Detection and Quantification of Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Levels in Early Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid: Investigation into a Possible Correlation with Abnormal Fetal Growth Velocity Patterns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doubilet, P.M.; Benson, C.B. Fetal growth disturbances. Semin. Roentgenol. 1990, 25, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Small-for-Gestational-Age Fetus, Investigation and Management (Green-Top Guideline No. 31). Available online: https://www.rcog.org.uk/media/t3lmjhnl/gtg_31.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Vrachnis, N.; Botsis, D.; Iliodromiti, Z. The fetus that is small for gestational age. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1092, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrachnis, N.; Loukas, N.; Vrachnis, D.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Zygouris, D.; Kοlialexi, A.; Pergaliotis, V.; Iavazzo, C.; Mastrakos, G.; Iliodromiti, Z. A Systematic Review of Bisphenol A from Dietary and Non-Dietary Sources during Preg-nancy and Its Possible Connection with Fetal Growth Restriction: Investigating Its Potential Effects and the Window of Fetal Vulnerability. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peebles, D.M. Fetal consequences of chronic substrate deprivation. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004, 9, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherjon, S.A.; Smolders-DeHaas, H.; Kok, J.H.; Zondervan, H.A. The “brain-sparing” effect: Antenatal cerebral Dop-pler findings in relation to neurologic outcome in very preterm infants. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1993, 169, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrachnis, N.; Loukas, N.; Vrachnis, D.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Christodoulaki, C.; Tsonis, O.; George, M.; Iliodromiti, Z. Phthalates and fetal growth velocity: Tracking down the suspected links. J. Matern. Neonatal. Med. 2021, 35, 4985–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, S.; Alexander, G.R.; Salihu, H.M.; Pass, M. Macrosomic births in the united states: Determinants, outcomes, and proposed grades of risk. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 188, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, Y.; Fattal-Valevski, A.; Geva, R.; Eshel, R.; Toledano-Alhadef, H.; Rotstein, M.; Bassan, H.; Radianu, B.; Bitchonsky, O.; Jaffa, A.J.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome of children with intrauterine growth retardation: A longitudi-nal, 10-year prospective study. J. Child Neurol. 2007, 22, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, S.; Harding, R. Brain development during fetal life: Influences of the intra-uterine environment. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 361, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: Roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pöyhönen, S.; Er, S.; Domanskyi, A.; Airavaara, M. Effects of Neurotrophic Factors in Glial Cells in the Central Nervous System: Expression and Properties in Neurodegeneration and Injury. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakopoulos, N.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Mastorakos, G.; Iavazzo, C.; Valsamakis, G.; Salakos, N.; Papageorghiou, A.; Margeli, A.; Kalantaridou, S.; Creatsas, G.; et al. Association between Brain-Derived Neu-rotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in 2nd Trimester Amniotic Fluid and Fetal Development. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 8476217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krey, F.C.; Stocchero, B.A.; Creutzberg, K.C.; Heberle, B.A.; Tractenberg, S.G.; Xiang, L.; Wei, W.; Kluwe-Schiavon, B.; Viola, T.W. Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review and Me-ta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 643576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sariola, H. The neurotrophic factors in non-neuronal tissues. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, M.J.; Hahn, R.; Tessarollo, L.; Hempstead, B.L. Identification of an essential non neuronal function of NT3 in mamma-lian cardiac development. Nat. Gen. 1996, 14, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloe, L.; Rocco, M.L.; Bianchi, P.; Manni, L. Nerve growth factor: From the early discoveries to the potential clinical use. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toti, P.; Ciarmela, P.; Florio, P.; Volpi, N.; Occhini, R.; Petraglia, F. Human placenta and fetal membranes express nerve growth factor mRNA and protein. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernfors, P.; Ibáñez, C.F.; Ebendal, T.; Olson, L.; Persson, H. Molecular cloning and neurotrophic activities of a protein with structural similarities to nerve growth factor: Developmental and topographical expression in the brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5454–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenthal, A.; Goeddel, D.V.; Nguyen, T.; Lewis, M.; Shih, A.; Laramee, G.R.; Nikolics, K.; Winslow, J.W. Primary structure and biological activity of a novel human neu-rotrophic factor. Neuron 1990, 4, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.F.; Rush, R.A. Functional roles of neurotrophin 3 in the developing and mature sympathetic nervous sys-tem. Mol. Neurobiol. 1996, 13, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaian, M.T.; Neet, E.K. Nerve growth factor in human amniotic and cerebrospinal fluid. Biofactors 1989, 2, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casciaro, A.; Arcuri, F.; Occhini, R.; Toti, M.S.; De Felice, C.; Toti, P. Expression of Placental Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) in Physiological Pregnancy, preeclampsia and chorioamnionitis. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolaides, K.H.; Wright, D.; Syngelaki, A.; Wright, A.; Akolekar, R. Fetal Medicine Foundation fetal and neonatal population weight charts. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 52, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalampokas, E.; Vrachnis, N.; Samoli, E.; Rizos, D.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Sifakis, S.; Kalampokas, T.; Vitoratos, N.; Creatsas, G.; Botsis, D. Association of adiponectin and placental growth factor in amniotic fluid with second trimester fetal growth. In Vivo 2012, 26, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vrachnis, N.; Karavolos, S.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Sifakis, S.; Siristatidis, C.; Mastorakos, G.; Creatsas, G. Review: Impact of mediators present in amniotic fluid on preterm labour. In Vivo 2012, 26, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vrachnis, N.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A.; Samoli, E.; Botsis, D.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Baka, S.; Hassiakos, D.; Creatsas, G. Elevated Mid-Trimester Amniotic Fluid ADAM-8 Concentrations as a Potential Risk Factor for Preterm Delivery. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2006, 13, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachnis, D.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Fotiou, A.; Pergialiotis, V.; Loukas, N.; Valsamakis, G.; Iavazzo, C.; Stavros, S.; Maroudias, G.; Panagopoulos, P.; et al. Is There a Correlation between Apelin and Insulin Concentrations in Early Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid with Fetal Growth Disorders? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, G.M.; Downey, L.A.; Stough, C. Neurotrophins as a reliable biomarker for brain function, structure and cognition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2020, 175, 107298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, R.; Doran, T.; Harkins, J.; Owen, V.J.; Porter, C. Composition of the amniotic fluid and maternal serum in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1974, 119, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, A.; Sadovsky, E.; Shafrir, E. Protein composition of early amniotic fluid and fetal serum with a case of bis-albuminemia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1964, 89, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, E.-K.; Shim, W.-S.; Song, K.-M.; Kim, S.M. Amniotic fluid exerts a neurotrophic influence on fetal neurodevelopment via the ERK/GSK-3 pathway. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levi-Montalcini, R.; Skaper, S.D.; Dal Toso, R.; Petrelli, L.; Leon, A. Nerve growth factor: From neurotrophin to neurokine. Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehler, M.F.; Kessler, J.A. Growth factor regulation of neuronal development. Dev. Neurosci. 1994, 16, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, J.E.; Jonakait, G.M. Interactions of the nervous and immune systems in development, normal brain homeostasis, and disease. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barde, Y.-A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron 1989, 2, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoenen, H. The changing scene of neurotrophic factors. Trends Neurosci. 1991, 14, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, C.E.; Vance, B.J.; Jarskog, L.; Chescheir, N.C.; Gilmore, J.H. Nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and neurotrophin-3 levels in human amniotic fluid. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 181, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Bergman, K.; O’Connor, T.G.; Glover, V. Maternal antenatal anxiety and amniotic fluid cortisol and testos-terone: Possible implications for foetal programming. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugatto, F.; Fernández-Deudero, A.; Bailén, A.; Fernández-Macías, R.; Hervías-Vivancos, B.; Bartha, J.L. Second-trimester amniotic fluid proinflammatory cytokine levels in normal and overweight women. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 115, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitre, M.; Mariga, A.; Chao, M.V. Neurotrophin signalling: Novel insights into mechanisms and pathophysiology. Clin. Sci. 2016, 131, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyosseva, S.V. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2004, 59, 201–220. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.-W.; Li, R.; Geetha, T.; Tao, Y.-X.; Babu, J.R. Nerve growth factor in metabolic complications and Alz-heimer’s disease: Physiology and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachnis, N.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Dafopoulos, K.; Siristatidis, C.; Pappa, K.I.; Deligeoroglou, E.; Vitoratos, N. Impact of maternal diabetes on epigenetic modifications leading to diseases in the offspring. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 538474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachnis, N.; Belitsos, P.; Sifakis, S.; Dafopoulos, K.; Siristatidis, C.; Pappa, K.I.; Iliodromiti, Z. Role of adipokines and other inflammatory mediators in gestational diabetes mellitus and previous gestational diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 549748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azar, S.T.; Major, S.C.; Safieh-Garabedian, B. Altered plasma levels of nerve growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta2 in type-1 diabetes mellitus. Brain Behav. Immun. 1999, 13, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.C.; Liao, C.H.; Liu, H.T. Association of urinary nerve growth factor levels with erectile function in young men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2017, 29, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulló, M.; Peeraully, M.R.; Trayhurn, P.; Folch, J.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Circulating nerve growth factor levels in relation to obesity and the metabolic syndrome in women. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Houtz, J.; Borden, P.; Ceasrine, A.; Minichiello, L.; Kuruvilla, R. Neurotrophin Signaling Is Required for Glucose-Induced Insulin Secretion. Dev. Cell 2016, 39, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sposato, V.; Canu, N.; Fico, E.; Fusco, S.; Bolasco, G.; Ciotti, M.T.; Spinelli, M.; Mercanti, D.; Grassi, C.; Triaca, V.; et al. The Medial Septum Is Insulin Resistant in the AD Presymptomatic Phase: Rescue by Nerve Growth Factor-Driven IRS1 Activation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 56, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Zou, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.; Gong, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liao, Y.; et al. NGF Attenuates High Glucose-Induced ER Stress, Preventing Schwann Cell Apoptosis by Activating the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β and ERK1/2 Pathways. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3005–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D. NGF receptors and PI3K/AKT pathway involved in glucose fluctuation-induced damage to neurons and α-lipoic acid treatment. BMC Neurosci. 2020, 21, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xita, N.; Tsatsoulis, A. Fetal origins of the metabolic syndrome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1205, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samario-Román, J.; Larqué, C.; Pánico, P.; Ortiz-Huidobro, R.I.; Velasco, M.; Escalona, R.; Hiriart, M. NGF and Its Role in Immunoendocrine Communication during Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantakou, P.; Mastorakos, G.; Vrachnis, N.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Valsamakis, G. Dysregulation of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: Im-plications during pregnancy and beyond. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 30, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.-Y.; Huang, X.-H.; Xia, Y.-X.; Zhang, W.-H. Changes of nerve growth factor in amniotic Fluid and correlation with ventriculomegaly. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2011, 26, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarr, O.; Yang, K.; Regnault, T.R.H. In Utero programming of later adiposity: The role of fetal growth restriction. J. Pregnancy 2012, 2012, 134758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kytikova, O.Y.; Novgorodtseva, T.P.; Antonyuk, V.; Denisenko, Y.K.; Atamas, O.V. Nerve growth factor and post-infarction cardiac remodeling. Acta Biomed. Sci. 2022, 7, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamitsi-Puchner, A.; Economou, E.; Boutsikou, T.; Nikolaou, K.E.; Vrachnis, E. Neurotrophin-3 and FLT3 tyrosine kinase receptor in per-inatal life. Mediat. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Mattson, M.P. NT-3 and BDNF protect CNS neurons against metabolic/excitotoxic insults. Brain Res. 1994, 640, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo-Weingart, L.; Ketschek, A.; Sainath, R.; Pacheco, A.; Smith, G.M.; Gallo, G. Neurotrophins induce fission of mitochondria along embryonic sensory axons. eLife 2019, 8, e49494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-J.; Sayers, N.; Verkhratsky, A.; Fernyhough, P. Neurotrophin-3 prevents mitochondrial dysfunction in sensory neurons of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 194, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Ichihara, J.; Nonomura, T.; Itakura, Y.; Taiji, M.; Nakayama, C.; Noguchi, H. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Reduces Blood Glucose Level in Obese Diabetic Mice but Not in Normal Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 238, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| AGA (n = 31) | SGA (n = 12) | LGA (n = 8) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal age (years) | 37 (18–43) | 35 (29–43) | 37.5 (31–41) | 0.295 |
| Maternal weight (kg) | 59 (47–92) | 63 (49–105) | 62 (58–100) | 0.223 |
| Maternal height (cm) | 161 (155–175) | 166 (152–174) | 170 (162–174) | 0.088 |
| Maternal BMI | 21 (20–25) | 22 (20–27) | 22 (21–26) | 0.621 |
| Parity (nulliparity) | 16/28 | 7/11 | 6/7 | 0.394 |
| Gestational age (days) | 275 (261–285) | 273 (240–277) | 267 (261–274) | 0.019 |
| Neonatal birth weight (g) | 3265 (2860–3750) | 2640 (1750–2860) | 3775 (3550–3950) | <0.001 |
| Neonatal sex (female) | 5/30 | 2/12 | 1/8 | >0.999 |
| Mode of delivery | 19/28 | 7/12 | 2/8 | 0.111 |
| Percentile | 45 (20–74) | 3.5 (1–9) | 93 (92–96) | <0.001 |
| Group | N | NGF Median Value (Q1–Q3) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGA | 12 | 10.15 (8.35–11.65) | 0.254 |
| LGA | 8 | 10.15 (8.87–12.4) | |
| AGA (Control) | 31 | 9.14 (7.12–10.8) |
| Group | N | NT-3 Median Value (Q1–Q3) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
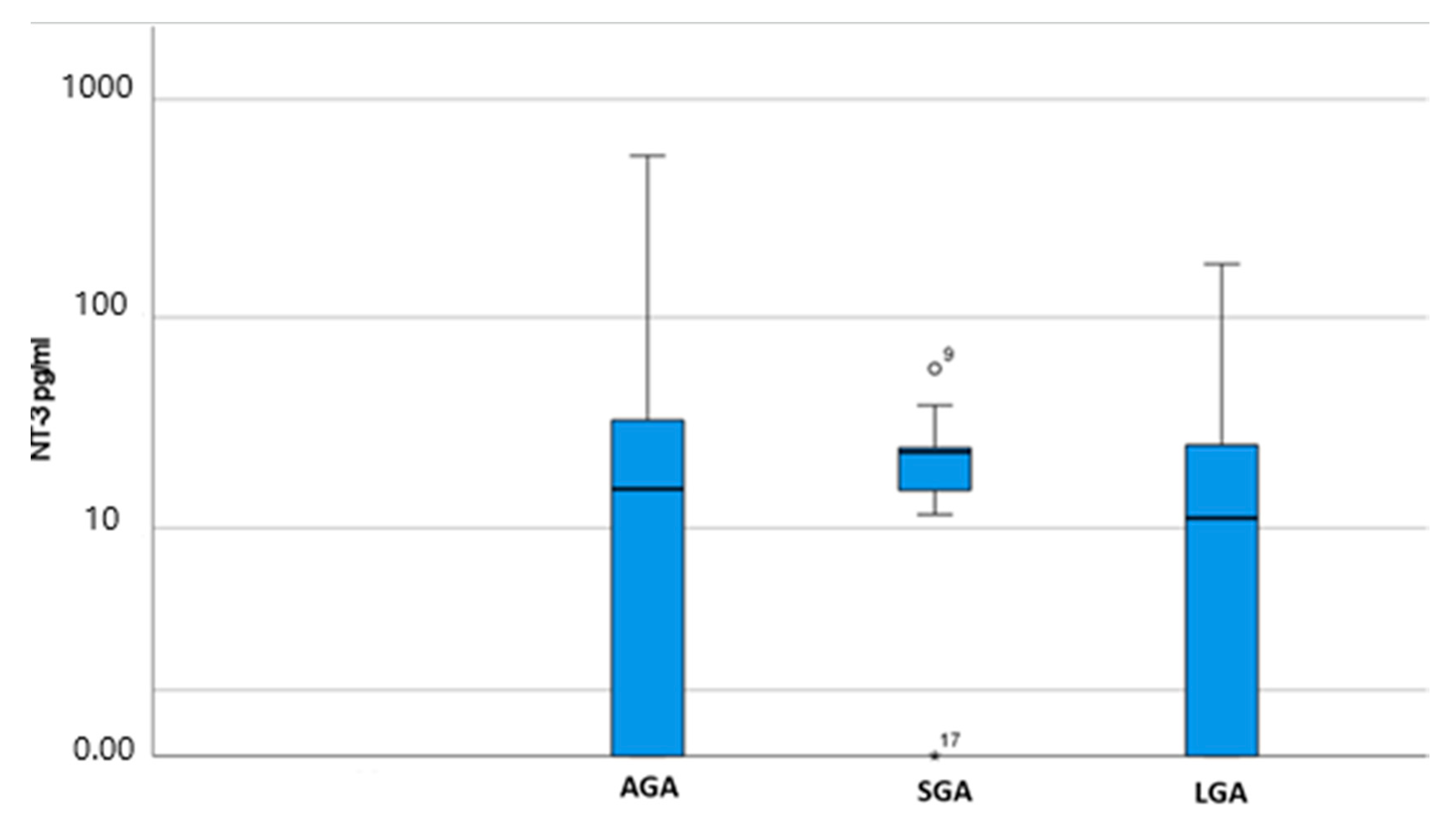
| SGA | 12 | 23.5 (15.5–24.6) | 0.398 |
| LGA | 8 | 11.87 (0–25.85) | |
| AGA (Control) | 31 | 15.9 (0–35.2) |
| NT-3 | NGF | Age | Weight | Height | Gestational Age | Birth Weight | Percentile | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT-3 | 1 | 0.317 | 0.159 | –0.109 | 0.122 | –0.104 | –0.218 | –0.043 |
| NGF | 1 | 0.047 | 0.130 | 0.066 | –0.157 | 0.265 | 0.111 | |
| Age | 1 | 0.127 | –0.092 | 0.131 | 0.009 | –0.212 | ||
| Weight | 1 | 0.447 * | 0.164 | 0.109 | 0.350 | |||
| Height | 1 | 0.118 | 0.465 | 0.110 | ||||
| Gestational age | 1 | 0.487 * | 0.006 | |||||
| Birth weight | 1 | 0.528 * | ||||||
| Percentile | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machairiotis, N.; Vrachnis, D.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Loukas, N.; Fotiou, A.; Pergialiotis, V.; Stavros, S.; Mantzou, A.; Maroudias, G.; Iavazzo, C.; et al. Detection and Quantification of Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Levels in Early Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid: Investigation into a Possible Correlation with Abnormal Fetal Growth Velocity Patterns. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124131
Machairiotis N, Vrachnis D, Antonakopoulos N, Loukas N, Fotiou A, Pergialiotis V, Stavros S, Mantzou A, Maroudias G, Iavazzo C, et al. Detection and Quantification of Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Levels in Early Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid: Investigation into a Possible Correlation with Abnormal Fetal Growth Velocity Patterns. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124131
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachairiotis, Nikolaos, Dionysios Vrachnis, Nikolaos Antonakopoulos, Nikolaos Loukas, Alexandros Fotiou, Vasilios Pergialiotis, Sofoklis Stavros, Aimilia Mantzou, Georgios Maroudias, Christos Iavazzo, and et al. 2023. "Detection and Quantification of Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Levels in Early Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid: Investigation into a Possible Correlation with Abnormal Fetal Growth Velocity Patterns" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124131
APA StyleMachairiotis, N., Vrachnis, D., Antonakopoulos, N., Loukas, N., Fotiou, A., Pergialiotis, V., Stavros, S., Mantzou, A., Maroudias, G., Iavazzo, C., Kanaka-Gantenbein, C., Drakakis, P., Troupis, T., Vlasis, K., & Vrachnis, N. (2023). Detection and Quantification of Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Levels in Early Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid: Investigation into a Possible Correlation with Abnormal Fetal Growth Velocity Patterns. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124131






