Correlations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Daytime Sleepiness with the Risk of Car Accidents in Adult Working Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Gender-Based Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy and Study Selection
- Pubmed: ((“working population” OR “working adults” OR “working class” OR “workers”) AND (“sleep apnea syndrome” OR “apnea” OR “obstructive sleep apnea”) AND (“accidents” OR “safety” OR “injuries”)).
- Scopus: TITLE-ABS-KEY ((working population OR working adults OR working class OR workers) AND (sleep apnea syndrome OR apnea OR obstructive sleep apnea) AND (accidents OR safety OR injuries)).
- Google Scholar: “working adults” AND “OSAS” AND “working accidents”.
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Items
2.5. Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias
2.6. Outcomes
- (i)
- car crashes in subjects with OSAS and total number of subjects with OSAS
- (ii)
- car accidents in subjects with OSAS and total number of car accidents, both of which were analyzed depending on the different types of drivers (CMVD, commercial motor vehicle drivers and NCMVD, noncommercial motor vehicle drivers)
- (iii)
- car crashes in subjects with ESS ≥ 10 and total subjects with ESS ≥ 10
- (iv)
- car crashes in subjects with SDB and total subjects with SDB.
- (i)
- car crashes in subjects without OSAS and total number of subjects without OSAS
- (ii)
- non-car accidents in subjects with OSAS and total number of non-car accidents, both of which were analyzed depending on the different types of drivers (CMVD, commercial motor vehicle drivers and NCMVD, non-commercial motor vehicle drivers)
- (iii)
- car crashes in subjects without ESS ≥ 10 and total subjects without ESS ≥ 10
- (iv)
- car crashes in subjects without SDB and total subjects without SDB.
2.7. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
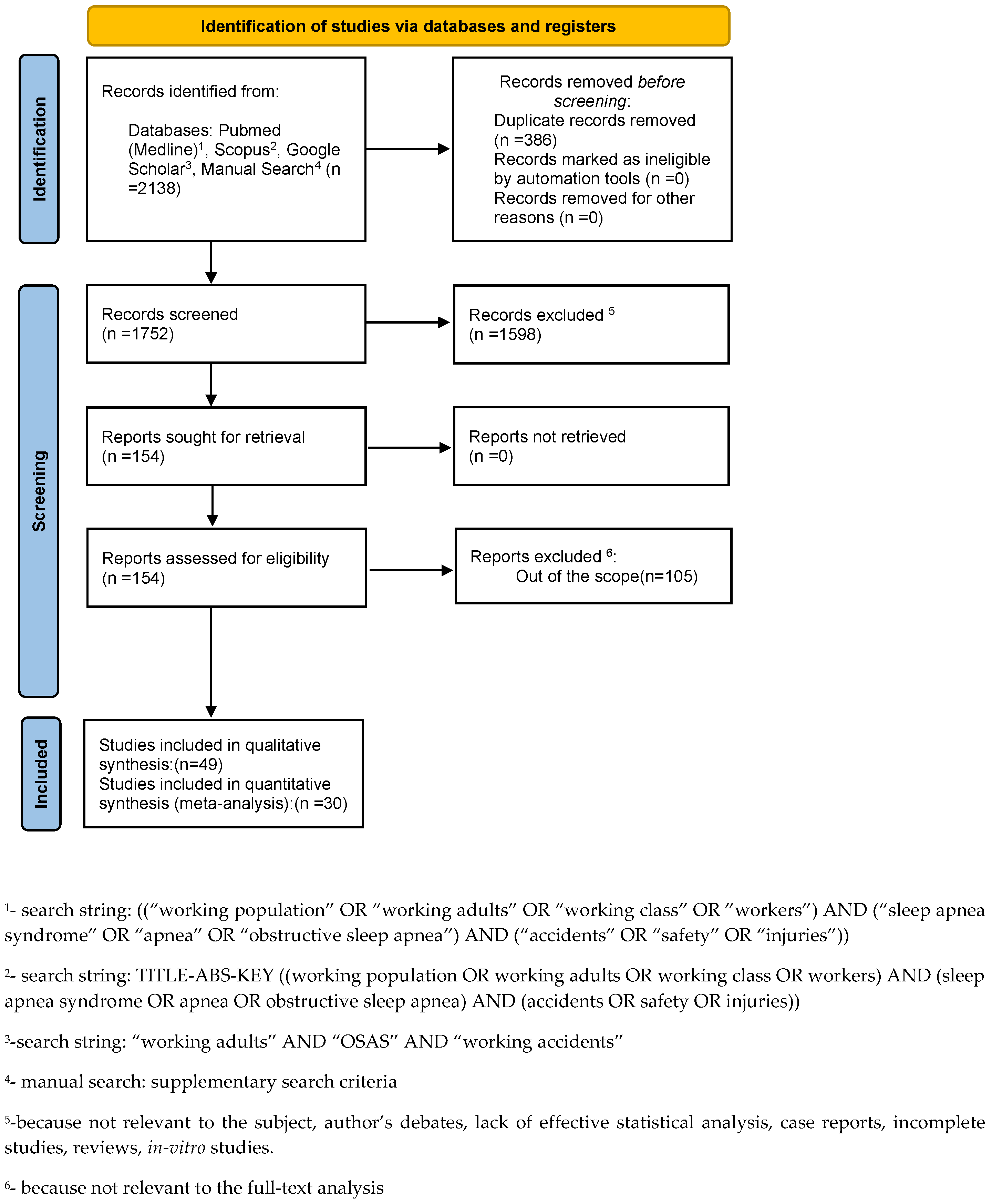
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias
3.3. Study Populations
- (i)
- (ii)
- (iii)
- (iv)
- (i)
- (ii)
- (iii)
- (iv)
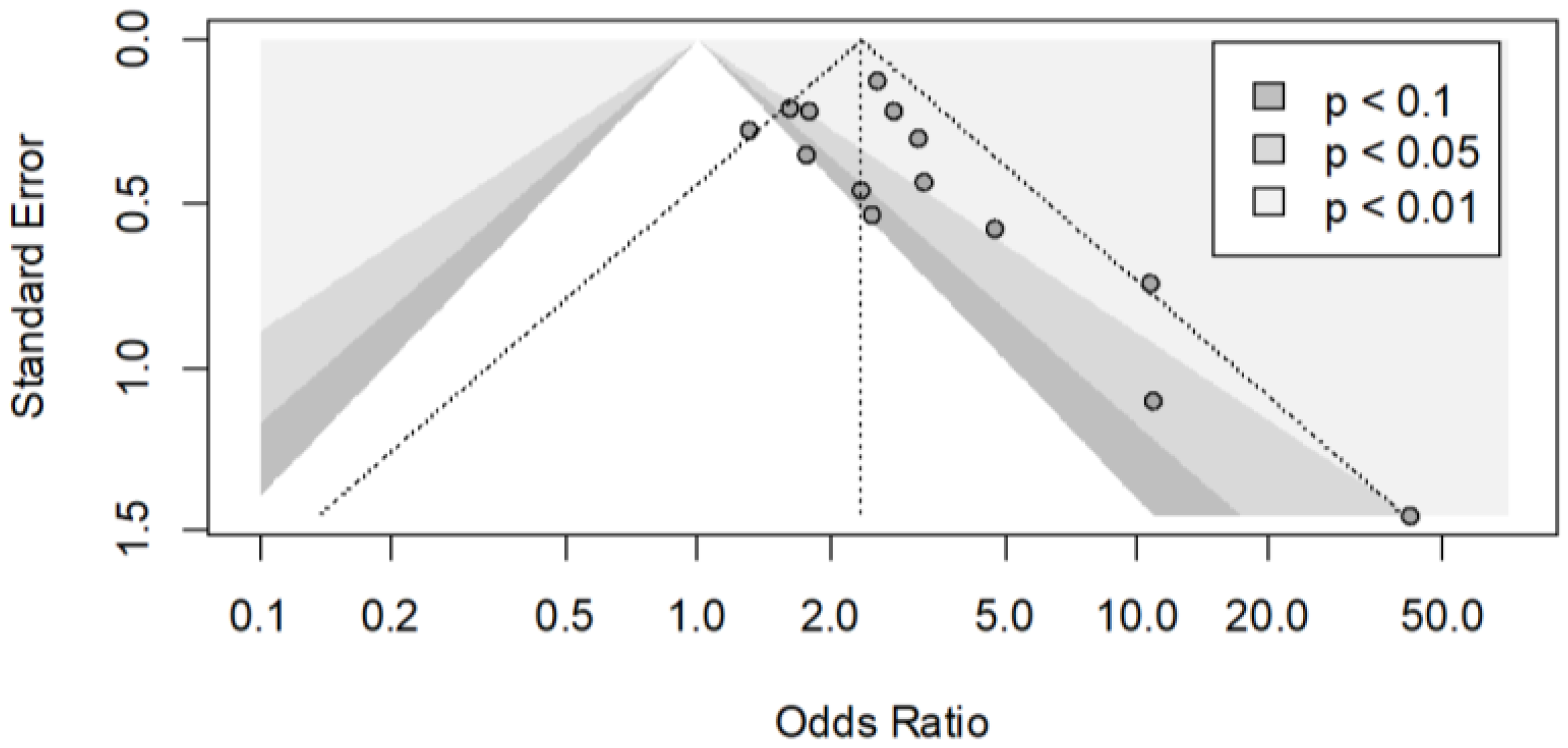
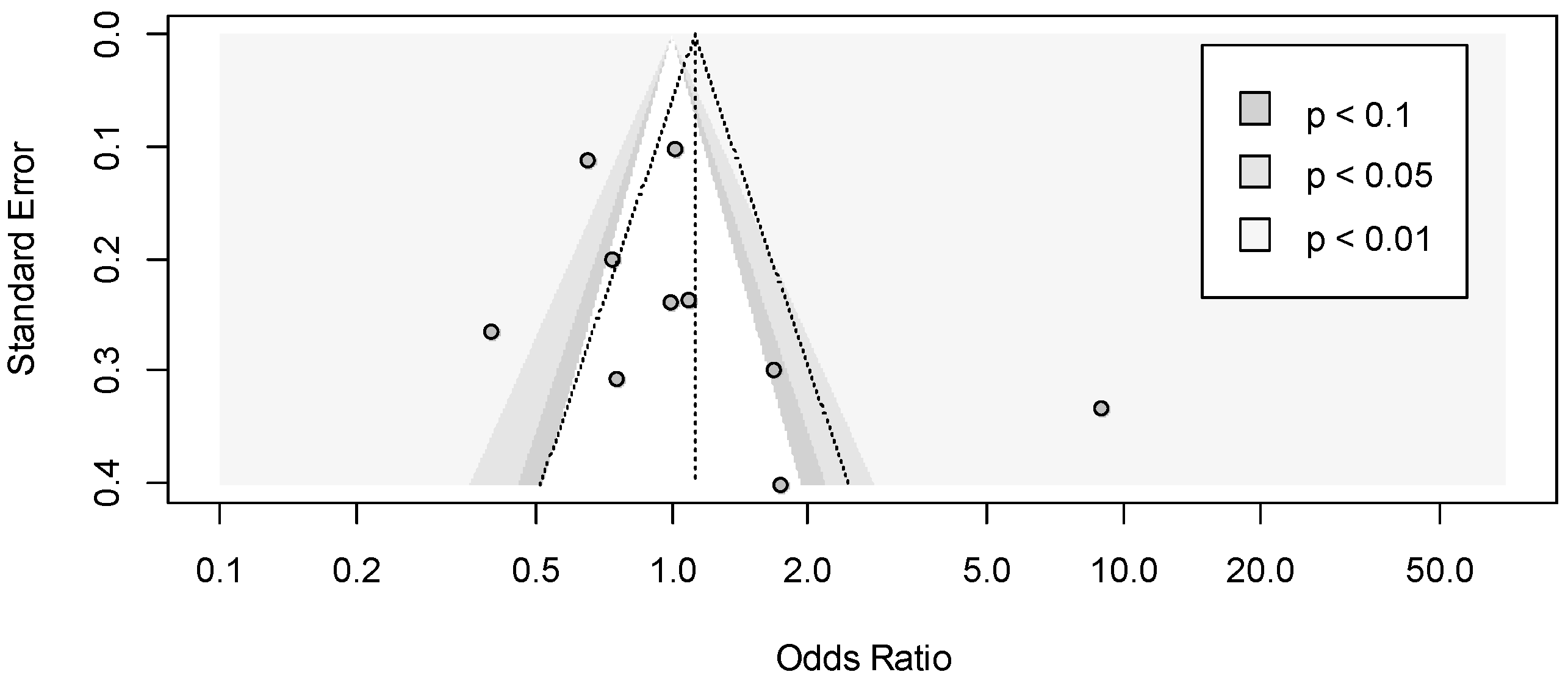
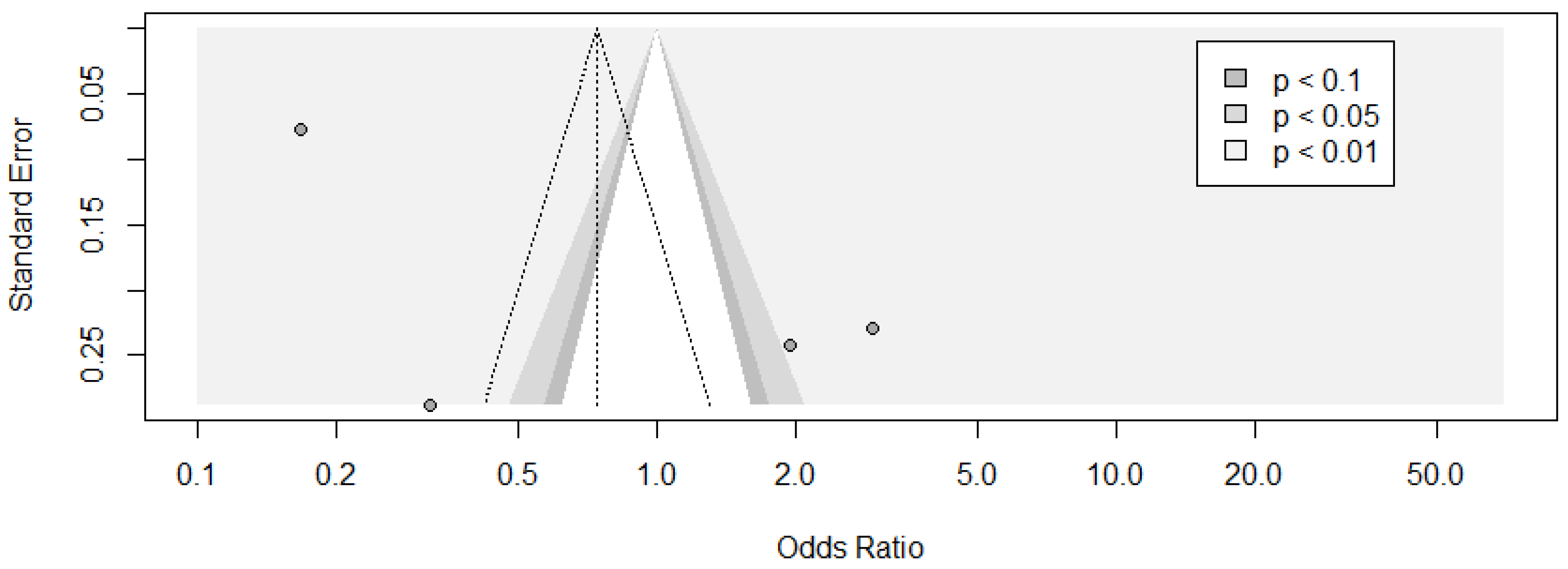
3.4. Meta-Analysis
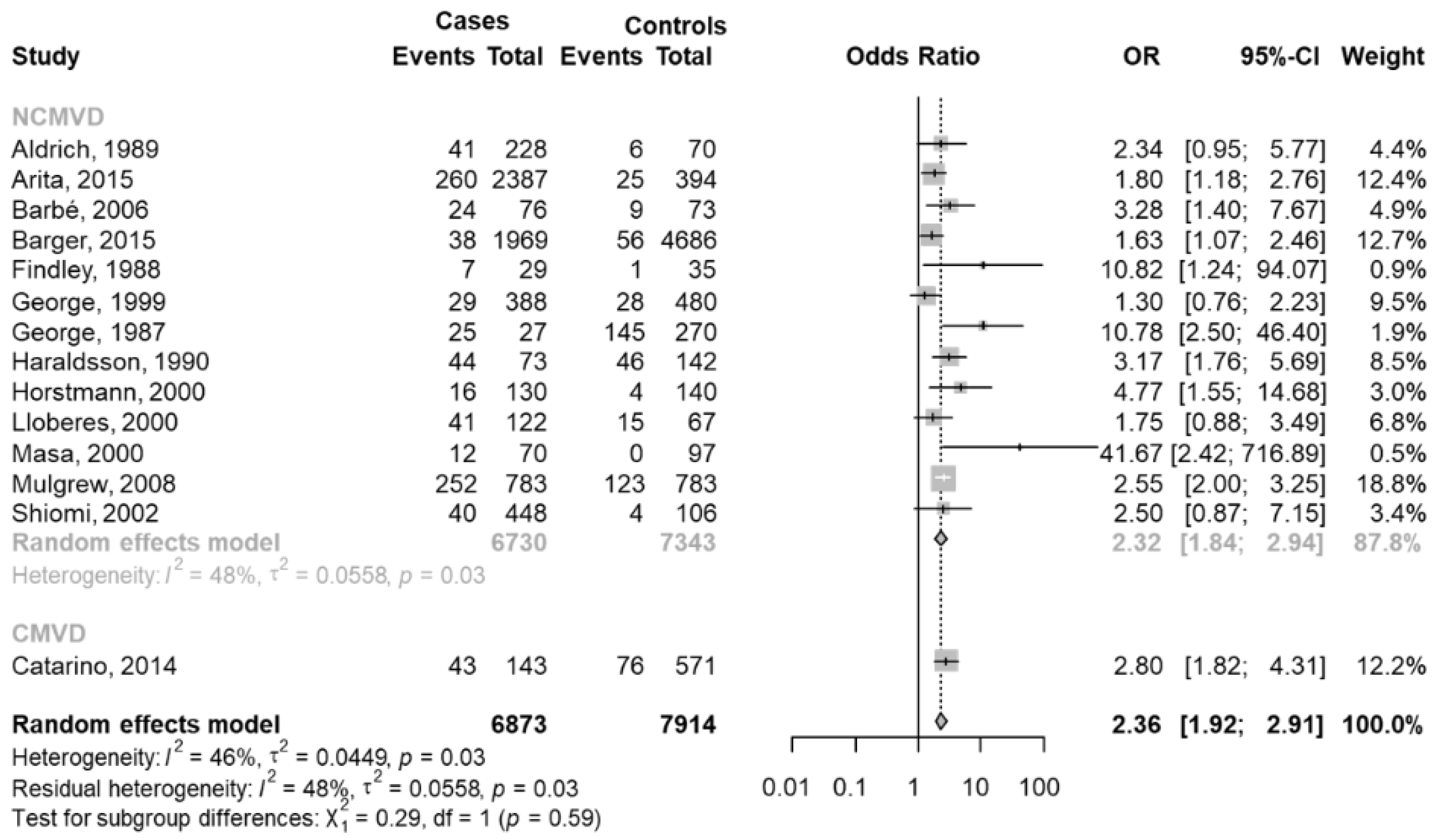
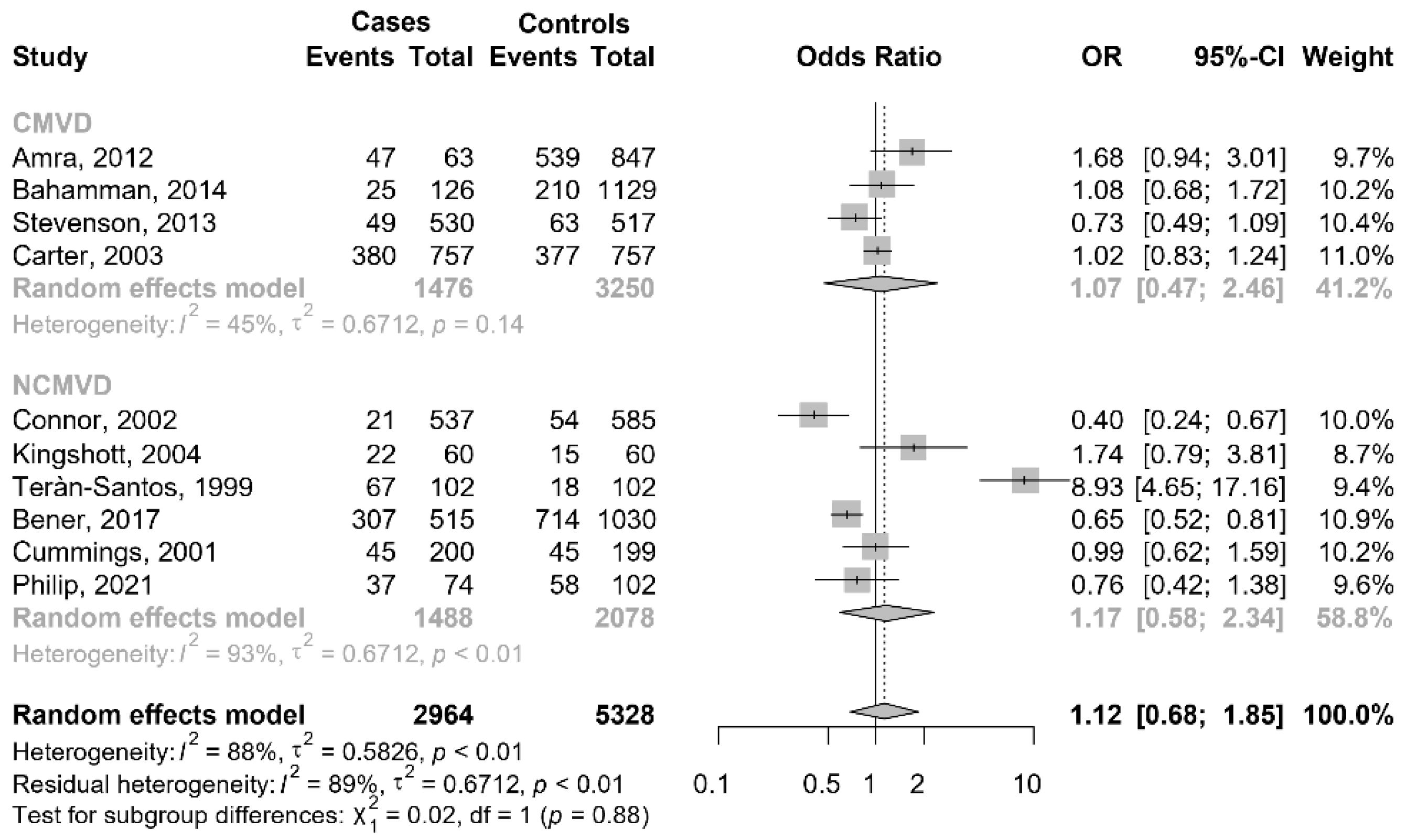
3.4.1. Car Crashes in Subjects with OSAS and Total Number of Subjects with OSAS
3.4.2. People with OSAS Reporting Car Accidents versus People with OSAS without Car Accidents
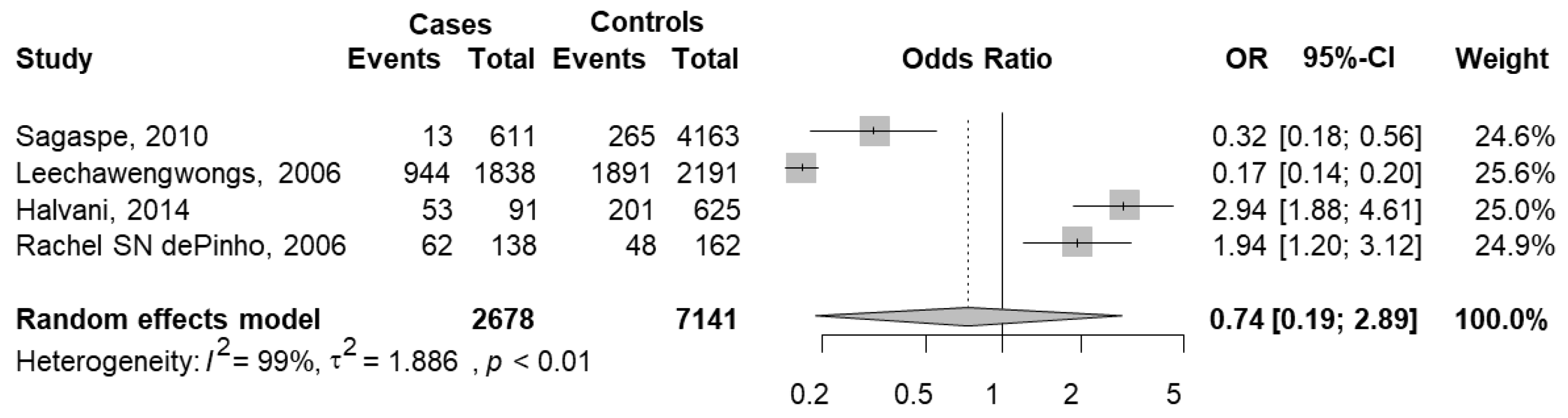
3.4.3. People Reporting Car Crashes with ESS ≥ 10 versus People Reporting Car Crashes without ESS ≥ 10
3.4.4. People Reporting Car Crashes with SDB versus People Reporting Car Crashes without SDB
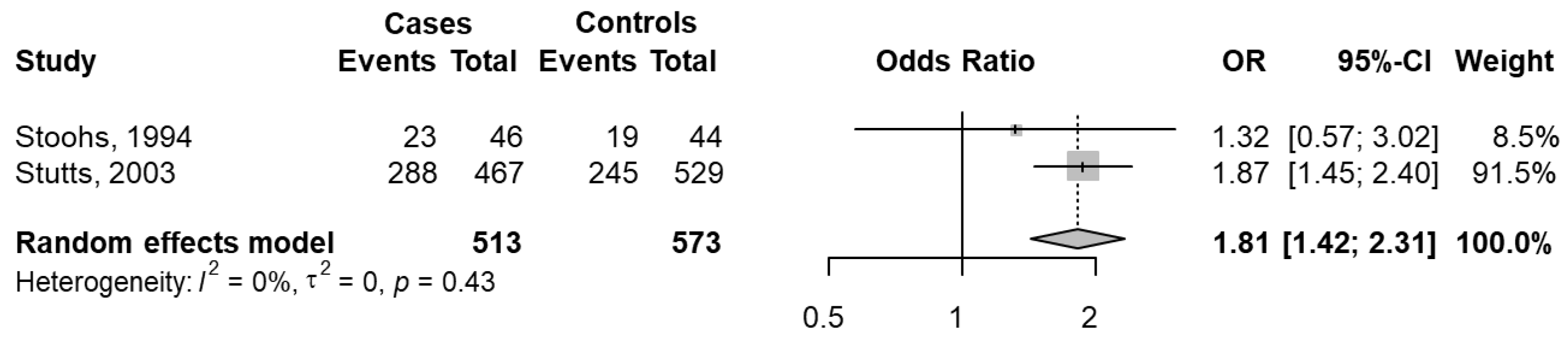
3.5. Gender-Based Analysis on Study Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martini, A.; Pietrafesa, E.; Luzzi, V.; Guaragna, M.; Polimeni, A. La Sindrome delle Apnee Ostruttive nel Sonno; Una Lettura Interdisciplinare del Fenomeno; Aracne: Rome, Italy, 2022; p. 200. ISBN 979-12-5994-547-1. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, A.; Luzzi, V.; Pietrafesa, E.; Di Carlo, G.; Guaragna, M.; Mazur, M.; Cotticelli, L.; Di Giacomo, P.; Piperno, G.; Brunori, M.; et al. Workers with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: Proposal of a clinical-anamnestic tool for the occupational health surveillance. Saf. Health Work 2022, 13, S113–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardo, G.; Luzzi, V.; Polimeni, A. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS): Evaluation and treatment of odontostomatological problems. Med. Lav. 2017, 108, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martini, A.; Bonafede, M.; Pietrafesa, E. Web survey sulla sicurezza stradale: Risultati preliminary. In Proceedings of the Atti dell’83° Congresso Nazionale di Medicina del Lavoro Società Italiana di Medicina del Lavoro (SIML), Parma, Italy, 15–17 September 2021. La Cultura della Prevenzione batte il Tempo; Giornale Italiano di Medicina del lavoro ed Ergonomia; Volume 43, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro, P.; Martini, A.; Pietrafesa, E.; D’Amelio, S. The obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA) at work. In Science for Democracy—Democracy for Science; X Seminar PhD Day; ISTISAN Congressi; Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Rome, Italy, 2019; ISSN 0393-5620. [Google Scholar]
- Luzzi, V.; Brunori, M.; Terranova, S.; Di Paolo, C.; Ierardo, G.; Vozza, I.; Polimeni, A. Difficult-to-treat OSAS: Combined continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and mandibular advancement devices (MADs) therapy. A case report. CRANIO 2020, 38, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannella, G.; Vicini, C.; Colizza, A.; Meccariello, G.; Polimeni, A.; Greco, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; de Vito, A.; Cammaroto, G.; Gobbi, R.; et al. Aging effect on sleepiness and apneas severity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A meta-analysis study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 3549–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, L.; Hillman, D.R.; Cooper, M.N.; Ward, K.L.; Hunter, M.; Cullen, S.; James, A.; Palmer, L.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Eastwood, P. High prevalence of undiagnosed obstructive sleep apnoea in the general population and methods for screening for representative controls. Sleep Breath. 2013, 17, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricosas. Available online: https://www.sleeposas.it/ (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Epstein, L.J.; Kristo, D.; Strollo, P.J.; Friedman, N.; Malhotra, A.; Patil, S.P.; Ramar, K.; Rogers, R.; Schwab, R.J.; Weaver, E.M.; et al. Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mobility & Transport—Road Safety. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/transport/road_safety/sites/default/files/pdf/behavior/sleep_apnoea.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Ward, K.; Hoare, K.J.; Gott, M. What is known about the experiences of using CPAP for OSA from the users’ perspective? A systematic integrative literature review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 18, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohl, K.P.; Redline, S. Recognition of obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hader, C.; Schroeder, A.; Hinz, M.; Micklefield, G.H.; Rasche, K. Sleep disordered breathing in the elderly: Comparison of women and men. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 56, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bardr, M.S.; Matejka, J.H. Gender Differences in Sleep-Disordered Breathing. In Sleep Apnea, 2nd ed.; Pack, A.I., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 176–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ip, M.S.; Lam, B.; Tang, L.C.; Lauder, I.J.; Ip, T.Y.; Lam, W.K. A community study of sleep-disordered breathing in middle-aged Chinese women in Hong Kong: Prevalence and gender differences. Chest 2004, 125, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Gallego, E.; Carmona-Bernal, C.; Capote, F.; Sánchez-Armengol, A.; Botebol-Benhamou, G.; Polo-Padillo, J.; Castillo-Gómez, J. Gender differences in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A clinical study of 1166 patients. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jordan, A.S.; McEvoy, R.D. Gender differences in sleep apnea: Epidemiology, clinical presentation and pathogenic mechanisms. Sleep Med. Rev. 2003, 7, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fietze, I.; Laharnar, N.; Obst, A.; Ewert, R.; Felix, S.B.; Garcia, C.; Gläser, S.; Glos, M.; Schmidt, C.O.; Stubbe, B.; et al. Prevalence and association analysis of obstructive sleep apnea with gender and age differences—Results of SHIP-Trend. J. Sleep Res. 2019, 28, e12770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2011. Available online: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org/ (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Gjerdevik, M.; Heuch, I. Improving the error rates of the Begg and Mazumdar test for publication bias in fixed effects meta-analysis. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, M.E.; Desai, A.V.; Grunstein, R.R.; Hukins, C.; Armstrong, J.G.; Joffe, D.; Swann, P.; Campbell, D.A.; Pierce, R.J. Sleepiness, sleep-disordered breathing, and accident risk factors in commercial vehicle drivers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amra, B.; Dorali, R.; Mortazavi, S.; Golshan, M.; Farajzadegan, Z.; Fietze, I.; Penzel, T. Sleep apnea symptoms and accident risk factors in Persian commercial vehicle drivers. Sleep Breath. 2012, 16, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, L.K.; Rajaratnam, S.M.; Wang, W.; O’Brien, C.S.; Sullivan, J.P.; Qadri, S.; Lockley, S.W.; Czeisler, C.A. Harvard Work Hours Health and Safety Group. Common sleep disorders increase risk of motor vehicle crashes and adverse health outcomes in firefighters. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catarino, R.; Spratley, J.; Catarino, I.; Lunet, N.; Pais-Clemente, M. Sleepiness and sleep-disordered breathing in truck drivers: Risk analysis of road accidents. Sleep Breath. 2014, 18, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.H.; Sadeghi, M.; Dehghani, M.; Niiat, K.S. Sleep habits and road traffic accident risk for Iranian occupational drivers. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2015, 28, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaspe, P.; Taillard, J.; Bayon, V.; Lagarde, E.; Moore, N.; Boussuge, J.; Chaumet, G.; Bioulac, B.; Philip, P. Sleepiness, near-misses and driving accidents among a representative population of French drivers. J. Sleep Res. 2010, 19, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahammam, A.S.; Alkhunizan, M.A.; Lesloum, R.H.; Alshanqiti, A.M.; Aldakhil, A.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Sharif, M.M. Prevalence of sleep-related accidents among drivers in Saudi Arabia. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2014, 9, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.; Peralta, A.R.; Monteiro Ferreira, J.; Guilleminault, C. Sleepiness and Motor Vehicle Crashes in a Representative Sample of Portuguese Drivers: The Importance of Epidemiological Representative Surveys. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2015, 16, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.; Amici, R.; Lucas, R.; Åkerstedt, T.; Cirignotta, F.; Horne, J.; Léger, D.; McNicholas, W.T.; Partinen, M.; Téran-Santos, J.; et al. Sleepiness at the wheel across Europe: A survey of 19 countries. J. Sleep Res. 2015, 24, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pinho, R.S.; da Silva-Júnior, F.P.; Bastos, J.P.; Maia, W.S.; de Mello, M.T.; de Bruin, V.M.; de Bruin, P.F. Hypersomnolence and accidents in truck drivers: A cross-sectional study. Chronobiol. Int. 2006, 23, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.B.; Schechtman, K.B.; Riley, R.W.; Li, K.; Guilleminault, C. Sleepy driving: Accidents and injury. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2002, 126, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoohs, R.A.; Guilleminault, C.; Itoi, A.; Dement, W.C. Traffic accidents in commercial long-haul truck drivers: The influence of sleep-disordered breathing and obesity. Sleep 1994, 17, 619–623. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T.; Blustein, J.; Finn, L.; Palta, M. Sleep-disordered breathing and motor vehicle accidents in a population-based sample of employed adults. Sleep 1997, 20, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gander, P.H.; Marshall, N.S.; Harris, R.B.; Reid, P. Sleep, sleepiness and motor vehicle accidents: A national survey. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2005, 29, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnardellis, C.; Tzamalouka, G.; Papadakaki, M.; Chliaoutakis, J.E. An investigation of the effect of sleepiness, drowsy driving, and lifestyle on vehicle crashes. Transp. Res. F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leechawengwongs, M.; Leechawengwongs, E.; Sukying, C.; Udomsubpayakul, U. Role of drowsy driving in traffic accidents: A questionnaire survey of Thai commercial bus/truck drivers. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2006, 89, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, K.L.; Hillman, D.R.; James, A.; Bremner, A.P.; Simpson, L.; Cooper, M.N.; Palmer, L.J.; Fedson, A.C.; Mukherjee, S. Excessive daytime sleepiness increases the risk of motor vehicle crash in obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accattoli, M.P.; Muzi, G.; dell’Omo, M.; Mazzoli, M.; Genovese, V.; Palumbo, G.; Abbritti, G. Infortuni e performances sul lavoro in lavoratori affetti da sindrome delle apnee ostruttive nel sonno (OSAS) [Occupational accidents, work performance and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS)]. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2008, 30, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, M.S. Automobile accidents in patients with sleep disorders. Sleep 1989, 12, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbé, F.; Sunyer, J.; de la Peña, A.; Pericas, J.; Mayoralas, L.R.; Antó, J.M.; Agustí, A.G. Effect of continuous positive airway pressure on the risk of road accidents in sleep apnea patients. Respiration 2007, 74, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, J.; Norton, R.; Ameratunga, S.; Robinson, E.; Civil, I.; Dunn, R.; Bailey, J.; Jackson, R. Driver sleepiness and risk of serious injury to car occupants: Population-based case control study. BMJ 2002, 324, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Findley, L.J.; Unverzagt, M.E.; Suratt, P.M. Automobile Accidents Involving Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 138, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findley, L.; Smith, C.; Hooper, J.; Dineen, M.; Suratt, P.M. Treatment with nasal CPAP decreases automobile accidents in patients with sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 857–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, C.F.; Nickerson, P.W.; Hanly, P.J.; Millar, T.W.; Kryger, M.H. Sleep apnoea patients have more automobile accidents. Lancet 1987, 2, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, C.F.; Smiley, A. Sleep apnea & automobile crashes. Sleep 1999, 22, 790–795. [Google Scholar]
- Haraldsson, P.O.; Carenfelt, C.; Diderichsen, F.; Nygren, Å.; Tingvall, C. Clinical symptoms of sleep apnea syndrome and automobile accidents. ORL 1990, 52, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, S.; Hess, C.W.; Bassetti, C.; Gugger, M.; Mathis, J. Sleepiness-related accidents in sleep apnea patients. Sleep 2000, 23, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kingshott, R.N.; Cowan, J.O.; Jones, D.R.; Flannery, E.M.; Smith, A.D.; Herbison, G.P.; Taylor, D.R. The role of sleep-disordered breathing, daytime sleepiness, and impaired performance in motor vehicle crashes—A case control study. Sleep Breath. 2004, 8, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulgrew, A.T.; Nasvadi, G.; Butt, A.; Cheema, R.; Fox, N.; Fleetham, J.A.; Ryan, C.F.; Cooper, P.; Ayas, N.T. Risk and severity of motor vehicle crashes in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea. Thorax 2008, 63, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terán-Santos, J.; Jiménez-Gómez, A.; Cordero-Guevara, J. The association between sleep apnea and the risk of traffic accidents. Cooperative Group Burgos-Santander. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloberes, P.; Levy, G.; Descals, C.; Sampol, G.; Roca, A.; Sagales, T.; de la Calzada, M.D. Self-reported sleepiness while driving as a risk factor for traffic accidents in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and in non-apnoeic snorers. Respir. Med. 2000, 94, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masa, J.F.; Rubio, M.; Findley, L.J. Habitually sleepy drivers have a high frequency of automobile crashes associated with respiratory disorders during sleep. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bener, A.; Yildirim, E.; Özkan, T.; Lajunen, T. Driver sleepiness, fatigue, careless behavior and risk of motor vehicle crash and injury: Population based case and control study. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2017, 4, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, P.; Koepsell, T.D.; Moffat, J.M.; Rivara, F.P. Drowsiness, countermeasures to drowsiness, and the risk of a motor vehicle crash. Inj. Prev. 2001, 7, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noda, A.; Yagi, T.; Yokota, M.; Kayukawa, Y.; Ohta, T.; Okada, T. Daytime sleepiness and automobile accidents in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1998, 52, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutts, J.C.; Wilkins, J.W.; Osberg, J.S.; Vaughn, B.V. Driver risk factors for sleep-related crashes. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2003, 35, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvani, G.H.; Salmani, I.; Khoshakhlagh, A.H.; Hoboubati, H.; Hajian, N.; Halvani, N. Role of Neck Circumference in Road Traffic Accidents of Commercial Bus and Truck Drivers. J. Community Health Res. 2013, 2, 276–285. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, M.R.; Elkington, J.; Sharwood, L.; Meuleners, L.; Ivers, R.; Boufous, S.; Williamson, A.; Haworth, N.; Quinlan, M.; Grunstein, R.; et al. The role of sleepiness, sleep disorders, and the work environment on heavy-vehicle crashes in 2 Australian states. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, N.; Ulfberg, J.; Nyström, B.; Edling, C. Sleep debt, sleepiness and accidents among males in the general population and male professional drivers. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2003, 35, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, P.; Guichard, K.; Strauss, M.; Léger, D.; Pepin, E.; Arnulf, I.; Sagaspe, P.; Barateau, L.; Lopez, R.; Taillard, J.; et al. Maintenance of wakefulness test: How does it predict accident risk in patients with sleep disorders? Sleep Med. 2021, 77, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalia, L.; Goldoni, M.; Spaggiari, M.C.; Roscelli, F.; Corradi, M.; Mutti, A. Sleep disorders, risk of accidents and traffic accidents in a group of drivers of public transport. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2012, 34, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gislason, T.; Tómasson, K.; Reynisdóttir, H.; Björnsson, J.K.; Kristbjarnarson, H. Medical risk factors amongst drivers in single-car accidents. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 241, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassel, W.; Ploch, T.; Becker, C.; Dugnus, D.; Peter, J.H.; von Wichert, P. Risk of traffic accidents in patients with sleep-disordered breathing: Reduction with nasal CPAP. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 2606–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiomi, T.; Arita, A.T.; Sasanabe, R.; Banno, K.; Yamakawa, H.; Hasegawa, R.; Ozeki, K.; Okada, M.; Ito, A. Falling asleep while driving and automobile accidents among patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2002, 56, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.T.; Tsai, S.S.; Liao, H.Y.; Lin, Y.J.; Lin, M.H.; Wu, T.N.; Shih, T.S.; Liou, S.H. Usefulness of overnight pulse oximeter as the sleep assessment tool to assess the 6-year risk of road traffic collision: Evidence from the Taiwan Bus Driver Cohort Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Perez, M.A.; Lau, N. The impact of sleep disorders on driving safety-findings from the Second Strategic Highway Research Program naturalistic driving study. Sleep 2018, 41, zsy023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, K.; Brameld, K.; Meuleners, L. The association between obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and motor vehicle crash (MVC)-related. Transport 2018, 44, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, P.; Sagaspe, P.; Lagarde, E.; Leger, D.; Ohayon, M.M.; Bioulac, B.; Boussuge, J.; Taillard, J. Sleep disorders and accidental risk in a large group of regular registered highway drivers. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, A.; Sasanabe, R.; Hasegawa, R.; Nomura, A.; Hori, R.; Mano, M.; Konishi, N.; Shiomi, T. Risk factors for automobile accidents caused by falling asleep while driving in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Torre, G.; Calzoni, L.; Colamesta, V.; Guzzo, A.S.; Mafongelli, E.; Mannocci, A.; Meggiolaro, A.; Mipatrini, D.; Pagano, L.; Saulle, R. Management Sanitario, un Approccio Metodologico; SEU Società Editrice Universo: Rome, Italy, 2014; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino, S.; Bardwell, W.A.; Guglielmi, O.; Chiorri, C.; Bonanni, E.; Magnavita, N. Association of Anxiety and Depression in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behav. Sleep Med. 2020, 18, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Nazari, S.S.H.; Rahmani, K. Sleepiness and the risk of road traffic accidents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of previous studies. Transp. Res. F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 65, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregear, S.; Reston, J.; Schoelles, K.; Phillips, B. Obstructive sleep apnea and risk of motor vehicle crash: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen, R.L.; Marshall, S.C.; Palayew, M.; Molnar, F.J.; Wilson, K.G.; Man-Son-Hing, M. Systematic review of motor vehicle crash risk in persons with sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2006, 2, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Bioulac, S.; Micoulaud-Franchi, J.A.; Arnaud, M.; Sagaspe, P.; Moore, N.; Salvo, F.; Philip, P. Risk of Motor Vehicle Accidents Related to Sleepiness at the Wheel: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Author | [22] | [23] | [24] | [25] | [26] | [27] | [28] | [29] | [30] | [31] | [32] | [33] | [34] | [35] | [36] | [37] | [38] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection: (Maximum 5 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||
| * | * | ** | * | ** | * | * | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | * | ** | * | ||
| Comparability: (Maximum 2 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| Outcome: (Maximum 3 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | * | * | * | * |
| ** | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||
| Total score= | 8 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 5 | |
| Author | [39] | [40] | [41] | [42] | [43] | [44] | [45] | [46] | [47] | [48] | [49] | [50] | [51] | [52] | [53] | [54] | [55] | [56] | [57] | [58] | [59] | [60] | [61] | [62] | [63] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection: (Maximum 4 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||
| Comparability: (Maximum 2 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| Outcome: (Maximum 3 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||||||||||
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total score= | 6 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 5 | |
| Author | [64] | [65] | [66] | [67] | [68] | [69] | [70] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection: (Maximum 4 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | ||
| * | |||||||
| * | * | ||||||
| Comparability: (Maximum 2 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| Outcome: (Maximum 3 stars) |
| * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| * | * | * | * | * | |||
| * | * | ||||||
| Total score= | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luzzi, V.; Mazur, M.; Guaragna, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Cotticelli, L.; Magliulo, G.; Marasca, B.; Pirro, V.; Di Giorgio, G.; Ndokaj, A.; et al. Correlations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Daytime Sleepiness with the Risk of Car Accidents in Adult Working Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Gender-Based Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143971
Luzzi V, Mazur M, Guaragna M, Di Carlo G, Cotticelli L, Magliulo G, Marasca B, Pirro V, Di Giorgio G, Ndokaj A, et al. Correlations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Daytime Sleepiness with the Risk of Car Accidents in Adult Working Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Gender-Based Approach. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(14):3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143971
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuzzi, Valeria, Marta Mazur, Mariana Guaragna, Gabriele Di Carlo, Luisa Cotticelli, Giuseppe Magliulo, Beatrice Marasca, Valentina Pirro, Gianni Di Giorgio, Artnora Ndokaj, and et al. 2022. "Correlations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Daytime Sleepiness with the Risk of Car Accidents in Adult Working Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Gender-Based Approach" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 14: 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143971
APA StyleLuzzi, V., Mazur, M., Guaragna, M., Di Carlo, G., Cotticelli, L., Magliulo, G., Marasca, B., Pirro, V., Di Giorgio, G., Ndokaj, A., Pasqualetti, P., Simonelli, I., Martini, A., Pietrafesa, E., & Polimeni, A. (2022). Correlations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Daytime Sleepiness with the Risk of Car Accidents in Adult Working Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Gender-Based Approach. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(14), 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143971











