A Crosstalk between the Cannabinoid Receptors and Nociceptin Receptors in Colitis—Clinical Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Endogenous Cannabinoid System
3. NOP Receptor
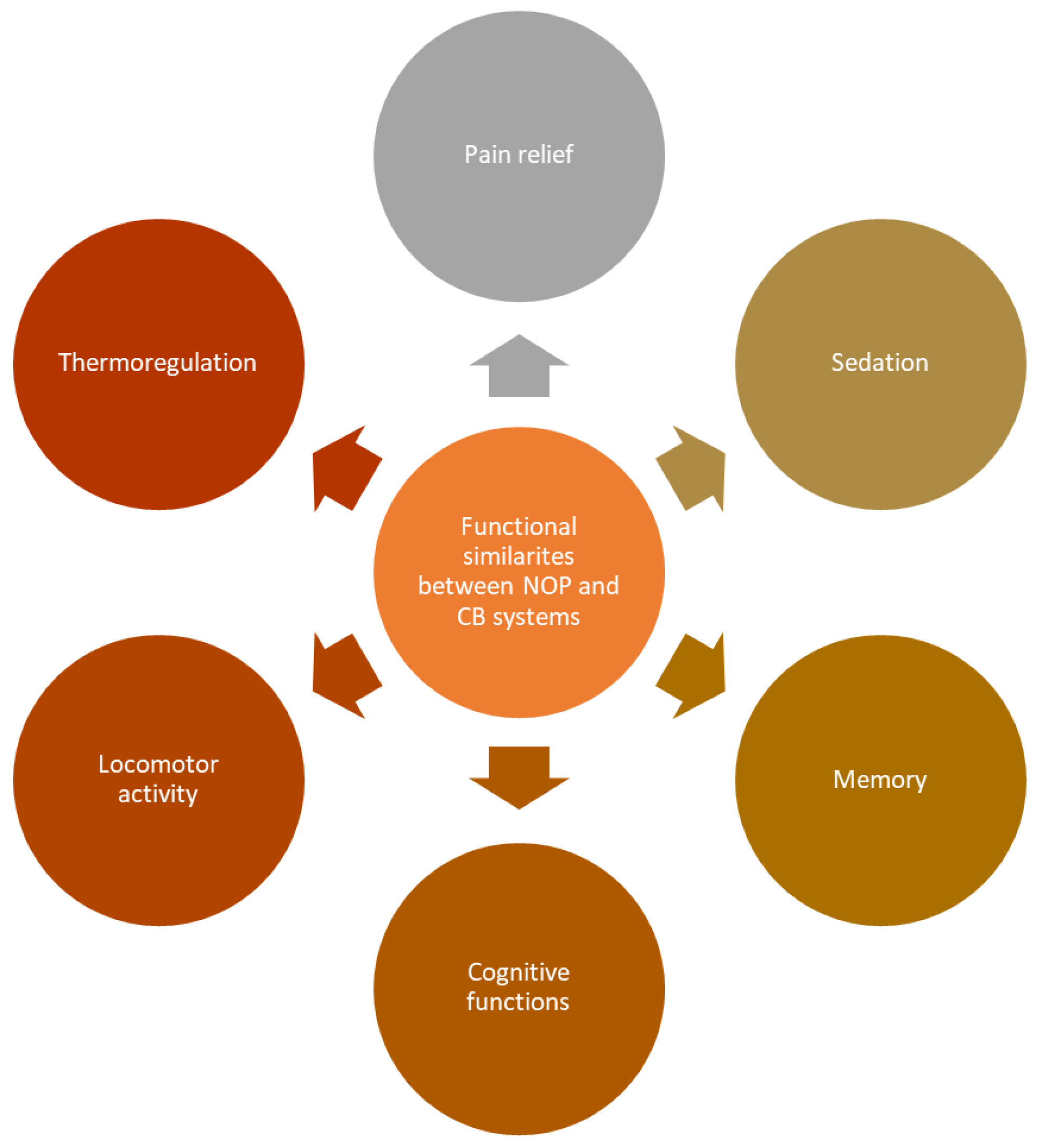
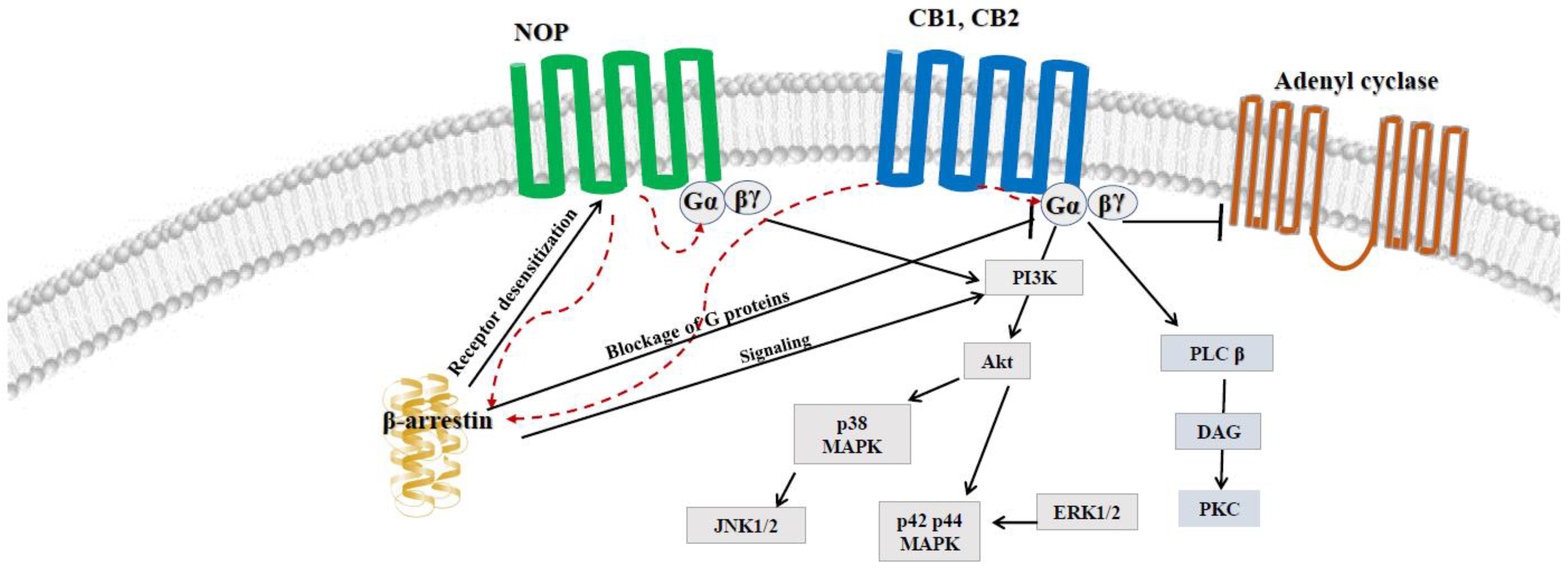
4. Possible Crosstalk between ECS and NOP
5. Possible Use of NOP Receptors in Intestinal Inflammation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambert, D.G. The nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor: A target with broad therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo, P.; Berrendero, F.; Ozaita, A.; Maldonado, R. Advances in the field of cannabinoid-opioid cross-talk. Addict. Biol. 2008, 13, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazantzis, N.P.; Casey, S.L.; Seow, P.W.; Mitchell, V.A.; Vaughan, C.W. Opioid and cannabinoid synergy in a mouse neuropathic pain model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 173, 2521–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczak, M.; Fabisiak, A.; Murawska, N.; Wesołowska, E.; Wierzbicka, P.; Wlazłowski, M.; Wójcikowska, M.; Zatorski, H.; Zwolińska, M.; Fichna, J. Current overview of extrinsic and intrinsic factors in etiology and progression of inflammatory bowel diseases. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N.E.; Schatz, A.R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R.; et al. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C. Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling. In Cannabinoids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 53–79. [Google Scholar]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology, Classification of Cannabinoid Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Katz, S. Therapeutic Use of Cannabis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 12, 668–679. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, M.; Mouihate, A.; Mackie, K.; Keenan, C.M.; Buckley, N.E.; Davison, J.S.; Patel, K.D.; Pittman, Q.J.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in the enteric nervous system modulate gastrointestinal contractility in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G78–G87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, K.; Nigam, S.; Di Marzo, V. Biochemistry and pharmacology of endovanilloids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 114, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, D.; Hu, S.S.; Rimmerman, N.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z.; Walker, J.M.; Bradshaw, H.B. N-arachidonoyl glycine, an abundant endogenous lipid, potently drives directed cellular migration through GPR18, the putative abnormal cannabidiol receptor. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.J. Novel cannabinoid receptors. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 152, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryberg, E.; Larsson, N.; Sjögren, S.; Hjorth, S.; Hermansson, N.-O.; Leonova, J.; Elebring, T.; Nilsson, K.; Drmota, T.; Greasley, P.J. The orphan receptor GPR55 is a novel cannabinoid receptor. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 152, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G. Receptors and Channels Targeted by Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists and Antagonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1360–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G. REVIEW Emerging strategies for exploiting cannabinoid receptor agonists as medicines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Bátkai, S.; Kunos, G. The Endocannabinoid System as an Emerging Target of Pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 389–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Oleas, N.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Nuñez-González, S.; Viteri-García, A.; Simancas-Racines, D. Therapeutic use of cannabis and cannabinoids: An evidence mapping and appraisal of systematic reviews. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Planella, E.; Marín, L.; Domènech, E.; Bernal, I.; Mañosa, M.; Zabana, Y.; Gassull, M.A. Utilización de medicinas alternativas y consumo de drogas por pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Med. Clín. 2007, 128, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, F.; Marsicano, G.; Hermann, H.; Cannich, A.; Monory, K.; Cravatt, B.F.; Ferri, G.-L.; Sibaev, A.; Storr, M.; Lutz, B. The endogenous cannabinoid system protects against colonic inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.P.; Singh, N.P.; Singh, B.; Price, R.L.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Cannabinoid receptor-2 (CB2) agonist ameliorates colitis in IL-10−/− mice by attenuating the activation of T cells and promoting their apoptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavone, J.; Sterling, R.; Van Bockstaele, E. Cannabinoid and opioid interactions: Implications for opiate dependence and withdrawal. Neuroscience 2013, 248, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałaga, M.; Polepally, P.R.; Zakrzewski, P.K.; Cygankiewicz, A.; Sobczak, M.; Kordek, R.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Krajewska, W.M.; Fichna, J. Novel orally available salvinorin A analog PR-38 protects against experimental colitis and reduces abdominal pain in mice by interaction with opioid and cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinscheid, R.K.; Ardati, A.; Monsma, F.J.; Civelli, O. Structure-Activity Relationship Studies on the Novel Neuropeptide Orphanin FQ. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14163–14168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, J.-C.; Mollereau, C.; Toll, L.; Suaudeau, C.; Moisand, C.; Alvinerie, P.; Butour, J.-L.; Guillemot, J.-C.; Ferrara, P.; Monsarrat, B.; et al. Isolation and structure of the endogenous agonist of opioid receptor-like ORL1 receptor. Nature 1995, 377, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollereau, C.; Mouledous, L. Tissue distribution of the opioid receptor-like (ORL1) receptor. Peptides 2000, 21, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, P.K.; Grace, M.K.; Fard, S.S.; le Grevès, M.; Klockars, A.; Massi, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; Levine, A.S. Central nociceptin/orphanin FQ system elevates food consumption by both increasing energy intake and reducing aversive responsiveness. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Simpson-Durand, C.D.; Standifer, K.M. Themed Section: Opioids New Pathways to Functional Selectivity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andero, R. Nociceptin and the nociceptin receptor in learning and memory. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 62, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaldi, M.; Cannella, N.; Ciccocioppo, R. Emerging targets for addiction neuropharmacology: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Prog Brain Res. 2016, 224, 251–284. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, G.; Arletti, R.; Ruggieri, V.; Cifani, C.; Massi, M. Anxiolytic-like effects of nociceptin/orphanin FQ in the elevated plus maze and in the conditioned defensive burying test in rats. Peptides 2006, 27, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, R.-J.; Harrison, R.S.; Ruiz-Gómez, G.; Hoang, H.N.; Shepherd, N.E.; Chow, S.; Hill, T.A.; Madala, P.K.; Fairlie, D.P. Helix-Constrained Nociceptin Peptides Are Potent Agonists and Antagonists of ORL-1 and Nociception. Vitam. Horm. 2015, 97, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaveri, N.T. Nociceptin Opioid Receptor (NOP) as a Therapeutic Target: Progress in Translation from Preclinical Research to Clinical Utility. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7011–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinscheid, R.K.; Nothacker, H.-P.; Bourson, A.; Ardati, A.; Henningsen, R.A.; Bunzow, J.R.; Grandy, D.K.; Langen, H.; Monsma, F.J.; Civelli, O.; et al. Orphanin FQ: A Neuropeptide That Activates an Opioidlike G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Science 1995, 270, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.A.; Liu, W.; Chun, E.; Katritch, V.; Wu, H.; Vardy, E.; Huang, X.-P.; Trapella, C.; Guerrini, R.; Calo, G.; et al. Structure of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor in complex with a peptide mimetic. Nature 2012, 485, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthan, S.; Khare, N.K.; Saini, S.K.; Seitz, L.E.; Bartlett, J.L.; Davis, P.; Dersch, C.M.; Porreca, F.; Rothman, R.B.; Bilsky, E.J. Identification of Opioid Ligands Possessing Mixed µ Agonist/δ Antagonist Activity among Pyridomorphinans Derived from Naloxone, Oxymorphone, and Hydropmorphone. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economidou, D.; Cippitelli, A.; Stopponi, S.; Braconi, S.; Clementi, S.; Ubaldi, M.; Martin-Fardon, R.; Weiss, F.; Massi, M.; Ciccocioppo, R. Activation of Brain NOP Receptors Attenuates Acute and Protracted Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms in the Rat. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bor Turu, G.; Szló Hunyady, L. REVIEW Signal transduction of the CB 1 cannabinoid receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 44, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, M.; Felder, C.C. Concurrent Stimulation of Cannabinoid CB1 and Dopamine D2 Receptors Augments cAMP Accumulation in Striatal Neurons: Evidence for a G s Linkage to the CB1 Receptor. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5327–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, C.C.; Albrecht, F.; Eisner, G.M.; Jose, P.A. The Signal Transducer for the Dopamine-1 Regulated Sodium Transport in Renal Cortical Brush Border Membrane Vesicles. Am. J. Hypertens. 1990, 3, 47S–50S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkinderen, P.; Ledent, C.; Parmentier, M.; Girault, J.-A. Cannabinoids activate p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases through CB1 receptors in hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A.; Wang, H.; Cannizzaro, C.; Dowd, E. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Stüber, F.; Lippuner, C.; Schiff, M.; Stamer, U.M. ERK and p38 contribute to the regulation of nociceptin and the nociceptin receptor in human peripheral blood leukocytes. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919828921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.L.; Silveira, G.T.; Wanderlei, C.W.; Cecilio, N.T.; Maganin, A.G.M.; Franchin, M.; Marques, L.M.; Lopes, N.P.; Crippa, J.A.; Guimarães, F.S. DMH-CBD, a cannabidiol analog with reduced cytotoxicity, inhibits TNF production by targeting NF-kB activity dependent on A2A receptor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 368, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.M.; Wong, Y.H. Mu-Opioid Receptor-Mediated Phosphorylation of IκB Kinase in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donica, C.L.; Awwad, H.O.; Thakker, D.R.; Standifer, K.M. Cellular Mechanisms of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) Peptide (NOP) Receptor Regulation and Heterologous Regulation by N/OFQ. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donica, C.L.; Ramirez, V.I.; Awwad, H.O.; Zaveri, N.T.; Toll, L.; Standifer, K.M. Orphanin FQ/Nociceptin Activates Nuclear Factor Kappa, B. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2011, 6, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chan, A.S.; Wong, Y.H. Regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase by the ORL(1) receptor through multiple G proteins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, K.; Shoda, T.; Morikawa, H.; Kato, S.; Mima, H.; Mori, K. Activation of phospholipase A2 by the nociceptin receptor expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.-G.; Ma, L.; Pei, G. Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ Activates Protein Kinase, C.; and This Effect Is Mediated through Phospholipase C/Ca2+Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 240, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-F. Potassium channels as molecular targets of endocannabinoids. Channels 2021, 15, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.P.; Hirasawa, M. GIRK channel-mediated inhibition of melanin-concentrating hormone neurons by nociceptin/orphanin FQ. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 105, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, T.R.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Stuenkel, E.; Mulholland, M.W. Ghrelin stimulates neurogenesis in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. J. Physiol. 2004, 559, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altier, C.; Zamponi, G.W. Signaling Complexes of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels and G Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2008, 28, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, T. Pharmacological characterization of inhibitory effects of postsynaptic opioid and cannabinoid receptors on calcium currents in neonatal rat nucleus tractus solitarius. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 147, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubovitch, V.; Gafni, M.; Sarne, Y. The cannabinoid agonist DALN positively modulates L-type voltage-dependent calcium-channels in N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 101, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Zamponi, G.W. T-type calcium channels: From molecule to therapeutic opportunities. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 108, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, F.A.; Smith, P.A. Nociceptin Inhibits T-Type Ca2+ Channel Current in Rat Sensory Neurons by a G-Protein-Independent Mechanism. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8721–8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K.; Hillet, B. Cannabinoids inhibit N-type calcium channels in neuroblastoma-glioma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3825–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beedle, A.M.; McRory, J.E.; Poirot, O.; Doering, C.J.; Altier, C.; Barrere, C.; Hamid, J.; Nargeot, J.; Bourinet, E.; Zamponi, G.W. Agonist-independent modulation of N-type calcium channels by ORL1 receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.S.; Napier, I.A.; Rycroft, B.K.; Christie, M. Opioid-related (ORL1) receptors are enriched in a subpopulation of sensory neurons and prolonged activation produces no functional loss of surface N-type calcium channels. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichewicz, D.L. Synergistic interactions between cannabinoid and opioid analgesics. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerak, L.R.; France, C.P. Combined Treatment with Morphine and D 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Rhesus Monkeys: Antinociceptive Tolerance and Withdrawal. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 357, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, D.P.; Beckett, S.R.G.; Roe, C.H.; Madjd, A.; Fone, K.C.F.; Kendall, D.A.; Marsden, C.A.; Chapman, V. Effects of coadministration of cannabinoids and morphine on nociceptive behaviour, brain monoamines and HPA axis activity in a rat model of persistent pain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, B.; Wilson-Poe, A.R. Emerging Evidence for Cannabis’ Role in Opioid Use Disorder. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2018, 3, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, D.I.; Couey, P.; Shade, S.B.; Kelly, M.E.; Benowitz, N.L. Cannabinoid–Opioid Interaction in Chronic Pain. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 90, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massi, P.; Vaccani, A.; Romorini, S.; Parolaro, D. Comparative characterization in the rat of the interaction between cannabinoids and opiates for their immunosuppressive and analgesic effects. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 117, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichewicz, D.L.; Haller, V.L.; Welch, S.P. Changes in opioid and cannabinoid receptor protein following short-term combination treatment with delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol and morphine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Cannarsa, R.; Carretta, D.; Lattanzio, F.; Candeletti, S.; Romualdi, P. Δ 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Decreases NOP Receptor Density and mRNA Levels in Human SH-SY5Y Cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 46, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; McClatchy, D.B.; Geller, E.B.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Tallarida, R.J.; Adler, M.W. Possible mechanism of hypothermia induced by intracerebroventricular injection of orphanin FQ/nociceptin. Brain Res. 2001, 904, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, S.M.; Schroeder, J.A.; Ding, Z.; Rodriguez, T.; Zaveri, N. NOP receptor antagonist, JTC-801, blocks cannabinoid-evoked hypothermia in rats. Neuropeptides 2007, 41, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, O.; Karadag, H.C.; Ulugol, A. Synergistic anti-allodynic effects of nociceptin/orphanin FQ and cannabinoid systems in neuropathic mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulugol, A.; Topuz, R.D.; Gunduz, O.; Kizilay, G.; Karadag, H.C. Changes in nociceptin/orphanin FQ levels in rat brain regions after acute and chronic cannabinoid treatment in conjunction with the development of antinociceptive tolerance. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 30, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagtmans, M.J.; Verspaget, H.W.; Lamers, C.; van Hogezand, R.A. Crohn’s disease in the elderly: A comparison with young adults. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1998, 27, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczak, M.; Sałaga, M.; Storr, M.; Fichna, J. Nociceptin / Orphanin FQ (NOP) Receptors as Novel Potential Target in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibaev, A.; Fichna, J.; Saur, D.; Yuece, B.; Timmermans, J.P.; Storr, M. Nociceptin effect on intestinal motility depends on opioid-receptor like-1 receptors and nitric oxide synthase co-localization. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Makharia, G.K. Understanding and treating abdominal pain and spasms in organic gastrointestinal diseases: Inflammatory bowel disease and biliary diseases. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, S89–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalakes, H.; Stylianides, T.J.; Amanakis, G.; Kolios, G. Exacerbation of inflammatory bowel diseases associated with the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Myth or reality? Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccum, B.; Moninuola, O.; Miller, K.; Khalili, H. Opioid Use among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 895–907.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, P.A.; Brierley, S.M.; Martin, C.M.; Brookes, S.J.H.; Linden, D.R.; A Blackshaw, L. Post-inflammatory colonic afferent sensitisation: Different subtypes, different pathways and different time courses. Gut 2009, 58, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyak, M.J.; Vanner, S. Inflammation-induced hyperexcitability of nociceptive gastrointestinal DRG neurones: The role of voltage-gated ion channels. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2005, 17, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajaczkowska, R.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Pilat, D.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Wordliczek, J.; Mika, J. Involvement of microglial cells in the antinociceptive effects of metamizol in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 175, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichna, J.; Sobczak, M.; Mokrowiecka, A.; Cygankiewicz, A.I.; Zakrzewski, P.K.; Cenac, N.; Sałaga, M.; Timmermans, J.-P.; Vergnolle, N.; Małecka-Panas, E.; et al. Activation of the endogenous nociceptin system by selective nociceptin receptor agonist SCH 221510 produces antitransit and antinociceptive effect: A novel strategy for treatment of diarrhea-predominant IBS. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, M.; Ben Haddou, T.; Cami-Kobeci, G.; Sałaga, M.; Jarmuż, A.; Padysz, M.; Kordek, R.; Spetea, M.; Husbands, S.M.; Fichna, J. Anti-inflammatory effect of dual nociceptin and opioid receptor agonist, BU08070, in experimental colitis in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 765, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrella, C.; Giuli, C.; Broccardo, M.; Eutamene, H.; Cartier, C.; Leveque, M.; Bedini, A.; Spampinato, S.; Bueno, L.; Theodorou, V.; et al. Protective and worsening peripheral nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor-mediated effect in a rat model of experimental colitis. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 70, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wołyniak, M.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E.; Zielińska, M.; Fabisiak, A. A Crosstalk between the Cannabinoid Receptors and Nociceptin Receptors in Colitis—Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226675
Wołyniak M, Małecka-Wojciesko E, Zielińska M, Fabisiak A. A Crosstalk between the Cannabinoid Receptors and Nociceptin Receptors in Colitis—Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226675
Chicago/Turabian StyleWołyniak, Maria, Ewa Małecka-Wojciesko, Marta Zielińska, and Adam Fabisiak. 2022. "A Crosstalk between the Cannabinoid Receptors and Nociceptin Receptors in Colitis—Clinical Implications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226675
APA StyleWołyniak, M., Małecka-Wojciesko, E., Zielińska, M., & Fabisiak, A. (2022). A Crosstalk between the Cannabinoid Receptors and Nociceptin Receptors in Colitis—Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6675. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226675







