Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Direct Acting Antivirals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
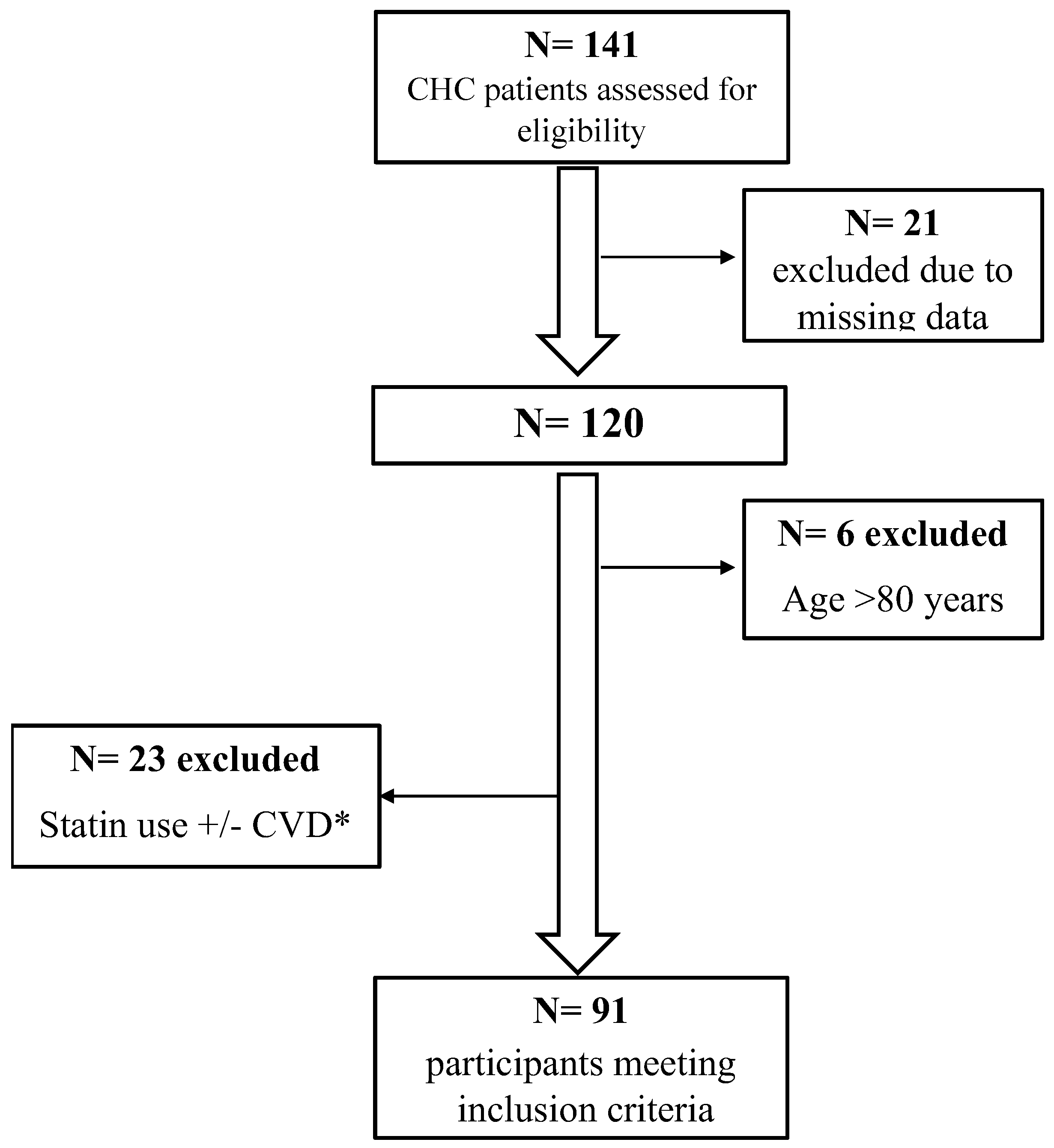
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Definition and Ascertainment of Outcomes
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Sample Size Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Subjects’ Characteristics
3.2. Changes in Liver Fibrosis after DAA Treatment
3.3. Dynamics of ASCVD and FIB-4 Scores over Time
3.4. Association between ASCVD and FIB-4 Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Hepatitis B and C Testing; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Blach, S.; Terrault, N.A.; Tacke, F.; Gamkrelidze, I.; Craxi, A.; Tanaka, J.; Waked, I.; Dore, G.J.; Abbas, Z.; Abdallah, A.R.; et al. Global change in hepatitis C virus prevalence and cascade of care between 2015 and 2020: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 396–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebely, J.; Page, K.; Sacks-Davis, R.; van der Loeff, M.S.; Rice, T.M.; Bruneau, J.; Morris, M.D.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Amin, J.; Cox, A.L.; et al. The effects of female sex, viral genotype, and IL28B genotype on spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2014, 59, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Zampino, R.; Restivo, L.; Lonardo, A.; Guerrera, B.; Marrone, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Florio, A.; Loria, P. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and atherosclerosis: Clinical impact and mechanisms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3410–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, A.; Jeudy, J.; Kligerman, S.; Khambaty, M.; Shah, A.; Bagchi, S. Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Due to Chronic Hepatitis C Infection: A Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golia, E.; Limongelli, G.; Natale, F.; Fimiani, F.; Maddaloni, V.; Pariggiano, I.; Bianchi, R.; Crisci, M.; D’Acierno, L.; Giordano, R.; et al. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: From pathogenesis to therapeutic target. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craxì, A.; Laffi, G.; Zignego, A.L. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection: A systemic disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2008, 29, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Gragnani, L.; Comarmond, C.; Zignego, A.L. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46 (Suppl. 5), S165–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Yang, H.I.; Lu, S.N.; Jen, C.L.; You, S.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, C.J. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection increases mortality from hepatic and extrahepatic diseases: A community-based long-term prospective study. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Maida, M.; Macaluso, F.S.; Barbara, M.; Licata, A.; Craxì, A.; Cammà, C. Hepatitis C Virus Infection Is Associated with Increased Cardiovascular Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 145–155.e144; quiz e115–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Stelzle, D.; Bing, R.; Anwar, M.; Strachan, F.; Bashir, S.; Newby, D.E.; Shah, J.S.; Chung, M.H.; Bloomfield, G.S.; et al. Global burden of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in people with hepatitis C virus infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, F.; Francoz, C. The future of liver transplantation for viral hepatitis. Liver Int. 2017, 37 (Suppl. 1), 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Rinaldi, L.; Nevola, R. Chronic hepatitis C, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease: What impact of direct-acting antiviral treatments? World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4617–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, M.S.; Russo, V.; Nigro, G.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Zampino, R. Interplay between Heart Disease and Metabolic Steatosis: A Contemporary Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyan, O.; Kacmaz, F.; Ozdemir, O.; Deveci, B.; Astan, R.; Celebi, A.S.; Ilkay, E. Hepatitis C infection is associated with increased coronary artery atherosclerosis defined by modified Reardon severity score system. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddi, M.; Abbate, R.; Chellini, B.; Giusti, B.; Giannini, C.; Pratesi, G.; Rossi, L.; Pratesi, C.; Gensini, G.F.; Paperetti, L.; et al. Hepatitis C virus RNA localization in human carotid plaques. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.P.; Jeffers, T.; Younoszai, Z.; Fazel, Y.; Younossi, Z.M. The changing landscape of hepatitis C virus therapy: Focus on interferon-free treatment. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, J.J.; Jacobson, I.M.; Hézode, C.; Asselah, T.; Ruane, P.J.; Gruener, N.; Abergel, A.; Mangia, A.; Lai, C.-L.; Chan, H.L.Y.; et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV Genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Afdhal, N.; Roberts, S.K.; Bräu, N.; Gane, E.J.; Pianko, S.; Lawitz, E.; Thompson, A.; Shiffman, M.L.; Cooper, C.; et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV Genotype 2 and 3 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2608–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degasperi, E.; Aghemo, A.; Colombo, M. Treatment of Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iossa, D.; Vitrone, M.; Gagliardi, M.; Falco, E.; Ragone, E.; Zampino, R.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Anthropometric parameters and liver histology influence lipid metabolic changes in HCV chronic hepatitis on direct-acting antiviral treatment. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Zhao, X.; Deng, J.L.; Li, S.N.; Du, X.; Dong, J.Z.; Ma, C.S. Antiviral treatment for hepatitis C is associated with a reduced risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Viral. Hepat. 2021, 28, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roguljic, H.; Nincevic, V.; Bojanic, K.; Kuna, L.; Smolic, R.; Vcev, A.; Primorac, D.; Vceva, A.; Wu, G.Y.; Smolic, M. Impact of DAA Treatment on Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Chronic HCV Infection: An Update. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 678546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaro, C.; Quartuccio, L.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Roccatello, D.; Pozzato, G.; Nevola, R.; Tonizzo, M.; Gitto, S.; Andreone, P.; Gattei, V. A Review on Extrahepatic Manifestations of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and the Impact of Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy. Viruses 2021, 13, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, E.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Osinusi, A.; Sims, Z.; Qin, J.; Sturdevant, D.; McHutchison, J.; Subramanian, M.; Sampson, M.; Naggie, S.; et al. Effect of sofosbuvir and ribavirin treatment on peripheral and hepatic lipid metabolism in chronic hepatitis C virus, genotype 1-infected patients. Hepatology 2015, 61, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.R.; Velosa, J.; Serejo, F. Lipids, glucose and iron metabolic alterations in chronic hepatitis C after viral eradication—Comparison of the new direct-acting antiviral agents with the old regimens. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, N.; Suda, G.; Nakamura, A.; Kimura, M.; Maehara, O.; Suzuki, K.; Nakamura, A.; Ohara, M.; Izumi, T.; Umemura, M.; et al. Liver steatosis and dyslipidemia after HCV eradication by direct acting antiviral agents are synergistic risks of atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, C.; Welzel, T.; Bogdanou, D.; Vermehren, J.; Beckel, A.; Bojunga, J.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Dietz, J.; Kubesch, A.; Mondorf, A.; et al. Hepatitis C Clearance by Direct-Acting Antivirals Impacts Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, M.; Rabiee, A.; Abdellatif, Z.; Abdel Alem, S.; Moustafa, A. Impact of sustained virological response on metabolic disorders in diabetic chronic hepatitis C virus patients after treatment with generic sofosbuvir and daclatasvir. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Dai, C.Y.; Yeh, M.L.; Huang, C.I.; Lee, H.C.; Lai, W.T.; Liang, P.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Hou, N.J.; et al. Cure or curd: Modification of lipid profiles and cardio-cerebrovascular events after hepatitis C virus eradication. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stine, J.G.; Wynter, J.A.; Niccum, B.; Kelly, V.; Caldwell, S.H.; Shah, N.L. Effect of Treatment with Direct Acting Antiviral on Glycemic Control in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Hepatitis C. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2015. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 199–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco (AIFA)—Pubblicato il Nuovo Algoritmo per la Terapia dell’Epatite C Cronica, 24.03.2015. Available online: http://www.regioni.it/news/2015/03/24/aifa-pubblicato-il-nuovo-algoritmo-per-la-terapia-dellepatite-c-cronica-24-03-2015-396169/ (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Negro, F.; Aghemo, A.; Berenguer, M.; Dalgard, O.; Dusheiko, G.; Marra, F.; Puoti, M.; Wedemeyer, H. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C: Final update of the series. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1170–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco (AIFA); Ridefinizione dei Criteri di Trattamento per la Terapia dell’Epatite C Cronica. (Determina n. 500/2017). (17A02374). 2017. Available online: https://www.aifa.gov.it/sites/default/files/Determina_n._500-2017_Epatite-C.pdf/ (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghany, M.G.; Strader, D.B.; Thomas, D.L.; Seeff, L.B. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: An update. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1335–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, D.C.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Bennett, G.; Coady, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Gibbons, R.; Greenland, P.; Lackland, D.T.; Levy, D.; O’Donnell, C.J.; et al. 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk. Circulation 2014, 129, S49–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Braun, L.T.; Ndumele, C.E.; Smith, S.C.; Sperling, L.S.; Virani, S.S.; Blumenthal, R.S. Use of Risk Assessment Tools to Guide Decision-Making in the Primary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Special Report From the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology. Circulation 2019, 139, e1162–e1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, S.M.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greater Boston Gastroenterology. Fibroscan™ (Sound Based Elastography). Available online: https://greaterbostongi.com/fibroscan-sound-based-elastography/ (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- Hsu, Y.C.; Lin, J.T.; Ho, H.J.; Kao, Y.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Hsiao, N.W.; Wu, M.S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wu, C.Y. Antiviral treatment for hepatitis C virus infection is associated with improved renal and cardiovascular outcomes in diabetic patients. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.W.; Bhattacharya, D.; McGinnis, K.A.; Horwich, T.B.; Tseng, C.H.; Currier, J.S.; Butt, A.A. Short Communication: Coronary Heart Disease Risk by Framingham Risk Score in Hepatitis C and HIV/Hepatitis C-Coinfected Persons. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2015, 31, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoberg, D.D.; Whiting, K.; Curry, M.; Lavery, J.A.; Larmarange, J. Reproducible Summary tables with the Gtsummary Package. R J. 2021, 13, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley Wickham, R.F.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R Package Version 1.0.7. 2021. Available online: https://dplyr.tidyverse.org, https://github.com/tidyverse/dplyr (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Champely, S. pwr: Basic Functions for Power Analysis. R Package Version 1.3-0. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/heliosdrm/pwr (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- Yan, J. geepack: Yet Another Package for Generalized Estimating Equations. R-News 2002, 2, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- R Studio Team. R Studio: Integrated Develoment Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Chu, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-L.; Lin, I.T.; Wu, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-K.; Hu, P.-J.; Bair, M.-J. Direct-acting antiviral therapy of chronic hepatitis C improves liver fibrosis, assessed by histological examination and laboratory markers. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2021, 120, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierwagen, R.; Uschner, F.E.; Magdaleno, F.; Klein, S.; Trebicka, J. Rationale for the use of statins in liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G407–G412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreidieh, M.; Hamadi, R.; Alsheikh, M.; Al Moussawi, H.; Deeb, L. Statin Use in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Curr. Evid. Future Dir. 2022, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Alswat, K.; Al-Sohaibani, F.; Khathlan, A.; Bashmail, A.; Alanazi, M.; Kurdi, A.; Almakadma, A.H.; Al-Hamoudi, W. Hepatic fibrosis changes in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection who respond to direct-acting antivirals. Ann. Saudi. Med. 2022, 42, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkawy, A.; Alem, S.A.; Fouad, R.; El Raziky, M.; El Akel, W.; Abdo, M.; Tantawi, O.; AbdAllah, M.; Bourliere, M.; Esmat, G. Changes in liver stiffness measurements and fibrosis scores following sofosbuvir based treatment regimens without interferon. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Rao, H.; Yang, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Ma, D.; Wei, L. Noninvasive Measurements Predict Liver Fibrosis Well in Hepatitis C Virus Patients After Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Allende, D.S.; McCullough, A.J. Assessing liver fibrosis without biopsy in patients with HCV or NAFLD. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2019, 86, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, K.; Baptista, A.; Bianchi, L.; Callea, F.; De Groote, J.; Gudat, F.; Denk, H.; Desmet, V.; Korb, G.; MacSween, R.N.; et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedossa, P.; Dargère, D.; Paradis, V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.A.; Xiaoqiang, W.; Budoff, M.; Leaf, D.; Kuller, L.H.; Justice, A.C. Hepatitis C virus infection and the risk of coronary disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothineni, N.V.K.C.; Delongchamp, R.; Vallurupalli, S.; Ding, Z.; Dai, Y.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Mehta, J.L. Impact of hepatitis C seropositivity on the risk of coronary heart disease events. Am. J. Cardiol 2014, 114, 1841–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Restivo, L.; Guerrera, B.; Sellitto, A.; Ciervo, A.; Iuliano, N.; Rinaldi, L.; Santoro, A.; Li Vigni, G.; Marrone, A. Chronic HCV infection is a risk factor of ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enger, C.; Forssen, U.M.; Bennett, D.; Theodore, D.; Shantakumar, S.; McAfee, A. Thromboembolic events among patients with hepatitis C virus infection and cirrhosis: A matched-cohort study. Adv. Ther. 2014, 31, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.A.; Yan, P.; Shuaib, A.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Shaikh, O.S.; Freiberg, M.S. Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy for HCV Infection Is Associated With a Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Events. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 987–996.e988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, A.; Berenguer, J.; Hontañón, V.; Navarro, J.; Hernández-Quero, J.; Galindo, M.J.; Quereda, C.; Santos, I.; Téllez, M.J.; Ortega, E.; et al. Effects of Eradication of HCV on Cardiovascular Risk and Preclinical Atherosclerosis in HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients. J. Acquir. Immun. Defic. Syndr. 2020, 83, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.W.; Bhattacharya, D.; Horwich, T.B.; Yan, P.; McGinnis, K.A.; Tseng, C.; Freiberg, M.S.; Currier, J.S.; Butt, A.A. Performance of the Pooled Cohort atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk score in hepatitis C virus-infected persons. J. Viral. Hepat. 2017, 24, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinami, L.; Block, R.C.; Adams, M.J.; Cohn, S.E.; Maliakkal, B.; Fisher, S.G. Risk of cardiovascular disease in HIV, hepatitis C, or HIV/hepatitis C patients compared to the general population. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2013, 67, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.P.; Kappel, C.R.; Siqueira, E.R.; Lima, V.M.; Stefano, J.T.; Michalczuk, M.T.; Marini, S.S.; Barbeiro, H.V.; Soriano, F.G.; Carrilho, F.J.; et al. Effects of hepatitis C virus on cardiovascular risk in infected patients: A comparative study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 164, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Chung, C.M.; Chang, M.L.; Chen, M.Y.; Chang, S.T.; Chu, P.H.; Chen, T.H.; Lin, W.Y.; Huang, T.J.; Lin, Y.S. The Unraveled Link Between Antiviral Therapy and Heart Failure Hospitalization in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection—A Nationwide Cohort Study. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahon, P.; Bourcier, V.; Layese, R.; Audureau, E.; Cagnot, C.; Marcellin, P.; Guyader, D.; Fontaine, H.; Larrey, D.; De Lédinghen, V.; et al. Eradication of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Patients with Cirrhosis Reduces Risk of Liver and Non-Liver Complications. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 142–156.e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Baseline 1 | End of DAA Treatment 1 | One Year | Two Years | Three Years After DAA 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| After DAA 1 | After DAA 1 | |||||
| Age (years) | 66 (58, 72) | 67 (59, 73) | 68 (60, 74) | 69 (61, 74) | 70 (63, 74) | 0.063 |
| Sex | 0.6 | |||||
| Female | 39 (43%) | 39 (43%) | 38 (43%) | 34 (42%) | 19 (32%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27 (24, 29) | 27 (24, 29) | 27 (24, 29) | 27 (24,29) | 27 (25, 30) | >0.9 |
| Current smoker | 25 (27%) | 25 (27%) | 25 (28%) | 21 (26%) | 11 (18%) | 0.7 |
| Alcohol dependence | 8 (9%) | 8 (9%) | 6 (7%) | 4 (5%) | 3 (5%) | 0.8 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 130 (120, 140) | 130 (120, 140) | 130 (120, 140) | 135 (124, 140) | 130 (120, 140) | 0.4 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80 (70, 80) | 80 (70, 85) | 80 (70, 85) | 80 (70, 85) | 80 (75, 81) | 0.6 |
| T2DM | 23 (19%) | 21 (18%) | 21 (18%) | 23 (22%) | 17 (22%) | >0.9 |
| Antidiabetic treatment | 16 (18%) | 15 (16%) | 15 (17%) | 15 (19%) | 12 (20%) | >0.9 |
| Total Cholesterol | 168 (149, 191) | 164 (148, 188) | 180 (161, 208) | 173 (157, 197) | 174 (162, 192) | 0.09 |
| LDL-C level (mg/dL) | 104 (87, 118) | 106 (94, 128) | 109 (102, 138) | 106 (85, 122) | 105 (82, 120) | 0.4 |
| HDL-C level (mg/dL) | 52 (42, 63) | 50 (42, 59) | 51 (45, 61) | 51 (41, 60) | 54 (45, 63) | 0.8 |
| Hypertension treatment | 57 (63%) | 59 (65%) | 60 (68%) | 58 (72%) | 44 (73%) | 0.6 |
| Statin treatment | 0 (0%) | 4 (4.4%) | 10 (11%) | 14 (17%) | 16 (27%) | <0.001 |
| HCV genotypes | - | |||||
| 1a | 4 (4.4%) | - | - | - | - | |
| 1b | 56 (62%) | - | - | - | - | |
| 2 | 21 (23%) | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | 7 (7.7%) | - | - | - | - | |
| 4 | 3 (3.3%) | - | - | - | - | |
| HCV RNA level (×106 IU/L) | 1.3 (0.5, 4.4) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | - |
| Steatosis | 32 (35%) | 19 (21%) | 26 (30%) | 27 (33%) | 24 (40%) | 0.105 |
| Variable | Baseline 1 | End of DAA Treatment 1 | One Year after DAA 1 | Two Years after DAA 1 | Three Years after DAA 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST groups | <0.001 | |||||
| ≤ULN | 54 (59%) | 87 (96%) | 85 (97%) | 81 (100%) | 60 (100%) | |
| >ULN | 37 (41%) | 4 (4.4%) | 3 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| ALT groups | <0.001 | |||||
| ≤ULN | 69 (76%) | 91 (100%) | 86 (98%) | 81 (100%) | 60 (100%) | |
| >ULN | 22 (24%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (2.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| GGT groups | <0.001 | |||||
| ≤ULN | 61 (67%) | 85 (93%) | 82 (93%) | 79 (98%) | 58 (97%) | |
| >ULN | 30 (33%) | 6 (6.6%) | 6 (6.8%) | 2 (2.5%) | 2 (3.3%) | |
| Fibrosis scores by transient elastography | NA | |||||
| F0–F1 | 30 (41%) | - | - | - | - | |
| F2 | 9 (12%) | - | - | - | - | |
| F3 | 15 (21%) | - | - | - | - | |
| F4 | 19 (26%) | - | - | - | - |
| Variable | Time Point | Mean (SD) | Mean Difference from Baseline (95% CI) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASCVD score | Baseline | 17.2% (12.7) | - | - |
| End of treatment | 17.7% (12.9) | +0.51% (−3.95, 4.97) | 0.50 | |
| one year | 16.9% (14.1) | −0.3% (−5.3, 4.7) | 0.76 | |
| two years | 17.1% (12.3) | −0.08% (−5, 4.83) | 0.11 | |
| three years | 17.2% (15.7) | +0.08% (−7.16, 7.32) | 0.68 | |
| FIB-4 score | Baseline | 3.29 (2.68) | - | - |
| End of treatment | 2.46 (1.61) | −0.83 (−1.48, −0.18) | <0.001 * | |
| one year | 2.6 (1.86) | −0.69 (−1.37, −0.01) | <0.001 * | |
| two years | 2.38 (1.3) | −0.91 (−1.54, −0.29) | <0.001 * | |
| three years | 2.53 (1.83) | −0.76 (−1.48, −0.03) | <0.001 * |
| Coefficients | Estimate | S.E. | Wald | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 15.396 | 2.663 | 33.44 | <0.001 * |
| Time | ||||
| End of treatment | −1.369 | 1.063 | 1.66 | 0.2 |
| 1 year | −1.793 | 1.317 | 1.86 | 0.17 |
| 2 years | 0.221 | 1.606 | 0.02 | 0.89 |
| 3 years | −2.553 | 1.597 | 2.56 | 0.11 |
| BMI | ||||
| overweight or obese | 2.215 | 2.745 | 0.65 | 0.42 |
| Creatinine | ||||
| >1 mg/dL | 7.252 | 2.501 | 8.41 | 0.0037 * |
| FIB-4 score | −0.324 | 0.361 | 0.80 | 0.37 |
| FIB-4 score: Time | ||||
| FIB-4 score: End of treatment | 0.422 | 0.356 | 1.40 | 0.24 |
| FIB-4 score: 1st year | 1.161 | 0.485 | 5.73 | 0.0166 * |
| FIB-4 score: 2nd year | 1.073 | 0.592 | 3.28 | 0.07 |
| FIB-4 score: 3rd year | 2.520 | 0.452 | 31.13 | <0.001 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramadan, M.S.; Boccia, F.; Moretto, S.M.; De Gregorio, F.; Gagliardi, M.; Iossa, D.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Zampino, R. Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Direct Acting Antivirals. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195781
Ramadan MS, Boccia F, Moretto SM, De Gregorio F, Gagliardi M, Iossa D, Durante-Mangoni E, Zampino R. Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Direct Acting Antivirals. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195781
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamadan, Mohammad Said, Filomena Boccia, Simona Maria Moretto, Fabrizio De Gregorio, Massimo Gagliardi, Domenico Iossa, Emanuele Durante-Mangoni, and Rosa Zampino. 2022. "Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Direct Acting Antivirals" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195781
APA StyleRamadan, M. S., Boccia, F., Moretto, S. M., De Gregorio, F., Gagliardi, M., Iossa, D., Durante-Mangoni, E., & Zampino, R. (2022). Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Direct Acting Antivirals. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195781






