The Addition of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis to a Pharmacological Intervention in Patients with Tension-Type Headache: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. Outcome Measurements
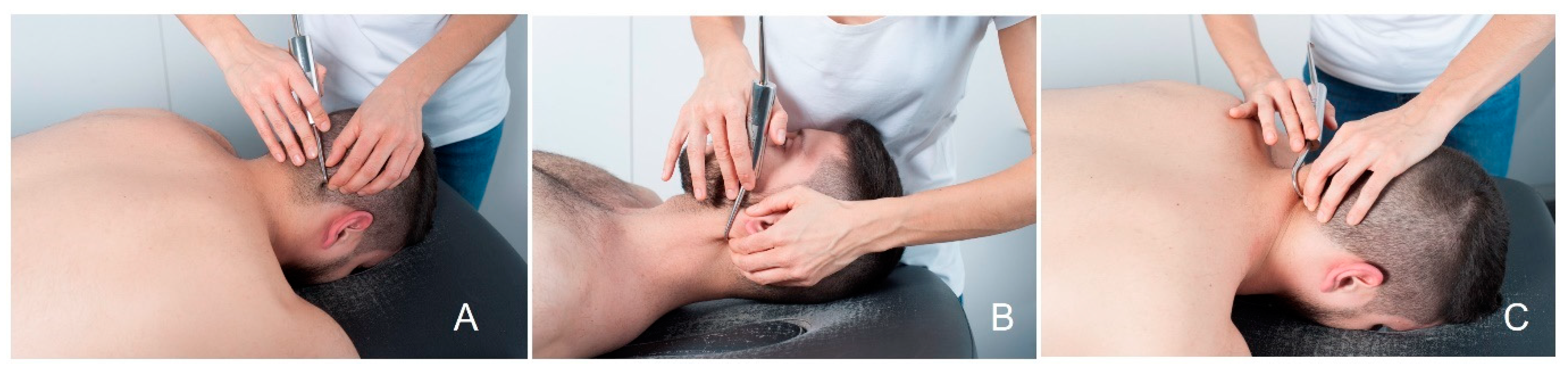
2.5. Interventions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
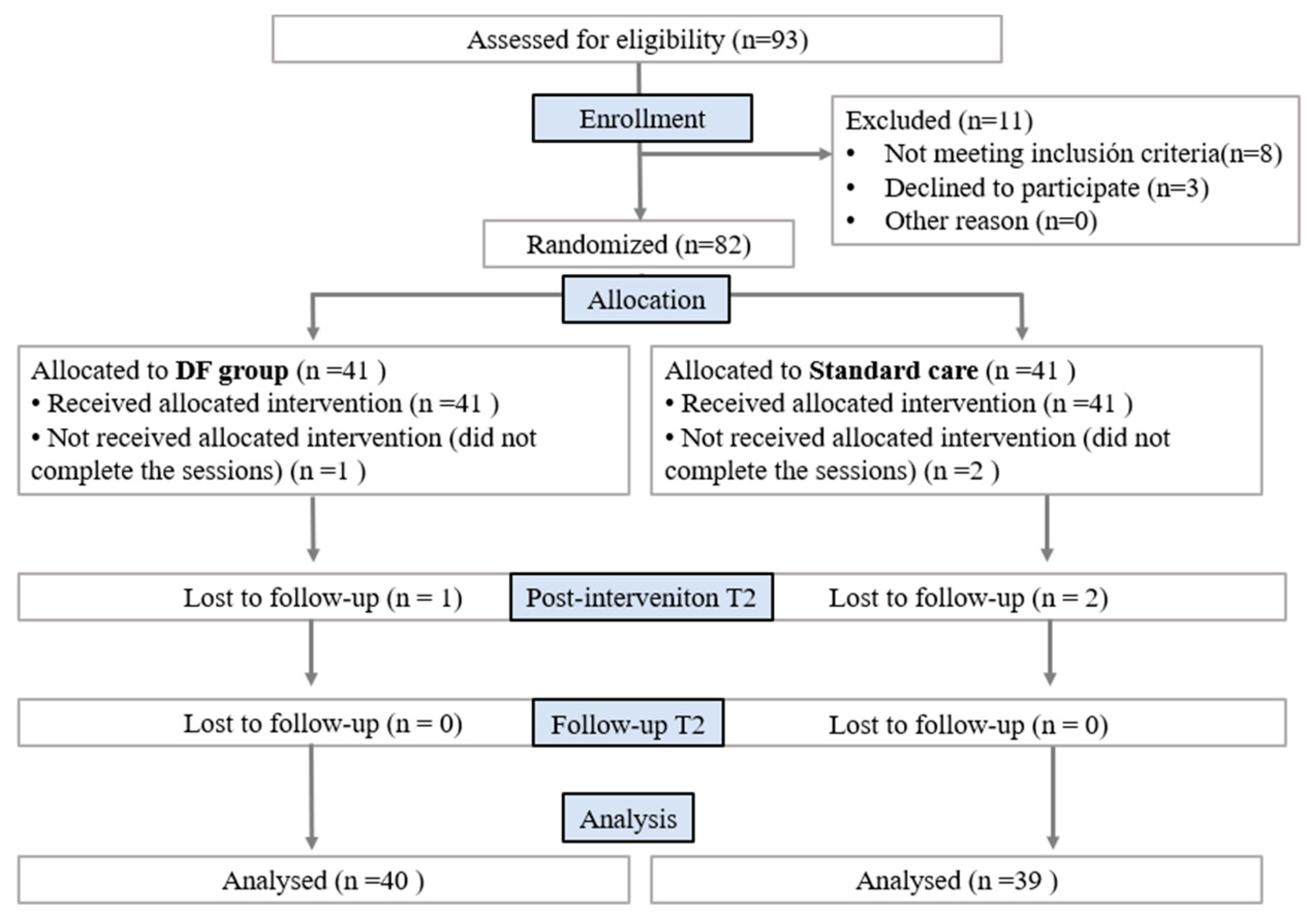
3. Results
3.1. Self-Perceived Impact Caused by the Headache, HIT-6, and Frequency of Headaches
3.2. Intensity of Headache, VAS
3.3. Range of Motion
3.4. Self-Perceived Improvement, Likert Scale
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovner, L.J.; Hagen, K.; Linde, M.; Steiner, T.J. The global prevalence of headache: An update, with analysis of the influences of methodological factors on prevalence estimates. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [CrossRef]
- Linde, M.; Gustavsson, A.; Stovner, L.J.; Steiner, T.J.; Barré, J.; Katsarava, Z.; Lainez, J.M.; Lampl, C.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Rastenyte, D.; et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: The Eurolight project. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 19, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldie, K.E.; Buckley, J. Tension-Type Headache: A Life-Course Review. J. Headache Pain Manag. 2015, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.S.; Sibbritt, D.W.; Adams, J. A critical review of manual therapy use for headache disorders: Prevalence, profiles, motivations, communication and self-reported effectiveness. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Puente, M.; Oliva-Pascual-Vaca, Á.; Rodriguez-Blanco, C.; Heredia-Rizo, A.M.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Ordoñez, F.J. Risk of Headache, Temporomandibular Dysfunction, and Local Sensitization in Male Professional Boxers: A Case-Control Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Coppieters, M.W.; Cuadrado, M.L.; Pareja, J.A. Patients With Chronic Tension-Type Headache Demonstrate Increased Mechano-Sensitivity of the Supra-Orbital Nerve. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2007, 48, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, L. Treatment guidelines: Implications for community-based headache treatment. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 69, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, J.M.; Alves, B.M.; Duarte, D.B.; Marques, L.A.; Santana, R.S. Quality appraisal of existing guidelines for the management of headache disorders by the AGREE II’s method. Cephalalgia 2021, 42, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnes, D.; Mars, T.S.; Mullinger, B.; Froud, R.; Underwood, M. Adverse events and manual therapy: A systematic review. Man. Ther. 2010, 15, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamonseki, D.H.; Lopes, E.P.; van der Meer, H.A.; Calixtre, L.B. Effectiveness of manual therapy in patients with tension-type headache. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 44, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadellans-Arróniz, A.; Llurda-Almuzara, L.; Campos-Laredo, B.; Cabanas-Valdés, R.; Garcia-Sutil, A.; López-De-Celis, C. The effectiveness of diacutaneous fibrolysis on pain, range of motion and functionality in musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 35, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-Celis, C.; Barra-López, M.E.; González-Rueda, V.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Rodríguez-Rubio, P.; Tricás-Moreno, J.M. Effectiveness of diacutaneous fibrolysis for the treatment of chronic lateral epicondylalgia: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 32, 644–653. [Google Scholar]
- Barra, M.; López, C.; Fernández, G.; Murillo, E.; Villar, E.; Raya, L. The immediate effects of diacutaneous fibrolysis on pain and mobility in patients suffering from painful shoulder: A randomized placebo-controlled pilot study. Clin. Rehabil. 2010, 25, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra López, M.E.; López De Celis, C.; Fernández-Jentsch, G.; Raya-de-Cárdenas, J.; Lucha López, M.; Tricás Moreno, J.M. Effectiveness of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis for the treatment of subacromial impingement syndrome: A randomised controlled trial. Man Ther. 2013, 18, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanlo-Mazas, P.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; de Escudero-Zapico, A.R.; López-De-Celis, C.; Hidalgo-García, C.; Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Lucha-López, M.O. The Effect of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis on Local and Widespread Hyperalgesia and Muscle Length in Patients With Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Secondary Analysis of a Pretest–Posttest Clinical Trial. J. Sport Rehabil. 2021, 30, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanlo-Mazas, P.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; de Escudero-Zapico Alazne, R.; Miguel, T.-M.J.; Orosia, L.-L.M. The Effect of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis on Patellar Position Measured Using Ultrasound Scanning in Patients With Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome. J. Sport Rehabil. 2019, 28, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Del Barrio, S.; Estébanez de Miguel, E.; Bueno Gracia, E.; Haddad Garay, M.; Tricás Moreno, J.M.; Hidalgo García, C. Effects of diacutaneous fibrolysis in patients with mild to moderate symptomatic carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 32, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Barrio, S.J.; Ceballos-Laita, L.; Bueno-Gracia, E.; Rodríguez-Marco, S.; Haddad-Garay, M.; Estébanez-De-Miguel, E. Effects of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis on Mechanosensitivity, Disability, and Nerve Conduction Studies in Mild to Moderate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. 2020, 101, pzaa222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castien, R.F.; van der Windt, D.A.; Grooten, A.; Dekker, J. Effectiveness of manual therapy for chronic tension-type headache: A pragmatic, randomised, clinical trial. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castien, R.F.; Blankenstein, A.H.; Windt, D.A.W.M.V.D.; Dekker, J. Minimal clinically important change on the Headache Impact Test-6 questionnaire in patients with chronic tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castien, R.F.; Van Der Windt, D.A.; Dekker, J.; Mutsaers, B.; Grooten, A. Effectiveness of manual therapy compared to usual care by the general practitioner for chronic tension-type headache: Design of a randomised clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Blaisdell, B.; Kwong, J.W.; Bjorner, J.B. The Short-Form Headache Impact Test (HIT-6) was psychometrically equivalent in nine languages. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.C.; de Azevedo, L.R.; de Souza, N.V.; Ferreira, F.V. Pain measurement in TMD patients: Evaluation of precision and sensitivity of different scales. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2001, 28, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousignant, M.; de Bellefeuille, L.; O’Donoughue, S.; Grahovac, S. Criterion validity of the cervical range of motion (CROM) goniometer for cervical flexion and extension. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000, 25, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, A.; Carlesso, L.C.; Flynn, T.; Kerry, W.A.; Rubinstein, R.; Vogel, S.M. International Framework for Examination of the Cervical Region for Potential of Vascular Pathologies of the Neck Prior to Orthopaedic Manual Therapy (OMT) Intervention: International IFOMPT Cervical Framework (2020). 2020. Available online: www.ifompt.org (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Cohen, J. The Concepts of Power Analysis BT-Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (Revised Edition). In Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, T.J.; Jensen, R.; Katsarava, Z.; Linde, M.; MacGregor, E.A.; Osipova, V.; Paemeleire, K.; Olesen, J.; Peters, M.; Martelletti, P. Aids to management of headache disorders in primary care (2nd edition): On behalf of the European Headache Federation and Lifting The Burden: The Global Campaign against Headache. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.J.; Saylor, D. The Global Burden of Headache. Skull Base 2018, 38, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovner, L.; Hagen, K.; Jensen, R.; Katsarava, Z.; Lipton, R.; Scher, A.; Steiner, T.; Zwart, J.-A. The Global Burden of Headache: A Documentation of Headache Prevalence and Disability Worldwide. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espí-López, G.V.; Rodríguez-Blanco, C.; Oliva-Pascual-Vaca, A.; Molina-Martínez, F.; Falla, D. Do manual therapy techniques have a positive effect on quality of life in people with tension-type headache? A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 52, 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Ferragut-Garcías, A.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; Rodríguez-Blanco, C.; Velasco-Roldán, O.; Pecos-Martín, D.; Oliva-Pascual-Vaca, J.; Llabrés-Bennasar, B.; Oliva-Pascual-Vaca, Á. Effectiveness of a Treatment Involving Soft Tissue Techniques and/or Neural Mobilization Techniques in the Management of Tension-Type Headache: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 211–219.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngberg, A.C.; Rasmussen, B.K.; Jørgensen, T.; Jensen, R. Prognosis of migraine and tension-type headache. Neurology 2005, 65, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, S.B.; Dickson, E.W. Clinically significant changes in pain along the visual analog scale. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001, 38, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumplido-Trasmonte, C.; Fernández-González, P.; Alguacil-Diego, I.; Molina-Rueda, F. Manual therapy in adults with tension-type headache: A systematic review. Neurologia 2020, 36, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro-Velasco, C.; Arroyo-Morales, M.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Cleland, J.A.; Barrero-Hernández, F.J. Short-Term Effects of Manual Therapy on Heart Rate Variability, Mood State, and Pressure Pain Sensitivity in Patients With Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Pilot Study. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2009, 32, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espí-López, G.V.; Rodríguez-Blanco, C.; Oliva-Pascual-Vaca, A.; Benítez-Martínez, J.C.; Lluch, E.; Falla, D. Effect of manual therapy on headache 642 european journal of physical and rehabilitation medicine. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 50, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demirturk, F.; Akarcali, I.; Akbayrak, T.; Citak, I.; Inan, L. Results of two different manual therapy techniques in chronic tension-type headache. Pain Clin. 2002, 14, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castien, R.F.; van der Windt, D.A.; Blankenstein, A.H.; Heymans, M.W.; Dekker, J. Clinical variables associated with recovery in patients with chronic tension-type headache after treatment with manual therapy. Pain 2012, 153, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, L.L. Reflexiones Sobre la Investigación de Resultados en Salud, Sociedad Española de Familia y Comunitaria. 2002, Volume 30, pp. 388–391. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=2895383 (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- D’Amico, D.; Grazzi, L.; Usai, S.; Leonardi, M.; Raggi, A. Disability and quality of life in headache: Where we are now and where we are heading. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetti, G.; Peres, M.F.P.; Lucchetti, A.L.G.; Mercante, J.P.P.; Guendler, V.Z.; Zukerman, E. Generalized anxiety disorder, subthreshold anxiety and anxiety symptoms in primary headache. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 67, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| DF Group (n = 40) M (SD) | Standard Care (n = 39) M (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender (M; F) | 11; 29 | 11; 28 |
| Age (years) | 37.25 (15.41) | 39.39 (16.26) |
| Weight (kg) | 67.17 (13.95) | 67.28 (13.33) |
| Height (m) | 1.67 (0.08) | 1.68 (0.06) |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | 24.08 (2.17) | 23.83 (1.70) |
| Frequency of headache (days) | 13.28 (11.90) | 13.26 (12.29) |
| HIT-6 | 57.65 (7.51) | 56.82 (7.22) |
| VAS | 1.75 (1.74) | 2.04 (1.77) |
| ROM sagittal plane | 98.15 (18.65) | 106.89 (20.07) |
| ROM frontal plane | 66.97 (14.90) | 67.46 (15.49) |
| ROM transverse plane | 115.27 (16.42) | 117.23 (17.07) |
| Pharmacological care | ||
| Acetaminophen | 14 (35%) | 16 (41%) |
| NSAIDs | 18 (45%) | 16 (41%) |
| Acetaminophen/NSAIDs | 8 (20%) | 7 (18%) |
| Group | Baseline T0 Mean (SD) | Follow-Up T2 Mean (SD) | Within-Group Score Changes T0–T2 (99% CI) | Between-Group Score Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIT-6 | ||||
| Standard Care | 56.82 (7.22) | 56.49 (7.89) | 0.33 (−1.63, 2.30) p < 0.649 d = 0.04 | F = 27.26 p < 0.001 d = 1.17 |
| DF group | 57.65 (7.51) | 49.84 (7.23) | 7.82 (4.50, 11.14) p < 0.001 d = 1.05 | |
| Frequency of Headache | ||||
| Standard Care | 13.26 (12.39) | 15.49 (11.98) | −2.23 (−5.06, 0.60) p < 0.039 d = 0.18 | F = 29.10 p < 0.001 d = 1.12 |
| DF group | 13.28 (11.97) | 5.82 (6.99) | 7.45 (3.52, 11.37) p < 0.001 d = 0.76 | |
| Group | Baseline T0 Mean (SD) | Post-Intervention T1 Mean (SD) | Within-Group Score Changes T0–T1 (99% CI) | Between-Group Score Changes T0–T1 | Follow-Up T2 Mean (SD) | Within-Group Score Changes T0–T2 (99% CI) | Between-Group Score Changes T0–T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS | |||||||
| Standard Care | 2.04 (1.77) | 2.52 (2.62) | −0.47 (−1.41, 0.47) p < 0.181 d = 0.21 | F = 11.28 p = 0.001 d = 0.76 | 1.82 (2.08) | 0.22 (−0.66, 1.11) p < 0.500 d = 0.11 | F = 2.36 p = 0.129 d = 0.35 |
| DF group | 1.75 (1.74) | 0.74 (1.22) | 1.00 (0.26, 1.74) p < 0.001 d = 0.67 | 0.86 (1.55) | 0.88 (0.12, 1.63) p < 0.003 d = 0.54 | ||
| ROM sagittal plane | |||||||
| Standard Care | 106.90 (20.07) | 96.10 (16.67) | 10.79 (3.89, 17.69) p < 0.001 d = 0.58 | F = 39.61 p < 0.001 d = 1.42 | 96.31 (18.37) | 10.58 (3.07, 18.10) p < 0.001 d =0.55 | F= 28.64 p < 0.001 d = 1.20 |
| DF group | 98.15 (18.65) | 112.60 (20.69) | −14.45 (−22.80, −6.09) p < 0.001 d = 0.73 | 109.27 (20.37) | −11.12 (−19.13, −3.11) p = 0.001 d = 0.57 | ||
| ROM frontal plane | |||||||
| Standard Care | 67.56 (15.49) | 65.46 (13.08) | 2.00 (−1.20, 5.20) p < 0.099 d = 0.15 | F = 46.87 p < 0.001 d = 1.54 | 63.54 (14.61) | 3.92 (0.20, 7.64) p < 0.007 d = 0.27 | F= 38.26 p < 0.001 d = 1.39 |
| DF group | 66.97 (14.90) | 79.22 (15.83) | −12.25 (−16.85, −7.64) p < 0.001 d = 0.79 | 75.37 (16.64) | −8.40 (−12.30, −4.49) p < 0.001 d = 0.40 | ||
| ROM Transverse plane | |||||||
| Standard Care | 117.23 (17.07) | 113.59 (15.97) | 3.64 (−2.56, 9.84) p < 0.120 d = 0.22 | F = 27.33 p < 0.001 d = 1.17 | 111.94 (17.69) | 5.28 (−0.80, 11.36) p < 0.024 d = 0.30 | F= 21.86 p < 0.001 d = 1.05 |
| DF group | 115.27 (16.42) | 128.92 (13.90) | −13.65 (−20.11, −7.18) p < 0.001 d = 0.90 | 125.45 (15.32) | −10.17 (−16.73, −3.61) p < 0.001 d = 0.64 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabanillas-Barea, S.; Ceballos-Laita, L.; Pérez-Guillén, S.; Jiménez-del-Barrio, S.; Pardos-Aguilella, P.; Rodríguez-Rubio, P.R.; Carrasco-Uribarren, A. The Addition of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis to a Pharmacological Intervention in Patients with Tension-Type Headache: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226716
Cabanillas-Barea S, Ceballos-Laita L, Pérez-Guillén S, Jiménez-del-Barrio S, Pardos-Aguilella P, Rodríguez-Rubio PR, Carrasco-Uribarren A. The Addition of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis to a Pharmacological Intervention in Patients with Tension-Type Headache: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226716
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabanillas-Barea, Sara, Luis Ceballos-Laita, Silvia Pérez-Guillén, Sandra Jiménez-del-Barrio, Pilar Pardos-Aguilella, Pere Ramón Rodríguez-Rubio, and Andoni Carrasco-Uribarren. 2022. "The Addition of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis to a Pharmacological Intervention in Patients with Tension-Type Headache: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226716
APA StyleCabanillas-Barea, S., Ceballos-Laita, L., Pérez-Guillén, S., Jiménez-del-Barrio, S., Pardos-Aguilella, P., Rodríguez-Rubio, P. R., & Carrasco-Uribarren, A. (2022). The Addition of Diacutaneous Fibrolysis to a Pharmacological Intervention in Patients with Tension-Type Headache: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226716








