Associated Pathologies following Luxatio Erecta Humeri: A Retrospective Analysis of 38 Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
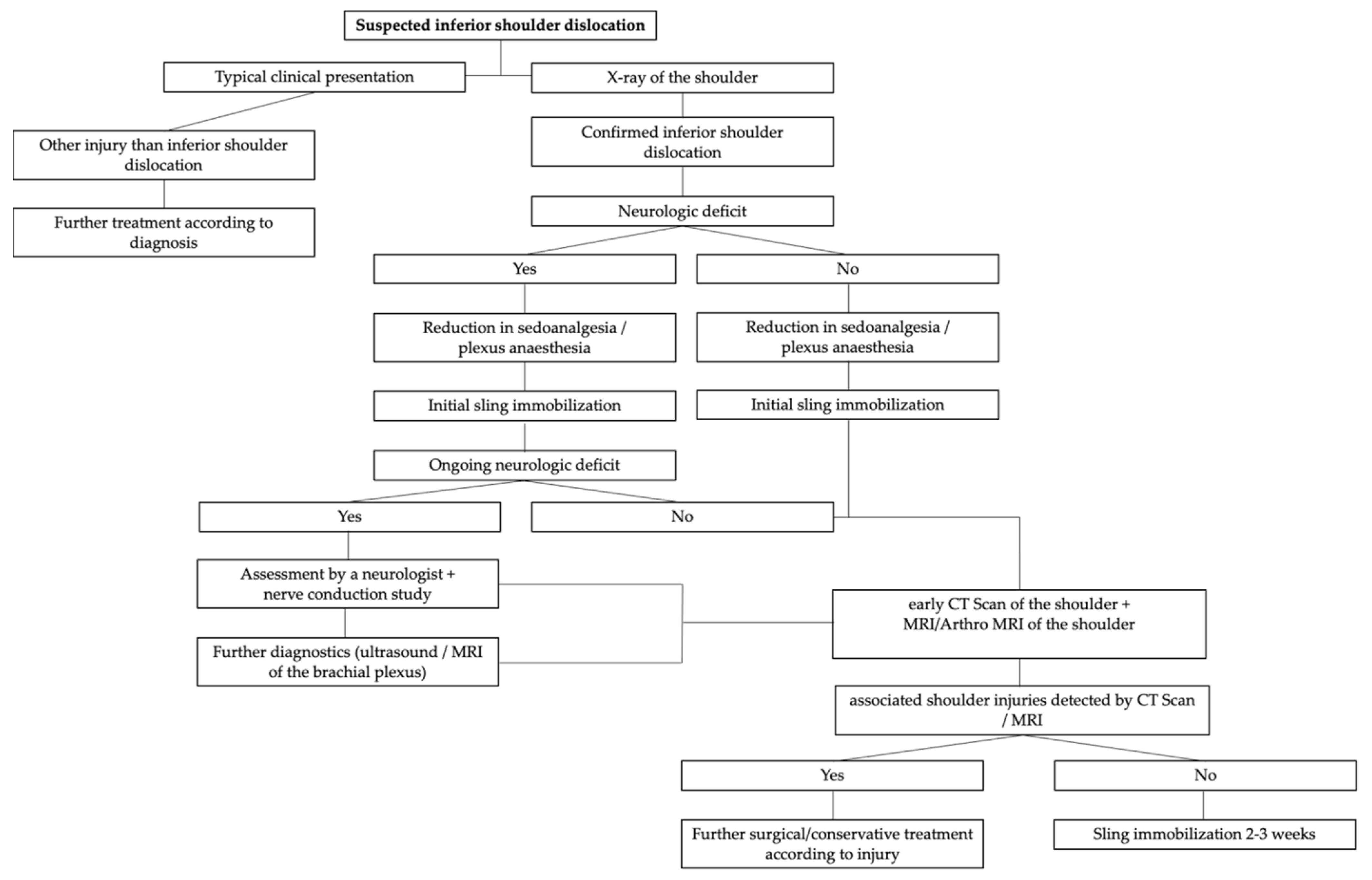
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerber, C.; Nyffeler, R.W. Classification of glenohumeral joint instability. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 400, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, M.; Owen, D.; Moore, P.; Carr, A.; Thomas, M. Traumatic inferior shoulder dislocation: A review of management and outcome. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2018, 44, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallon, W.J.; Bassett, F.H., 3rd; Goldner, R.D. Luxatio erecta: The inferior glenohumeral dislocation. J. Orthop. Trauma 1990, 4, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanturali, S.; Aksay, E.; Holliman, C.J.; Duman, O.; Ozen, Y.K. Luxatio erecta: Clinical presentation and management in the emergency department. J. Emerg. Med. 2005, 29, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, G.I.; Wirth, M.A.; Rockwood, C.A., Jr. Results of treatment of luxatio erecta (inferior shoulder dislocation). J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010, 19, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh, E.; Chang, C.Y.; Huang, A.J.; Shaqdan, K.; Mansouri, M.; Aran, S.; Abujudeh, H.H. CT and MRI manifestations of luxatio erecta humeri and a review of the literature. Clin. Imaging 2015, 39, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yoshiya, S.; Kurosaka, M.; Nagira, K.; Nabeshima, Y. Luxatio erecta (inferior dislocation of the shoulder): A report of 5 cases and a review of the literature. Am. J. Orthop. Belle Mead NJ 2003, 32, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bottoni, C.R.; Wilckens, J.H.; DeBerardino, T.M.; D’Alleyrand, J.C.; Rooney, R.C.; Harpstrite, J.K.; Arciero, R.A. A prospective, randomized evaluation of arthroscopic stabilization versus nonoperative treatment in patients with acute, traumatic, first-time shoulder dislocations. Am. J. Sports Med. 2002, 30, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, B.W.; Johannsen, H.V.; Suder, P.; Søjbjerg, J.O. Primary repair versus conservative treatment of first-time traumatic anterior dislocation of the shoulder: A randomized study with 10-year follow-up. Arthroscopy 2007, 23, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkley, A.; Werstine, R.; Ratjek, A.; Griffin, S. Prospective randomized clinical trial comparing the effectiveness of immediate arthroscopic stabilization versus immobilization and rehabilitation in first traumatic anterior dislocations of the shoulder: Long-term evaluation. Arthroscopy 2005, 21, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liavaag, S.; Svenningsen, S.; Reikerås, O.; Enger, M.; Fjalestad, T.; Pripp, A.H.; Brox, J.I. The epidemiology of shoulder dislocations in Oslo. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2011, 21, e334–e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacchilli, M.A.; Owens, B.D. Epidemiology of shoulder dislocations presenting to emergency departments in the United States. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, M.; Resch, H.; Forstner, R.; Raffl, M.; Schauer, J. Reasons for failure after surgical repair of anterior shoulder instability. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004, 13, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Wakitani, S.; Hayashida, K. Histologic analysis of bony Bankart lesions in recurrent anterior instability of the shoulder. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006, 15, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, G.E.; Griffith, J.F.; Yu, A.B.; Yung, P.S.; Chan, K.M.; Ahuja, A.T. First-time shoulder dislocation: High prevalence of labral injury and age-related differences revealed by MR arthrography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannakopoulos, C.K.; Mataragas, E.; Antonogiannakis, E. A comparison of the spectrum of intra-articular lesions in acute and chronic anterior shoulder instability. Arthroscopy 2007, 23, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, E.; Tabata, S. Rotator cuff tears in anterior dislocation of the shoulder. Int. Orthop. 1992, 16, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasila, M.; Jaroma, H.; Kiviluoto, O.; Sundholm, A. Early complications of primary shoulder dislocations. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1978, 49, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, B. Acute anterior dislocation of the shoulder. Clinical and experimental studies. Ann. R Coll. Surg. Engl. 1969, 44, 255–273. [Google Scholar]
- Simank, H.G.; Dauer, G.; Schneider, S.; Loew, M. Incidence of rotator cuff tears in shoulder dislocations and results of therapy in older patients. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2006, 126, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonides, P.P. The significance of the subscapularis muscle in the pathogenesis of recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1972, 54, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijmes, J.; Loyd, H.M.; Tullos, H.S. Arthrography in acute shoulder dislocations. South. Med. J. 1979, 72, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, T.B.; Walch, G.; Sirveaux, F.; Molé, D.; Nové-Josserand, L.; Boulahia, A.; Neyton, L.; Szabo, I.; Lindgren, B.; O’Connor, D.P. Repair of tears of the subscapularis. Surgical technique. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2006, 88 Pt 1 (Suppl. 1), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermeyer, P.; Gleyze, P.; Rickert, M. Evolution of lesions of the labrum-ligament complex in posttraumatic anterior shoulder instability: A prospective study. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999, 8, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, R. Topographie und funktionelle Anatomie des Schultergürtels und des Schultergelenks; Elsevier, Urban & Fischer Verlag: München, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Apaydin, N.; Uz, A.; Bozkurt, M.; Elhan, A. The anatomic relationships of the axillary nerve and surgical landmarks for its localization from the anterior aspect of the shoulder. Clin. Anat. 2007, 20, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antal, C.S.; Conforty, B.; Engelberg, M.; Reiss, R. Injuries to the axillary due to anterior dislocation of the shoulder. J. Trauma 1973, 13, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curr, J.F. Rupture of the axillary artery complicating dislocation of the shoulder. Report of a case. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1970, 52, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gugenheim, S.; Sanders, R.J. Axillary artery rupture caused by shoulder dislocation. Surgery 1984, 95, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jardon, O.M.; Hood, L.T.; Lynch, R.D. Complete avulsion of the axillary artery as a complication of shoulder dislocation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1973, 55, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumina, S.; Postacchini, F. Anterior dislocation of the shoulder in elderly patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1997, 79, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, S.E.; Weissman, B.N. CT findings in normal and dislocating shoulders. J. Can. Assoc. Radiol. 1985, 36, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singson, R.D.; Feldman, F.; Bigliani, L. CT arthrographic patterns in recurrent glenohumeral instability. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, K.J.; Preston, B.J.; Wallace, W.A.; Kerslake, R.W. CT imaging and three-dimensional reconstructions of shoulders with anterior glenohumeral instability. Clin. Anat. 1999, 12, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

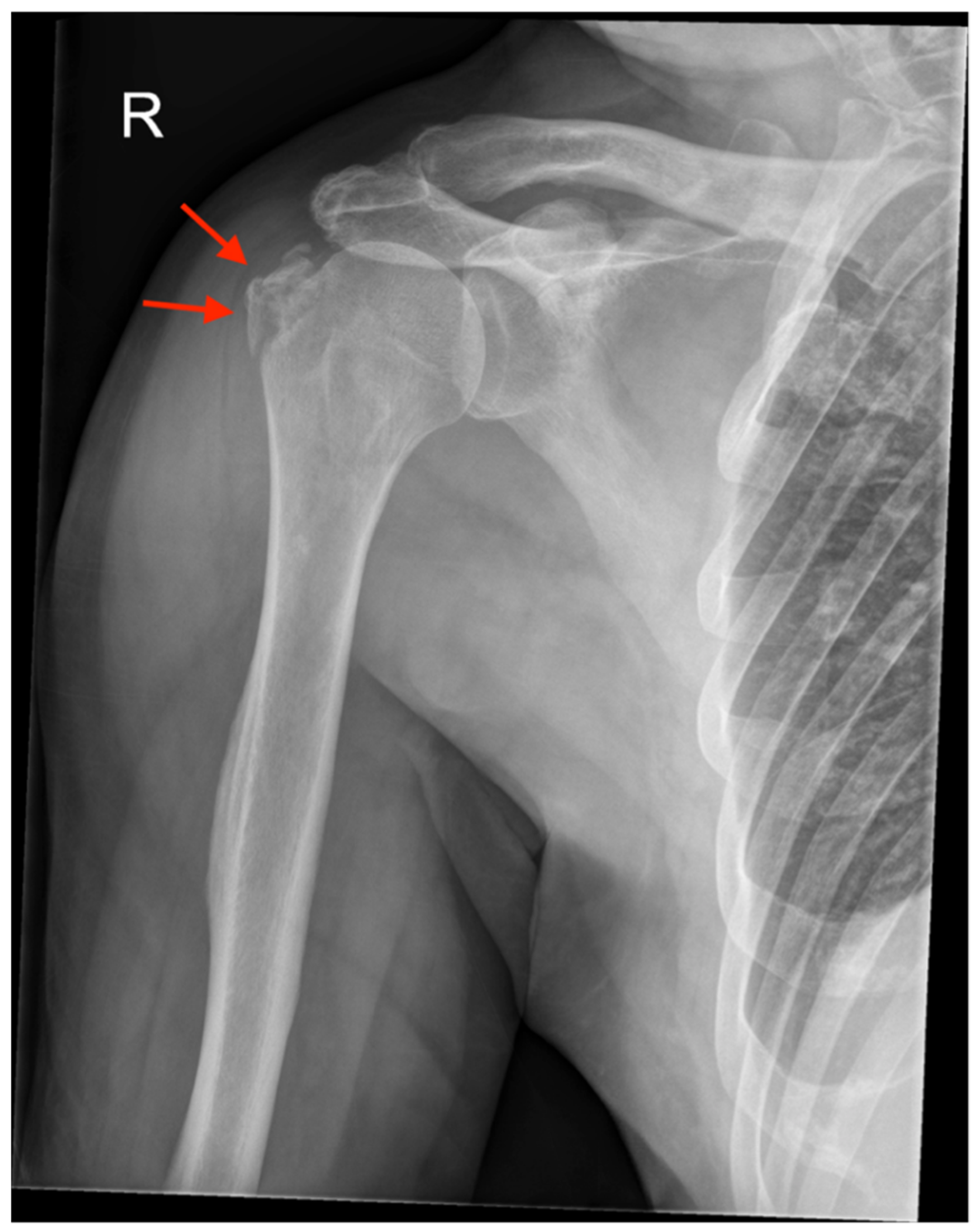
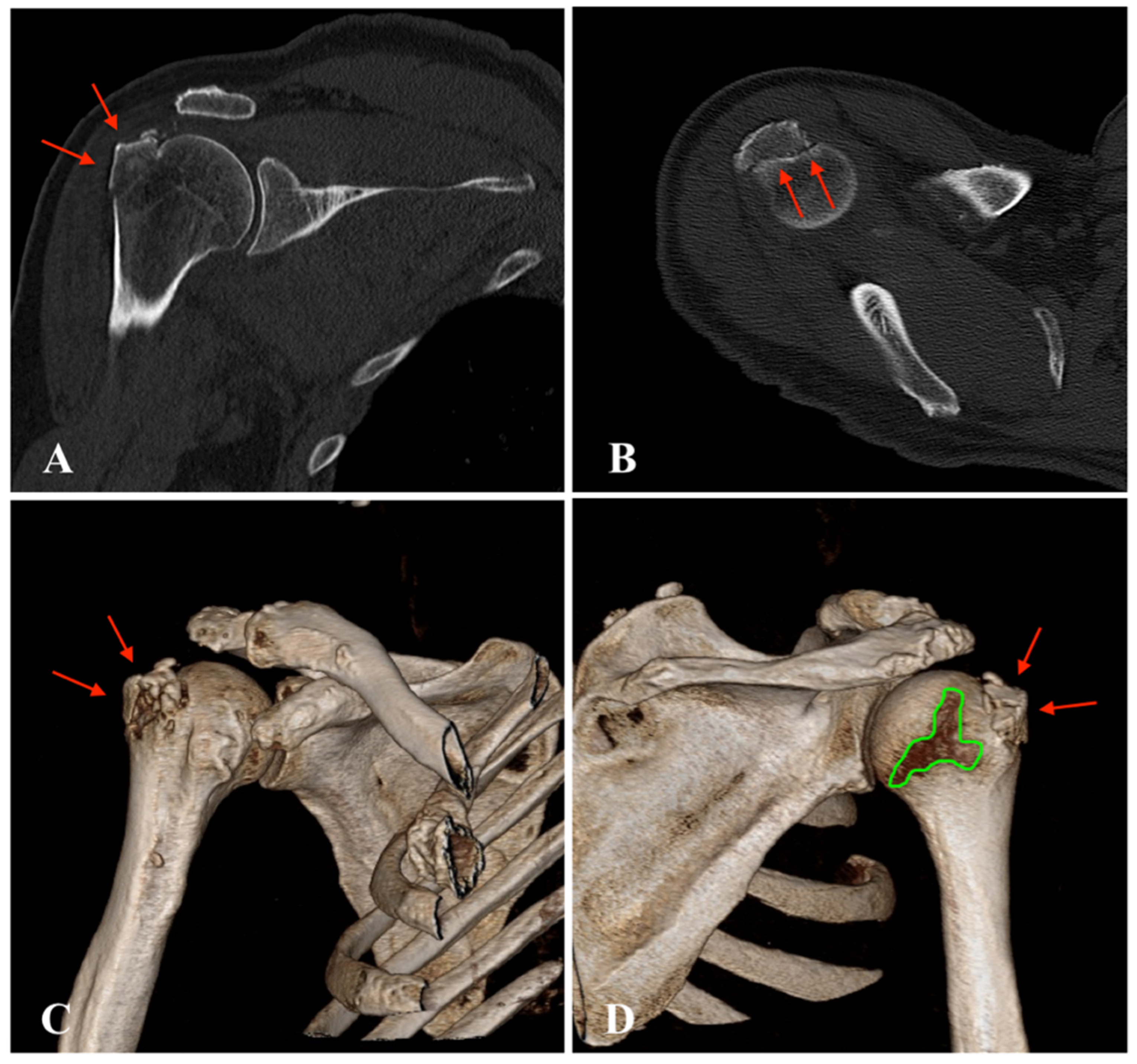
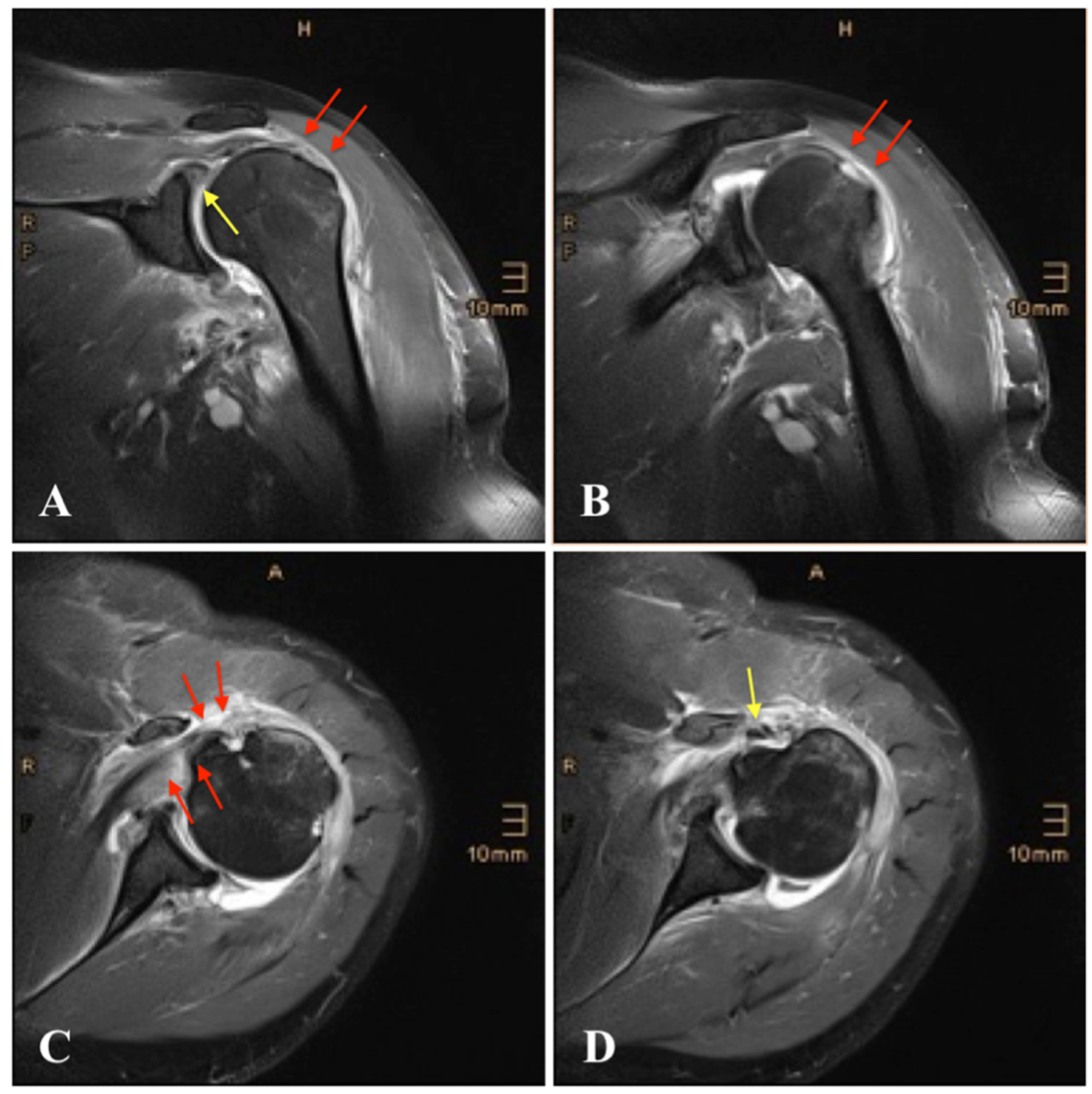
| Patient | Sex | Age | Affected Side | Injury Pattern | Radiologic Examination | Method of Reduction | Immobilization (in Weeks) | Follow-Up (in Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 15 | Right | Volleyball | - Radiography - CT | Short anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | M | 16 | Left | Handstand | - Radiography - CT - MRI | Short anesthesia | 3 | 4 |
| 3 | F | 17 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 4 | M | 18 | Right | Shadowboxing | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 5 | M | 23 | Right | Accident | - Radiography - US - MRI | Conservative, without anesthesia (from outside) | 3 | 1 |
| 6 | M | 27 | Right | Shoring up | Radiography | Interscalene block | 3 | 1 |
| 7 | M | 28 | Right | Sports | Radiography | Fluroscopy, without anesthesia | 3 | 2 |
| 8 | F | 32 | Left | Fall from ladder | - Radiography - MRI | Interscalene block | 2 | 4 |
| 9 | M | 33 | Left | Fall | Radiography | Short anesthesia | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | M | 46 | Left | Bicycle accident | - Radiography - MRI | Short anesthesia | 3 | 5 |
| 11 | M | 48 | Right | Fall | - Radiography - CT | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 12 | M | 49 | Right | Fall | - Radiography - MRI | Short anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 13 | F | 51 | Left | Bicycle accident | - Radiography - CT - MR-arthrography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 4 |
| 14 | M | 56 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 2 |
| 15 | M | 58 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 2 |
| 16 | M | 60 | Right | Fall | - Radiography - MR-arthrography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 11 |
| 17 | M | 63 | Left | Tennis | - Radiography - MRI | Conservative, without anesthesia | 2 | 4 |
| 18 | M | 64 | Left | Bicycle accident | Radiography | Short anesthesia | 3 | 2 |
| 19 | M | 66 | Left | Sports | - Radiography - CT | Interscalene block | 3 | 4 |
| 20 | F | 69 | Left | Fall | Radiography | Short anesthesia | 5 | 4 |
| 21 | M | 69 | Right | Fall | - Radiography - MRI | Short anesthesia | 3 | 3 |
| 22 | F | 71 | Left | Fall | Radiography | Fluroscopy, without anesthesia | 1 1 | 1 |
| 23 | M | 72 | Right | Fall | - Radiography - CT | Conservative, without anesthesia | 4 | 3 |
| 24 | M | 77 | Right | Fall, alcohol intoxication | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 4 | 4 |
| 25 | F | 77 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Short anesthesia | 3 | 3 |
| 26 | M | 77 | Left | Fall | Radiography | Short anesthesia | 3 | 5 |
| 27 | F | 79 | Left | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 1 2 | 3 |
| 28 | F | 86 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 2 | 1 |
| 29 | F | 87 | Right | Fall | - Radiography - CT | Short anesthesia | 1 | 1 |
| 30 | F | 90 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 31 | F | 91 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 32 | M | 20 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 33 | F | 67 | Right | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 2 |
| 34 | M | 63 | Left | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, with anesthesia | 4 | 8 |
| 35 | M | 40 | Right | Sport | Radiography | Conservative, with anesthesia | 3 | 2 |
| 36 | M | 29 | Right | Sport | Radiography | Conservative, with anesthesia | 3 | 3 |
| 37 | W | 68 | Left | Fall | Radiography | Conservative, without anesthesia | 3 | 1 |
| 38 | M | 57 | Right | Fall, Epilepsia | Radiography | Operative treatment | 3 | 25 |
| Patient | Bony Injuries | Rotator Cuff and LHBT Injuries | Capsule and Ligament Injuries | Neurologic Injuries | Further Surgical Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | None | None | None | None |
| 2 | - Bony Bankart lesion - Greater tuberosity fracture - Hill-Sachs lesion | None | Bony Bankart lesion | None | Arthroscopic Bankart repair |
| 3 | None | None | None | None | None |
| 4 | None | None | None | None | None |
| 5 | Bony avulsion of supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendon | Bony avulsion of supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendon | None | None | None |
| 6 | ALPSA lesion with glenoid bone loss (chronic luxations) | None | ALPSA lesion with glenoid bone loss | Mixed, not relatable (numbness in all fingers) 1 | Open Latarjet procedure |
| 7 | None | None | Subluxation of humeral head in standard radiographs, suspected Bankart lesion | Ulnar nerve palsy (4th and 5th finger) 1 | None |
| 8 | - Bony Bankart lesion - Hill-Sachs lesion | None | Bony Bankart lesion | None | None |
| 9 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 10 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 11 | None | None | None | None | None |
| 12 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 13 | None | Partial rupture of supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendon | SLAP III lesion | None | None |
| 14 | None | None | None | None | None |
| 15 | Greater tuberosity fracture | Restricted ROM, highly suspectable of rotator cuff lesion | None | None | None |
| 16 | None | - Rupture of the supraspinatus - tendon - Partial rupture of the LHBT | None | Axillary nerve palsy, after reduction 1 | Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, subacromial decompression and biceps tenodesis |
| 17 | Hill-Sachs lesion | - Rupture of the supraspinatus, - infraspinatus and subscapularis - tendon | - SLAP III lesion - Avulsion of posterior and inferior labrum | None | Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, subacromial decompression and biceps tenotomy |
| 18 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 19 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 20 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 21 | None | - Rupture of the supraspinatus and subscapularis tendon - Partial rupture of the infraspinatustendon - Rupture of the LHBT | - SLAP III lesion | None | None |
| 22 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 23 | Greater tuberosity fracture | Restricted ROM, highly suspectable of rotator cuff lesion | None | Mixed, not relatable (numbness in 2nd, 3rd and 4th finger), after reduction 1 | None |
| 24 | Bony avulsion of inferior glenoid | Proximal migration of humeral head in standard radiographs, highly suspectable of rotator cuff lesion | Bony avulsion of inferior glenoid | None | None |
| 25 | Greater tuberosity fracture | Restricted ROM, highly suspectable of rotator cuff lesion | None | Mixed, not relatable (numbness in all fingers) 1 | None |
| 26 | Greater tuberosity fracture | Restricted ROM, highly suspectable of rotator cuff lesion | None | None | None |
| 27 | Proximal humeral head fracture with dislocation into the axilla | Total rupture of rotator cuff | None | None | Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty |
| 28 | None | None | None | None | None |
| 29 | Bony avulsion of inferior glenoid | None | Bony avulsion of inferior glenoid | Axillary nerve palsy | None |
| 30 | None | Restricted ROM, highly suspectable of rotator cuff lesion | None | None | None |
| 31 | None | Proximal migration of humeral head in standard radiographs, highly suspectable of rotator cuff lesion | None | Axillary nerve palsy, after reduction 1 | None |
| 32 | None | None | SLAP III lesion | None | Outside hospital |
| 33 | None | None | None | Radialis palsy | None |
| 34 | None | None | None | None | None |
| 35 | posterior Hill-Sachs Lesion | Lesion of the LHBT | Labrum lesion anterior inferior | None | None |
| 36 | Greater tuberosity fracture | None | None | None | None |
| 37 | posterior Hill-Sachs Lesion | None | None | None | None |
| 38 | Impression of the humeral head | None | None | None | None |
| Associated Shoulder Injuries (Patient Number/Percentage) | Associated Injuries to Other Body Regions (Patient Number/Percentage) | Associated Bony Shoulder Injuries (Patient Number/Percentage) | Associated Rotator Cuff/Tendon Injuries (Patient Number/Percentage); Numbers in Comma Include Suspected RC Injuries Due to X-ray or Clinical Findings | Associated Injuries to the Capsule-Ligament Complex (Patient Number/Percentage) | Associated Neurological Findings (Patient Number/Percentage) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31/82 | 6/16 | 23/61 | 7/18 (14/37) | 7/18 | 8/21 |
| Bony injuries broken down in total numbers | Rotator cuff/tendon injuries broken down in total numbers | Capsule-ligament complex injuries broken down in total numbers | Neurological findings broken down in total numbers | ||
| 2 bony Bankart lesions 1 ALPSA lesion with bony flinge 2 bony avulsions of inferior glenoid 1 bony avulsion of rotator cuff 5 Hill-Sachs lesions 2 proximal humeral head FXs 13 FXs of the greater tuberosity | 3 partial tears of SSP + ISP 4 complete SSP tears 1 complete ISP tear 2 complete SSC tear 1 total cuff tear 1 bony avulsion of the rotator cuff 1 partial rupture of the long head of the biceps 2 total ruptures of the long head of the biceps | 1 avulsion of the posterior and inferior labrum 4 SLAP type III lesions 2 bony avulsions of the inferior glenoid 2 bony Bankart lesions 1 ALPSA lesion with bony flinge | 1 ulnar nerve palsy 1 radial nerve palsy 3 axillary nerve palsies 3 mixed nerve palsies | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ostermann, R.C.; Joestl, J.; Hofbauer, M.; Fialka, C.; Schanda, J.E.; Gruber, M.; Binder, H.; Tiefenboeck, T.M. Associated Pathologies following Luxatio Erecta Humeri: A Retrospective Analysis of 38 Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020453
Ostermann RC, Joestl J, Hofbauer M, Fialka C, Schanda JE, Gruber M, Binder H, Tiefenboeck TM. Associated Pathologies following Luxatio Erecta Humeri: A Retrospective Analysis of 38 Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(2):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020453
Chicago/Turabian StyleOstermann, Roman C., Julian Joestl, Marcus Hofbauer, Christian Fialka, Jakob E. Schanda, Maximilian Gruber, Harald Binder, and Thomas M. Tiefenboeck. 2022. "Associated Pathologies following Luxatio Erecta Humeri: A Retrospective Analysis of 38 Cases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 2: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020453
APA StyleOstermann, R. C., Joestl, J., Hofbauer, M., Fialka, C., Schanda, J. E., Gruber, M., Binder, H., & Tiefenboeck, T. M. (2022). Associated Pathologies following Luxatio Erecta Humeri: A Retrospective Analysis of 38 Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(2), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020453








