Effect of Obesity on the Expression of Genes Associated with Severe Asthma—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Blood Collection and PBMCs Isolation
2.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Real-Time qPCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
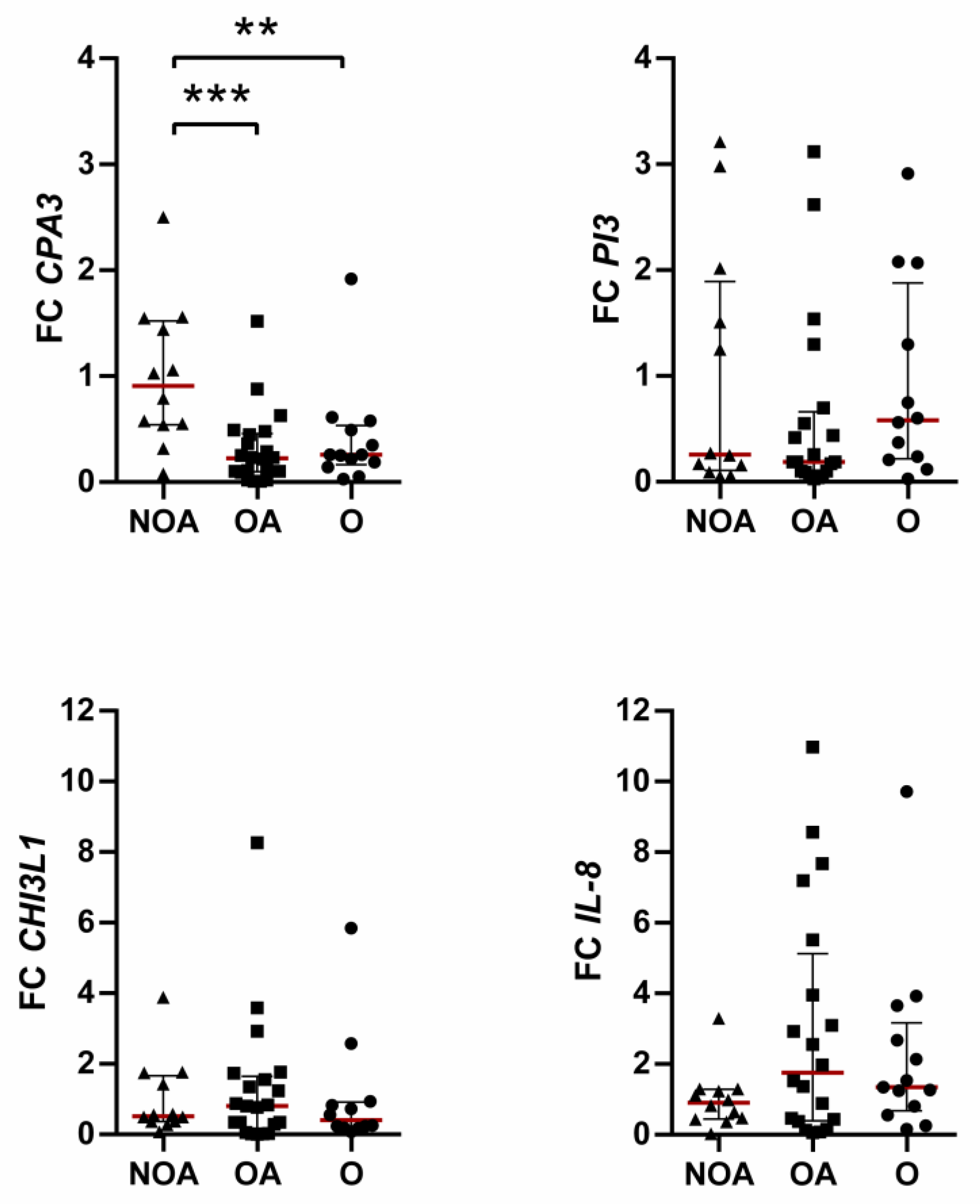
3.1. Effects of Obesity on Overexpressed Genes
3.2. Effects of Obesity on Underexpressed Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantulà, M.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Arismendi, E.; Picado, C. Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 6, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, E.; Parronchi, P.; Azzarone, B.G.; Moretta, L. A pathogenic integrated view explaining the different endotypes of asthma and allergic disorders. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 77, 3267–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Pelaia, G.; Maglio, A.; Tinello, C.; Gallelli, L.; Lombardo, N.; Terracciano, R.; Vatrella, A. Pathobiology of Type 2 Inflammation in Asthma and Nasal Polyposis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portelli, M.A.; Rakkar, K.; Hu, S.; Guo, Y.; Adcock, I.M.; Sayers, I. Translational Analysis of Moderate to Severe Asthma GWAS Signals into Candidate Causal Genes and Their Functional, Tissue-Dependent and Disease-Related Associations. Front. Allergy 2021, 18, 738741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Hunkapiller, J.; Bhangale, T.; Reeder, J.; Mukhyala, K.; Tom, J.; Cowgill, A.; Vogel, J.; Forrest, W.F.; Khan, Z.; et al. A whole genome sequencing study of moderate to severe asthma identifies a lung function locus associated with asthma risk. Sci. Rep. 2022, 2, 5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.U.; Kim, M.K.; Min, S.A.; Park, C.S.; Chang, H.S. A genome-wide association study on frequent exacerbation of asthma depending on smoking status. Respir. Med. 2022, 199, 106877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugier, P.E.; Sarnowski, C.; Granell, R.; Laprise, C.; Ege, M.J.; Margaritte-Jeannin, P.; Dizier, M.H.; Minelli, C.; Moffatt, M.F.; Lathrop, M.; et al. Genome-wide interaction study of early-life smoking exposure on time-to-asthma onset in childhood. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalışkan, M.; Bochkov, Y.A.; Kreiner-Møller, E.; Bønnelykke, K.; Stein, M.M.; Du, G.; Bisgaard, H.; Jackson, D.J.; Gern, J.E.; Lemanske, R.F.; et al. Rhinovirus wheezing illness and genetic risk of childhood-onset asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 11, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulet, L.P.; Franssen, E. Influence of obesity on response to fluticasone with or without salmeterol in moderate asthma. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bantulà, M.; Tubita, V.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Mullol, J.; Valero, A.; Bobolea, I.; Pascal, M.; de Hollanda, A.; Vidal, J.; Picado, C.; et al. Weight loss and vitamin D improve hyporesponsiveness to corticosteroids in obese asthma. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantulà, M.; Tubita, V.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Mullol, J.; Valero, A.; Bobolea, I.; Pascal, M.; de Hollanda, A.; Vidal, J.; Picado, C.; et al. Differences in Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Obesity-Associated Asthma: Effects of Weight Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 29, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Martínez, M.; Lorente-Sorolla, C.; Naharro, S.; Rodrigo-Muñoz, J.M.; del Pozo, V. Advances and Highlights of miRNAs in Asthma: Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirra, D.; Cione, E.; Spaziano, G.; Esposito, R.; Sorgenti, M.; Granato, E.; Cerqua, I.; Muraca, L.; Iovino, P.; Gallelli, L.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs Expression Profile in Lung Inflammation: A Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baos, S.; Calzada, D.; Cremades, L.; Sastre, J.; Quiralte, J.; Florido, F.; Lahoz, C.; Cárdaba, B. Data set on a study of gene expression in peripheral samples to identify biomarkers of severity of allergic and nonallergic asthma. Data Brief 2016, 22, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baos, S.; Calzada, D.; Cremades, L.; Sastre, J.; Quiralte, J.; Florido, F.; Lahoz, C.; Cárdaba, B. Biomarkers associated with disease severity in allergic and nonallergic asthma. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 82, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of Spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haldar, P.; Pavord, I.D.; Shaw, D.E.; Berry, M.A.; Thomas, M.; Brightling, C.E.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Green, R.H. Cluster analysis and clinical asthma phenotypes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, A.; Oriss, T.B.; Wenzel, S.E. Emerging molecular phenotypes of asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L130–L140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutherland, E.R.; Goleva, E.; King, T.S.; Lehman, E.; Stevens, A.D.; Jackson, L.P.; Stream, A.R.; Fahy, J.V. Cluster analysis of obesity and asthma phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin, F. Obesity as a risk factor for increased asthma severity and allergic inflammation; cause or effect? Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 612–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulet, L.P.; Lavoie, K.L.; Raherison-Semjen, C.; Kaplan, A.; Singh, D.; Jenkins, C.R. Addressing sex and gender to improve asthma management. Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2022, 32, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonpiyathad, T.; Satitsuksanoa, P.; Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Il-10 producing T and B cells in allergy. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 44, 101326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, S.; Krause, C.D.; Sarkar, D.; Walter, M.R.; Shi, Y.; Fisher, P.B. Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 929–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borish, L.; Aarons, A.; Rumbyrt, J.; Cvietusa, P.; Negri, J.; Wenzel, S. Interleukin-10 regulation in normal subjects and patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 97, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Pontillo, A.; Giugliano, F.; Giugliano, G.; Marfella, R.; Nicoletti, G.; Giugliano, D. Association of low interleukin-10 levels with the metabolic syndrome in obese women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge-Aubry, C.E.; Somm, E.; Pernin, A.; Alizadeh, N.; Giusti, V.; Dayer, J.M.; Meier, C.A. Adipose tissue is a regulated source of interleukin-10. Cytokine 2005, 29, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, N.; Tavira, B.; Hofwimmer, K.; Gutsmann, B.; Massier, L.; Abildgaard, J.; Juul, A.; Rydén, M.; Arner, P.; Laurencikiene, J. Sex-specific regulation of IL-10 production in human adipose tissue in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 996954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medcalf, R.L. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 2: Still an enigmatic serpin but a model for gene regulation. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 499, 105–134. [Google Scholar]
- Schroder, W.A.; Major, L.; Suhrbier, A. The role of SerpinB2 in immunity. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 31, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.H.; Park, S.R.; Lee, J.W.; Lim, S.; Lee, S.H.; Nam, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Hah, S.Y.; Hong, I.S.; Lee, H.Y. SERPINB2 Is a novel Indicator of cancer stem cell tumorigenicity in multiple cancer yypes. Cancers 2019, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woodruff, P.G.; Boushey, H.A.; Dolganov, G.M.; Barker, C.S.; Yang, Y.H.; Donnelly, S.; Ellwanger, A.; Sidhu, S.S.; Dao-Pick, T.P.; Pantoja, C.; et al. Genome-wide profiling identifies epithelial cell genes associated with asthma and with treatment response to corticosteroids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15858–15863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.J. Macrophage polarization. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girodet, P.O.; Nguyen, D.; Mancini, J.D.; Hundal, M.; Zhou, X.; Israel, E.; Cernadas, M. Alternative Macrophage Activation Is Increased in Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.H.; Tsai, M.L.; Li, C.H.; Hsiao, H.P.; Chao, M.C.; Lee, M.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Hung, C.H. Altered Pattern of Macrophage Polarization as a Biomarker for Severity of Childhood Asthma. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6011–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, A.; Naffah de Souza, C.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M. The macrophage switch in obesity development. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gudgeon, J.; Marín-Rubio, J.L.; Trost, M. The role of macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1) in inflammatory disorders and cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Jazwa, A.; Jozkowicz, A.; Molema, G.; Dulak, J. Angiogenic transcriptome of human microvascular endothelial cells: Effect of hypoxia, modulation by atorvastatin. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2006, 44, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gough, P.J.; Greaves, D.R.; Suzuki, H.; Hakkinen, T.; Hiltunen, M.O.; Turunen, M.; Herttuala, S.Y.; Kodama, T.; Gordon, S. Analysis of macrophage scavenger receptor (SR-A) expression in human aortic atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Husemann, J.; Silverstein, S.C. Expression of scavenger receptor class B, type I, by astrocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells in normal adult mouse and human brain and in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baos, S.; Calzada, D.; Cremades-Jimeno, L.; De Pedro, M.; Sastre, J.; Picado, C.; Quiralte, J.; Florido, F.; Lahoz, C.; Cárdaba, B. Discriminatory molecular biomarkers of allergic and non-allergic asthma and Its severity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baos, S.; Calzada, D.; Cremades-Jimeno, L.; Sastre, J.; Picado, C.; Quiralte, J.; Florido, F.; Lahoz, C.; Cárdaba, B. Non-allergic asthma and its severity: Biomarkers for its discrimination in peripheral samples. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baos, S.; Cremades-Jimeno, L.; López-Ramos, M.; de Pedro, M.; Uriarte, S.A.; Sastre, J.; González-Mangado, N.; Rodríguez-Nieto, M.J.; Peces-Barba, G.; Cárdaba, B. Expression of macrophage scavenger receptor (MSR1) in peripheral blood cells from patients with different respiratory diseases: Beyond monocytes. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaere, O.; Petersen, S.K.; Martinez-Lopez, N.; Wouters, J.; Van Haele, M.; Mancina, R.M.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Bilkei-Gorzo, O.; Lassen, P.B.; Darlay, R.; et al. Macrophage scavenger receptor 1 mediates lipid-induced inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Fernández, C.; Martín-Reyes, F.; Tome, M.; Gutierrez-Repiso, C.; Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Ocaña-Wilhelmi, L.; Rivas-Becerra, J.; Tatzber, F.; Pursch, E.; Tinahones, F.J.; et al. Oxidized LDL Increase the proinflammatory profile of human visceral adipocytes produced by hypoxia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, Y.; Liu, L. Correlation of decreased expression of PHLDA1 protein with malignant phenotype of gastric adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5230–5235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Liang, W.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J. PHLDA1 knockdown inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating JNK/ERK pathway, and plays a protective role in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2022, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.A. Pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1 (PHLDA1) and cancer. Biomed Rep. 2016, 4, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orita, F.; Ishikawa, T.; Ishiguro, M.; Okazaki, S.; Kikuchi, A.; Yamauchi, S.; Matsuyama, T.; Tokunaga, M.; Uetake, H.; Kinugasa, Y. PHLDA1 expression in ulcerative colitis: A potential role in the management of dysplasia. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Immune characteristics analysis and transcriptional regulation prediction based on gene signatures of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2021, 16, 3027–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chu, T.; Dedousis, N.; Mantell, B.S.; Sipula, I.; Li, L.; Bunce, K.D.; Shaw, P.A.; Katz, L.S.; Zhu, J.; et al. DNA methylation alters transcriptional rates of differentially expressed genes and contributes to pathophysiology in mice fed a high fat diet. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basseri, S.; Lhoták, Š.; Fullerton, M.D.; Palanivel, R.; Jiang, H.; Lynn, E.G.; Ford, R.J.; Maclean, K.N.; Steinberg, G.R.; Austin, R.C. Loss of TDAG51 results in mature-onset obesity, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance by regulating lipogenesis. Diabetes 2013, 62, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chupp, G.L.; Lee, C.G.; Jarjour, N.; Shim, Y.M.; Holm, C.T.; He, S.; Dziura, J.D.; Reed, J.; Coyle, A.J.; Kiener, P.; et al. A chitinase-like protein in the lung and circulation of patients with severe asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Shimizu, K.; Tanabe, N.; Makita, H.; Taniguchi, N.; Kimura, H.; Suzuki, M.; Abe, Y.; Matsumoto-Sasaki, M.; Oguma, A.; et al. Further Evidence for association of YKL-40 with severe asthma airway remodeling. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 24, S1081–S1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- lmarinen, P.; Tuomisto, L.E.; Niemelä, O.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, E.; Kankaanranta, H. YKL-40 and adult-onset asthma: Elevated levels in clusters with poorest outcome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2466–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradsen, J.R.; James, A.; Nordlund, B.; Reinius, L.E.; Söderhäll, C.; Melén, E.; Wheelock, Å.; Carlsen, K.C.; Lidegran, M.; Verhoek, M.; et al. The chitinase-like protein YKL-40: A possible biomarker of inflammation and airway remodeling in severe pediatric asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempen, M.; Kopp, H.-P.; Elhenicky, M.; Höbaus, C.; Brix, J.-M.; Koppensteiner, R.; Schernthaner, G.; Schernthaner, G.-H. YKL-40 Is elevated in morbidly obese patients and declines after weight loss. Obes. Surg. 2009, 19, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgios, I.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A.; Stylianou, C.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Arvanitidou, M.; Haidich, A.B. Elevated circulating levels of the serum acute-phase protein YKL-40 (Chitinase 3-like Protein 1) re a marker of obesity and insulin resistance in prepubertal children. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2012, 61, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specjalski, K.; Chełminska, M.; Jassem, E. YKL-40 protein correlates with the phenotype of asthma. Lung 2015, 193, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vezir, E.; Civelek, E.; Misirlioglu, E.D.; Toyran, M.; Capanoglu, M.; Karakus, E.; Kahraman, T.; Ozguner, M.; Demirel, F.; Gursel, I.; et al. Effects of obesity on airway and systemic inflammation in asthmatic children. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, T.C.; Hannila, S.S. Working from within: How secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory genes. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 100, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.; Weldon, S.; Taggart, C.C. SLPI and elafin: Multifunctional antiproteases of the WFDC family. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Q.Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.F.; Peng, L.J.; Jiang, Z.S. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor promising protective roles in obesity-associated atherosclerosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.-S.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Chen, P.-S.; Lin, M.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Huang, M.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Chen, K.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wang, T.-N. Protective effects of elafin against adult asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2016, 37, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.G.; Simpson, J.L.; Saltos, N. Heterogeneity of airway inflammation in persistent asthma: Evidence of neutrophilic inflammation and increased sputum interleukin-8. Chest 2001, 119, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosoki, K.; Ying, S.; Corrigan, C.; Qi, H.; Kurosky, A.; Jennings, K.; Sun, Q.; Boldogh, I.; Sur, S. Analysis of a panel of 48 cytokines in BAL fluids specifically identifies IL-8 levels as the only cytokine that distinguishes controlled asthma from uncontrolled asthma, and correlates inversely with FEV1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jatakanon, A.; Uasuf, C.; Maziak, W.; Lim, S.; Chung, K.F.; Barnes, P.J. Neutrophilic inflammation in severe persistent asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1532–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teran, L.M.; Carroll, M.P.; Frew, A.J.; Redington, A.E.; Davies, D.E.; Lindley, I.; Howarth, P.H.; Church, M.K.; Holgate, S.T. Leukocyte recruitment after local endobronchial allergen challenge in asthma. Relationship to procedure and to airway interleukin-8 release. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, A.; Reiss, S.; Wu, P.; Chen, N.; Han, W.; Do, R.-H.; Abdolrasulnia, R.; Dworski, R. Asthmatic airway neutrophilia after allergen challenge is associated with the glutathione S-transferase M1 genotype. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.-S.; Park, H.-S.; Kawada, T.; Kim, J.-H.; Lim, D.; Hubbard, N.E.; Kwon, B.-S.; Erickson, K.L.; Yu, R. Circulating levels of MCP-1 and IL-8 are elevated in human obese subjects and associated with obesity-related parameters. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Spanevello, A.; Sabato, R.; Depalo, A.; Palladino, G.P.; Bergantino, L.; Barbaro, M.P. Systemic and airway inflammation in sleep apnea and obesity: The role of ICAM-1 and IL-8. Trans. Res. 2010, 155, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiakshin, D.; Kostin, A.; Trotsenko, I.; Samoilova, V.; Buchwalow, I.; Tiemann, M. Carboxypeptidase A3-A Key Component of the Protease Phenotype of Mast cells. Cells 2022, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, R.H.; Sidhu, S.S.; Raman, K.; Solon, M.; Solberg, O.D.; Caughey, G.H.; Woodruff, P.G.; Fahy, J.V. Accumulation of intraepithelial mast cells with a unique protease phenotype in T(H)2-high asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winter, N.A.; Qin, L.; Gibson, P.G.; McDonald, V.M.; Baines, K.J.; Faulkner, J.; Evans, T.J.; Fricker, M. Sputum mast cell/basophil gene expression relates to inflammatory and clinical features of severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, N.A.; Gibson, P.G.; McDonald, V.M.; Fricker, M. Sputum gene expression reveals dysregulation of mast cells and basophils in eosinophilic COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2021, 16, 2165–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmelař, J.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Chung, K.J.; Prucnal, M.; Voehringer, D.; Roers, A.; Chavakis, T. No role for mast cells in obesity-related metabolic dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finlin, B.S.; Confides, A.L.; Zhu, B.; Boulanger, M.C.; Memetimin, H.; Taylor, K.W.; Johnson, Z.R.; Westgate, P.M.; Dupont-Versteegden, E.E.; Kern, P.A. Adipose tissue mast cells promote human adipose beiging in response to cold. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Detector |
|---|---|---|
| CD86 | CD86 molecule | Hs01567026_m1 |
| CHI3L1 | Chitinase 3-like 1 (cartilage glycoprotein-39) | Hs00609691_m1 |
| CPA3 | Carboxypeptidase A3 (mast cell) | Hs00157019_m1 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin 8 | Hs00174103_m1 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 | Hs00961622_m1 |
| MSR1 | Macrophage scavenger receptor 1 | Hs00234007_m1 |
| PHLDA1 | Pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1 | Hs00705810_s1 |
| PI3 | Peptidase inhibitor 3, skin-derived | Hs00160066_m1 |
| SERPINB2 | Serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B, member 2 | Hs01010736_m1 |
| 18S | Eukaryotic 18S rRNA | Hs99999901_s1 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Hs02758991_g1 |
| NOA (n = 12) | OA (n = 22) | O (n = 13) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 54.5 (41.5–59.5) | 57.0 (51.0–61.5) | 47.0 (45.5–61.5) |
| Female, n (%) | 10 (83.3) | 18 (81.8) | 11 (84.6) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.2 (22.0–25.0) | 38.0 (35.1–45.0) * | 42.2 (38.4–47.9) * |
| Mild asthma, n (%) | 0 (0) | 4 (18.2) | N/A |
| Moderate asthma, n (%) | 5 (41.7) | 5 (22.7) | N/A |
| Severe asthma, n (%) | 7 (58.3) | 13 (59.1) | N/A |
| FVC, % predicted | 128.0 (112.3–138.5) | 110.5 (94.5–119.3) * | 118.5 (105.5–125.8) |
| FEV1, % predicted | 79.0 (69.8–98.5) | 79.0 (61.5–93.5) | 90.0 (87.0–100.8) |
| FEV1/FVC | 65.5 (57.0–74.8) | 76.0 (66.5–80.5) | 80.5 (75.0–82.8) * |
| Use of ICS §, n (%) | 10 (83.3) | 16 (72.7) | N/A |
| Atopia, n (%) | 8 (66.7) | 9 (40.9) | N/A |
| Serum total IgE, kU/L | 122.0 (42.3–409.0) | 63.7 (14.4–149.0) | 50.0 (17.9–112.5) |
| BEC, % | 4.8 (3.3–6.6) | 3.3 (2.3–4.9) | 2.8 (1.4–3.5) * |
| BEC, cells/µL | 300 (200–500) | 200 (200–400) | 200 (100–300) |
| BEC ≥ 300 cells/µL, n (%) | 8 (66.7) | 7 (31.8) | 3 (23.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bantulà, M.; Arismendi, E.; Tubita, V.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Mullol, J.; de Hollanda, A.; Sastre, J.; Valero, A.; Baos, S.; Cremades-Jimeno, L.; et al. Effect of Obesity on the Expression of Genes Associated with Severe Asthma—A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134398
Bantulà M, Arismendi E, Tubita V, Roca-Ferrer J, Mullol J, de Hollanda A, Sastre J, Valero A, Baos S, Cremades-Jimeno L, et al. Effect of Obesity on the Expression of Genes Associated with Severe Asthma—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134398
Chicago/Turabian StyleBantulà, Marina, Ebymar Arismendi, Valeria Tubita, Jordi Roca-Ferrer, Joaquim Mullol, Ana de Hollanda, Joaquín Sastre, Antonio Valero, Selene Baos, Lucía Cremades-Jimeno, and et al. 2023. "Effect of Obesity on the Expression of Genes Associated with Severe Asthma—A Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134398
APA StyleBantulà, M., Arismendi, E., Tubita, V., Roca-Ferrer, J., Mullol, J., de Hollanda, A., Sastre, J., Valero, A., Baos, S., Cremades-Jimeno, L., Cárdaba, B., & Picado, C. (2023). Effect of Obesity on the Expression of Genes Associated with Severe Asthma—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134398







