The Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Analyse the SARD patient population with COVID-19 in terms of baseline characteristics, severity, course and outcomes of the disease and compare it with non-SARD group results;
- Identify factors associated with prognosis;
- Assess the effect of remdesivir therapy on the course of COVID-19 in patients with SARD.
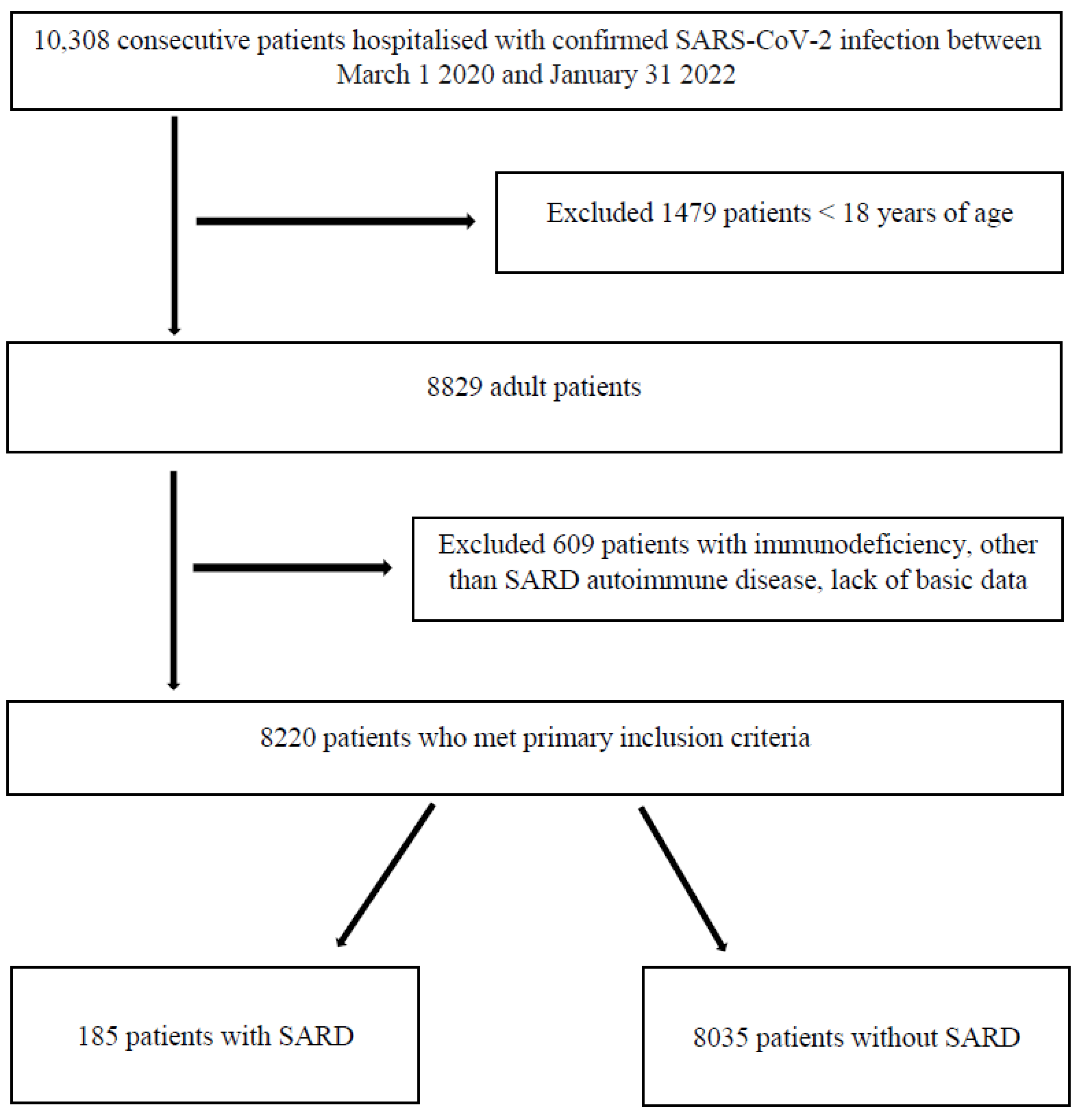
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SARD Basic Characteristics
3.2. SARD versus Non-SARD Comparison
3.3. Remdesivir Treatment in SARD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Data Explorer. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/explorers/coronavirus-data-explorer (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- Harrison, A.G.; Lin, T.; Wang, P. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 1100–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Sathi, N.J. Risk Factors of the Severity of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Rogalska, M.; Lorenc, B.; Rorat, M.; Szymanek-Pasternak, A.; Piekarska, A.; Berkan-Kawińska, A.; Sikorska, K.; Tudrujek-Zdunek, M.; et al. Impact of Kidney Failure on the Severity of COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, A.M.; Burns, S.O.; Savic, S.; Richter, A.G. UK PIN COVID-19 Consortium COVID-19 in Patients with Primary and Secondary Immunodeficiency: The United Kingdom Experience. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 870–875.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.H.; Sena, A.G.; Prats-Uribe, A.; You, S.C.; Ahmed, W.-U.-R.; Kostka, K.; Reich, C.; Duvall, S.L.; Lynch, K.E.; Matheny, M.E.; et al. COVID-19 in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases: Characteristics and Outcomes in a Multinational Network of Cohorts across Three Countries. Rheumatology 2021, 60, SI37–SI50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flisiak, R.; Horban, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kozielewicz, D.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Owczuk, R.; Parczewski, M.; Pawłowska, M.; Piekarska, A.; Simon, K.; et al. Management of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Recommendations of the Polish Association of Epidemiologists and Infectiologists as of April 26, 2021. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2021, 131, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yi, Z.; Cai, R.; Chen, R.; Thong, B.Y.-H.; Mu, R. Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Global Data. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakota, K.; Perdan-Pirkmajer, K.; Hočevar, A.; Sodin-Semrl, S.; Rotar, Ž.; Čučnik, S.; Žigon, P. COVID-19 in Association with Development, Course, and Treatment of Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 611318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, G.A.; Christensen, A.B.; Pusch, T.; Goulet, D.; Chang, S.-C.; Grunkemeier, G.L.; McKelvey, P.A.; Robicsek, A.; French, T.; Parsons, G.T.; et al. Remdesivir and Mortality in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, E.; Chandak, A.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, S.; Thrun, M.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Sax, P.E.; Wohl, D.A.; Casciano, R.; et al. Remdesivir Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Comparative Analysis of in-Hospital All-Cause Mortality in a Large Multi-Center Observational Cohort. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 2021, ciab875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flisiak, R.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Berkan-Kawińska, A.; Tudrujek-Zdunek, M.; Rogalska, M.; Piekarska, A.; Kozielewicz, D.; Kłos, K.; Rorat, M.; Bolewska, B.; et al. Remdesivir-Based Therapy Improved the Recovery of Patients with COVID-19 in the Multicenter, Real-World SARSTer Study. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2021, 131, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.E.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric Preprocessing for Parametric Causal Inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, M.; Fuzzi, E.; Astorri, D.; Saccon, F.; Padoan, R.; Ienna, L.; Cozzi, G.; Depascale, R.; Zanatta, E.; Gasparotto, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases in Northeast Italy: A Cross-Sectional Study on 916 Patients. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 112, 102502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmi, G.; Bettiol, A.; Mattioli, I.; Silvestri, E.; Di Scala, G.; Urban, M.L.; Vaglio, A.; Prisco, D. SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favalli, E.G.; Monti, S.; Ingegnoli, F.; Balduzzi, S.; Caporali, R.; Montecucco, C. Incidence of COVID-19 in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Targeted Immunosuppressive Drugs: What Can We Learn from Observational Data? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartuccio, L.; Valent, F.; Pasut, E.; Tascini, C.; De Vita, S. Prevalence of COVID-19 among Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Biologic Agents or Small Molecules: A Population-Based Study in the First Two Months of COVID-19 Outbreak in Italy. Jt. Bone Spine 2020, 87, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, S.; Hamdeh, S.; Micic, D.; Sakuraba, A. Prevalence and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, R.; Kim, A.H.J.; Conway, R.; Yazdany, J.; Robinson, P.C. COVID-19 in People with Rheumatic Diseases: Risks, Outcomes, Treatment Considerations. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Silva, K.M.; Serling-Boyd, N.; Wallwork, R.; Hsu, T.; Fu, X.; Gravallese, E.M.; Choi, H.K.; Sparks, J.A.; Wallace, Z.S. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Rheumatic Disease: A Comparative Cohort Study from a US “Hot Spot”. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, J.L.; Galindo, M.; Carmona, L.; Lledó, A.; Retuerto, M.; Blanco, R.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Martinez-Lopez, D.; Castrejón, I.; Alvaro-Gracia, J.M.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19 and Chronic Inflammatory and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: A Multicentric Matched Cohort Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, T.; He, J.; Jin, Z. Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: A Retrospective Cohort Study and Synthesis Analysis in Wuhan, China. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.L.; Fazio-Eynullayeva, E.; Lane, D.A.; Underhill, P.; Lip, G.Y.H. Comorbidities Associated with Mortality in 31,461 Adults with COVID-19 in the United States: A Federated Electronic Medical Record Analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.H.; Shin, J.I.; Moon, S.Y.; Jin, H.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, M.; Park, Y.; et al. Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e698–e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordtz, R.; Lindhardsen, J.; Soussi, B.G.; Vela, J.; Uhrenholt, L.; Westermann, R.; Kristensen, S.; Nielsen, H.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Dreyer, L. Incidence and Severeness of COVID-19 Hospitalization in Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Denmark. Rheumatology 2021, 60, SI59–SI67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors Associated with COVID-19-Related Death Using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfrancesco, M.; Hyrich, K.L.; Al-Adely, S.; Carmona, L.; Danila, M.I.; Gossec, L.; Izadi, Z.; Jacobsohn, L.; Katz, P.; Lawson-Tovey, S.; et al. Characteristics Associated with Hospitalisation for COVID-19 in People with Rheumatic Disease: Data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Physician-Reported Registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjee, K.; Kim, H.; Bonomo, E.; Dolma, R. Prevalence and Predictors of Death and Severe Disease in Patients Hospitalized Due to COVID-19: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 77 Studies and 38,000 Patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorat, M.; Szymański, W.; Jurek, T.; Karczewski, M.; Zelig, J.; Simon, K. When Conventional Oxygen Therapy Fails—The Effectiveness of High-Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy in Patients with Respiratory Failure in the Course of COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, L.S.; Tanaka, Y.; Handa, R.; Li, Z.; Lorenzo, J.P.; Louthrenoo, W.; Hill, C.; Pile, K.; Robinson, P.C.; Dans, L.F.; et al. Updated APLAR Consensus Statements on Care for Patients with Rheumatic Diseases during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 24, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flisiak, R.; Horban, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kozielewicz, D.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Owczuk, R.; Parczewski, M.; Pawłowska, M.; Piekarska, A.; Simon, K.; et al. Management of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Recommendations of the Polish Association of Epidemiologists and Infectiologists as of February 23, 2022. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2022, 132, 16230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gay, M.A.; Mayo, J.; Castañeda, S.; Cifrián, J.M.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J. Tocilizumab: From the rheumatology practice to the fight against COVID-19, a virus infection with multiple faces. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Baseline Characteristic | All n = 185 | Survived n = 143 | Deceased n = 42 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female gender, n (%) | 137 (74.1) | 107 (74.8) | 30 (71.4) | 0.691 |
| Age in years, mean (SD); median (IQR) | 66.9 (13.3); 69 (59–76) | 65 (13.7); 66 (56–75) | 73.3 (9.3); 73 (69–80) | <0.001 |
| BMI, mean (SD); median (IQR) | 26.8 (5); 26.1 (23.4–30.5) | 27 (5); 26.2 (24–30.5) | 26.2 (4.7); 25.8 (23–28.1) | 0.473 |
| Concomitant diseases, n (%) | ||||
| Cardiovascular disease | 122 (65.9) | 85 (59.4) | 37 (88.1) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory disease | 27 (14.6) | 22 (15.4) | 5 (11.9) | 0.804 |
| Diabetes | 34 (18.4) | 25 (17.5) | 9 (21.4) | 0.651 |
| Malignant neoplasm | 10 (5.4) | 7 (4.9) | 3 (7.1) | 0.697 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 14 (7.6) | 10 (7) | 4 (9.5) | 0.525 |
| Obesity | 37 (20) | 32 (22.4) | 5 (11.9) | 0.136 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis, n (%) | 136 (73.5) | 106 (74.1) | 30 (71.4) | 0.843 |
| Immunosuppressive treatment, n (%) | 95 (51.4) | 71 (49.6) | 24 (57.1) | 0.483 |
| Methotrexate | 35 (18.9) | 32 (22.4) | 3 (7.1) | 0.026 |
| Corticosteroids | 62 (33.5) | 45 (31.5) | 17 (40.5) | 0.353 |
| SpO2 in % on hospital admission, mean (SD); median (IQR) | 89.7 (7); 91 (87–94) | 90.8 (5.8); 92 (88–94) | 85.8 (9.1); 88 (85–93) | <0.001 |
| Classification on hospital admission, n (%): | <0.001 | |||
| Asymptomatic | 3 (1.6) | 2 (1.4) | 1 (2.4) | |
| Symptomatic stable with SpO2 > 95% | 50 (27) | 44 (30.8) | 6 (14.3) | |
| Symptomatic unstable with SpO2 ≤ 95% | 63 (34.1) | 56 (39.1) | 7 (16.7) | |
| Symptomatic unstable with SpO2 ≤ 90% | 65 (35.1) | 40 (28) | 25 (59.5) | |
| ARDS | 4 (2.2) | 1 (0.7) | 3 (7.1) | |
| Remdesivir, n (%) | 56 (30.3) | 47 (32.9) | 9 (21.4) | 0.181 |
| Dexamethasone, n (%) | 95 (51.4) | 65 (45.4) | 30 (73.2) | 0.002 |
| Tocilizumab, n (%) | 23 (12.4) | 14 (9.8) | 9 (21.9) | 0.058 |
| Characteristic | All n = 185 | Survived n = 143 | Deceased n = 42 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) | 84.8 (73.4); 66.1 (22.8–139.5) | 72.8 (64.8); (17.6–118.1) | 126.9 (86.4); 109.5 (74.1–146.5) | <0.001 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | 1.5 (14.2); 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.19 (0.54); 0.07 (0.05–0.13) | 5.12 (27.5); 0.3 (0.15–0.57) | <0.001 |
| WBC (/uL) | 7146.4 (14.2); 6150 (4600–8700) | 6660.0 (4016.7); 5885 (4360–7635) | 8766.2 (4256.6); 8345 (6100–10590) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes (/uL) | 1085.9 (680.8); 950 (600–1360) | 1057.1 (660.4); 920 (600–1335) | 1209.0 (761.5); 1005 (700–1500) | 0.301 |
| Neutrocytes (/uL) | 5374.7 (3744.8); 4145 (3050–6480) | 4919 (3522.1); 3980 (2855–5465) | 7319.3 (4094.4); 6420 (4140–8450) | <0.001 |
| PLT (/uL) | 217,714.3 (94,330.7); 195,000 (154,000–277,000) | 222,612.7 (98,117.8); 198,500 (154,000–279,000) | 200,325.0 (78,063.6); 186,500 (149,500–245,000) | 0.285 |
| D-dimers (ug/mL) | 2222.6 (5691.3); 968.5 (680–1610) | 2255.4 (6226.3); 921 (670–1457) | 2090.8 (2660.2); 1200 (730–2325) | 0.163 |
| eGFR < 60 mL/min/m2, n (%) | 42 (22.7) | 26 (18.2) | 16 (39.1) | 0.001 |
| LDH (IU/L) | 445 (266.3); 375 (287–529) | 394.1 (230.4); 319 (268–453) | 599.1 (337.9); 492 (424–668) | <0.001 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 33.8 (27.9); 24 (17–42) | 32 (26.7); 23 (16–39) | 40.4 (31.4); 30 (23–51) | 0.018 |
| AST (IU/L) | 54.5 (46.7); 43 (30–60) | 47.4 (41.9); 38 (25–55) | 75.5 (54.0); 60 (40–103) | <0.001 |
| RDV n = 56 | No RDV n = 129 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFNO/NIV | No | 46 (82.1%) | 102 (79.1%) | 0.631 |
| Yes | 10 (17.9%) | 27 (20.9%) | ||
| IMV | No | 48 (85.7%) | 119 (92.2%) | 0.852 |
| Yes | 8 (14.3%) | 10 (7.8%) | ||
| Death | No | 47 (83.9%) | 96 (74.4%) | 0.156 |
| Yes | 9 (16.1%) | 33 (25.6%) | ||
| RDV n = 56 | No RDV n = 56 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFNO/NIV | No | 46 (51.1%) | 44 (48.9%) | 0.634 |
| Yes | 10 (45.5%) | 12 (54.6%) | ||
| IMV | No | 48 (48.5%) | 51 (51.5%) | 0.376 |
| Yes | 8 (61.5%) | 5 (38.5%) | ||
| Death | No | 47 (52.2%) | 43 (47.8%) | 0.341 |
| Yes | 9 (40.9%) | 13 (59.1%) | ||
| Characteristic | SARD n = 185 | Non-SARD n = 8035 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Female, n (%) | 137 (74.1) | 3690 (45.9) | <0.001 |
| Age (y), mean (SD), median (IQR) | 66.9 (13.3); 69 (59–76) | 62.8 (16.8); 64 (51–75) | <0.001 |
| Concomitant diseases, n (%) | 122 (65.9) | 4602 (57.3) | 0.018 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 27 (14.6) | 740 (9.2) | 0.013 |
| Pulmonary diseases | 10 (5.4) | 564 (7) | 0.394 |
| Malignant neoplasm | 37 (20) | 2184 (27.2) | 0.030 |
| Obesity | 34 (18.4) | 1658 (20.6) | 0.453 |
| Diabetes | 14 (7.6) | 354 (4.4) | 0.040 |
| Chronic kidney disease | |||
| Neurological and psychiatric disorders | 14 (7.6) | 810 (10.1) | 0.260 |
| SpO2 on hospital admission (%), mean (SD), median (IQR) | 89.7 (7); 91 (87–94) | 90.2 (6.9); 92 (88–95) | 0.308 |
| Duration of oxygen therapy (days), mean (SD); median (IQR) | 8.4 (8.5); 7 (1.5–12) | 7.1 (8.7); 6 (0–10) | 0.047 |
| Length of hospitalisation (days), mean (SD); median (IQR) | 14.6 (9.6); 12 (9–18) | 12.5 (8); 11 (8–15) | 0.003 |
| Death, n (%) | 42 (22.7) | 1155 (14.4) | 0.002 |
| Laboratory test results, mean (SD); median (IQR) | |||
| CRP (mg/L) | 84.8 (73.4); 66.1 (22.8–129.4) | 81.4 (77.7); 59.5 (21–120.3) | 0.559 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | 1.5 (14.2); 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.8 (7.9); 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.318 |
| WBC (/uL) | 7146.4 (14.2); 6150 (4600–8700) | 6992.9 (4674.9); 6000 (4500–8210) | 0.664 |
| Lymphocytes (/uL) | 1085.9 (680.8); 950 (600–1360) | 1229.7 (2374.9); 1000 (700–1400) | 0.447 |
| Neutrocytes (/uL) | 5374.7 (3744.8); 4145 (3050–6480) | 5241.5 (10396.2); 4300 (2900–6400) | 0.872 |
| PLT (/uL) | 217,714.3 (94,330.7); 195,000 (154,000–277,000) | 207,416.8 (99,902.1); 192,000 (145,000–254,000) | 0.169 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 69.4 (78.5); 40.5 (16.8–96.7) | 87 (305.6); 37.8 (14.6–80) | 0.553 |
| D-dimers (ug/mL) | 2222.6 (5691.3); 968.5 (680–1610) | 2148.3 (6444.7); 846.1 (500–1551) | 0.883 |
| eGFR < 60 mL/min/m2, n (%) | 42 (22.7) | 1725 (21.5) | 0.624 |
| LDH (IU/L) | 445 (266.3); 375 (287–529) | 422.1 (273.1); 369 (268–501.5) | 0.417 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 33.8 (27.9); 24 (17–42) | 46.6 (98.4); 31.2 (21–51) | 0.082 |
| AST (IU/L) | 54.5 (46.7); 43 (30–60) | 69.9 (546.3); 42 (30–63) | 0.762 |
| Treatment mean (SD), median (IQR) | |||
| Remdesivir—time to start of treatment (days) | |||
| From onset of symptoms | 6.3 (3.5); 6.5 (3–8.5) | 6.3 (3.3); 6 (4–8) | 0.980 |
| From diagnosis | 2.3 (2.6); 1 (1–3) | 2.3 (2.6); 1 (1–3) | 0.928 |
| Tocilizumab—time to start of treatment (days) | |||
| From onset of symptoms | 9.6 (5.9); 7 (5–14) | 9.2 (4.7); 9 (7–12) | 0.692 |
| From diagnosis | 5.2 (5.2); 3 (2–6) | 4.6 (3.5); 4 )2–7) | 0.407 |
| Dexamethasone—time to start of treatment (days) | |||
| From onset of symptoms | 7.5 (4); 7 (5–10) | 7.8 (4.4); 8 (5–10) | 0.520 |
| From diagnosis | 2.4 (2.7); 1 (1–4) | 3 (3.3); 1 (1–5) | 0.073 |
| HFNO/NIV, n (%) | 37 (20) | 903 (11.2) | <0.001 |
| IMV, n (%) | 18 (9.7) | 563 (7) | 0.153 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rorat, M.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Kowalska, J.; Kujawa, K.; Rogalska, M.; Kozielewicz, D.; Lorenc, B.; Sikorska, K.; Czupryna, P.; Bolewska, B.; et al. The Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247342
Rorat M, Zarębska-Michaluk D, Kowalska J, Kujawa K, Rogalska M, Kozielewicz D, Lorenc B, Sikorska K, Czupryna P, Bolewska B, et al. The Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247342
Chicago/Turabian StyleRorat, Marta, Dorota Zarębska-Michaluk, Justyna Kowalska, Krzysztof Kujawa, Magdalena Rogalska, Dorota Kozielewicz, Beata Lorenc, Katarzyna Sikorska, Piotr Czupryna, Beata Bolewska, and et al. 2022. "The Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247342
APA StyleRorat, M., Zarębska-Michaluk, D., Kowalska, J., Kujawa, K., Rogalska, M., Kozielewicz, D., Lorenc, B., Sikorska, K., Czupryna, P., Bolewska, B., Maciukajć, J., Piekoś, T., Podlasin, R., Dworzańska, A., Mazur, W., Brzdęk, M., Szymanek-Pasternak, A., & Flisiak, R. (2022). The Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247342










