3 ± 6.9 | 23.3 ± 6.3 | 0.795 | 14.4 ± 5.16 | 17.3 ± 5.5 | 0.093 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 49.2 ± 16.2 | 52 ± 16.5 | 1.000 | 39.4 ± 11.9 | 38.9 ± 11.7 | 0.878 |
| MCP-1 (pg/mL) | 562 ± 80 | 534 ± 73 | 0.968 | 598 ± 53 | 614 ±64 | 0.696 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 21.7 ± 4.32 | 13.7 ± 3.1 | 0.008 † | 20.1± 2.91 | 19 ± 3.7 | 0.301 |
| IL-8 (pg/mL) | 210 ± 42 | 199 ± 43 | 0.557 | 174 ± 46.9 | 214 ± 50 | 0.306 |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 22.8 ± 8.3 | 20.9 ± 7.9 | 0.532 | 71.7 ± 52.8 | 82.9 ± 62.7 | 0.246 |
| IL-12p70 (pg/mL) | 17.2 ± 6.7 | 16 ± 7.1 | 0.374 | 11.6 ± 4.4 | 14 ± 4.4 | 0.507 |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | 2.11 ± 0.85 | 1.85 ± 0.87 | 0.484 | 1.02 ± 0.82 | 1.89 ± 0.8 | 0.075 |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | 34 ± 23 | 72 ± 36.6 | 0.144 | 119 ± 72.2 | 62 ± 29.8 | 0.767 |
| IL-23 (pg/mL) | 24.2 ± 9.9 | 20.3 ± 9.3 | 0.401 | 23.3 ± 8.4 | 26.4 ± 8.7 | 0.386 |
| IL-33 (pg/mL) | 127 ± 45 | 106 ± 42 | 0.241 | 89 ± 32 | 108 ± 36 | 0.071 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gotzmann, M.; Henk, P.; Stervbo, U.; Blázquez-Navarro, A.; Mügge, A.; Babel, N.; Westhoff, T.H. Empagliflozin Reduces Interleukin-6 Levels in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134458
Gotzmann M, Henk P, Stervbo U, Blázquez-Navarro A, Mügge A, Babel N, Westhoff TH. Empagliflozin Reduces Interleukin-6 Levels in Patients with Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134458
Chicago/Turabian StyleGotzmann, Michael, Pauline Henk, Ulrik Stervbo, Arturo Blázquez-Navarro, Andreas Mügge, Nina Babel, and Timm H. Westhoff. 2023. "Empagliflozin Reduces Interleukin-6 Levels in Patients with Heart Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134458
APA StyleGotzmann, M., Henk, P., Stervbo, U., Blázquez-Navarro, A., Mügge, A., Babel, N., & Westhoff, T. H. (2023). Empagliflozin Reduces Interleukin-6 Levels in Patients with Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134458






