Unattended versus Attended Blood Pressure Measurement: Relationship with Retinal Microcirculation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Blood Pressure Measurement
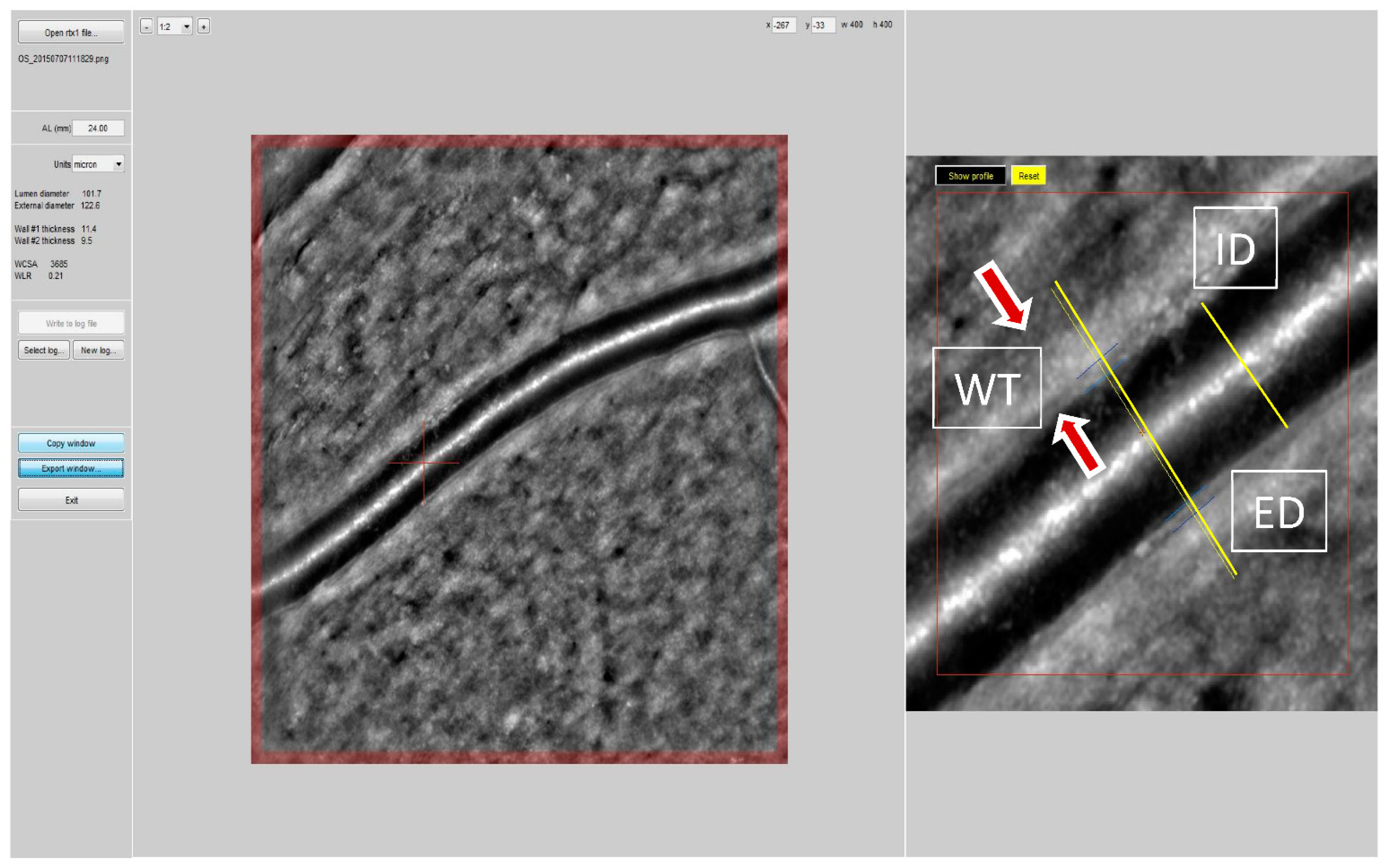
2.2. Evaluation of the Retinal Microcirculation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Results
2.5. Vascular Organ Damage
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Conclusions
Disclosures
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosures
References
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Fagard, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Redón, J.; Zanchetti, A.; Böhm, M.; Christiaens, T.; Cifkova, R.; De Backer, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1281–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Ovbiagele, B.; Casey, D.E.; Smith, S.C.; Collins, K.J.; Spencer, C.C.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Stafford, R.S.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association T. Hypertension 2018, 71, e13–e115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.A.; Nerenberg, K.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; McBrien, K.; Zarnke, K.B.; Dasgupta, K.; Cloutier, L.; Gelfer, M.; Lamarre-Cliche, M.; Milot, A.; et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2016 Canadian Hypertension Education Program Guidelines for Blood Pressure Measurement, Diagnosis, Assessment of Risk, Prevention, and Treatment of Hypertension. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Dominiczak, A.S.G.; Kahan, T.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1953–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Parati, G.; Pomidossi, G.; Grassi, G.; Casadei, R.; Zanchetti, A. Alerting reaction and rise in blood pressure during measurement by physician and nurse. Hypertension 1987, 9, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Parati, G.; Asmar, R.; O’Brien, E. Requirements for professional office blood pressure monitors. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G. A Short History of Automated Office Blood Pressure—15 Years to SPRINT. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2016, 18, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G.; Valdivieso, M.; Kiss, A. Use of automated office blood pressure measurement to reduce the white coat response. J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, S.E.; Lund-Johansen, P.; Nilsson, P.M.; Mancia, G. Unattended blood pressure measurements in the systolic blood pressure intervention trial: Implications for entry and achieved blood pressure values compared with other trials. Hypertension 2016, 67, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, S.E.; Grassi, G.; Kreutz, R.; Mancia, G. Attended vs. unattended blood pressure—Learnings beyond SPRINT. Blood Press. 2021, 30, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPRINTResearch Group Wright, J.T.; Williamson, J.D.; Whelton, P.K.; Snyder, J.K.; Sink, K.M.; Rocco, M.V.; Reboussin, D.M.; Rahman, M.; Oparil, S.; Lewis, C.E.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Intensive versus Standard Blood-Pressure Control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.C.; Whelton, P.K.; Cushman, W.C.; Cutler, J.A.; Evans, G.W.; Snyder, J.K.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Beddhu, S.; Cheung, A.K.; Fine, L.J.; et al. Blood Pressure Measurement in SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial). Hypertension 2018, 71, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G.; de La Sierra, A.; Roerecke, M.; Kaczorowski, J. Attended versus unattended automated office blood pressure measurement in the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, G.; Quarti-Trevano, F.; Seravalle, G.; Dell’Oro, R.; Vanoli, J.; Perseghin, G.; Mancia, G. Sympathetic Neural Mechanisms Underlying Attended and Unattended Blood Pressure Measurement. Hypertension 2021, 78, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paini, A.; Bertacchini, F.; Stassaldi, D.; Aggiusti, C.; Maruelli, G.; Arnoldi, C.; De Ciuceis, C.; Rosei, C.A.; Rizzoni, D.; Gatta, R.; et al. Unattended versus attended blood pressure measurement: Mean values and determinants of the difference. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 274, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parati, G.; Ochoa, J.E.; Bilo, G.; Zanchetti, A. SPRINT Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2017, 69, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerli, F.H.; Bangalore, S.; Kjeldsen, S.E. the Implications of Blood Pressure Measurement Methods on Treatment Targets for Blood Pressure. Circulation 2017, 135, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovský, J.; Seidlerová, J.; Kratochvíl, Z.; Karnosová, P.; Hronová, M.; Mayer, O. Automated compared to manual office blood pressure and to home blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Blood Press. 2016, 25, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G.; Kaczorowski, J.; Paterson, J.M.; Dolovich, L.; Tu, K. Thresholds for Diagnosing Hypertension Based on Automated Office Blood Pressure Measurements and Cardiovascular Risk. Hypertension 2015, 66, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G.; Kaczorowski, J.; Dolovich, L.; Tu, K.; Paterson, J.M. Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertension in Relation to Achieved Blood Pressure Using Automated Office Blood Pressure Measurement. Hypertension 2016, 68, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.R.C.; McKay, D.W.; Conradson, H.; Lonn, E.; Title, L.M.; Anderson, T. Automated oscillometric blood pressure versus auscultatory blood pressure as a predictor of carotid intima–medial thickness in male firefighters. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2007, 21, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Salvetti, M.; Paini, A.; Aggiusti, C.; Bertacchini, F.; Stassaldi, D.; Capellini, S.; De Ciuceis, C.; Rizzoni, D.; Gatta, R.; Rosei, E.A.; et al. Unattended Versus Attended Blood Pressure Measurement. Hypertension 2019, 73, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadis, E.A.; Agaliotis, G.D.; Angelopoulos, E.T.; Tsakanikas, A.P.; Chaveles, I.A.; Mousoulis, G.P. Automated Office Blood Pressure and 24-h Ambulatory Measurements are Equally Associated with Left Ventricular Mass Index. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paini, A.; Aggiusti, C.; Bertacchini, F.; Stassaldi, D.; Capellini, S.; de Ciuceis, C.; Sacca’, G.; Verzeri, L.; Gatta, R.; Rosei, E.A.; et al. Relationship between arterial stiffness and unattended or attended blood pressure values. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Rizzoni, D. Microvascular structure as a prognostically relevant endpoint. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heagerty, A.M. Predicting hypertension complications from small artery structure. J. Hypertens. 2007, 25, 939–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, J.; Konieczka, K.; Bruno, R.M.; Virdis, A.; Flammer, A.J.; Taddei, S. The eye and the heart. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoni, D.; Mengozzi, A.; Masi, S.; Rosei, C.A.; De Ciuceis, C.; Virdis, A. New Noninvasive Methods to Evaluate Microvascular Structure and Function. Hypertension 2022, 79, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cífková, R.; Harazny, J.M.; Bruthans, J.; Wohlfahrt, P.; Krajčoviechová, A.; Lánská, V.; Gelžinský, J.; Mateřánková, M.; Mareš, Š.; Filipovský, J.; et al. Reference values of retinal microcirculation parameters derived from a population random sample. Microvasc. Res. 2021, 134, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. 510K Summary for HEM-9000AI. 2005. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf5/K050233.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2018).
- Rosenbaum, D.; Mattina, A.; Koch, E.; Rossant, F.; Gallo, A.; Kachenoura, N.; Paques, M.; Redheuil, A.; Girerd, X. Effects of age, blood pressure and antihypertensive treatments on retinal arterioles remodeling assessed by adaptive optics. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ciuceis, C.; Rosei, C.A.; Caletti, S.; Trapletti, V.; Coschignano, M.A.; Tiberio, G.A.; Duse, S.; Docchio, F.; Pasinetti, S.; Zambonardi, F.; et al. Comparison between invasive and noninvasive techniques of evaluation of microvascular structural alterations. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoni, D.; Agabiti-Rosei, C.; De Ciuceis, C. State of The Art Review: Vascular Remodeling In Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Savoia, C.; Grassi, G.; Lembo, G.; Vecchione, C.; Seravalle, G.; Taddei, S.; Volpe, M.; Rosei, E.A.; Rizzoni, D. Evaluation of microvascular structure in humans. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoloni, E.; Angeli, F.; Marcucci, E.; Perricone, C.; Cafaro, G.; Riccini, C.; Spighi, L.; Gildoni, B.; Cavallini, C.; Verdecchia, P.; et al. Unattended compared to traditional blood pressure measurement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomised cross-over study. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiesan, M.L.; Salvetti, M.; Rizzoni, D.; Paini, A.; Agabiti-Rosei, C.; Aggiusti, C.; Bertacchini, F.; Stassaldi, D.; Gavazzi, A.; Porteri, E.; et al. Pulsatile hemodynamics and microcirculation: Evidence for a close relationship in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2013, 61, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paini, A.; Muiesan, M.L.; Agabiti-Rosei, C.; Aggiusti, C.; De Ciuceis, C.; Bertacchini, F.; Duse, S.; Semeraro, F.; Rizzoni, D.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; et al. Carotid stiffness is significantly correlated with wall-to-lumen ratio of retinal arterioles. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvetti, M.; Rosei, C.A.; Paini, A.; Aggiusti, C.; Cancarini, A.; Duse, S.; Semeraro, F.; Rizzoni, D.; Rosei, E.A.; Muiesan, M.L. Relationship of Wall-to-Lumen Ratio of Retinal Arterioles With Clinic and 24-Hour Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2014, 63, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritt, M.; Harazny, J.M.; Ott, C.; Schlaich, M.P.; Schneider, M.P.; Michelson, G.; Schmieder, R.E. Analysis of retinal arteriolar structure in never-treated patients with essential hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, E.; Rosenbaum, D.; Brolly, A.; Sahel, J.A.; Chaumet-Riffaud, P.; Girerd, X.; Rossant, F.; Paques, M. Morphometric analysis of small arteries in the human retina using adaptive optics imaging: Relationship with blood pressure and focal vascular changes. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.; Meglis, G.; Polemidiotis, G. The impact of physician vs automated blood pressure readings on office-induced hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1997, 11, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G.; Godwin, M.; Dawes, M.; Kiss, A.; Tobe, S.W.; Kaczorowski, J. Conventional versus automated measurement of blood pressure in the office (CAMBO) trial. Fam. Pract. 2012, 29, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreadis, E.A.; Papademetriou, V.; Geladari, C.V.; Kolyvas, G.N.; Angelopoulos, E.T.; Aronis, K.N. Home, automated office, and conventional office blood pressure as predictors of cardiovascular risk. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2017, 11, 165–170.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | N = 142 Patients |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57 ± 12 |
| Sex (males/females) (%) | 334/230 (59%, 41%) |
| Height (cm) | 169 ± 9 |
| Weight (kg) | 75 ± 16 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26 ± 4 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 85 (60%) |
| Antihypertensive treatment (%) | 71 (84%) |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 17 (12%) |
| β-blockers, n (%) | 25 (18%) |
| CC-blockers, n (%) | 29 (21%) |
| ACE-i or ARB, n (%) | 26 (20%) |
| Potassium-sparing diuretics, n (%) | 27 (19%) |
| α-blockers, n (%) | 11 (8%) |
| Dyslipidaemia, n (%) | 84 (34) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 34 (11) |
| Smoking (yes) (%) | 17/80/45 (12/56/32) |
| Mean Value | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|
| Internal lumen diameter (µm) | 94.27 | 12.8 |
| External diameter (µm) | 119.7 | 14.7 |
| WCSA (µm2) | 4305.7 | 943.1 |
| Wall-to-lumen ratio (WLR) | 0.27 | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paini, A.; Agabiti Rosei, C.; De Ciuceis, C.; Aggiusti, C.; Bertacchini, F.; Cacciatore, M.; Capellini, S.; Gatta, R.; Malerba, P.; Stassaldi, D.; et al. Unattended versus Attended Blood Pressure Measurement: Relationship with Retinal Microcirculation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236966
Paini A, Agabiti Rosei C, De Ciuceis C, Aggiusti C, Bertacchini F, Cacciatore M, Capellini S, Gatta R, Malerba P, Stassaldi D, et al. Unattended versus Attended Blood Pressure Measurement: Relationship with Retinal Microcirculation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236966
Chicago/Turabian StylePaini, Anna, Claudia Agabiti Rosei, Carolina De Ciuceis, Carlo Aggiusti, Fabio Bertacchini, Marco Cacciatore, Sara Capellini, Roberto Gatta, Paolo Malerba, Deborah Stassaldi, and et al. 2022. "Unattended versus Attended Blood Pressure Measurement: Relationship with Retinal Microcirculation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236966
APA StylePaini, A., Agabiti Rosei, C., De Ciuceis, C., Aggiusti, C., Bertacchini, F., Cacciatore, M., Capellini, S., Gatta, R., Malerba, P., Stassaldi, D., Rizzoni, D., Salvetti, M., & Muiesan, M. L. (2022). Unattended versus Attended Blood Pressure Measurement: Relationship with Retinal Microcirculation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236966







