Maximal Reduction of STIC Acquisition Time for Volumetric Assessment of the Fetal Heart—Benefits and Limitations of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Static Mode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Acquisition of STIC Volumes
2.3. Examination with FINE and FINE Static Mode
2.4. Virtual Intelligent Sonographer Assistance (VIS-Assistance)
2.5. Analysis by the Investigators
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aydin, E.; Aypar, E.; Oktem, A.; Ozyuncu, O.; Yurdakok, M.; Guvener, M.; Demircin, M.; Beksac, M.S. Congenital heart defects: The 10-year experience at a single center. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 33, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Improved national prevalence estimates for 18 selected major birth defects--United States, 1999–2001. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2006, 54, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlicek, J.; Klaskova, E.; Prochazka, M.; Dolezalkova, E.; Matura, D.; Spacek, R.; Simetka, O.; Gruszka, T.; Polanska, S.; Kacerovsky, M. Congenital heart defects according to the types of the risk factors—A single center experience. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 32, 3606–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. New and advanced features of fetal intelligent navigation echocardiography (FINE) or 5D heart. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 35, 1498–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiron, R.; Glaser, J.; Gelernter, I.; Hegesh, J.; Yagel, S. Extended fetal echocardiographic examination for detecting cardiac malformations in low risk pregnancies. BMJ 1992, 304, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, L. Antenatal diagnosis of heart disease. Heart 2000, 83, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Lodge, J. Prenatal therapy for fetal cardiac disorders. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 32, 3871–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembruch, U. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease. Prenat. Diagn. 1997, 17, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.N.; Simpson, L.L.; Abuhamad, A.Z. Screening For Fetal Heart Disease With Ultrasound. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 46, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smythe, J.F.; Copel, J.A.; Kleinman, C.S. Outcome of prenatally detected cardiac malformations. Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 69, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE): A novel method for rapid, simple, and automatic examination of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 42, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeggi, E.T.; Sholler, G.F.; Jones, O.D.H.; Cooper, S.G. Comparative analysis of pattern, management and outcome of pre- versus postnatally diagnosed major congenital heart disease: A population-based study. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 17, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, N.M.; Keenan, H.T.; Minich, L.L.; Puchalski, M.D.; Heywood, M.; Botto, L.D. Barriers to prenatal detection of congenital heart disease: A population-based study. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 40, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Capponi, A.; Muscatello, A.; Cavicchioni, O.; Vendola, M.; Arduini, D. Examination of the Fetal Heart by Four-Dimensional Ultrasound with Spatiotemporal Image Correlation during Routine Second-Trimester Examination: The ‘Three-Steps Technique’. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2008, 24, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaoui, R.; Hoffmann, J.; Heling, K.S. Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography using spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC). Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 23, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVore, G.R.; Falkensammer, P.; Sklansky, M.S.; Platt, L.D. Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC): New technology for evaluation of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 22, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.F.; Lee, W.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Espinoza, J.; Schoen, M.L.; Falkensammer, P.; Treadwell, M.; Romero, R. Four-dimensional ultrasonography of the fetal heart with spatiotemporal image correlation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 189, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagel, S.; Cohen, S.M.; Shapiro, I.; Valsky, D.V. 3D and 4D ultrasound in fetal cardiac scanning: A new look at the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 29, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaanse, B.M.E.; van Vugt, J.M.G.; Haak, M.C. Three- and four-dimensional ultrasound in fetal echocardiography: An up-to-date overview. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J. Contemporary clinical applications of spatio-temporal image correlation in prenatal diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 23, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. How to Acquire Cardiac Volumes for Sonographic Examination of the Fetal Heart: Part 1. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. How to Acquire Cardiac Volumes for Sonographic Examination of the Fetal Heart: Part 2. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 1043–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Intelligent navigation to improve obstetrical sonography. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 47, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.; Yeo, L.; Romero, R.; Haggerty, D.; Giardina, I.; Hassan, S.S.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Hernandez-Andrade, E. Prospective evaluation of the fetal heart using Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE). Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 47, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, P.; Bogana, G.; Cerutti, A.; Yeo, L.; Romero, R.; Gervasi, M.T. A Prospective Study of the Use of Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) to Obtain Standard Fetal Echocardiography Views. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2016, 41, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Luewan, S.; Markush, D.; Gill, N.; Romero, R. Prenatal Diagnosis of Dextrocardia with Complex Congenital Heart Disease Using Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) and a Literature Review. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2017, 43, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, A. Medical ultrasound diagnosis in the near future as we move toward the era of the singularity. J. Med Ultrason. 2016, 43, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of Obstetric Ultrasound Examinations. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 1083–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology; Carvalho, J.; Allan, L.; Chaoui, R.; Copel, J.; DeVore, G.; Hecher, K.; Lee, W.; Munoz, H.; Paladini, D.; et al. ISUOG Practice Guidelines (updated): Sonographic screening examination of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 41, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembicki, M.; Hartge, D.R.; Dracopoulos, C.; Weichert, J. Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography Has the Potential to Aid Cardiac Evaluations Even in Less Experienced Hands. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 39, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.; Luewan, S.; Romero, R. Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Detects 98% of Congenital Heart Disease. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 2577–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Prenatal diagnosis of hypoplastic left heart and coarctation of the aorta with color Doppler FINE. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Color and power Doppler combined with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) to evaluate the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gembicki, M.; Hartge, D.R.; Fernandes, T.; Weichert, J. Feasibility of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography for Different Fetal Spine Positions: A Matter of “Time”? J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 40, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, B.W.; Chen, R.; Pang, H.S.; Pan, M.; Peng, X.H.; Wang, B. Is Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography Helpful in Screening for d-Transposition of the Great Arteries? J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 39, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, R.M.; Ramy, A.R.M.; Abdelhady, A.M. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Automated Fetal Heart Echocardiography by Five Dimensional Compared to Two-Dimensional Ultrasound in the Second Trimester of Pregnancy. Open J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 8, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.; Markush, D.; Romero, R. Prenatal diagnosis of tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia using: Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE). J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 32, 3699–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, R.; Huang, C.; Mao, Y.; Zhao, B. Diagnostic performance of fetal intelligent navigation echocardiography (FINE) in fetuses with double-outlet right ventricle (DORV). Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 36, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaes, J.Y.; Zamith, M.M.; Júnior, E.A.; Barreto, E.Q.D.S.; Barros, F.S.B.; Moron, A.F. Screening of Congenital Heart Diseases by Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Using Spatiotemporal Image Correlation: Influence of Professional Experience. Echocardiography 2015, 33, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennasar, M.; Martínez, J.M.; Olivella, A.; Del Río, M.; Gómez, O.; Figueras, F.; Puerto, B.; Gratacos, E. Feasibility and accuracy of fetal echocardiography using four-dimensional spatiotemporal image correlation technology before 16 weeks’ gestation. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 33, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uittenbogaard, L.B.; Haak, M.C.; Spreeuwenberg, M.D.; Van Vugt, J.M.G. Fetal cardiac function assessed with four-dimensional ultrasound imaging using spatiotemporal image correlation. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 33, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, S.; Turan, O.M.; Ty-Torredes, K.; Harman, C.R.; Baschat, A.A. Standardization of the first-trimester fetal cardiac examination using spatiotemporal image correlation with tomographic ultrasound and color Doppler imaging. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 33, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D. How best to improve antenatal detection of congenital heart defects. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 32, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, S.; Heads, A.; Wyllie, J.; Robson, S. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the northern region of England: Benefits of a training programme for obstetric ultrasonographers. Heart 2000, 84, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

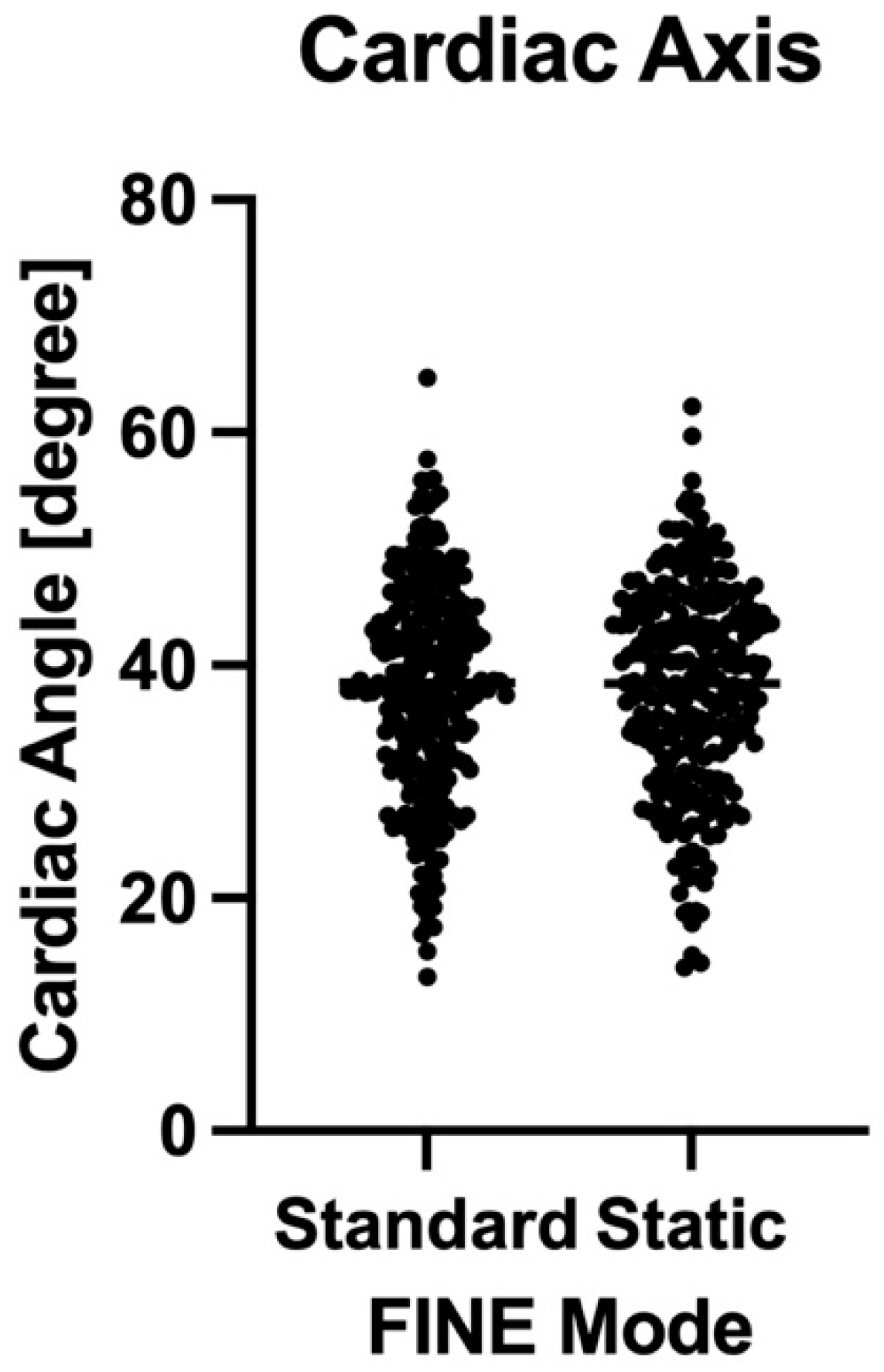
| Mode | Depiction Rate ≥7 Planes (% of All Cases) | p-Value |
| Standard | 96.9 | 0.0961 |
| Static | 94.2 | |
| Mode | Overall Depiction Rate (% of All Planes) | p-Value |
| Standard | 96.9 | 0.0098 |
| Static | 95.2 |
| Plane | Standard Mode Drop-Out Rate (%) | Static Mode Drop-Out Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Three-vessel–trachea view | 3.1 | 4.7 |
| four-chamber view | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| five-chamber view | 1.2 | 7.0 |
| left ventricular outflow tract | 2.3 | 5.1 |
| right ventricular outflow tract | 1.9 | 4.3 |
| abdomen | 0.0 | 1.2 |
| ductal arch | 8.2 | 8.6 |
| aortic arch | 7.4 | 5.8 |
| vena cava | 4.3 | 6.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gembicki, M.; Scharf, J.L.; Dracopoulos, C.; Welp, A.; Weichert, J. Maximal Reduction of STIC Acquisition Time for Volumetric Assessment of the Fetal Heart—Benefits and Limitations of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Static Mode. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144062
Gembicki M, Scharf JL, Dracopoulos C, Welp A, Weichert J. Maximal Reduction of STIC Acquisition Time for Volumetric Assessment of the Fetal Heart—Benefits and Limitations of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Static Mode. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(14):4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144062
Chicago/Turabian StyleGembicki, Michael, Jann Lennard Scharf, Christoph Dracopoulos, Amrei Welp, and Jan Weichert. 2022. "Maximal Reduction of STIC Acquisition Time for Volumetric Assessment of the Fetal Heart—Benefits and Limitations of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Static Mode" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 14: 4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144062
APA StyleGembicki, M., Scharf, J. L., Dracopoulos, C., Welp, A., & Weichert, J. (2022). Maximal Reduction of STIC Acquisition Time for Volumetric Assessment of the Fetal Heart—Benefits and Limitations of Semiautomatic Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) Static Mode. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(14), 4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144062







