Prediction of Survival and Prognosis Migration from Gold-Standard Scores in Myelofibrosis Patients Treated with Ruxolitinib Applying the RR6 Prognostic Model in a Monocentric Real-Life Setting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Baseline Features
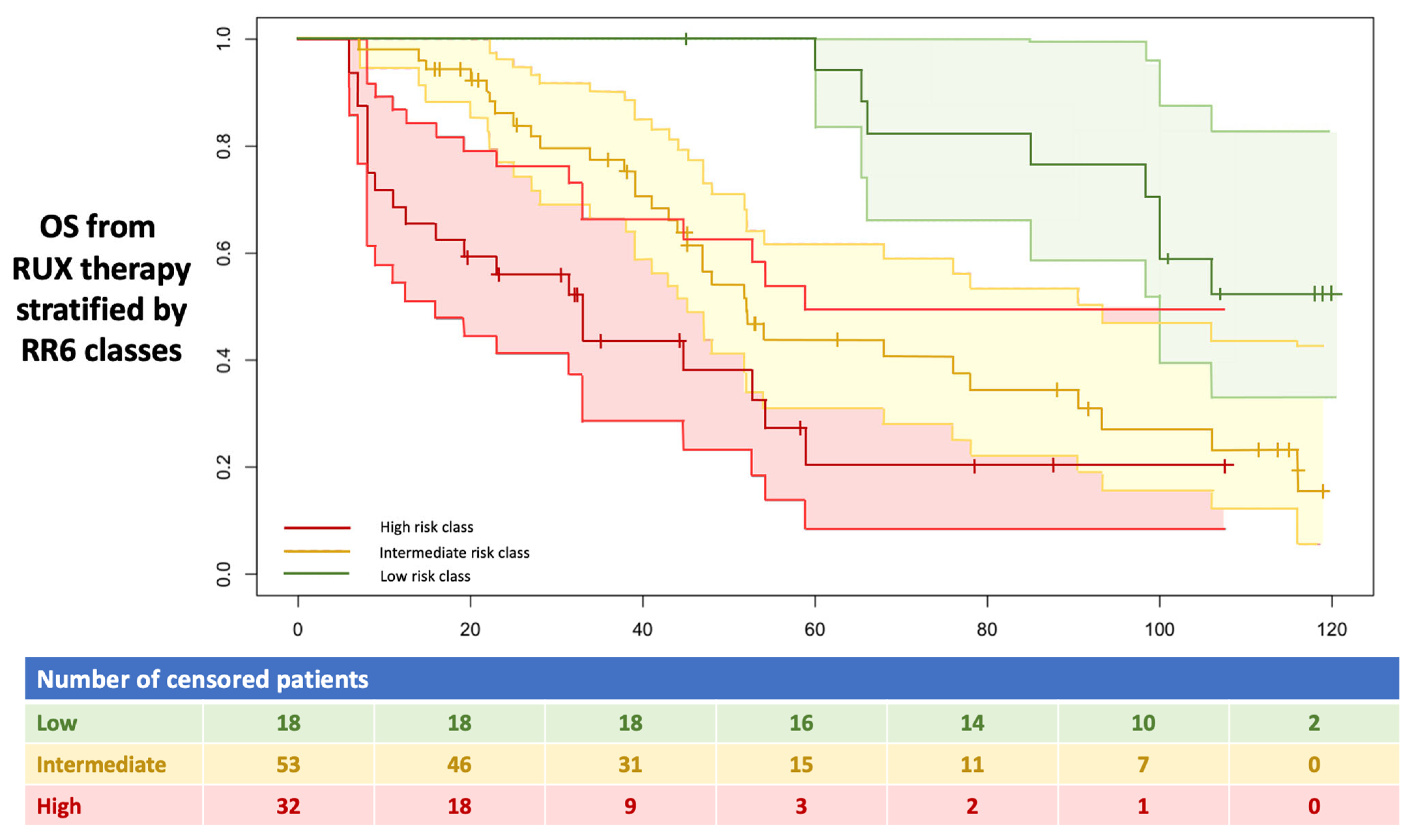
3.2. Patient Outcomes
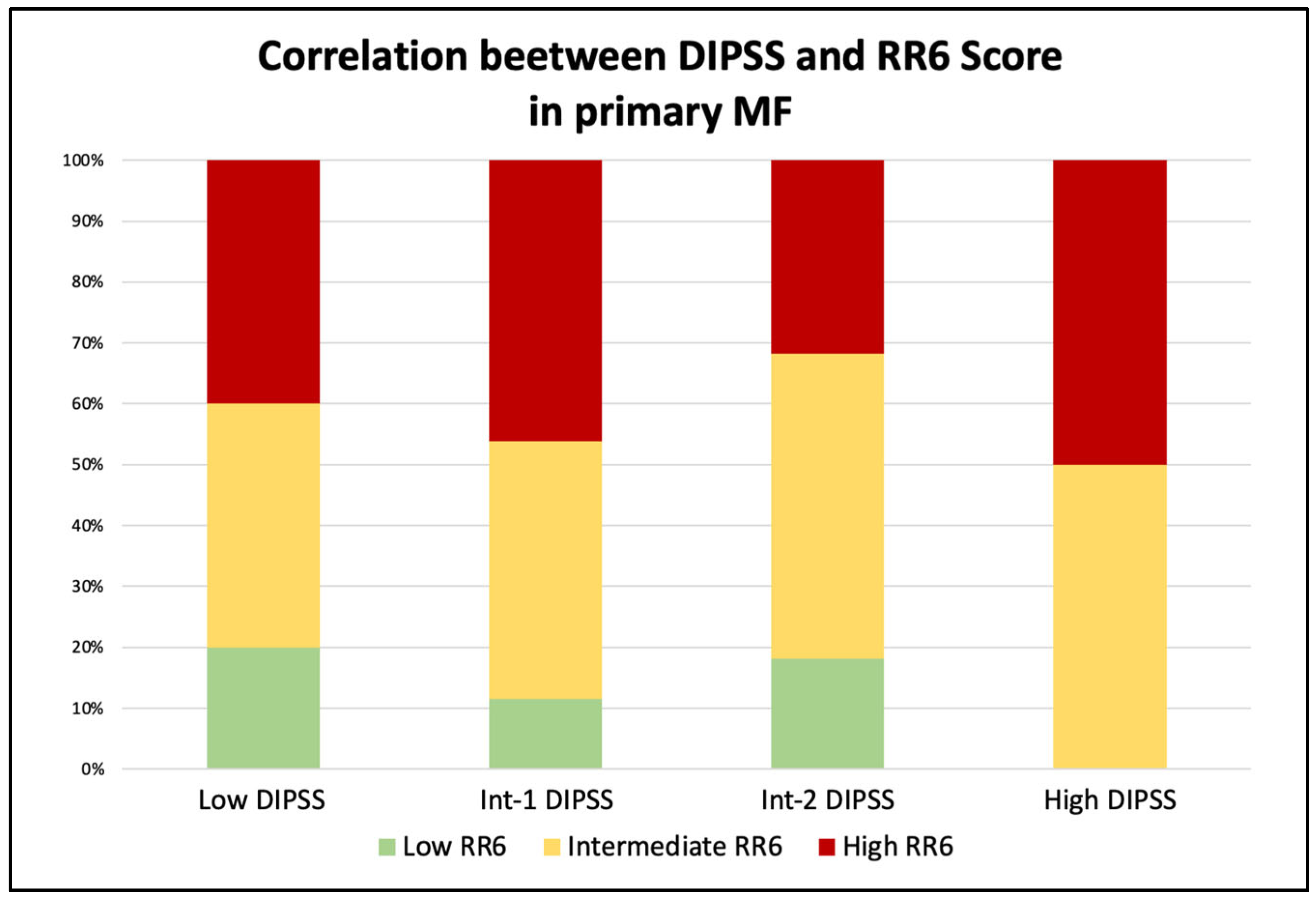
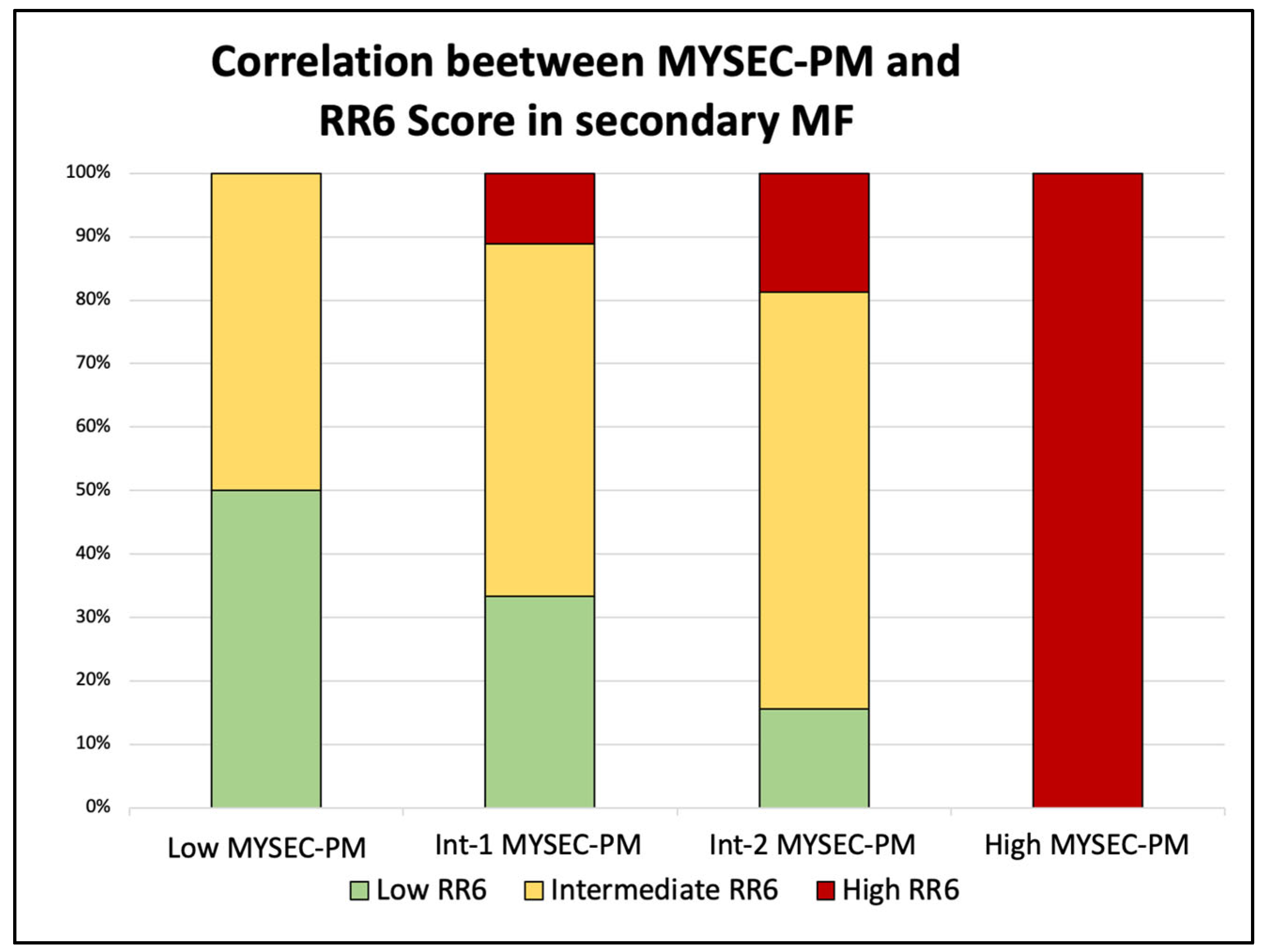
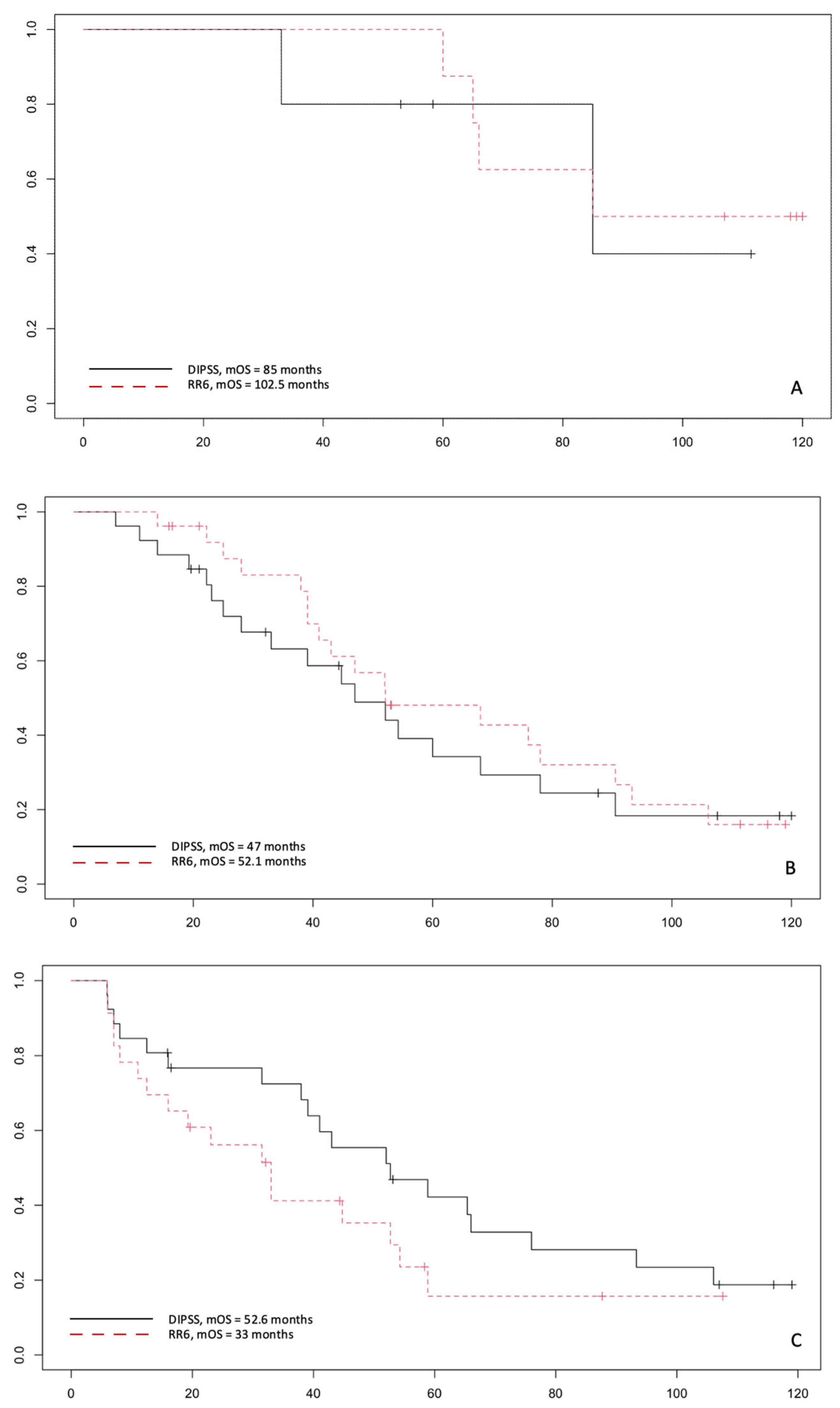
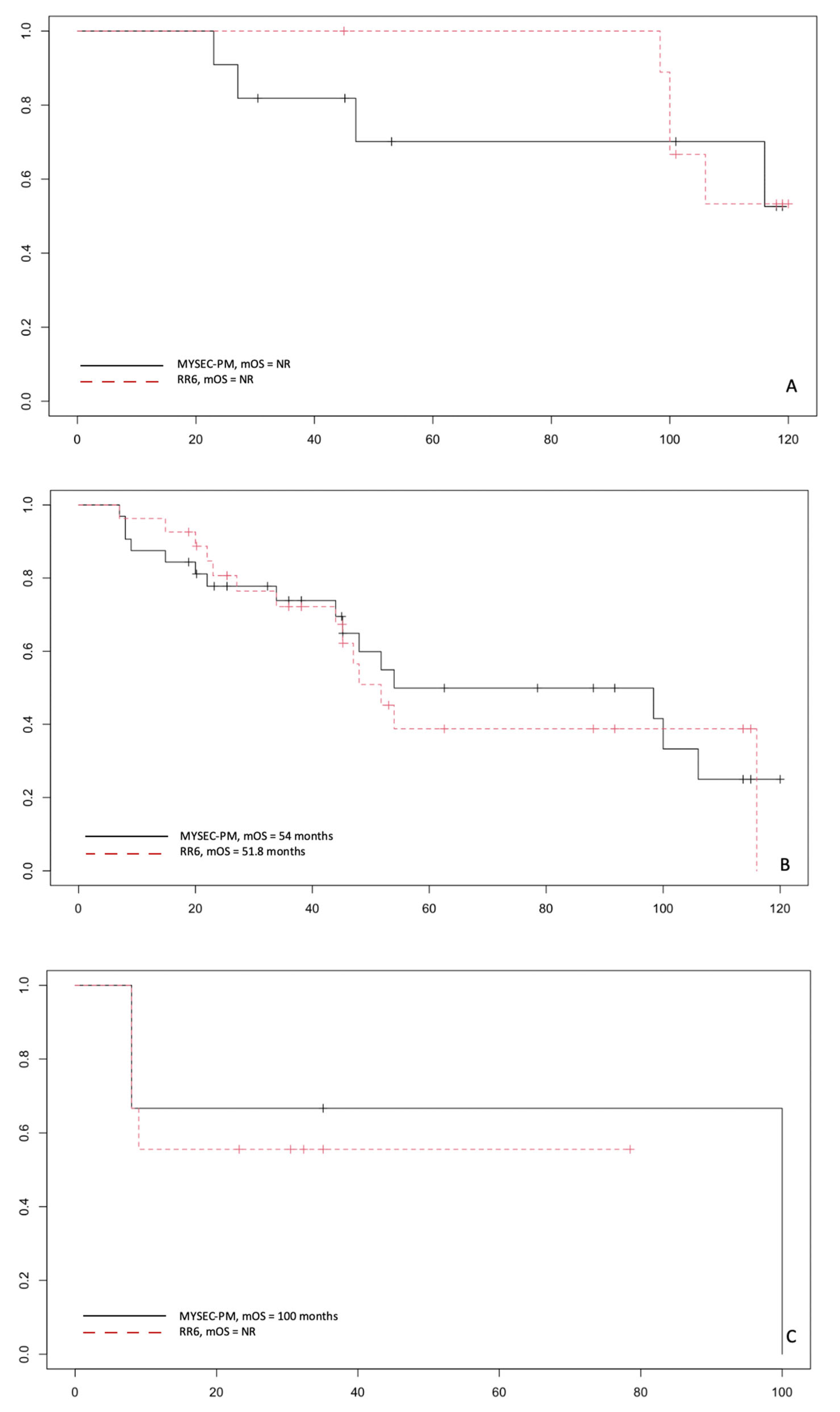
3.3. Correlation by RR6 Risk Classes with DIPSS and MYSEC-PM with OS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tefferi, A.; Lasho, T.L.; Jimma, T.; Finke, C.M.; Gangat, N.; Vaidya, R.; Begna, K.H.; Al-Kali, A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Hanson, C.A.; et al. One Thousand Patients With Primary Myelofibrosis: The Mayo Clinic Experience. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumi, E.; Pietra, D.; Pascutto, C.; Guglielmelli, P.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Casetti, I.; Colomer, D.; Pieri, L.; Pratcorona, M.; Rotunno, G.; et al. Clinical Effect of Driver Mutations of JAK2, CALR, or MPL in Primary Myelofibrosis. Blood 2014, 124, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masarova, L.; Bose, P.; Daver, N.; Pemmaraju, N.; Newberry, K.J.; Manshouri, T.; Cortes, J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Verstovsek, S. Patients with Post-Essential Thrombocythemia and Post-Polycythemia Vera Differ from Patients with Primary Myelofibrosis. Leuk. Res. 2017, 59, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Guglielmelli, P.; Biamonte, F.; Pardanani, A.; Pereira, A.; Finke, C.; Score, J.; Gangat, N.; Mannarelli, C.; et al. Mutations and Prognosis in Primary Myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, F.; Dupriez, B.; Pereira, A.; Passamonti, F.; Reilly, J.T.; Morra, E.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Mesa, R.A.; Demory, J.L.; Barosi, G.; et al. New Prognostic Scoring System for Primary Myelofibrosis Based on a Study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood 2009, 113, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, F.; Cervantes, F.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Morra, E.; Rumi, E.; Pereira, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Pungolino, E.; Caramella, M.; Maffioli, M.; et al. A Dynamic Prognostic Model to Predict Survival in Primary Myelofibrosis: A Study by the IWG-MRT (International Working Group for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment). Blood 2010, 115, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangat, N.; Caramazza, D.; Vaidya, R.; George, G.; Begna, K.; Schwager, S.; van Dyke, D.; Hanson, C.; Wu, W.; Pardanani, A.; et al. DIPSS plus: A Refined Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System for Primary Myelofibrosis That Incorporates Prognostic Information from Karyotype, Platelet Count, and Transfusion Status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, F.; Giorgino, T.; Mora, B.; Guglielmelli, P.; Rumi, E.; Maffioli, M.; Rambaldi, A.; Caramella, M.; Komrokji, R.; Gotlib, J.; et al. A Clinical-Molecular Prognostic Model to Predict Survival in Patients with Post Polycythemia Vera and Post Essential Thrombocythemia Myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2726–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Gisslinger, H.; Waltzman, R.; Stalbovskaya, V.; McQuitty, M.; Hunter, D.S.; Levy, R.; Knoops, L.; et al. JAK Inhibition with Ruxolitinib versus Best Available Therapy for Myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Baratè, C.; Benevolo, G.; Bonifacio, M.; Elli, E.M.; Guglielmelli, P.; Maffioli, M.; Malato, A.; Mendicino, F.; Palumbo, G.A.; et al. Tracing the Decision-Making Process for Myelofibrosis: Diagnosis, Stratification, and Management of Ruxolitinib Therapy in Real-Word Practice. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palandri, F.; Tiribelli, M.; Benevolo, G.; Tieghi, A.; Cavazzini, F.; Breccia, M.; Bergamaschi, M.; Sgherza, N.; Polverelli, N.; Crugnola, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Ruxolitinib in Intermediate-1 IPSS Risk Myelofibrosis Patients: Results from an Independent Study. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palandri, F.; Palumbo, G.A.; Iurlo, A.; Polverelli, N.; Benevolo, G.; Breccia, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Tiribelli, M.; Bonifacio, M.; Tieghi, A.; et al. Differences in Presenting Features, Outcome and Prognostic Models in Patients with Primary Myelofibrosis and Post-Polycythemia Vera and/or Post-Essential Thrombocythemia Myelofibrosis Treated with Ruxolitinib. New Perspective of the MYSEC-PM in a Large Multicenter Study. Semin. Hematol. 2018, 55, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ali, H.K.; Griesshammer, M.; Foltz, L.; Palumbo, G.A.; Martino, B.; Palandri, F.; Liberati, A.M.; le Coutre, P.; García-Hernández, C.; Zaritskey, A.; et al. Primary Analysis of JUMP, a Phase 3b, Expanded-Access Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Ruxolitinib in Patients with Myelofibrosis, Including Those with Low Platelet Counts. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstovsek, S.; Mesa, R.A.; Gotlib, J.; Levy, R.S.; Gupta, V.; DiPersio, J.F.; Catalano, J.V.; Deininger, M.; Miller, C.; Silver, R.T.; et al. A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Ruxolitinib for Myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palandri, F.; Breccia, M.; Bonifacio, M.; Polverelli, N.; Elli, E.M.; Benevolo, G.; Tiribelli, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Iurlo, A.; Heidel, F.H.; et al. Life after Ruxolitinib: Reasons for Discontinuation, Impact of Disease Phase, and Outcomes in 218 Patients with Myelofibrosis. Cancer 2020, 126, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffioli, M.; Mora, B.; Ball, S.; Iurlo, A.; Elli, E.M.; Finazzi, M.C.; Polverelli, N.; Rumi, E.; Caramella, M.; Carraro, M.C.; et al. A Prognostic Model to Predict Survival after 6 Months of Ruxolitinib in Patients with Myelofibrosis. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalzulli, E.; Ielo, C.; Luise, C.; Musiu, P.; Bisegna, M.L.; Carmosino, I.; Assanto, G.M.; Martelli, M.; Breccia, M. RR6 Prognostic Model Provides Information about Survival for Myelofibrosis Treated with Ruxolitinib: Validation in a Real-Life Cohort. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4424–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecien, R.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Blettner, M. Concordance Analysis: Part 16 of a Series on Evaluation of Scientific Publications. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2011, 108, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed Taherdoost, A.; Lumpur, K. Validity and Reliability of the Research Instrument; How to Test the Validation of a Questionnaire/Survey in a Research. Int. J. Acad. Res. Manag. 2016, 5, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Mascarenhas, J.; Kremyanskaya, M.; Rampal, R.K.; Talpaz, M.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Vannucchi, A.; Verstovsek, S.; Colak, G.; Dey, D.; et al. MPN-379 Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison (MAIC) of Pelabresib (CPI-0610) in Combination With Ruxolitinib vs. JAK Inhibitor Monotherapy in Patients With Intermediate or High-Risk Myelofibrosis. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22 (Suppl. S2), S336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chifotides, H.T.; Verstovsek, S. EXABS-164-MPN Novel Therapeutics in Development for Myelofibrosis. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22 (Suppl. S2), S72–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerds, A.; Verstovsek, S.; Vannucchi, A.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Lavie, D.; Kuykendall, A.; Grosicki, S.; Iurlo, A.; Goh, Y.T.; Lazaroiu, M.; et al. MPN-483 Thrombocytopenic Myelofibrosis (MF) Patients Previously Treated With a JAK Inhibitor in a Phase 3 Randomized Study of Momelotinib (MMB) versus Danazol (DAN) [MOMENTUM]. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 2 (Suppl. S2), S340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, M.; Quek, L.; Psaila, B. The Immune Landscape in BCR-ABL Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Inflammation, Infections and Opportunities for Immunotherapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loscocco, G.G.; Vannucchi, A.M. Role of JAK Inhibitors in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Current Point of View and Perspectives. Int. J. Hematol. 2022, 115, 626–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| At RUX Treatment Start | |
|---|---|
| Median age, years (range) | 69.4 (38–83) |
| Sex M/F, n (%) | 62 (60.2)/41 (39.8) |
| PMF, n (%) | 57 (55.4) |
| SMF, n (%) | 46 (44.7) |
| PET-MF, n (%) | 22 (21.4) |
| PPV-MF, n (%) | 24 (23.3) |
| BM fibrosis grade 0/1/2/3, n (%) | 1 (0.9)/39 (37.9)/46 (44.7)/17 (16.5) |
| Mutation status | |
| JAK2-mutated, n (%) | 80 (77.7) |
| CALR-mutated, n (%) | 15 (14.6) |
| MPL-mutated, n (%) | 3 (1.9) |
| ‘Triple negative’, n (%) | 6 (5.8) |
| Normal/abnormal karyotype, n (%) | 98 (95.2)/5 (4.8) |
| PMF, DIPSS LR/Int-1/Int-2/HR-n (% of PMF patients) | 0 (0)/15 (26.3)/32 (56.2)/10 (17.5) |
| SMF, MYSEC-PM LR/int-1/int-2/HR-n (% of SMF patients) | 0 (0)/16 (34.8)/19 (41.3)/11 (23.9) |
| Median WBC, × 109/L (IQR) | 11.6 (7.8–20.3) |
| Median Hb (g/dL) (IQR) | 10.8 (8.7–13) |
| Median PLT × 109/L (IQR) | 371 (220–554) |
| Presence of 1–2% blasts in PB, n (%) | 4 (3.9) |
| Constitutional symptoms Y/N, n (%) | 87 (84.5)/16 (15.5) |
| Median palpable splenomegaly, cm below LCM (IQR) | 8 (4–10) |
| RBC transfusions 3 months before RUX start Y/N-n (%) | 29 (28.1)/74 (71.9) |
| RUX dose 5 mg BID, i.e., 10 mg total daily dose n (%) | 7 (6.8) |
| RUX dose 10 mg BID, i.e., 20 mg total daily dose n (%) | 10 (9.7) |
| RUX dose 15 mg BID, i.e., 30 mg total daily dose n (%) | 21 (2.4) |
| RUX dose 20 mg BID, i.e., 40 mg total daily dose n (%) | 65 (63.1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duminuco, A.; Nardo, A.; Garibaldi, B.; Vetro, C.; Longo, A.; Giallongo, C.; Di Raimondo, F.; Palumbo, G.A. Prediction of Survival and Prognosis Migration from Gold-Standard Scores in Myelofibrosis Patients Treated with Ruxolitinib Applying the RR6 Prognostic Model in a Monocentric Real-Life Setting. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7418. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247418
Duminuco A, Nardo A, Garibaldi B, Vetro C, Longo A, Giallongo C, Di Raimondo F, Palumbo GA. Prediction of Survival and Prognosis Migration from Gold-Standard Scores in Myelofibrosis Patients Treated with Ruxolitinib Applying the RR6 Prognostic Model in a Monocentric Real-Life Setting. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7418. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247418
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuminuco, Andrea, Antonella Nardo, Bruno Garibaldi, Calogero Vetro, Anna Longo, Cesarina Giallongo, Francesco Di Raimondo, and Giuseppe A. Palumbo. 2022. "Prediction of Survival and Prognosis Migration from Gold-Standard Scores in Myelofibrosis Patients Treated with Ruxolitinib Applying the RR6 Prognostic Model in a Monocentric Real-Life Setting" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7418. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247418
APA StyleDuminuco, A., Nardo, A., Garibaldi, B., Vetro, C., Longo, A., Giallongo, C., Di Raimondo, F., & Palumbo, G. A. (2022). Prediction of Survival and Prognosis Migration from Gold-Standard Scores in Myelofibrosis Patients Treated with Ruxolitinib Applying the RR6 Prognostic Model in a Monocentric Real-Life Setting. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7418. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247418








