Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy after Liver Transplantation: Peri-Operative Associated Factors and Impact on Survival
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Differences among Patients on CRRT or Not on CRRT in the First Postoperative Week
3.2. Preoperative and Intraoperative Factors Associated with the Use of Bypass Technique
3.3. Peri-Operative Factors Associated with the Use of CRRT
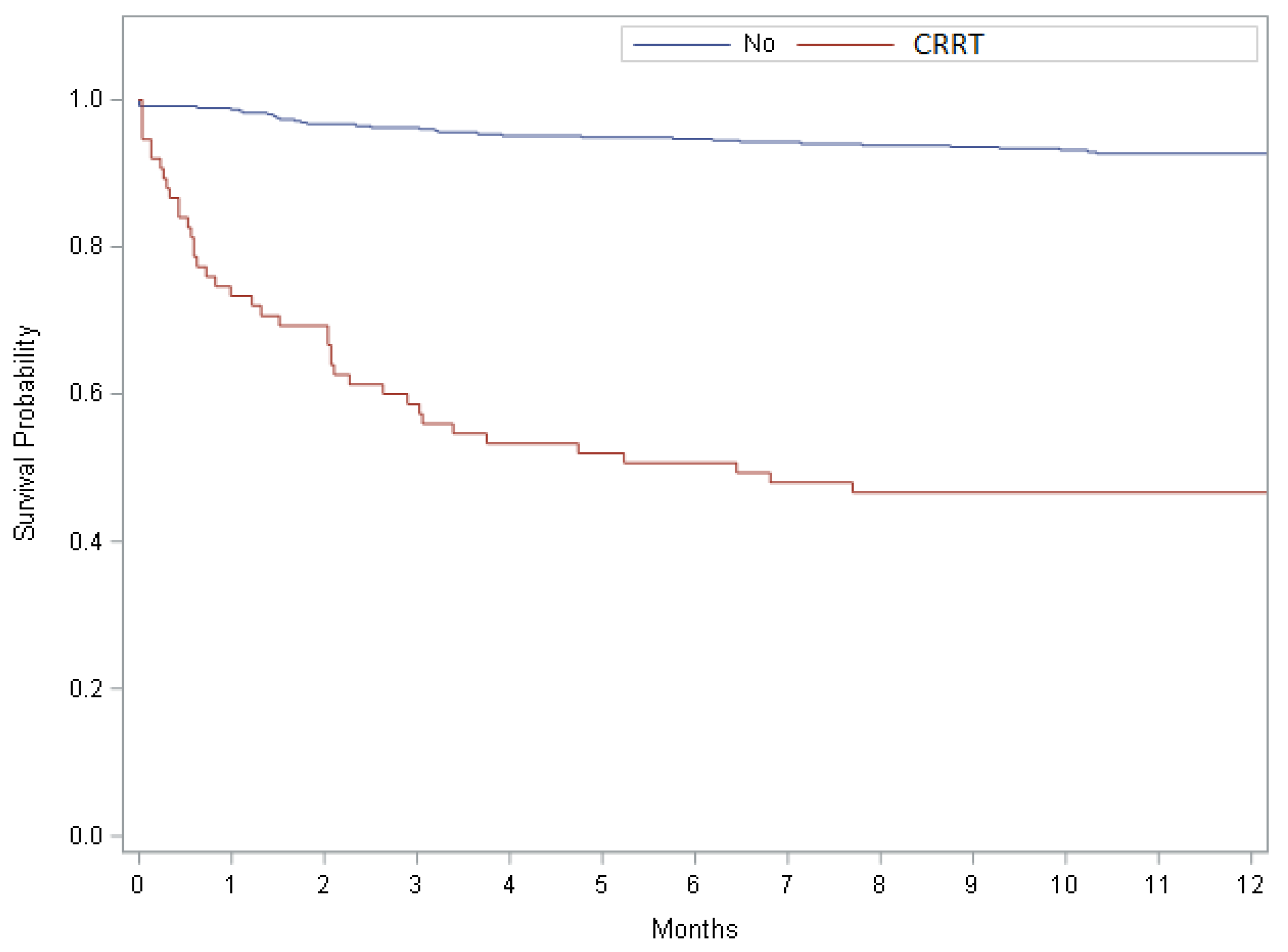
3.4. The Impact of CRRT on Mortality after OLT
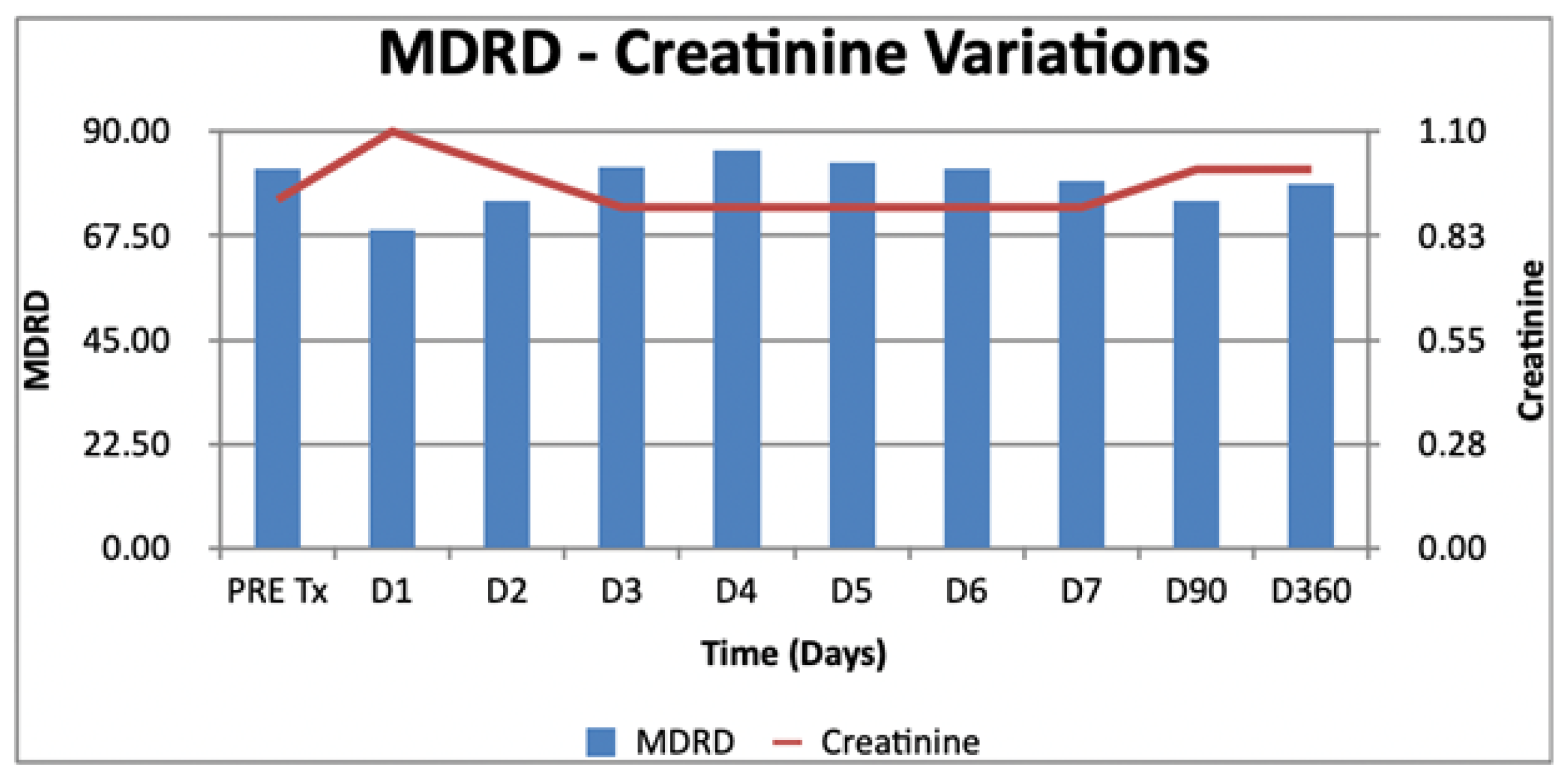
3.5. Postoperative Longitudinal Evolution of Creatinine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pham, P.T.; Slavov, C.; Pham, P.T. Acute Kidney Injury After Liver, Heart, and Lung Transplants: Dialysis Modality, Predictors of Renal Function Recovery, and Impact on Survival. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2009, 16, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, G.; Garces, G.; Quartin, A.A.; Cely, C.; Lagatta, M.A.; Barreto, G.A.; Roth, D.; Gomez, E. An Epidemiologic Study of Early Renal Replacement Therapy after Orthotopic Liver Transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayhan, A.; Ersoy, Z.; Ulas, A.; Zeyneloglu, P.; Pirat, A.; Haberal, M. Incidence and patient outcomes in renal replacement therapy after orthotopic liver transplant. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 15, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagioni, E.; Cavazzuti, I.; Busani, S.; Trevisan, D.; Zavatti, L.; Ferrari, E.; Massimo, G. Acute Renal Failure and Renal Replacement Therapy in the Postoperative Period of Orthotopic Liver Transplant Patients Versus Nonelective Abdominal Surgery Patients. Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuang, F.; Lin, C.; Wang, P.; Cheng, Y.; Hsu, K.; Chen, Y.; Lee, C.; Chen, C. Acute Renal Failure After Cadaveric Related Liver Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 2328–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staufer, K.; Roedl, K.; Kivaranovic, D.; Drolz, A.; Horvatits, T.; Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; Zauner, C.; Trauner, M.; Fuhrmann, V. Renal replacement therapy in critically ill liver cirrhotic patients-outcome and clinical implications. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-Y.; Cacciarelli, T.V.; Wagener, M.M.; Singh, N. Impact of the duration of posttransplant renal replacement therapy on bacterial infections in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2011, 17, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, D.W.; Oliver, J.A. The pathogenesis of vasodilatory shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezuelo, J.B.; Ramirez, P.; Acosta, F.; Torres, D.; Sansano, T.; Pons, J.A.; Bru, M.; Montoya, M.; Rios, A.; Robles, R.; et al. Does the Standard vs Piggyback Surgical Technique Affect The Development of Early Acute Renal Failure After Orthotopic Liver Transplantation? Transplant. Proc. 2003, 35, 1913–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, P.-T.T.; Pham, P.-C.T.; Wilkinson, A.H. Management of renal dysfunction in the liver transplant recipient. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2009, 14, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajjoka, I.; Hsaiky, L.; Brown, K.; Abouljoud, M. Preserving Renal Function in Liver Transplant Recipients with Rabbit Anti-Thymocyte Globulin and Delayed Initiation of Calcineurin Inhibitors. Liver Transpl. 2008, 14, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, M.C.C.; de Souza, N.K.G.; Ammirati, A.L.; Matsui, T.N.; Carneiro, F.D.; de Souza Ramos, A.C.M.; Iizuca, I.J.; Coelho, M.P.V.; Afonso, R.C.; Ferraz-Neto, B.-H.; et al. Predictors of renal function recovery among patients undergoing renal replacement therapy following orthotopic liver transplantation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukhtar, A.; Lotfy, A.; Hussein, A.; Fouad, E. Splanchnic and systemic circulation cross talks: Implications for hemodynamic management of liver transplant recipients. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2020, 34, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Yi, W.; Liu, H.; Haixia, L.; Dongdong, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, G. Early prediction of acute kidney injury after liver transplantation by scoring system and decision tree. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, K.; Weigand, M.A.; Hillebrand, N.; Büchler, M.W.; Schmidt, J.; Schemmer, P. Is veno-venous bypass still needed during liver transplantation? A review of the literature. Clin. Transplant. 2009, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Silva, M.A.; Tan, Y.M.; John, A.; Gunson, B.; Buckels, J.A.C.; David Mayer, A.; Bramhall, S.R.; Mirza, D.F. Conventional versus piggyback technique of caval implantation; without extra-corporeal veno-venous bypass. A comparative study. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, L.; Ma, X.; Miao, G.; Chu, H. Modifiable risk factors of acute kidney injury after liver transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, A.; Lucidi, V.; Ickx, B.; Van Obbergh, L.; Germanova, D.; Berna, A.; Alexander, B.; Desebbe, O.; Carrier, F.-M.; Cherqui, D.; et al. Intraoperative hypotension during liver transplant surgery is associated with postoperative acute kidney injury: A historical cohort study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, R.S.; Gan, T.J.; Robertson, K.M.; Bass, K.; Camargo, C.A.; Greig, P.D.; Clavien, P.A. Venovenous bypass in adult orthotopic liver transplantation: Routine or selective use? J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1998, 186, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.E.C.; de Melo, P.S.V.; Sabat, B.D.; Tenório, A.L.; Lima, D.L.; Neto, O.C.L.F.; Amorim, A.G.; Fernandez, J.L.; de Macedo, F.I.B.; Lacerda, C.M. Orthotopic liver transplantation without venovenous bypass: 125 cases from a single center. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Overall n = 528 | CRRT n = 75 | NO CRRT n = 453 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative variables | ||||
| Age, years | 54.00 (44.00–61.00) | 50.00 (38.00–60.00) | 54.00 (46.00–61.00) | 0.0486 |
| Male gender | 382 (72.4) | 54 (72) | 328 (72.4) | 0.9419 |
| BMI | 26.40 (23.65–29.45) | 26.20 (21.50–28.80) | 26.40 (23.90–29.50) | 0.4681 |
| MELD | 22.00 (19.00–23.00) | 27.00 (22.00–36.00) | 22.00 (18.00–22.00) | <0.0001 |
| Blood urea nitrogen | 33.50 (24.00–48.00) | 64.00 (27.00–129.00) | 32.00 (24.00–44.00) | <0.0001 |
| Creatinine | 0.92 (0.80–1.30) | 1.30 (0.90–3.00) | 0.90 (0.70–1.20) | <0.0001 |
| MDRD pre | 81.86 (58.78–107.69) | 57.74 (21.95–87.80) | 84.07 (62.63–108.76) | <0.0001 |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 2.80 (1.21–6.79) | 6.79 (2.78–16.64) | 2.41 (1.10–5.68) | <0.0001 |
| Hepatocarcinoma | 194 (36.7) | 12 (16) | 182 (40.2) | <0.0001 |
| Acute hepatitis | 34 (6.4) | 19 (25.3) | 15 (3.3) | <0.0001 |
| Other diagnoses | 294 (56.32) | 44 (14.97) | 250 (85.03) | 0.6582 |
| Intraoperative variables | ||||
| Surgery duration, hours | 6.00 (5.00–7.00) | 7.00 (5.00–8.00) | 6.00 (5.00–7.00) | 0.0306 |
| Intraoperative bypass | 89 (16.9) | 17 (22.7) | 72 (15.9) | 0.1467 |
| No intraoperative transfusion | 131 (24.8) | 8 (10.7) | 123 (27.15) | 0.0022 |
| Platelet transfusion, yes/no | 107 (20.27) | 31 (41.3) | 76 (16.8) | <0.0001 |
| Platelets, mL | 300.00 (260.00−500.00) | 400.00 (260.00−500.00) | 276.50 (260.00−500.00) | 0.1053 |
| Plasma transfusion, yes/no | 321 (60.80) | 63 (84) | 258 (57) | <0.0001 |
| Plasma, units | 5.00 (3.00–8.00) | 8.00 (5.00–12.00) | 4.00 (2.00–6.00) | <0.0001 |
| PRBC transfusion, yes/no | 355 (67.23%) | 65 (86.7) | 290 (64.1) | 0.0001 |
| PRBC, units | 4.00 (2.00–7.00) | 7.00 (4.00–12.00) | 4.00 (2.00–6.00) | <0.0001 |
| Intraoperative use of noradrenaline, n (%) | 258 (48.86%) | 43 (57.3) | 215 (47.5) | 0.1131 |
| Noradrenaline maximum dosage, mcg/kg/min | 0.20 (0.10–0.30) | 0.30 (0.15–0.50) | 0.15 (0.10–0.25) | <0.0001 |
| Outcomes | ||||
| ICU length of stay, days | 2 (1–5) | 10 (5–21) | 2 (1–4) | <0.0001 |
| Hospital length of stay, days | 17.00 (12–32) | 37 (20–74) | 16 (11–27) | <0.0001 |
| Deceased at 1 year | 73 (13.8) | 40 (53.3) | 33 (7.3) | <0.0001 |
| Odds Ratio (OR) | Confidence Interval (CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male vs. Female | 1.117 | 0.665–1.876 | 0.6758 |
| Hepatocarcinoma | 0.960 | 0.597–1.543 | 0.8663 |
| Acute | 1.569 | 0.686–3.589 | 0.2861 |
| Other | 0.917 | 0.579–1.454 | 0.7126 |
| Age | 1.018 | 1.002–1.034 | 0.0267 |
| Body mass index | 0.984 | 0.916–1.056 | 0.6468 |
| MELD | 1.044 | 1.010–1.078 | 0.0095 |
| Blood urea nitrogen | 1.008 | 1.003–1.013 | 0.0023 |
| Creatinine | 1.135 | 0.979–1.315 | 0.0941 |
| MDRD pre | 0.996 | 0.993–1.000 | 0.0475 |
| Total Bilirubin | 1.024 | 1.001–1.046 | 0.0375 |
| Surgery duration | 1.055 | 0.973–1.144 | 0.1941 |
| Platelets unit (just transfused: n = 107) | 1.001 | 0.998–1.003 | 0.6011 |
| Plasma unit (just transfused: n = 321) | 1.070 | 1.010–1.135 | 0.0223 |
| PRBC units (just transfused: n = 355) | 1.046 | 0.999–1.095 | 0.0542 |
| Hypotension | 1.022 | 1.005–1.040 | 0.0110 |
| Noradrenaline max dose, 0.1 increase | 0.906 | 0.663–1.237 | 0.5330 |
| Odds Ratio (OR) | Confidence Interval (CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male vs. Female | 0.980 | 0.568–1.689 | 0.9417 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.284 | 0.149–0.541 | 0.0001 |
| Acute | 9.907 | 4.765–20.596 | <0.001 |
| Other | 1.118 | 0.681–1.837 | 0.6583 |
| End stage liver disease | 2.780 | 0.834–9.266 | 0.0961 |
| Alcohol | 0.570 | 0.237–1.370 | 0.2086 |
| Biliary | 0.898 | 0.367–2.198 | 0.8134 |
| Other | 1.924 | 1.088–3.404 | 0.0245 |
| Criptogenetic | 0.588 | 0.175–1.976 | 0.3901 |
| Bypass | 1.551 | 0.854–2.816 | 0.1492 |
| Age, year | 0.990 | 0.977–1.003 | 0.1369 |
| BMI | 1.015 | 0.946–1.088 | 0.6828 |
| MDRD pre-OLT | 1.000 | 0.998–1.001 | 0.5062 |
| Surgery duration, hours | 1.075 | 0.988–1.168 | 0.0914 |
| Platelet, unit | 1.002 | 1.000–1.004 | 0.0847 |
| Plasma, unit | 1.130 | 1.068–1.195 | <0.0001 |
| PRBC, unit | 1.142 | 1.081–1.206 | <0.0001 |
| Hypotension | 1.018 | 1.000–1.037 | 0.0500 |
| Noradrenaline, 0.1 increase | 1.076 | 0.910–1.273 | 0.3901 |
| Vasopressin, 0.1 unit | 1.610 | 0.802–3.230 | 0.1802 |
| Creatinine day 1 | 2.238 | 1.611–3.109 | <0.0001 |
| MDRD day 1 | 0.999 | 0.998–1.001 | 0.3546 |
| Total bilirubin day 1 | 1.134 | 1.078–1.193 | <0.0001 |
| Tacrolimus day1 | 0.794 | 0.559–1.128 | 0.1975 |
| Platelets day 1 | 0.988 | 0.980–0.997 | 0.0097 |
| Urine output D1 | 0.998 | 0.998–0.999 | <0.0001 |
| Variable | Estimate Variation | 95% Confidence Limits | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female gender | −0.108 | −0.243; 0.028 | 0.120 |
| Age | 0.009 | 0.006; 0.011 | <0.001 |
| Body Mass Index | 0.012 | −0.10; 0.034 | 0.274 |
| MELD | 0.007 | −0.002; 0.015 | 0.114 |
| Preoperative Blood Urea Nitrogen | 0.002 | −0.001; 0.005 | 0.097 |
| Preoperative Total Bilirubin | 0.001 | −0.007; 0.008 | 0.834 |
| Diagnosis | |||
| -Acute Hepatitis vs. Cirrhosis | −0.020 | −0.205; 0.165 | 0.834 |
| -Hepatocarcinoma vs. Cirrhosis | −0.069 | −0.161; 0.022 | 0.139 |
| Intraoperative Bypass | −0.043 | −0.104; 0.181 | 0.567 |
| Surgery Duration, minutes | 0.001 | −0.019; 0.021 | 0.898 |
| Platelet Transfusion, unit | 0.148 | −0.078; 0.374 | 0.199 |
| Plasma Transfusion, unit | 0.006 | −0.008; 0.020 | 0.422 |
| PRBC Transfusion, unit | 0.007 | −0.007; 0.022 | 0.316 |
| Intraoperative Hypotension | −0.008 | −0.012; 0.003 | <0.001 |
| Noradrenaline maximum dosage, per 0.01 mcg/kg/min increase | 0.105 | 0.053; 0.157 | <0.001 |
| CRRT in the first week | 0.246 | 0.056; 0.436 | 0.011 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martucci, G.; Rossetti, M.; Li Petri, S.; Alduino, R.; Volpes, R.; Panarello, G.; Gruttadauria, S.; Burgio, G.; Arcadipane, A. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy after Liver Transplantation: Peri-Operative Associated Factors and Impact on Survival. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133803
Martucci G, Rossetti M, Li Petri S, Alduino R, Volpes R, Panarello G, Gruttadauria S, Burgio G, Arcadipane A. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy after Liver Transplantation: Peri-Operative Associated Factors and Impact on Survival. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(13):3803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133803
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartucci, Gennaro, Matteo Rossetti, Sergio Li Petri, Rossella Alduino, Riccardo Volpes, Giovanna Panarello, Salvatore Gruttadauria, Gaetano Burgio, and Antonio Arcadipane. 2022. "Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy after Liver Transplantation: Peri-Operative Associated Factors and Impact on Survival" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 13: 3803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133803
APA StyleMartucci, G., Rossetti, M., Li Petri, S., Alduino, R., Volpes, R., Panarello, G., Gruttadauria, S., Burgio, G., & Arcadipane, A. (2022). Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy after Liver Transplantation: Peri-Operative Associated Factors and Impact on Survival. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(13), 3803. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133803







