Obesity as a Risk Factor of Severe Outcome of COVID-19: A Pair-Matched 1:2 Case–Control Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
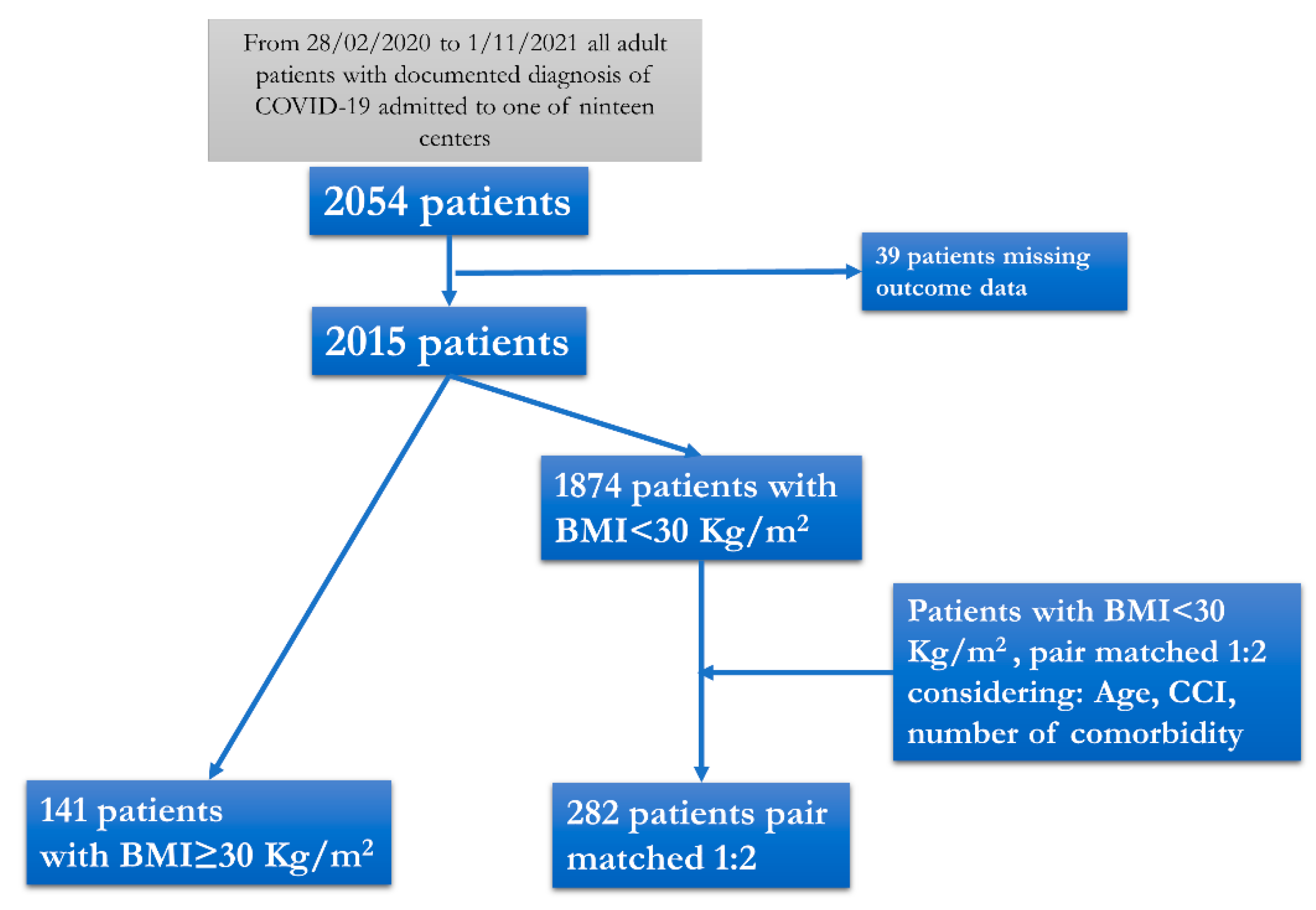
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Macera, M.; De Angelis, G.; Sagnelli, C.; Coppola, N. Vanvitelli COVID-19 group Clinical Presentation of COVID-19: Case Series and Review of the literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monari, C.; Sagnelli, C.; Maggi, P.; Sangiovanni, V.; Numis, F.G.; Gentile, I.; Masullo, A.; Rescigno, C.; Calabria, G.; Megna, A.S.; et al. More Severe COVID-19 in Patients with Active Cancer: Results of a Multicenter Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 662746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisaturo, M.; Calò, F.; Russo, A.; Camaioni, C.; Giaccone, A.; Pinchera, B.; Gentile, I.; Simeone, F.; Iodice, A.; Maggi, P.; et al. Dementia as Risk Factor for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Case-Control Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 698184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Pisaturo, M.; Palladino, R.; Maggi, P.; Numis, F.G.; Gentile, I.; Sangiovanni, V.; Esposito, V.; Punzi, R.; Calabria, G.; et al. Prognostic Value of Transaminases and Bilirubin Levels at Admission to Hospital on Disease Progression and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19—An Observational Retrospective Study. Pathogens 2022, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, B.G.; Aghagoli, G.; Lavine, K.; Yang, L.; Siff, E.J.; Chiang, S.S.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; Dumenco, L.; Savaria, M.C.; Aung, S.N.; et al. Predictors of COVID-19 severity: A literature review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, T.; Pantic, I.; Dragasevic, S.; Lugonja, S.; Dumic, I.; Rajilic-Stojanovic, M. The Interrelationship Among Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Colonic Diverticulosis and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2021, 30, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Almahmeed, W.; Bays, H.; Cuevas, A.; Di Angelantonio, E.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Sun, M.C.; Wittert, G.; Pinto, F.J.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Mechanistic insights and management strategies. A joint position paper by the World Heart Federation and World Obesity Federation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 2218–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perone, F.; Pingitore, A.; Conte, E.; Halasz, G.; Ambrosetti, M.; Peruzzi, M.; Cavarretta, E. Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk: Systematic Intervention Is the Key for Prevention. Healthcare 2023, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’errico, M.; Pavlova, M.; Spandonaro, F. The economic burden of obesity in Italy: A cost-of-illness study. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2022, 23, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chi, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori di Rischio Per la Salute: Fumo, Obesità, Alcol e Sedentarietà—Anno 2021. Available online: https://www.istat.it/it/archivio/270163 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R.; Mantzoros, C.S. Commentary: COVID-19 and obesity pandemics converge into a syndemic requiring urgent and multidisciplinary action. Metabolism 2021, 114, 154408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalil, A.C.; Thomas, P.G. Influenza virus-related critical illness: Pathophysiology and epidemiology. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pisaturo, M.; Russo, A.; Pattapola, V.; Astorri, R.; Maggi, P.; Numis, F.G.; Gentile, I.; Sangiovanni, V.; Rossomando, A.; Gentile, V.; et al. Clinical Characterization of the Three Waves of COVID-19 Occurring in Southern Italy: Results of a Multicenter Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Pisaturo, M.; De Luca, I.; Schettino, F.; Maggi, P.; Numis, F.G.; Gentile, I.; Sangiovanni, V.; Rossomando, A.M.; Gentile, V.; et al. Lactate dehydrogenase and PaO2/FiO2 ratio at admission helps to predict CT score in patients with COVID-19: An observational study. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, F.; Russo, A.; Palamone, M.; Maggi, P.; Allegorico, E.; Gentile, I.; Sangiovanni, V.; Russomando, A.; Gentile, V.; Calabria, G.; et al. Pre-existing chronic kidney disease (CDK) was not associated with a severe clinical outcome of hospitalized COVID-19: Results of a case-control study in Southern Italy. Infez. Med. 2022, 30, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 16; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22 (Suppl. 7), s176–s185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Leeuw, A.J.M.; Oude Luttikhuis, M.A.M.; Wellen, A.C.; Müller, C.; Calkhoven, C.F. Obesity and its impact on COVID-19. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatraju, P.K.; Ghassemieh, B.J.; Nichols, M.; Kim, R.; Jerome, K.R.; Nalla, A.K.; Greninger, A.L.; Pipavath, S.; Wurfel, M.M.; Evans, L.; et al. COVID-19 in critically ill patients in the seattle region—Case series. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartof, S.Y.; Qian, L.; Hong, V.; Wei, R.; Nadjafi, R.F.; Fischer, H.; Li, Z.; Shaw, S.F.; Caparosa, S.L.; Nau, C.L.; et al. Obesity and mortality among patients diagnosed with COVID-19: Results from an integrated health care organization. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Feng, C.; et al. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Elia, L.; Giaquinto, A.; Zarrella, A.F.; Rendina, D.; Idelson, P.I.; Strazzullo, P.; Galletti, F. Hypertension and mortality in SARS-COV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of observational studies after 2 years of pandemic. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 108, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Voort, P.H.J.; Moser, J.; Zandstra, D.F.; Muller Kobold, A.C.; Knoester, M.; Calkhoven, C.F.; Hamming, I.; van Meurs, M. Leptin levels in SARS-CoV-2 infection related respiratory failure:a cross-sectional study and a pathophysiological framework on therole of fat tissue. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Case Group | Control Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 141 | 282 | |
| Males, No. (%) | 95 (67.4) | 190(67.4) | 1 a |
| Age, years, median (Q1–Q3) | 58 (48–69) | 58 (48–69) | 0.925 b |
| Charlson comorbidity index, median (Q1–Q3) | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–4) | 0.497 c |
| Number of comorbidities for each patient, median (Q1–Q3) | 1(1–2) | 1(0–2) | 0.197 c |
| No. (%) of patients with hypertension | 86 (61) | 140 (49.6) | 0.027 a |
| No. (%) of patients with cardiovascular disease | 34 (24.1) | 90 (31.9) | 0.097 a |
| No. (%) of patients with diabetes | 37 (26.2) | 57 (20.2) | 0.160 a |
| No. (%) of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 22 (15.6) | 27 (9.6) | 0.068 a |
| No. (%) of patients with chronic liver disease | 6 (4.3) | 8 (2.8) | 0.438 a |
| No. (%) of patients with chronic kidney disease | 16(11.3) | 22(7.8) | 0.229 a |
| No. (%) of patients with malignancy | 5 (3.5) | 13 (4.6) | 0.609 a |
| No. (%) of patients with dementia | 2 (1.4) | 13 (4.6) | 0.095 a |
| Case Group | Control Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No.of patients | 141 | 282 | |
| No. (%) of patients with fever | 87 (62.6) | 156 (55.5) | 0.167 a |
| No. (%) of patients with dyspnea | 103 (74.6) | 193 (68.7) | 0.208 a |
| No. (%) of patients with asthenia | 23 (16.7) | 79 (28.2) | 0.01 a |
| No. (%) of patients with cough | 45 (32.6) | 89 (31.8) | 0.865 a |
| No. (%) of patients with ageusia/dysgeusia | 4 (2.9) | 4 (1.4) | 0.302 a |
| No. (%) of patients with anosmia/hyposmia | 3 (2.2) | 6 (2.1) | 0.984 a |
| No. (%) of patients with diarrhea | 10 (7.2) | 8 (2.9) | 0.038 a |
| No. (%) of patients with skin lesions | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Days from admission to discharge, median (Q1–Q3) | 14 (10–20) | 15 (10–21) | 0.555 c |
| No. (%) of patients with pneumonia | 138 (97.9) | 263 (93.6) | 0.057 a |
| Median (Q1–Q3) PaO2/FiO2 Ratio (P/F) | 194 (119.5–300) | 232 (156–329) | 0.014 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) white blood cells | 7900 (5425–10355) | 7820 (5430–10730) | 0.858 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) International Normalized Ratio (INR) | 1.11 (1.04–1.19) | 1.11 (1.04–1.21) | 0.775 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) Blood creatinine | 0.9 (0.8–1.1) | 0.84 (0.7–1.025) | 0.050 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) ALT | 36 (26–49) | 31 (21–51) | 0.130 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) AST | 38 (26–58) | 33 (22–63.5) | 0.230 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) total bilirubin | 0.6 (0.5–0.8) | 0.6 (0.41–0.85) | 0.946 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) creatine phosphokinase (CPK) at admission | 99 (54.5–298) | 88 (57–166) | 0.347 c |
| Median (Q1–Q3) lacticodehydrogenase (LDH) | 323 (254–419) | 288 (229–411) | 0.099 c |
| Case Group | Control Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No.of patients | 141 | 282 | |
| No. (%) of patients with mild or moderate outcome | 65(46.1) | 189(67) | 0.0001 a |
| No. (%) of patients needing intensive care treatment | 59 (41.8) | 75 (26.6) | 0.001 a |
| No. (%) of patients who died during hospitalization | 17 (12.1) | 18 (6.4) | 0.046 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, A.; Pisaturo, M.; Zollo, V.; Martini, S.; Maggi, P.; Numis, F.G.; Gentile, I.; Sangiovanni, N.; Rossomando, A.M.; Bianco, V.; et al. Obesity as a Risk Factor of Severe Outcome of COVID-19: A Pair-Matched 1:2 Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124055
Russo A, Pisaturo M, Zollo V, Martini S, Maggi P, Numis FG, Gentile I, Sangiovanni N, Rossomando AM, Bianco V, et al. Obesity as a Risk Factor of Severe Outcome of COVID-19: A Pair-Matched 1:2 Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Antonio, Mariantonietta Pisaturo, Verdiana Zollo, Salvatore Martini, Paolo Maggi, Fabio Giuliano Numis, Ivan Gentile, Nadia Sangiovanni, Anna Maria Rossomando, Vincenzo Bianco, and et al. 2023. "Obesity as a Risk Factor of Severe Outcome of COVID-19: A Pair-Matched 1:2 Case–Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124055
APA StyleRusso, A., Pisaturo, M., Zollo, V., Martini, S., Maggi, P., Numis, F. G., Gentile, I., Sangiovanni, N., Rossomando, A. M., Bianco, V., Calabria, G., Pisapia, R., Codella, A. V., Masullo, A., Manzillo, E., Russo, G., Parrella, R., Dell’Aquila, G., Gambardella, M., ... Coppola, N., on behalf of CoviCam Group. (2023). Obesity as a Risk Factor of Severe Outcome of COVID-19: A Pair-Matched 1:2 Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124055







