Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors with Osteomyelitis and Other Lower Limb Safety Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Analysis
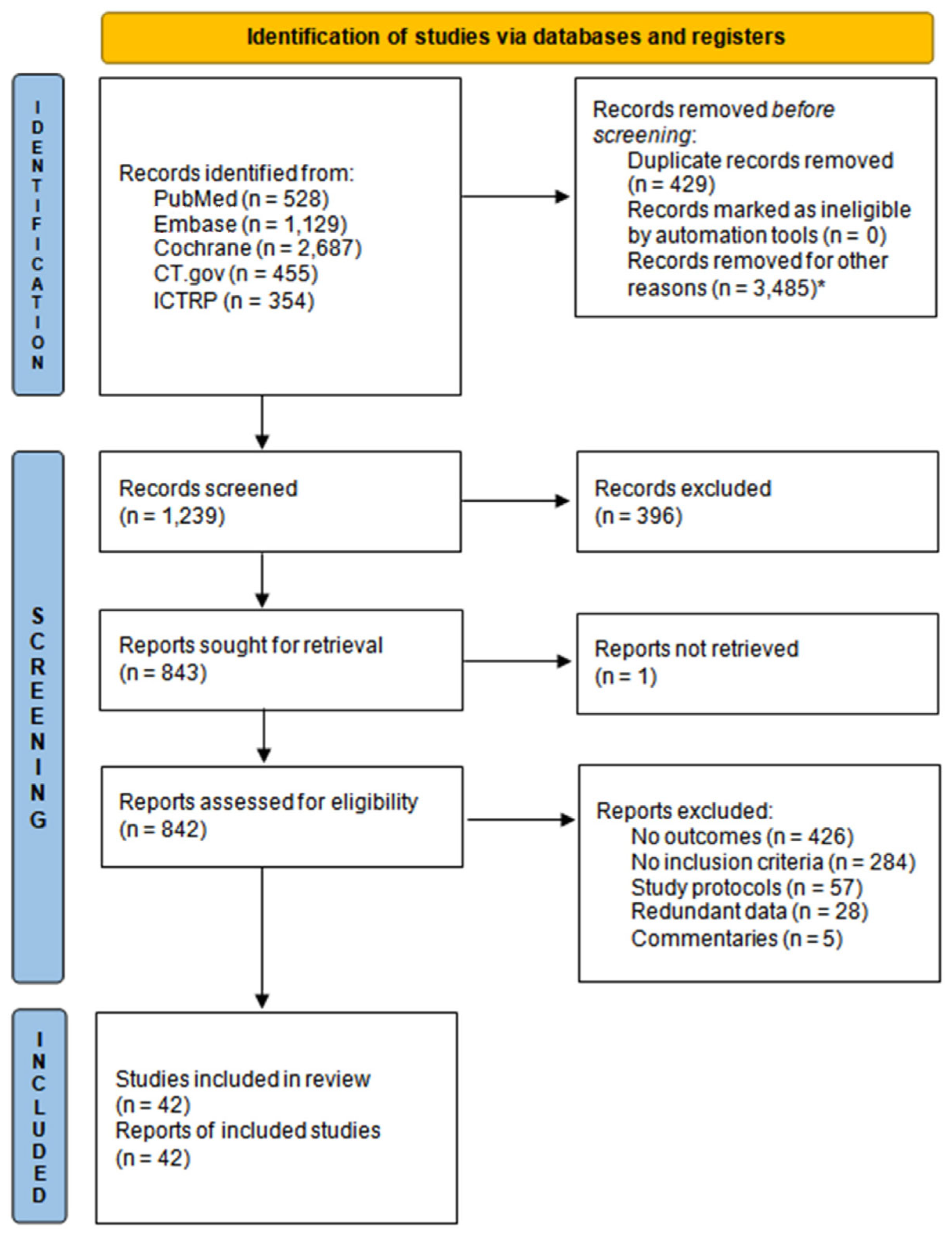
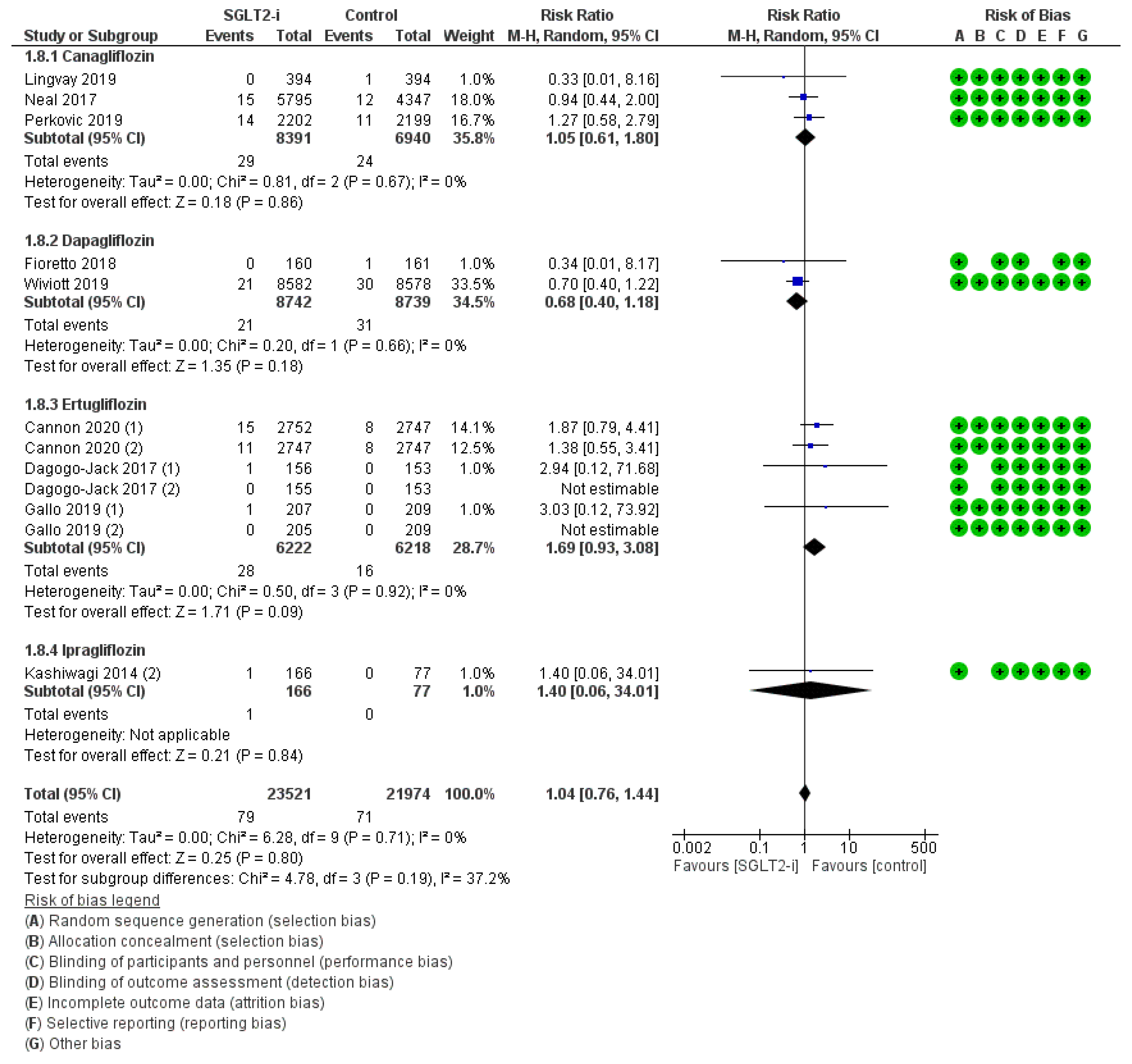
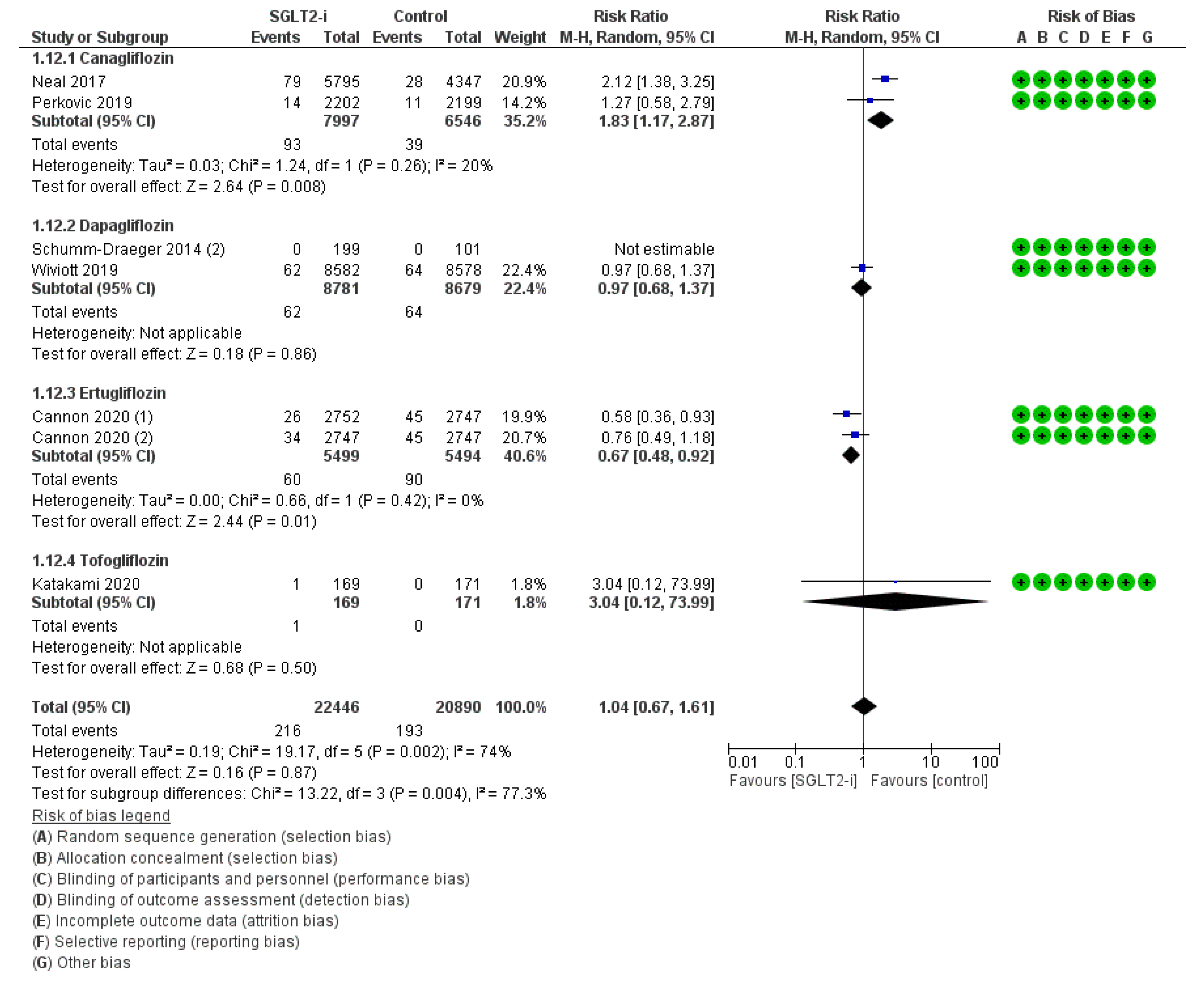
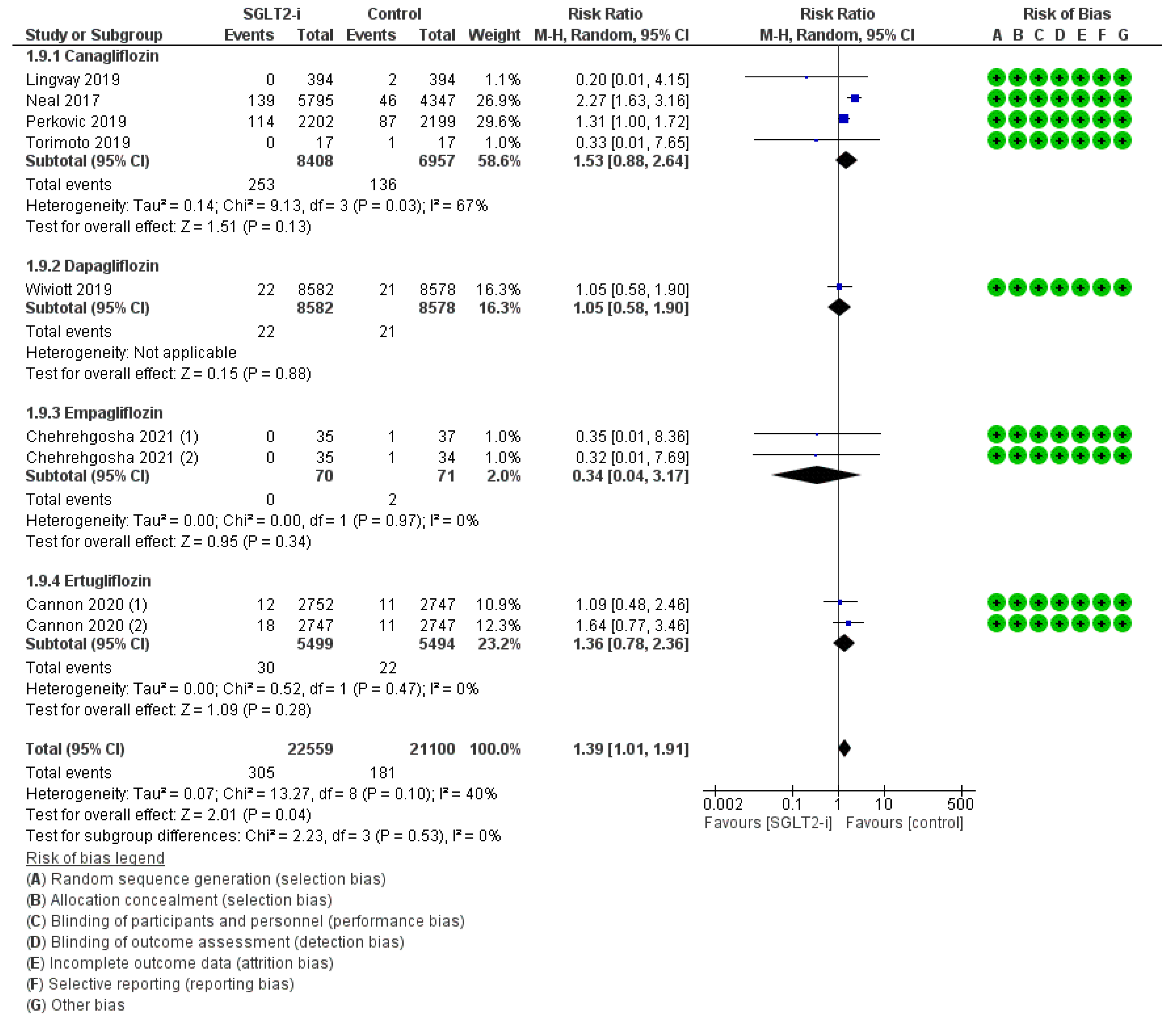
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salah, H.M.; Al’aref, S.J.; Khan, M.S.; Al-Hawwas, M.; Vallurupalli, S.; Mehta, J.L.; Mounsey, J.P.; Greene, S.J.; McGuire, D.K.; Lopes, R.D.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors initiation in patients with acute heart failure, with and without type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Efficacy and safety profile of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnan, J.R.; Grandy, C.A.; Chibrikov, E.; Marra, C.A.; Aubrey-Bassler, K.; Johnston, K.; Swab, M.; Hache, J.; Curnew, D.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Comparative safety of the sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cannon, C.P.; Pratley, R.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Mancuso, J.; Huyck, S.; Masiukiewicz, U.; Charbonnel, B.; Frederich, R.; Gallo, S.; Cosentino, F.; et al. Cardiovascular Outcomes with Ertugliflozin in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, A.Y.; Tecson, K.M.; Lee, A.Y.; Lerma, E.; Rangaswami, J.; Lepor, N.E.; Cobble, M.E.; McCullough, P.A. Class effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiorenal outcomes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.-C.; Zheng, C.-M.; Yen, T.-H.; Lu, K.-C. Molecular Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitor on Cardiorenal Protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Yuan, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X. SGLT2i: Beyond the glucose-lowering effect. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Braunwald, E. Mechanisms of Cardiorenal Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A. Effects of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors on Pancreatic β-Cell Mass and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-X.; Liang, S.; Gao, L.; Liu, H. Cardiovascular outcomes associated with SGLT-2 inhibitors versus other glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: A real-world systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrie, D.; Getnet, D.; Manyazewal, T. Cardiovascular safety and efficacy of metformin-SGLT2i versus metformin-sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahrani, A.A.; Barnett, A.H.; Bailey, C.J. SGLT inhibitors in management of diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, M.E.; Argyropoulos, C. The cardiovascular outcomes, heart failure and kidney disease trials tell that the time to use Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 inhibitors is now. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custódio, J.S., Jr.; Roriz-Filho, J.; Cavalcanti, C.A.J.; Martins, A.; Salles, J.E.N. Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Older Adults: Scientific Evidence and Practical Aspects. Drugs Aging 2020, 37, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicembrini, I.; Tomberli, B.; Nreu, B.; Baldereschi, G.I.; Fanelli, F.; Mannucci, E.; Monami, M. Peripheral artery disease and amputations with Sodium-Glucose co-Transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 153, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kremers, H.M.; Nwojo, M.E.; Ransom, J.E.; Wood-Wentz, C.M.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Huddleston, P.M., 3rd. Trends in the epidemiology of osteomyelitis: A population-based study, 1969 to 2009. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2015, 97, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akasaka, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Shintani, A.; Taniuchi, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Iwakura, K.; Okamura, A.; Takiuchi, S.; Fukuda, M.; Kamide, K.; et al. Effects of ipragliflozin on left ventricular diastolic function in patients with type 2 diabetes and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The EXCEED randomized controlled multicenter study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2022, 22, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.B.; Wang, X.; Jain, S.M.; Lee, D.S.; Nucci, G.; Rusnak, J.M. Dose-ranging efficacy and safety study of ertugliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes on a background of metformin. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Shigiyama, F.; Hirose, T.; Kumashiro, N. Simplification of complex insulin regimens using canagliflozin or liraglutide in patients with well-controlled type 2 diabetes: A 24-week randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Huh, J.H.; Lee, M.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, B.-W. Glycaemic control with add-on thiazolidinedione or a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes after the failure of an oral triple antidiabetic regimen: A 24-week, randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes.Metab. 2021, 23, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.H.; Mithal, A.; Manassie, J.; Jones, R.; Rattunde, H.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Billingsley, H.; Canada, J.M.; Bressi, E.; Ba, B.R.; Kadariya, D.; Dixon, D.L.; Markley, R.; Trankle, C.R.; Cooke, R.; et al. The effects of canagliflozin compared to sitagliptin on cardiorespiratory fitness in type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The CANA-HF study. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehrehgosha, H.; Sohrabi, M.R.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Malek, M.; Babaei, M.R.; Zamani, F.; Ajdarkosh, H.; Khoonsari, M.; Fallah, A.E.; Khamseh, M.E. Empagliflozin Improves Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 843–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, S.; Liu, J.; Eldor, R.; Amorin, G.; Bs, J.J.; Hille, D.; Liao, Y.; Huyck, S.; Golm, G.; Terra, S.G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the addition of ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin and sitagliptin: The VERTIS SITA2 placebo-controlled randomized study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, P.; Del Prato, S.; Buse, J.B.; Goldenberg, R.; Giorgino, F.; Reyner, D.; Langkilde, A.M.; Sjöström, C.D.; Sartipy, P. On Behalf of the DERIVE Study Investigators Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (chronic kidney disease stage 3A): The DERIVE Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallo, S.; Charbonnel, B.; Bs, A.G.; Shi, H.; Huyck, S.; Darekar, A.; Lauring, B.; Terra, S.G. Long-term efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy: 104-week VERTIS MET trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hollander, P.; Liu, J.; Hill, J.; Johnson, J.; Jiang, Z.W.; Golm, G.; Huyck, S.; Terra, S.G.; Mancuso, J.P.; Engel, S.S.; et al. Ertugliflozin Compared with Glimepiride in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled on Metformin: The VERTIS SU Randomized Study. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inagaki, N.; Harashima, S.-I.; Maruyama, N.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Goda, M.; Iijima, H. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with insulin: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isshiki, M.; Sakuma, I.; Hayashino, Y.; Sumita, T.; Hara, K.; Takahashi, K.; Shiojima, I.; Satoh-Asahara, N.; Kitazato, H.; Ito, D.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system under renin-angiotensin system inhibitor administration. Endocr. J. 2020, 67, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.; Omar, M.; Kistorp, C.; Poulsen, M.K.; Tuxen, C.; Gustafsson, I.; Køber, L.; Gustafsson, F.; Faber, J.; Fosbøl, E.L.; et al. Twelve weeks of treatment with empagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: A double-blinded, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial. Am. Heart J. 2020, 228, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, K.; Watada, H.; Iwamoto, Y.; Utsunomiya, K.; Terauchi, Y.; Tobe, K.; Tanizawa, Y.; Araki, E.; Ueda, M.; Suganami, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of monotherapy with the novel sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor tofogliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A combined Phase 2 and 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group comparative study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashiwagi, A.; Kazuta, K.; Takinami, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Utsuno, A.; Nagase, I. Ipragliflozin improves glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The BRIGHTEN study. Diabetol. Int. 2015, 6, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, A.; Akiyama, N.; Shiga, T.; Kazuta, K.; Utsuno, A.; Yoshida, S.; Ueyama, E. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on to a sulfonylurea in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: Results of the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase III EMIT study. Diabetol. Int. 2014, 6, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakami, N.; Mita, T.; Yoshii, H.; Shiraiwa, T.; Yasuda, T.; Okada, Y.; Torimoto, K.; Umayahara, Y.; Kaneto, H.; Osonoi, T.; et al. Tofogliflozin does not delay progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective, randomized, open-label, parallel-group comparative study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamori, R.; Haneda, M.; Suzaki, K.; Cheng, G.; Shiki, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Solimando, F.; Lee, C.; Lee, J.; George, J. Empagliflozin as add-on to linagliptin in a fixed-dose combination in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: Glycaemic efficacy and safety profile in a 52-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2200–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, T.; Seino, H.; Ohashi, H.; Inazawa, T.; Inoue, M.; Ai, M.; Fujishiro, M.; Kuroda, H.; Yamada, M.; Anai, M.; et al. Comparison of tofogliflozin versus glimepiride as the third oral agent added to metformin plus a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, 24-week, open-label, controlled trial (STOP-OB). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers Heerspink, H.J.; de Zeeuw, D.; Wie, L.; Leslie, B.; List, J. Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lingvay, I.; Catarig, A.-M.; Frias, J.P.; Kumar, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; le Roux, C.W.; Thielke, D.; Viljoen, A.; McCrimmon, R.J. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus daily canagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 8): A double-blind, phase 3b, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, S.; Krumins, T.; Zhou, H.; Huyck, S.; Johnson, J.; Golm, G.; Terra, S.G.; Mancuso, J.P.; Engel, S.S.; Lauring, B. Ertugliflozin and Sitagliptin Co-initiation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The VERTIS SITA Randomized Study. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassif, M.E.; Windsor, S.L.; Tang, F.; Khariton, Y.; Husain, M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; McGuire, D.K.; Pitt, B.; Scirica, B.M.; Austin, B.; et al. Dapagliflozin Effects on Biomarkers, Symptoms, and Functional Status in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: The DEFINE-HF Trial. Circulation 2019, 140, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palau, P.; Amiguet, M.; Domínguez, E.; Sastre, C.; Mollar, A.; Seller, J.; Pinilla, J.M.G.; Larumbe, A.; Valle, A.; Doblas, J.J.G.; et al. Short-term effects of dapagliflozin on maximal functional capacity in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (DAPA-VO 2): A randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollock, C.; Stefánsson, B.; Reyner, D.; Rossing, P.; Sjöström, C.D.; Wheeler, D.C.; Langkilde, A.M.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Albuminuria-lowering effect of dapagliflozin alone and in combination with saxagliptin and effect of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (DELIGHT): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 429–441. [Google Scholar]
- Pratley, R.E.; Eldor, R.; Raji, A.; Golm, G.; Huyck, S.B.; Qiu, Y.; Sunga, S.; Bs, J.J.; Terra, S.G.; Mancuso, J.P.; et al. Ertugliflozin plus sitagliptin versus either individual agent over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin: The VERTIS FACTORIAL randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rau, M.; Thiele, K.; Hartmann, N.-U.K.; Schuh, A.; Altiok, E.; Möllmann, J.; Keszei, A.P.; Böhm, M.; Marx, N.; Lehrke, M. Empagliflozin does not change cardiac index nor systemic vascular resistance but rapidly improves left ventricular filling pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Vico, M.; Wei, L.; Salsali, A.; List, J.F. Effects of Dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 Inhibitor, on HbA1c, Body Weight, and Hypoglycemia Risk in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled on Pioglitazone Monotherapy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sargeant, J.A.; King, J.A.; Yates, T.; Redman, E.L.; Bodicoat, D.H.; Chatterjee, S.; Edwardson, C.L.; Gray, L.J.; Poulin, B.; Waheed, G.; et al. The effects of empagliflozin, dietary energy restriction, or both on appetite-regulatory gut peptides in individuals with type 2 diabetes and overweight or obesity: The SEESAW randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm-Draeger, P.-M.; Burgess, L.; Koranyi, L.; Hruba, V.; Hamer-Maansson, J.E.; De Bruin, T.W.A. Twice-daily dapagliflozin co-administered with metformin in type 2 diabetes: A 16-week randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, H.; Kaneko, T.; Shiki, K.; Tachibana, Y.; Pfarr, E.; Lee, J.; Tajima, N. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin as add-on to insulin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spertus, J.A.; Birmingham, M.C.; Nassif, M.; Damaraju, C.V.; Abbate, A.; Butler, J.; Lanfear, D.E.; Lingvay, I.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Januzzi, J.L. The SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin in heart failure: The CHIEF-HF remote, patient-centered randomized trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Nagura, C.; Furukawa, T.; Tei, R.; Maruyama, T.; Maruyama, N.; Abe, M. Renoprotective effects of canagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease: A randomized open-label prospective trial. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torimoto, K.; Okada, Y.; Goshima, Y.; Tokutsu, A.; Sato, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Addition of canagliflozin to insulin improves glycaemic control and reduces insulin dose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2174–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: A prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Kim, J.H.; Zhao, J.; Ptaszynska, A. Dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on insulin with or without oral antihyperglycemic drugs: A randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes 2018, 10, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Han, P.; Min, K.-W.; Wang, B.; Mansfield, T.; T’Joen, C.; Iqbal, N.; Johnsson, E.; Ptaszynska, A. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes after metformin failure: A randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes 2016, 8, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, S.C.; Tendal, B.; Mustafa, R.A.; Vandvik, P.O.; Li, S.; Hao, Q.; Tunnicliffe, D.; Ruospo, M.; Natale, P.; Saglimbene, V.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2021, 372, m4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, D.K.; Shih, W.J.; Cosentino, F.; Charbonnel, B.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Pratley, R.; Greenberg, M.; Wang, S.; Huyck, S.; et al. Association of SGLT2 Inhibitors With Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaze, A.D.; Zhuo, M.; Kim, S.C.; Patorno, E.; Paik, J.M. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular, kidney, and safety outcomes among patients with diabetic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyward, J.; Mansour, O.; Olson, L.; Singh, S.; Alexander, G.C. Association between sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhib-itors and lower extremity amputation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-Y.; Singh, S.; Mansour, O.; Baksh, S.; Alexander, G.C. Association Between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Lower Extremity Amputation Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, S.K.; Bhatt, D.L.; Montvida, O. The association of amputations and peripheral artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving sodium-glucose cotransporter type-2 inhibitors: Real-world study. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-K. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and major adverse limb events: A trial-level meta-analysis including 51 713 individuals. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, S.; Gao, Y.; Ran, X. Global mortality of diabetic foot ulcer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 25, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.K.; Deeb, W.E.; Choksi, R.; Epstein, B.J. Dapagliflozin: A Novel Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Type 2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2012, 32, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

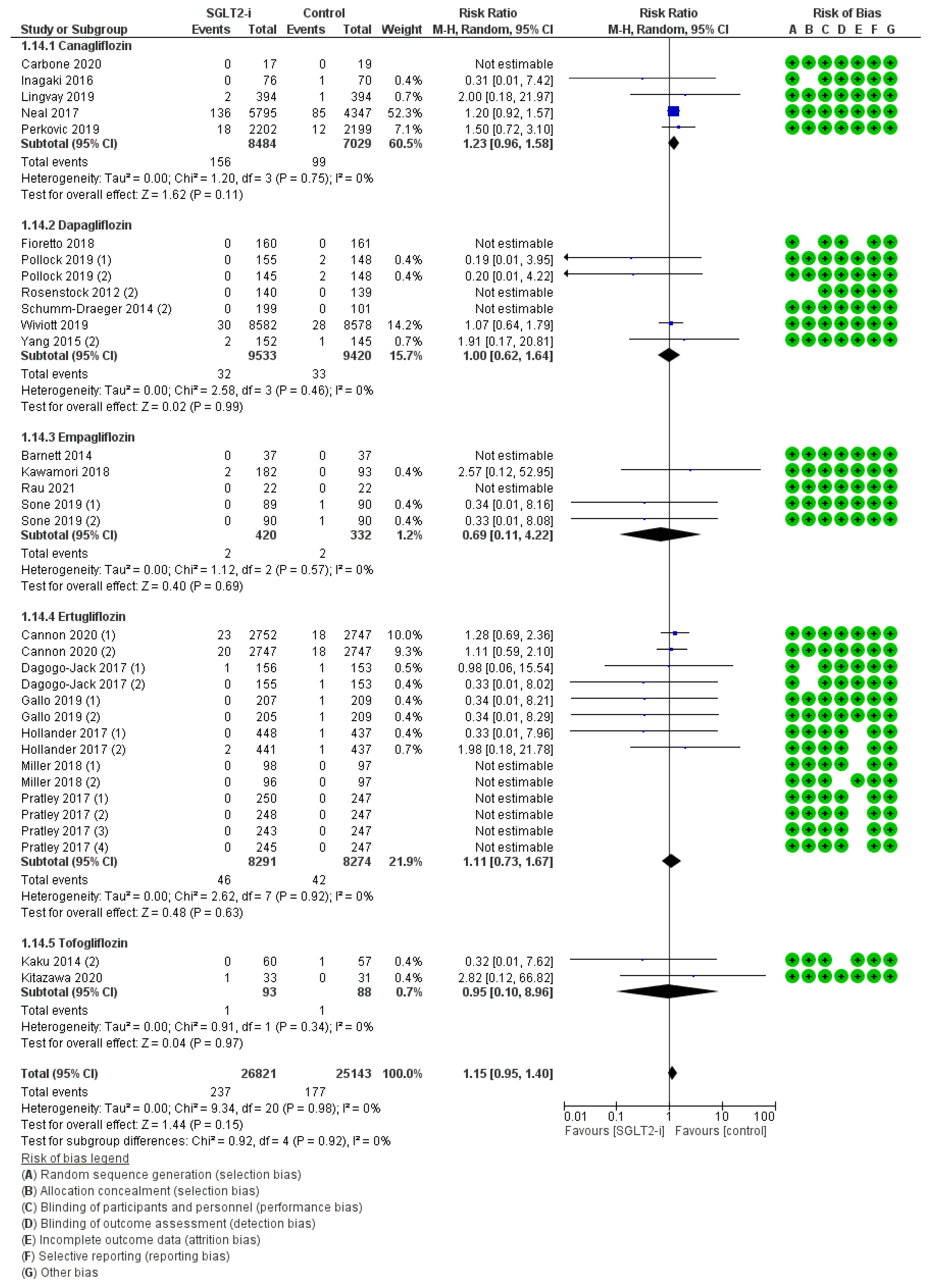
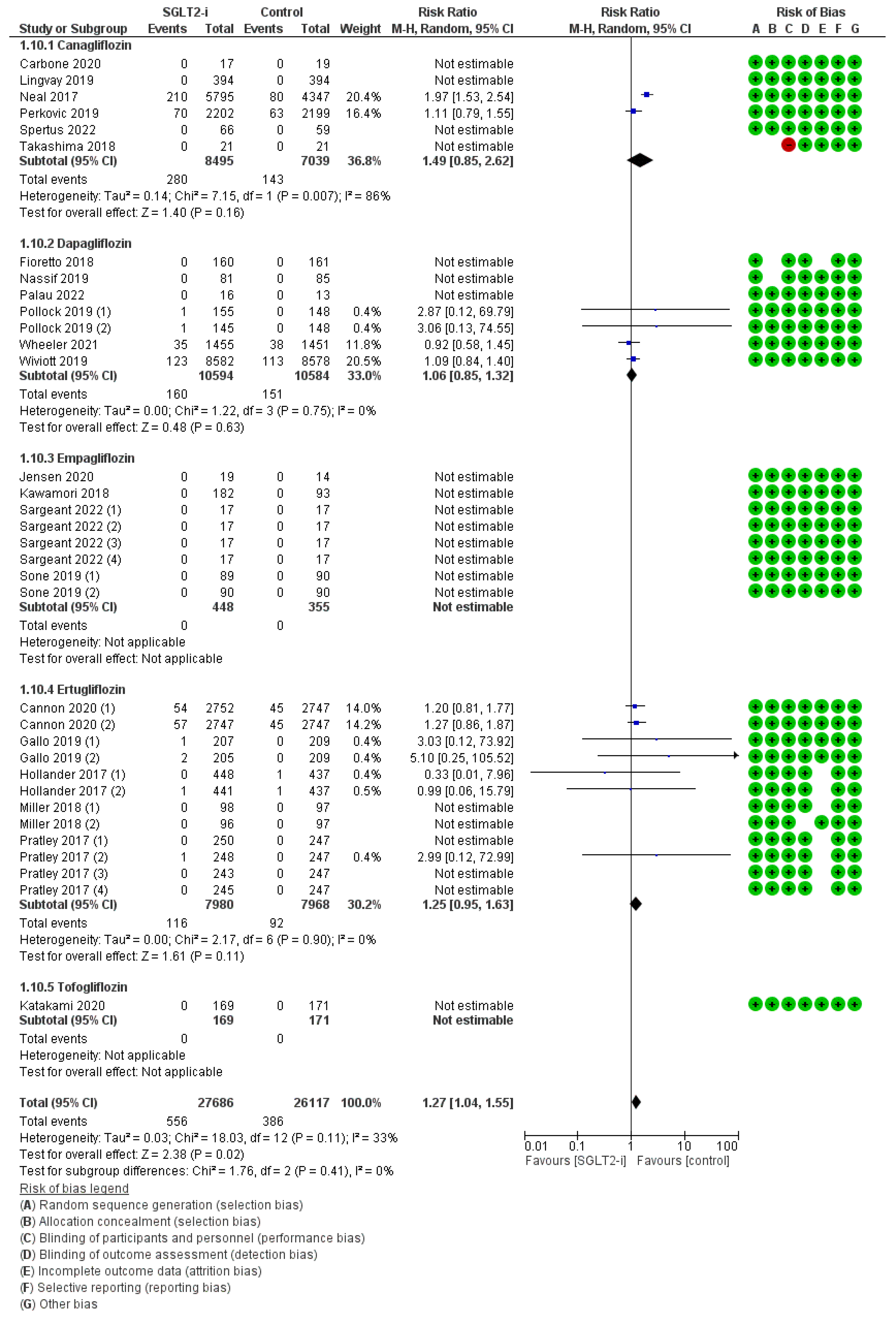
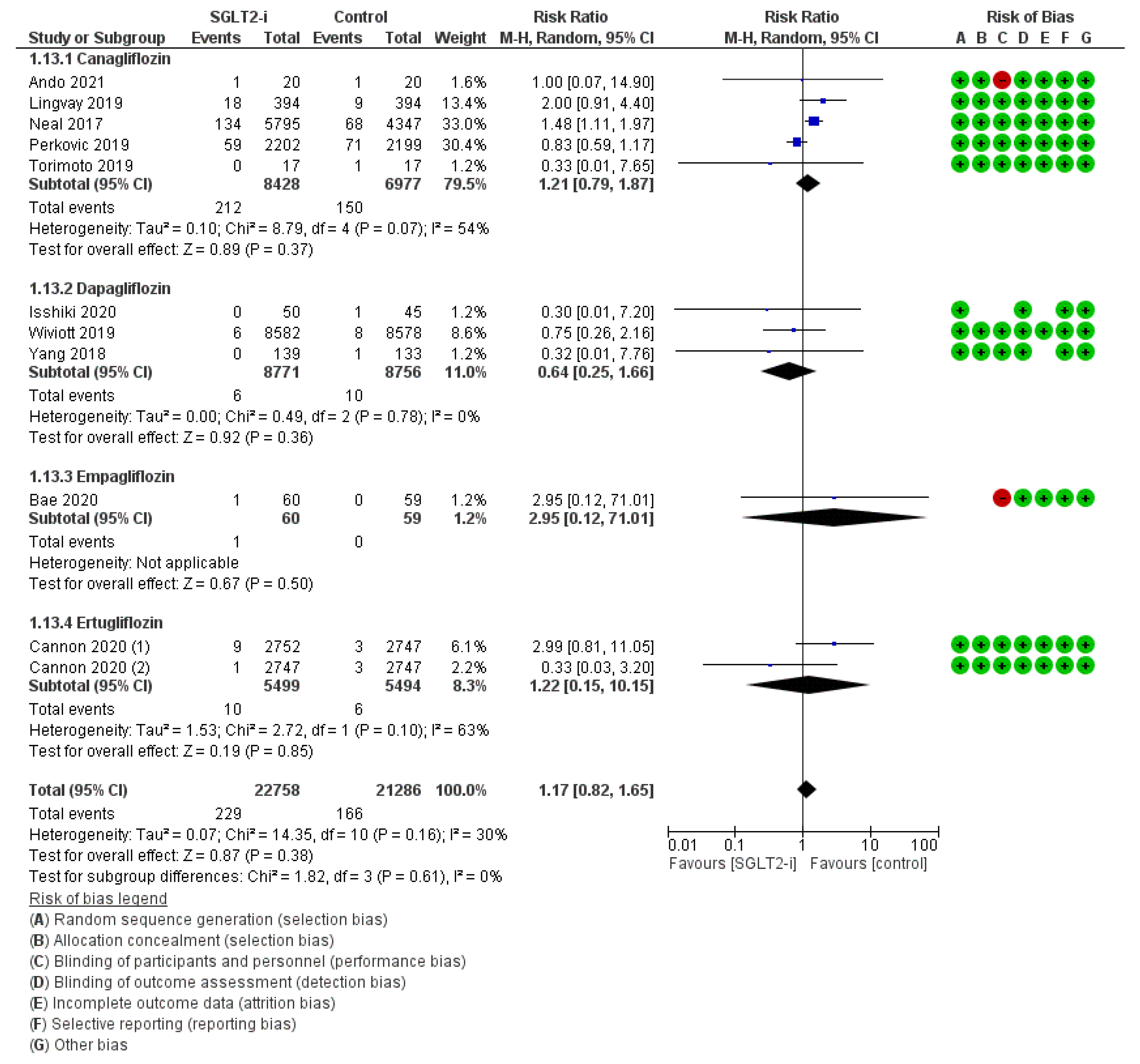
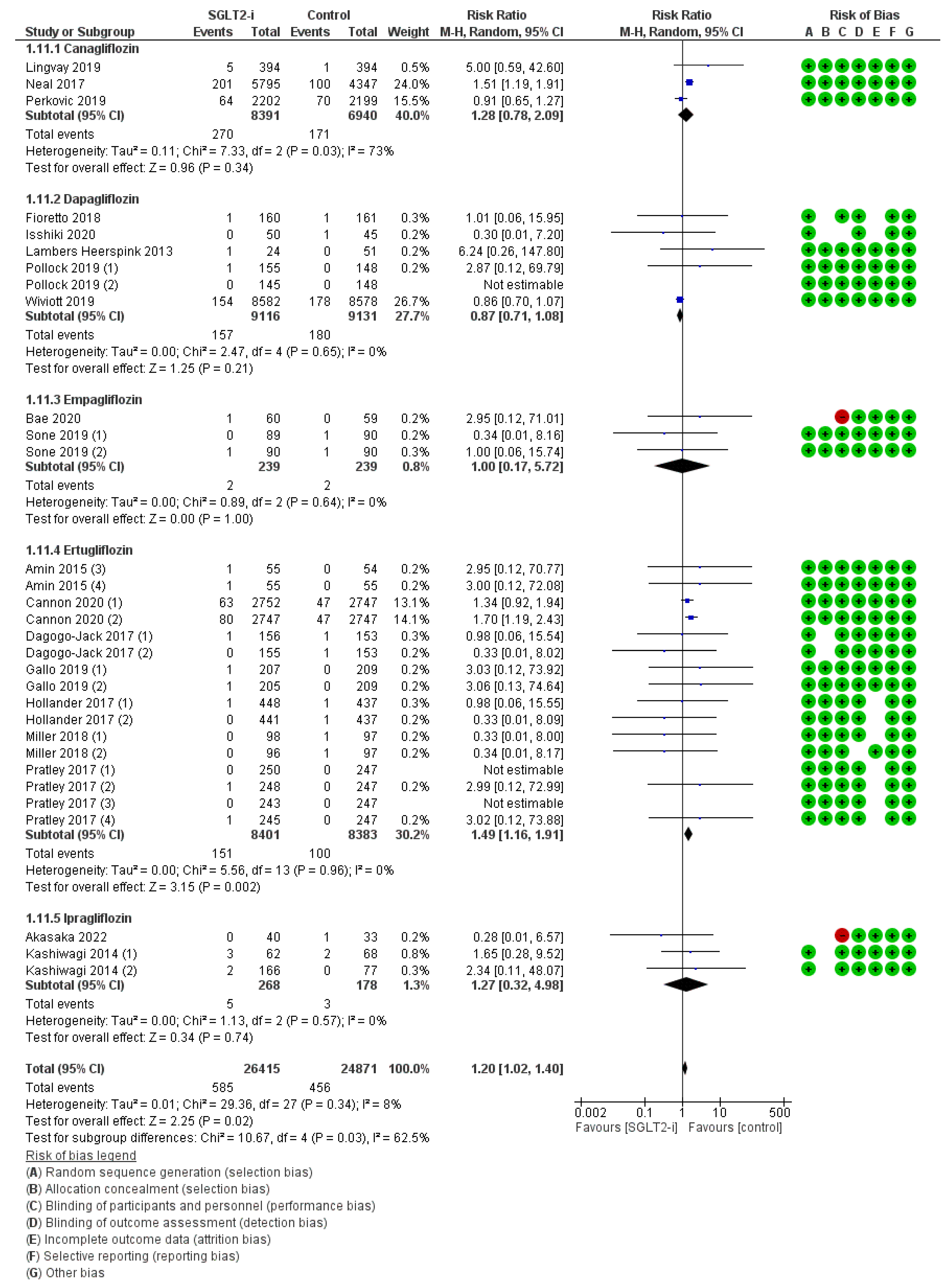
| Population | Study Type | Dates | Intervention | Participants | Controls | Osteomyelitis RR (95% CI) | Peripheral Artery Disease RR (95% CI) | Ulcers RR (95% CI) | Fractures RR (95% CI) | Amputations RR (95% CI) | Symmetric Polineuropathy RR (95% CI) | Infections RR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akasaka et al., 2022 [21] | Japanese adults with T2DM and HFpEF aged ≥20 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2017–2019 | Ipragliflozin 25 mg + Ipragliflozin50 mg | 40 | 33 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.28 (0.01–6.57) |
| Amin et al., 2015 (1)1(2)1(3)(4)(5)1(6)1(7)1(8)1 [22] | Adults with T2DM aged 18–70 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2010–2011 | Ertugliflozin 1 mg; Ertugliflozin 1 mg; Ertugliflozin 5 mg; Ertugliflozin 5 mg; Ertugliflozin 10 mg; Ertugliflozin 10 mg; Ertugliflozin 25 mg; Ertugliflozin 25 mg | 54 54 55 55 55 55 55 55 | 54 55 54 55 54 55 54 55 | NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA | NA NA 2.95 (0.12–70.77) 3.00 (0.12–72.08) NA NA NA NA |
| Ando et al., 2021 [23] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged ≥20 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2015–2018 | Canagliflozin 100 mg | 20 | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.00 (0.07–14.90) | NA |
| Bae et al., 2020 [24] | Korean adults with T2DM aged 19–80 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2019–2020 | Empagliflozin 10 mg + Empagliflozin25 mg2 | 60 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2.95 (0.12–71.01) | 2.95 (0.12–71.01) |
| Barnett et al., 2014 [25] | Adults with T2DM and CKD aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2010–2012 | Empagliflozin 25 mg | 37 | 37 | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA | NA |
| Cannon et al., 2020 (1)(2) [4] | Adults with T2DM and ACVD aged ≥40 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2013–2019 | Ertugliflozin 5 mg; Ertugliflozin 15 mg | 2752 2747 | 2747 2747 | 1.87 (0.79–4.41) 1.38 (0.55–3.41) | 0.58 (0.36–0.93) 0.76 (0.49–1.18) | 1.09 (0.48–2.46) 1.64 (0.77–3.46) | 1.28 (0.69–2.36) 1.11 (0.59–2.10) | 1.20 (0.81–1.77) 1.27 (0.86–1.87) | 2.99 (0.81–11.05) 0.33 (0.03–3.20) | 1.34 (0.92–1.94) 1.70 (1.19–2.43) |
| Carbone et al., 2020 [26] | Adults with T2DM and HFrEF aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2016–2018 | Canagliflozin 100 mg | 17 | 19 | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Chehrehgosha et al., 2021 (1)(2) [27] | Iranian adults with T2DM and NAFLD aged 20–65 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2019–2020 | Empagliflozin 10 mg; Empagliflozin 10 mg | 35 35 | 37 34 | NA NA | NA NA | 0.35 (0.01–8.36) 0.32 (0.01–7.69) | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA |
| Dagogo-Jack et al., 2017 (1)(2) [28] | Adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2014–2016 | Ertugliflozin 5 mg; Ertugliflozin 15 mg | 156 155 | 153 153 | 2.94 (0.12–71.68) NE3 | NA NA | NA NA | 0.98 (0.06–15.54) 0.33 (0.01–8.02) | NA NA | NA NA | 0.98 (0.06–15.54) 0.33 (0.01–8.02) |
| Fioretto et al., 2018 [29] | Adults with T2DM and CKD 3A aged 18–74 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2015–2017 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 160 | 161 | 0.34 (0.01–8.17) | NA | NA | NE3 | NE3 | NA | 1.01 (0.06–15.95) |
| Gallo et al., 2019 (1)(2) [30] | Adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2013–2017 | Ertugliflozin 5 mg; Ertugliflozin 15 mg | 207 205 | 209 209 | 3.03 (0.12–73.92) NE3 | NA NA | NA NA | 0.34 (0.01–8.21) 0.34 (0.01-8.29) | 3.03 (0.12-73.92) 5.10 (0.25–105.52) | NA NA | 3.03 (0.12–73.92) 3.06 (0.13–74.64) |
| Hollander et al., 2017 (1)(2) [31] | Adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2013–2016 | Ertugliflozin 5 mg; Ertugliflozin 15 mg | 448 441 | 437 437 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA | 0.33 (0.01–7.96) 1.98 (0.18–21.78) | 0.33 (0.01-7.96) 0.99 (0.06–15.79) | NA NA | 0.98 (0.06–15.55) 0.33 (0.01–8.09) |
| Inagaki et al., 2016 [32] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged ≥20 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2014–2015 | Canagliflozin 100 mg | 76 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | 0.31 (0.01–7.42) | NA | NA | NA |
| Isshiki et al., 2020 [33] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged 20–74 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2016–2019 | Dapagliflozin 5 mg4 + Dapagliflozin10 mg | 50 | 45 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.30 (0.01–7.20) | 0.30 (0.01–7.20) |
| Jensen et al., 2020 [34] | Adults with HFrEF aged 18–84 years5 | Randomised controlled trial | 2017–2020 | Empagliflozin 10 mg | 19 | 14 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Kaku et al., 2014 (1)1(2)(3)1 [35] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged 20–74 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2010–2012 | Tofogliflozin 10 mg; Tofogliflozin 20 mg; Tofogliflozin 40 mg | 59 60 59 | 57 57 57 | NA NA NA | NA NA NA | NA NA NA | NA 0.32 (0.01–7.62) NA | NA NA NA | NA NA NA | NA NA NA |
| Kashiwagi et al., 2014 (1) [36] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged ≥20 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2010 | Ipragliflozin 50 mg | 62 | 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.65 (0.28–9.52) |
| Kashiwagi et al., 2014 (2) [37] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged ≥20 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2010 | Ipragliflozin 50 mg | 166 | 77 | 1.40 (0.06–34.01) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 2.34 (0.11–48.07) |
| Katakami et al., 2020 [38] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged 30–74 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2016–2019 | Tofogliflozin 20 mg | 169 | 171 | NA | 3.04 (0.12–73.99) | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Kawamori et al., 2018 [39] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged ≥20 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2015–2017 | Empagliflozin 10 mg + Empagliflozin25 mg | 182 | 93 | NA | NA | NA | 2.57 (0.12–52.95) | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Kitazawa et al., 2020 [40] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged 20–74 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2017–2018 | Tofogliflozin 20 mg | 33 | 31 | NA | NA | NA | 2.82 (0.12–66.82) | NA | NA | NA |
| Lambers Heerspink et al., 2013 [41] | Adults with T2DM aged 18–70 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2009–2010 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 24 | 51 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6.24 (0.26–147.80) |
| Lingvay et al., 2019 [42] | Adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2017–2018 | Canagliflozin 300 mg6 + Canagliflozin 100 mg6 | 394 | 394 | 0.33 (0.01–8.16) | NA | 0.20 (0.01–4.15) | 2.00 (0.18–21.97) | NE3 | 2.00 (0.91–4.40) | 5.00 (0.59–42.60) |
| Miller et al., 2018 (1)(2) [43] | Adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2014–2016 | Ertugliflozin 5 mg + Sitagliptin 100 mg; Ertugliflozin 15 mg + Sitagliptin 100 mg | 98 96 | 97 97 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA | NE3 NE3 | NE3 NE3 | NA NA | 0.33 (0.01–8.00) 0.34 (0.01–8.17) |
| Nassif et al., 2019 [44] | Adults with HFrEF aged >185 | Randomised controlled trial | 2016–2019 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 81 | 85 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Neal et al., 2017 [7] | Adults with T2DM and ACVD aged ≥30 years OR Adults with T2DM and ≥2 CV risk factors aged ≥50 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2009–2017 | Canagliflozin 100 mg + Canagliflozin 300 mg | 5795 | 4347 | 0.94 (0.44–2.00) | 2.12 (1.38–3.25) | 2.27 (1.63–3.16) | 1.20 (0.92–1.57) | 1.97 (1.53–2.54) | 1.48 (1.11–1.97) | 1.51 (1.19–1.91) |
| Palau et al., 2022 [45] | Adults with HFrEF aged >18 years5 | Randomised controlled trial | 2019–2021 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 16 | 13 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Perkovic et al., 2019 [46] | Adults with T2DM and CKD aged ≥30 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2014–2018 | Canagliflozin 100 mg | 2202 | 2199 | 1.27 (0.58–2.79) | 1.27 (0.58–2.79) | 1.31 (1.00–1.72) | 1.50 (0.72–3.10) | 1.11 (0.79–1.55) | 0.83 (0.59–1.17) | 0.91 (0.65–1.27) |
| Pollock et al., 2019 (1)(2) [47] | Adults with T2DM and CKD aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2015–2018 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg + Saxagliptin 2.5 mg; Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 155 145 | 148 148 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA | 0.19 (0.01–3.95) 0.20 (0.01–4.22) | 2.87 (0.12–69.79) 3.06 (0.13–74.55) | NA NA | 2.87 (0.12–69.79) NE3 |
| Pratley et al., 2017 (1)(2)(3)(4) [48] | Adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2014–2016 | Ertugliflozin 5 mg; Ertugliflozin 15 mg; Ertugliflozin 5 mg + Sitagliptin 100 mg; Ertugliflozin 15 mg + Sitagliptin 100 mg | 250 248 243 245 | 247 247 247 247 | NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA | NE3 NE3 NE3 NE3 | NE3 2.99 (0.12–72.99) NE3 NE3 | NA NA NA NA | NE3 2.99 (0.12–72.99) NE3 3.02 (0.12–73.88) |
| Rau et al., 2021 [49] | Adults with T2DM aged 18–84 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2017–2019 | Empagliflozin 10 mg | 22 | 22 | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA | NA |
| Rosenstock et al., 2012 (1)1(2) [50] | Adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2008–2010 | Dapagliflozin 5 mg; Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 141 140 | 139 139 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA | NA NE3 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA |
| Sargeant et al., 2022 (1)(2)(3)(4) [51] | Adults with T2DM and BMI ≥25 kg/m2 aged 30–75 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2017–2019 | Empagliflozin 25 mg; Empagliflozin 25 mg; Empagliflozin 25 mg + ERD; Empagliflozin 25 mg + ERD | 17 17 17 17 | 17 17 17 17 | NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA | NE3 NE3 NE3 NE3 | NA NA NA NA | NA NA NA NA |
| Schumm-Draeger et al., 2014 (1)1(2) [52] | Adults with T2DM aged 18–77 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2010–2011 | Dapagliflozin 5 mg; Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 100 199 | 101 101 | NA NA | NA NE3 | NA NA | NA NE3 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA |
| Sone et al., 2019 (1)(2) [53] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged 20–74 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2015–2018 | Empagliflozin 10 mg; Empagliflozin 25 mg | 89 90 | 90 90 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA | 0.34 (0.01–8.16) 0.33 (0.01–8.08) | NE3 NE3 | NA NA | 0.34 (0.01–8.16) 1.00 (0.06–15.74) |
| Spertus et al., 2022 [54] | Adults with HF aged ≥18 years5 | Randomised controlled trial | 2020–2021 | Canagliflozin 100 mg | 66 | 59 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Takashima et al., 2018 [55] | Japanese adults with T2DM and CKD aged 20–80 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2016–2017 | Canagliflozin 100 mg | 21 | 21 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NE3 | NA | NA |
| Torimoto et al., 2019 [56] | Japanese adults with T2DM aged 18–79 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2015–2018 | Canagliflozin 100 mg | 17 | 17 | NA | NA | 0.33 (0.01–7.65) | NA | NA | 0.33 (0.01–7.65) | NA |
| Wheeler et al., 2021 [57] | Adults with proteinuric CKD aged ≥18 years5 | Randomised controlled trial | 2017–2020 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 1455 | 1451 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.92 (0.58–1.45) | NA | NA |
| Wiviott et al., 2019 [6] | Adults with T2DM and ACVD or multiple CV risk factors aged ≥40 years OR Men with T2DM and ≥1 CV risk factor aged ≥55 years OR Women with T2DM and ≥1 CV risk factor aged ≥60 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2013–2018 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 8582 | 8578 | 0.70 (0.40–1.22) | 0.97 (0.68–1.37) | 1.05 (0.58–1.90) | 1.07 (0.64–1.79) | 1.09 (0.84–1.40) | 0.75 (0.26–2.16) | 0.86 (0.70–1.07) |
| Yang et al., 2018 [58] | Asian adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2014–2016 | Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 139 | 133 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.32 (0.01–7.76) | NA |
| Yang et al., 2015 (1)1(2) [59] | Asian adults with T2DM aged ≥18 years | Randomised controlled trial | 2010–2013 | Dapagliflozin 5 mg; Dapagliflozin 10 mg | 147 152 | 145 145 | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA | NA 1.91 (0.17–20.81) | NA NA | NA NA | NA NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nani, A.; Carrara, F.; Paulesu, C.M.E.; Dalle Fratte, C.; Padroni, M.; Enisci, S.; Bilancio, M.C.; Romio, M.S.; Bertuzzi, F.; Pintaudi, B. Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors with Osteomyelitis and Other Lower Limb Safety Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123958
Nani A, Carrara F, Paulesu CME, Dalle Fratte C, Padroni M, Enisci S, Bilancio MC, Romio MS, Bertuzzi F, Pintaudi B. Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors with Osteomyelitis and Other Lower Limb Safety Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123958
Chicago/Turabian StyleNani, Alessandro, Federica Carrara, Chiara Maria Eleonora Paulesu, Chiara Dalle Fratte, Matteo Padroni, Silvia Enisci, Maria Concetta Bilancio, Maria Silvia Romio, Federico Bertuzzi, and Basilio Pintaudi. 2023. "Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors with Osteomyelitis and Other Lower Limb Safety Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123958
APA StyleNani, A., Carrara, F., Paulesu, C. M. E., Dalle Fratte, C., Padroni, M., Enisci, S., Bilancio, M. C., Romio, M. S., Bertuzzi, F., & Pintaudi, B. (2023). Association of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors with Osteomyelitis and Other Lower Limb Safety Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123958







