Lung Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Endpoint Definition
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients Characteristics
3.2. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses and Screen for Predictive Factors
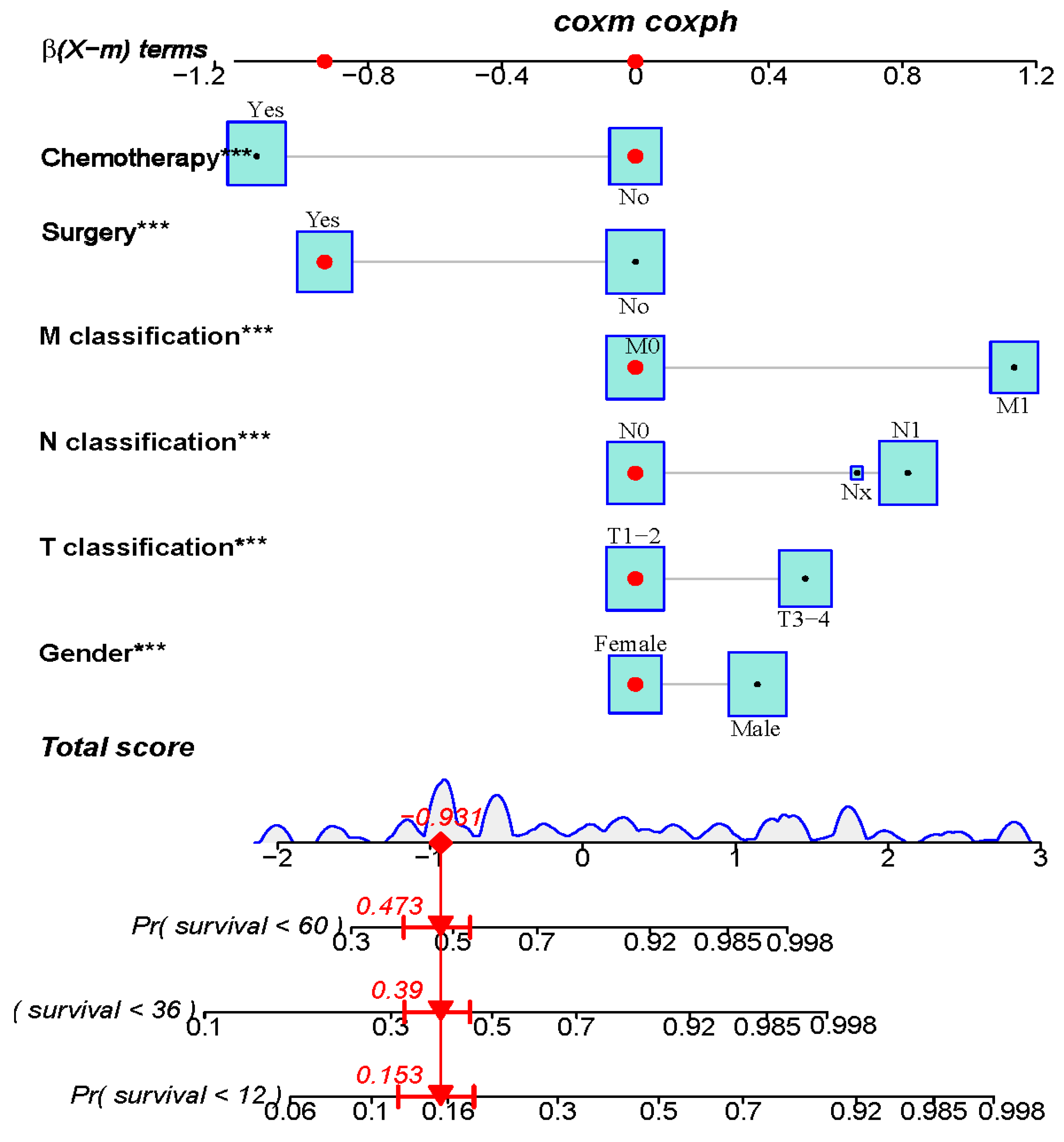
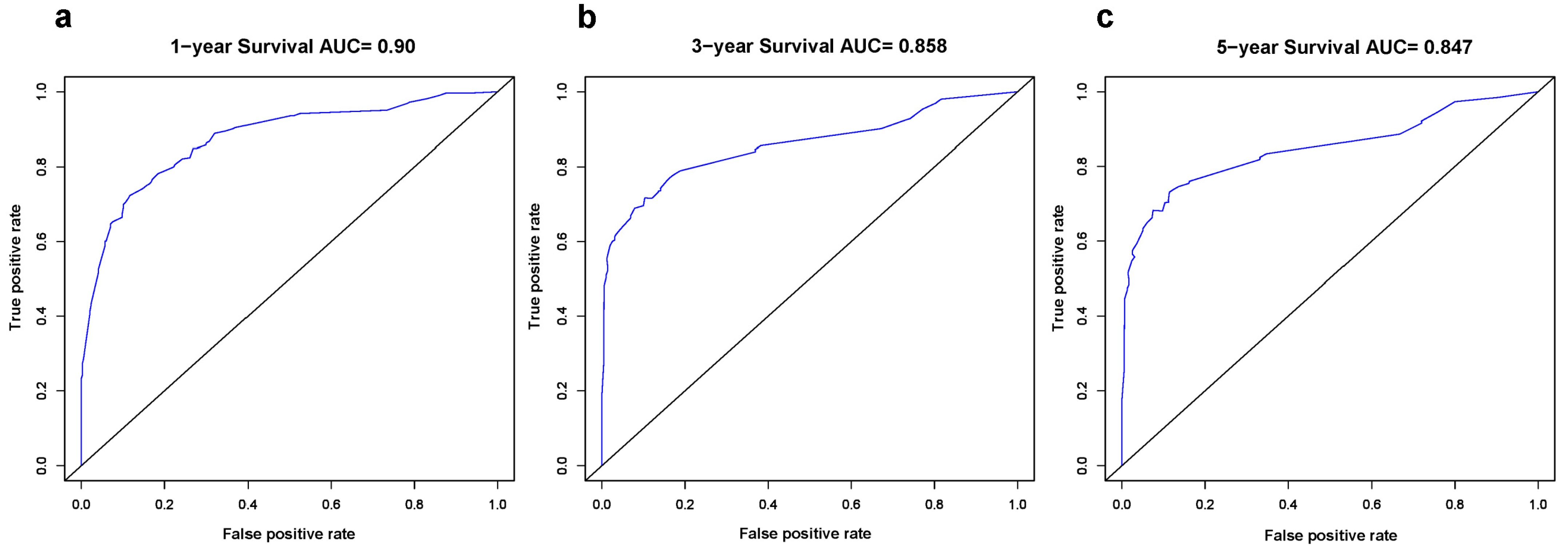
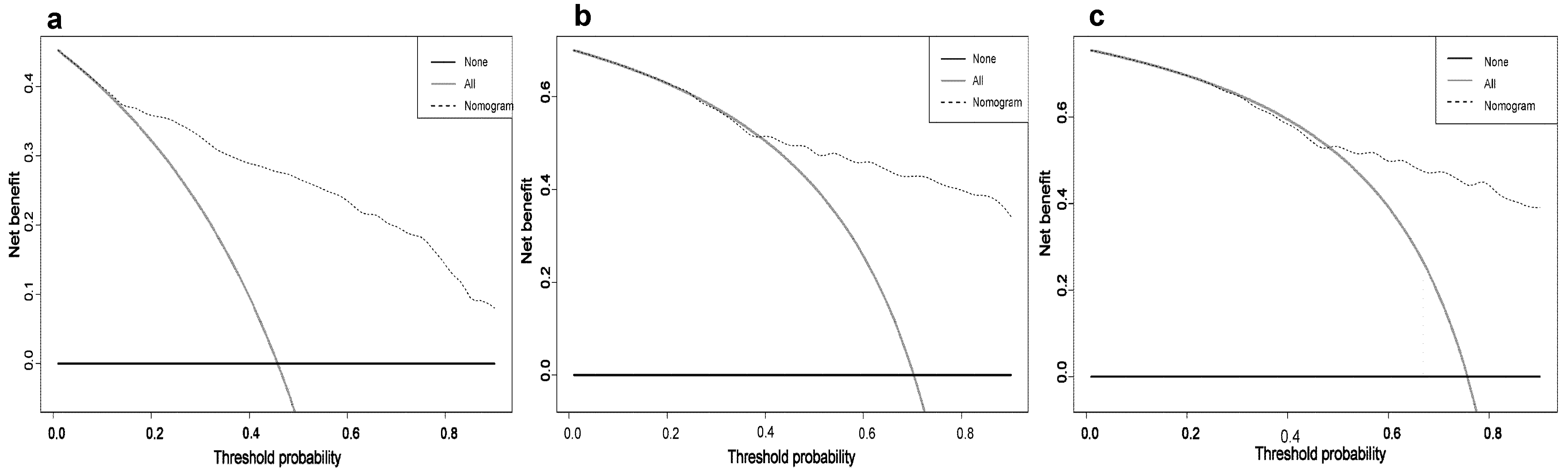
3.3. Constructing and Validating the Nomogram
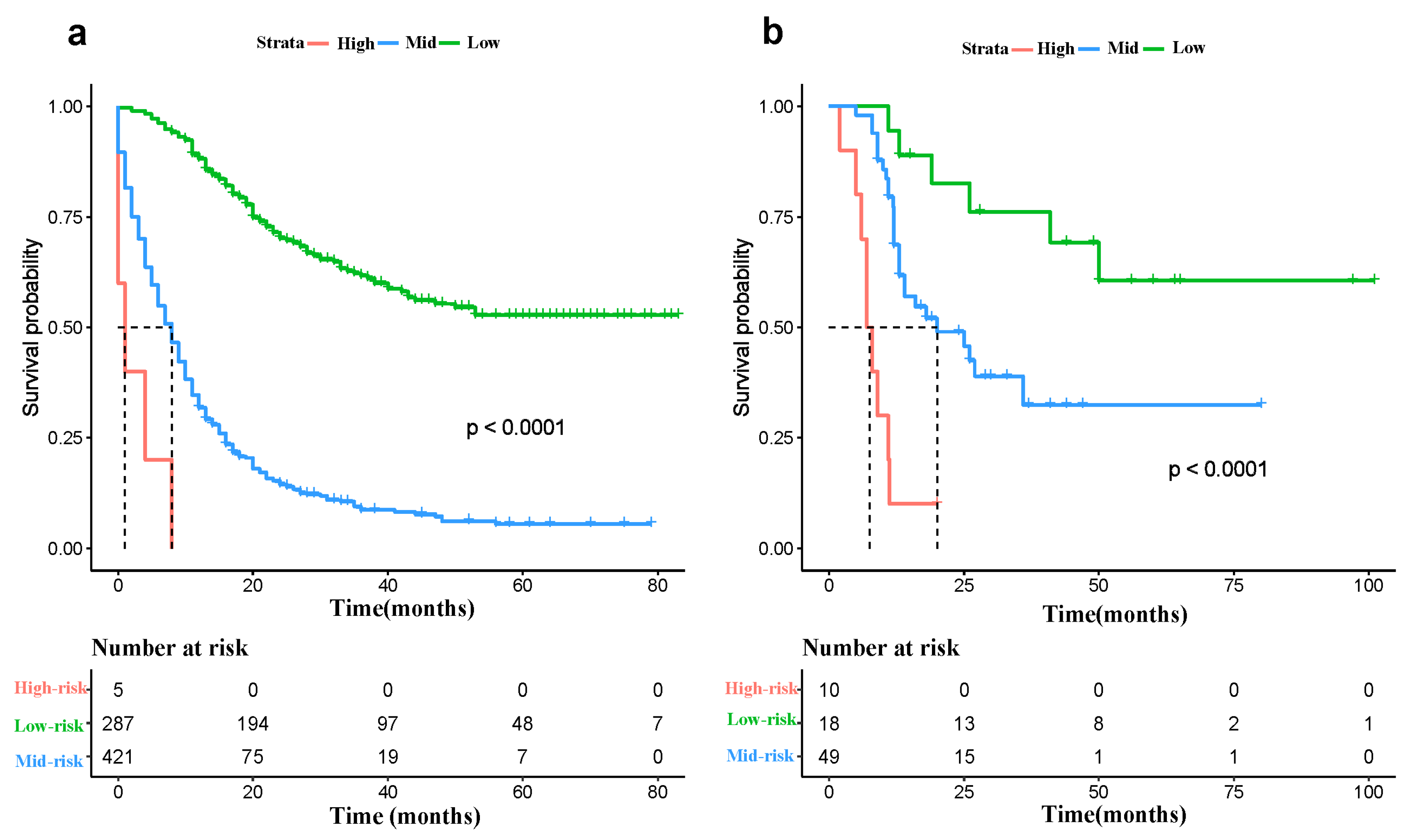
3.4. Risk Classification System
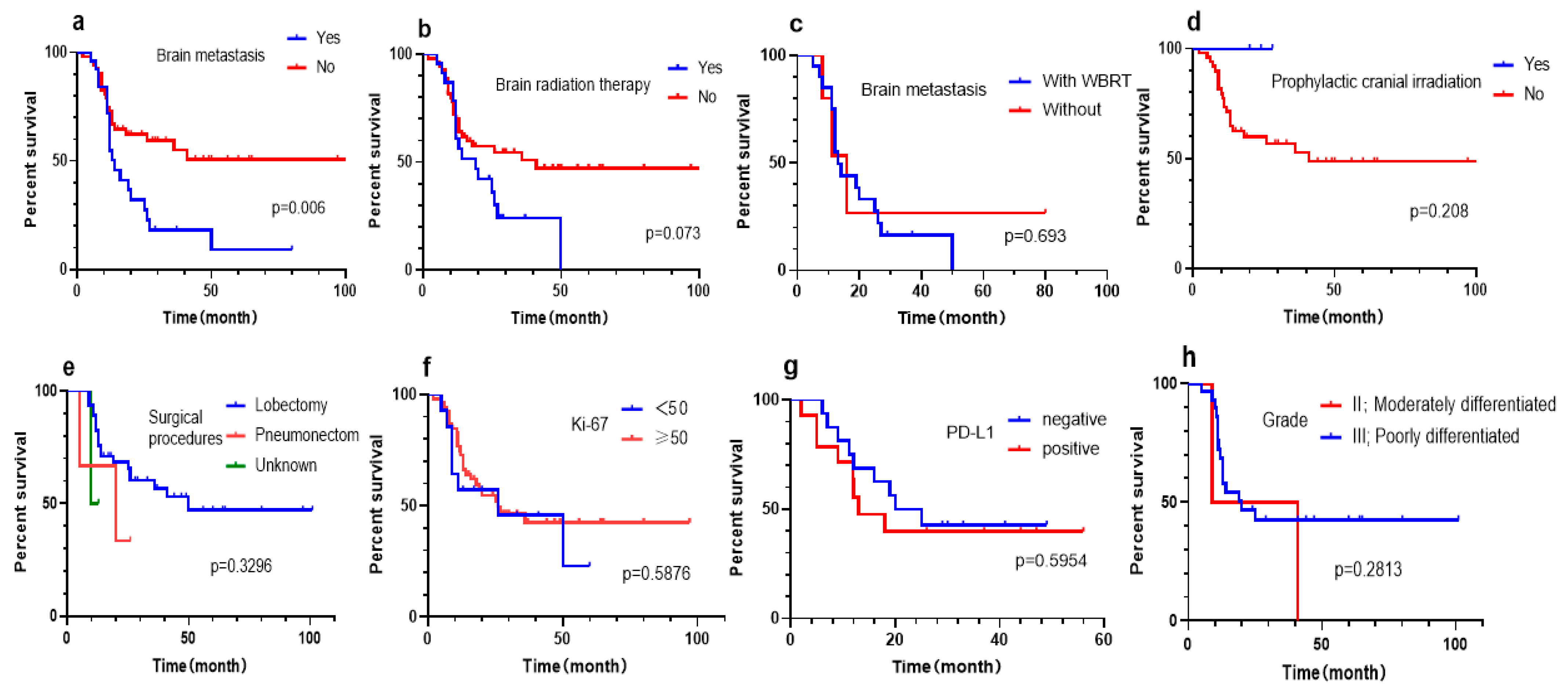
3.5. Subgroup Analysis of West China Hospital cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hendifar, A.E.; Marchevsky, A.M.; Tuli, R. Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Lung: Current Challenges and Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Well-Differentiated Disease. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollard, R.; Jhatakia, S.; Elliott, M.; Kosty, M. Large cell/neuroendocrine carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2010, 69, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Linnoila, R.I.; Tsokos, M.G.; Hitchcock, C.L.; Cutler, G.B., Jr.; Nieman, L.; Chrousos, G.; Pass, H.; Doppman, J. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung with proposed criteria for large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. An ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric study of 35 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1991, 15, 529–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Gosain, R.; Groman, A.; Gosain, R.; Dasari, A.; Halfdanarson, T.R.; Mukherjee, S. Incidence and Survival Outcomes in Patients with Lung Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in the United States. Cancers 2021, 13, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamura, H.; Kameya, T.; Matsuno, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Tada, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yokose, T.; Jiang, S.X.; Inoue, T.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung: A prognostic spectrum. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyoda, A.; Makino, T.; Koezuka, S.; Otsuka, H.; Hata, Y. Treatment options for patients with large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 62, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Russo, G.; Pusceddu, S.; Proto, C.; Macerelli, M.; Signorelli, D.; Vitali, M.; Ganzinelli, M.; Gallucci, R.; Zilembo, N.; Platania, M.; et al. Treatment of lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 7047–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, X.; Guo, C.; Liu, H.; Li, S. Survival outcomes of surgery in patients with pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A retrospective single-institution analysis and literature review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, F.; Dienemann, H.; Muley, T.; Warth, A.; Hoffmann, H. Predictors of survival after operation among patients with large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 99, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroshima, K.; Abe, S.; Ebihara, Y.; Ogura, S.; Kikui, M.; Kodama, T.; Komatsu, H.; Saito, Y.; Sagawa, M.; Sato, M.; et al. Cytological characteristics of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2005, 48, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Yuste, M.; Matilla, J.M.; Alvarez-Gago, T.; Duque, J.L.; Heras, F.; Cerezal, L.J.; Ramos, G. Prognostic factors in neuroendocrine lung tumors: A Spanish Multicenter Study. Spanish Multicenter Study of Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Lung of the Spanish Society of Pneumonology and Thoracic Surgery (EMETNE-SEPAR). Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2000, 70, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, H.; Asamura, H.; Maeshima, A.; Suzuki, K.; Kondo, H.; Niki, T.; Yamada, T.; Tsuchiya, R.; Matsuno, Y. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung: A clinicopathologic study of eighty-seven cases. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 124, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.; Cavazza, A.; Marchioni, A.; Longo, L.; Migaldi, M.; Sartori, G.; Bigiani, N.; Schirosi, L.; Casali, C.; Morandi, U.; et al. Role of chemotherapy and the receptor tyrosine kinases KIT, PDGFRalpha, PDGFRbeta, and Met in large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8774–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, Q.; Xiong, X.; et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iasonos, A.; Schrag, D.; Raj, G.V.; Panageas, K.S. How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. A Clinical Nomogram for Predicting Cancer-Specific Survival in Pulmonary Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Patients: A Population-Based Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 7299–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez de Cos Escuin, J. Diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine lung tumors. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2014, 50, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N.R.; Qi, Y.; Shi, Q.; Krook, J.E.; Kugler, J.W.; Jett, J.R.; Molina, J.R.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A.; Mandrekar, S.J. Tumor response and progression-free survival as potential surrogate endpoints for overall survival in extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: Findings on the basis of North Central Cancer Treatment Group trials. Cancer 2011, 117, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournel, L.; Falcoz, P.E.; Alifano, M.; Charpentier, M.C.; Boudaya, M.S.; Magdeleinat, P.; Damotte, D.; Regnard, J.F. Surgical management of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas: A 10-year experience. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2013, 43, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, J.L.; Hendriks, L.E.; Buikhuisen, W.A.; Groen, H.J.; Thunnissen, E.; van Suylen, R.J.; Houben, R.; Damhuis, R.A.; Speel, E.J.; Dingemans, A.M. Clinical features of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A population-based overview. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddoli, C.; Barlesi, F.; Chetaille, B.; Garbe, L.; Thomas, P.; Giudicelli, R.; Fuentes, P. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung: An aggressive disease potentially treatable with surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 77, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinslow, C.J.; May, M.S.; Saqi, A.; Shu, C.A.; Chaudhary, K.R.; Wang, T.J.C.; Cheng, S.K. Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung: A Population-Based Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, e99–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, S.; Aigner, C.; Roesel, C. The role of surgery in high grade neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, S1474–S1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saji, H.; Tsuboi, M.; Matsubayashi, J.; Miyajima, K.; Shimada, Y.; Imai, K.; Kato, Y.; Usuda, J.; Kajiwara, N.; Uchida, O.; et al. Clinical response of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung to perioperative adjuvant chemotherapy. Anticancer Drugs 2010, 21, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, G.; Morandi, U.; Alloisio, M.; Terzi, A.; Cardillo, G.; Filosso, P.; Rea, F.; Facciolo, F.; Pelosi, G.; Gandini, S.; et al. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung: A retrospective analysis of 144 surgical cases. Lung Cancer 2006, 53, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filosso, P.L.; Guerrera, F.; Evangelista, A.; Galassi, C.; Welter, S.; Rendina, E.A.; Travis, W.; Lim, E.; Sarkaria, I.; Thomas, P.A.; et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for large-cell neuroendocrine lung carcinoma: Results from the European Society for Thoracic Surgeons Lung Neuroendocrine Tumours Retrospective Database. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkaria, I.S.; Iyoda, A.; Roh, M.S.; Sica, G.; Kuk, D.; Sima, C.S.; Pietanza, M.C.; Park, B.J.; Travis, W.D.; Rusch, V.W. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy in resected pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas: A single institution experience. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 1180–1186, discussion 1186–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhong, Y. Survival and prognosis of lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Bull. Cancer 2021, 108, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, J.; Lili, X.; Xiang, S. The role of postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) in pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (PLCNEC). Cancer Radiother. 2020, 24, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieber, J.; Schmitt, J.; Warth, A.; Muley, T.; Kappes, J.; Eichhorn, F.; Hoffmann, H.; Heussel, C.P.; Welzel, T.; Debus, J.; et al. Outcome and prognostic factors of multimodal therapy for pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2015, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prelaj, A.; Rebuzzi, S.E.; Del Bene, G.; Giron Berrios, J.R.; Emiliani, A.; De Filippis, L.; Prete, A.A.; Pecorari, S.; Manna, G.; Ferrara, C.; et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of cisplatin-etoposide and the role of thoracic radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation in LCNEC. ERJ Open Res. 2017, 3, 00128-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, T.; Jiang, S.X.; Kameya, T.; Asamura, H.; Sato, Y.; Nagai, K.; Okayasu, I. Divergent cyclin B1 expression and Rb/p16/cyclin D1 pathway aberrations among pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pelosi, G.; Rindi, G.; Travis, W.D.; Papotti, M. Ki-67 antigen in lung neuroendocrine tumors: Unraveling a role in clinical practice. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, F.; Harms, A.; Warth, A.; Muley, T.; Winter, H.; Eichhorn, M.E. PD-L1 expression in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 2018, 118, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y. Prognostic nomogram predicts overall survival in pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, J.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, C.; Jiang, W.; Lu, T.; et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting the overall survival of patients with lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 4943–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Training Cohort N = 713 | Validation Cohort N = 77 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.0007 | ||
| <50 | 40 (5.6%) | 5 (6.4%) | |
| 50–59 | 167 (23.4%) | 32 (41.6%) | |
| 60–69 | 276 (38.7%) | 31 (40.3%) | |
| 70–79 | 177 (24.8%) | 8 (10.4%) | |
| ≥80 | 53 (7.5%) | 1 (1.3%) | |
| Sex | <0.0001 | ||
| Female | 323 (45.3%) | 9 (11.7%) | |
| Male | 390 (54.7%) | 68 (88.3%) | |
| Race | <0.0001 | ||
| White | 589 (82.6%) | 0 | |
| Black | 95 (13.3%) | 0 | |
| Other | 29 (4.1%) | 77 (100%) | |
| Laterality | 0.4721 | ||
| Left | 291 (40.8%) | 37 (48.1%) | |
| Right | 411 (57.6%) | 39 (50.6%) | |
| Other (Bilateral and Paired site) | 11 (1.6%) | 1 (1.3%) | |
| T classification | 0.8490 | ||
| T1-2 | 397 (55.7%) | 42 (54.5%) | |
| T3-4 | 316 (44.3%) | 35 (45.5%) | |
| N classification | 0.0054 | ||
| N0 | 342 (48%) | 24 (31.2%) | |
| N1-3 | 357 (50%) | 53 (68.8%) | |
| Nx | 14 (2%) | 0 | |
| M classification | 0.2213 | ||
| M0 | 429 (60.2%) | 52 (67.5%) | |
| M1 | 284 (39.8%) | 25 (32.5%) | |
| AJCC Stage | 0.0004 | ||
| I | 193 (27.1%) | 9 (11.7%) | |
| II | 100 (14%) | 16 (20.8%) | |
| III | 136 (19.1%) | 27 (35.1%) | |
| IV | 284 (39.8%) | 25 (32.4%) | |
| Brain metastasis | <0.0001 | ||
| Yes | 99 (13.9%) | 25 (32.5%) | |
| No/Unknown | 614 (86.1%) | 52 (67.5%) | |
| Surgery | 0.0026 | ||
| Yes | 342 (48%) | 51 (66.2%) | |
| No/unknown | 371 (52%) | 26 (33.8%) | |
| Radiation | <0.0001 | ||
| Yes | 102 (14.3%) | 39 (50.6%) | |
| No/unknown | 611 (85.7%) | 38 (49.4%) | |
| Chemotherapy | <0.0001 | ||
| Yes | 396 (55.5%) | 67 (87%) | |
| No/unknown | 317 (44.5%) | 10 (13%) | |
| Surgical procedures | 0.1595 | ||
| Lobectomy | 325 (95.0%) | 46 (90.2%) | |
| Pneumonectomy | 14 (4.1%) | 3 (5.9%) | |
| Unknown | 3 (0.9%) | 2 (3.9%) | |
| Grade | 6 (7.8%) 38 (49.4%) | / | |
| Grade I | 7 (1%) | ||
| Grade II | 14 (2%) | ||
| Grade III | 522 (73.2%) | ||
| Undifferentiated | 170 (23.8%) | ||
| Ki-67 | / | ||
| <50% | / | 14 (18.2%) | |
| ≥50% | / | 52 (67.5%) | |
| Unknown | / | 11 (14.3%) | |
| PD-L1 | / | ||
| Negative (TPS < 1%) | / | 16 (20.8%) | |
| Positive | / | 14 (18.2%) | |
| Unknown | / | 47 (61%) | |
| Whole brain radiotherapy | |||
| Yes | / | 23 (29.9%) | / |
| No | / | 54 (70.1%) | |
| Prophylactic-cranial irradiation | |||
| Yes | / | 3 (4%) | |
| No | / | 74 (96%) | / |
| Univariate Analyses | HR | 95% CI | p Value † | C-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (vs. <50) | 0.011 | 0.546 | ||
| 50–59 | 0.767 | 0.514–1.145 | ||
| 60–69 | 0.837 | 0.572–1.225 | ||
| 70–79 | 1.077 | 0.728–1.594 | ||
| ≥80 | 1.266 | 0.799–2.006 | ||
| Sex | <0.001 | 0.551 | ||
| Male vs. Female | 1.412 | 1.180–1.690 | ||
| Race | 0.281 | 0.51 | ||
| Black vs. White | 0.949 | 0.732–1.231 | ||
| Other vs. White | 1.363 | 0.910–2.042 | ||
| Grade | 0.959 | 0.501 | ||
| II vs. I | 0.751 | 0.257–2.199 | ||
| III vs. I | 0.863 | 0.357–2.087 | ||
| IV vs. I | 0.856 | 0.349–2.098 | ||
| Laterality | 0.001 | 0.519 | ||
| Right vs. left | 1.051 | 0.877–1.261 | ||
| Other vs. left | 3.335 | 1.813–6.137 | ||
| T classification | <0.001 | 0.67 | ||
| T3-4 vs. T1-2 | 2.684 | 2.240–3.215 | ||
| N classification | <0.001 | 0.676 | ||
| N1-3 vs. N0 | 3.217 | 2.656–3.896 | ||
| Nx vs. N0 | 6.196 | 3.575–10.740 | ||
| M classification | <0.001 | 0.698 | ||
| M1 vs. M0 | 4.991 | 4.138–6.021 | ||
| Brain metastasis | <0.001 | 0.569 | ||
| Yes vs. No | 3.098 | 2.462–3.898 | ||
| AJCC stage | <0.001 | 0.755 | ||
| II vs. I | 2.57 | 1.790–3.689 | ||
| III vs. I | 4.426 | 3.199–6.123 | ||
| IV vs. I | 10.928 | 8.151–14.653 | ||
| Radiation | 0.4 | 0.497 | ||
| Yes vs. No | 1.11 | 0.871–1.413 | ||
| Surgery | <0.001 | 0.691 | ||
| Yes vs. No | 0.218 | 0.170–0.265 | ||
| Chemotherapy | 0.284 | 0.483 | ||
| Yes vs. No | 1.103 | 0.922–1.321 |
| Multivariate Analysis | HR | 95% CI | p Value ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male vs. Female | 1.529 | 1.273–1.837 | <0.001 |
| T classification | |||
| T3-4 vs. T1-2 | 1.676 | 1.368–2.054 | <0.001 |
| N classification | |||
| N1-3 vs. N0 | 2.324 | 1.858–2.906 | <0.001 |
| Nx vs. N0 | 1.953 | 1.092–3.491 | 0.024 |
| M classification | |||
| M1 vs. M0 | 3.292 | 2.620–4.137 | <0.001 |
| Surgery | |||
| Yes vs. No | 0.415 | 0.321–0.537 | <0.001 |
| Chemotherapy | |||
| Yes vs. No | 0.356 | 0.288–0.440 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, X.; Pu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yin, L.; Li, Y. Lung Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124126
Mu X, Pu D, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Wu Q, Liu Q, Yin L, Li Y. Lung Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124126
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Xiaoli, Dan Pu, Yajuan Zhu, Yixin Zhou, Qiang Wu, Qing Liu, Liyuan Yin, and Yan Li. 2023. "Lung Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124126
APA StyleMu, X., Pu, D., Zhu, Y., Zhou, Y., Wu, Q., Liu, Q., Yin, L., & Li, Y. (2023). Lung Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124126







