Differences in Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Obesity-Associated Asthma: Effects of Weight Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Blood Collection and Serum Extraction
2.3. Measurement of Serum Cytokine Levels and Immunoglobulin E
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Leptin, Adiponectin, and Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio before and after BS
3.2. Comparison of Serum Inflammatory Markers between HC and the NOA, OA and O Groups
3.3. Comparisons between Obese Subjects with and without Asthma
3.4. Comparisons between NOA, OA, and HC
3.5. Correlations
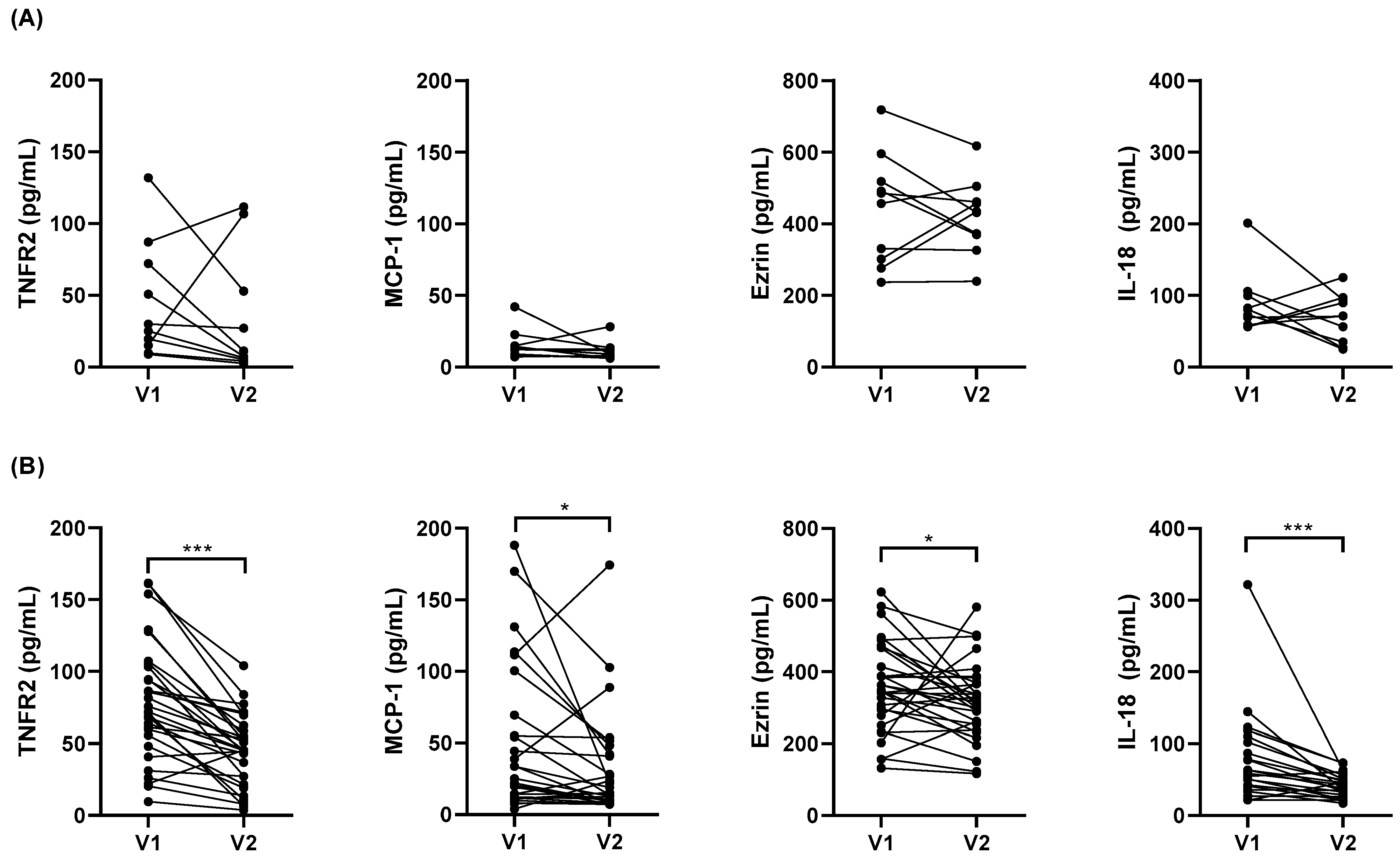
3.6. Impact of Weight Loss on Serum Cytokine Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. Leptin and Adiponectin in Asthma Are Regulated by Obesity-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms
4.2. Obesity Is Associated with a Systemic Inflammation (TGF-β1, TNFR2, MCP-1, Ezrin, YKL-40, and ST2) Which Is More Active Than That Associated with Asthma
4.3. IL-9 Was the Only Cytokine Presenting Significantly Higher Levels in OA with Respect to O Subjects
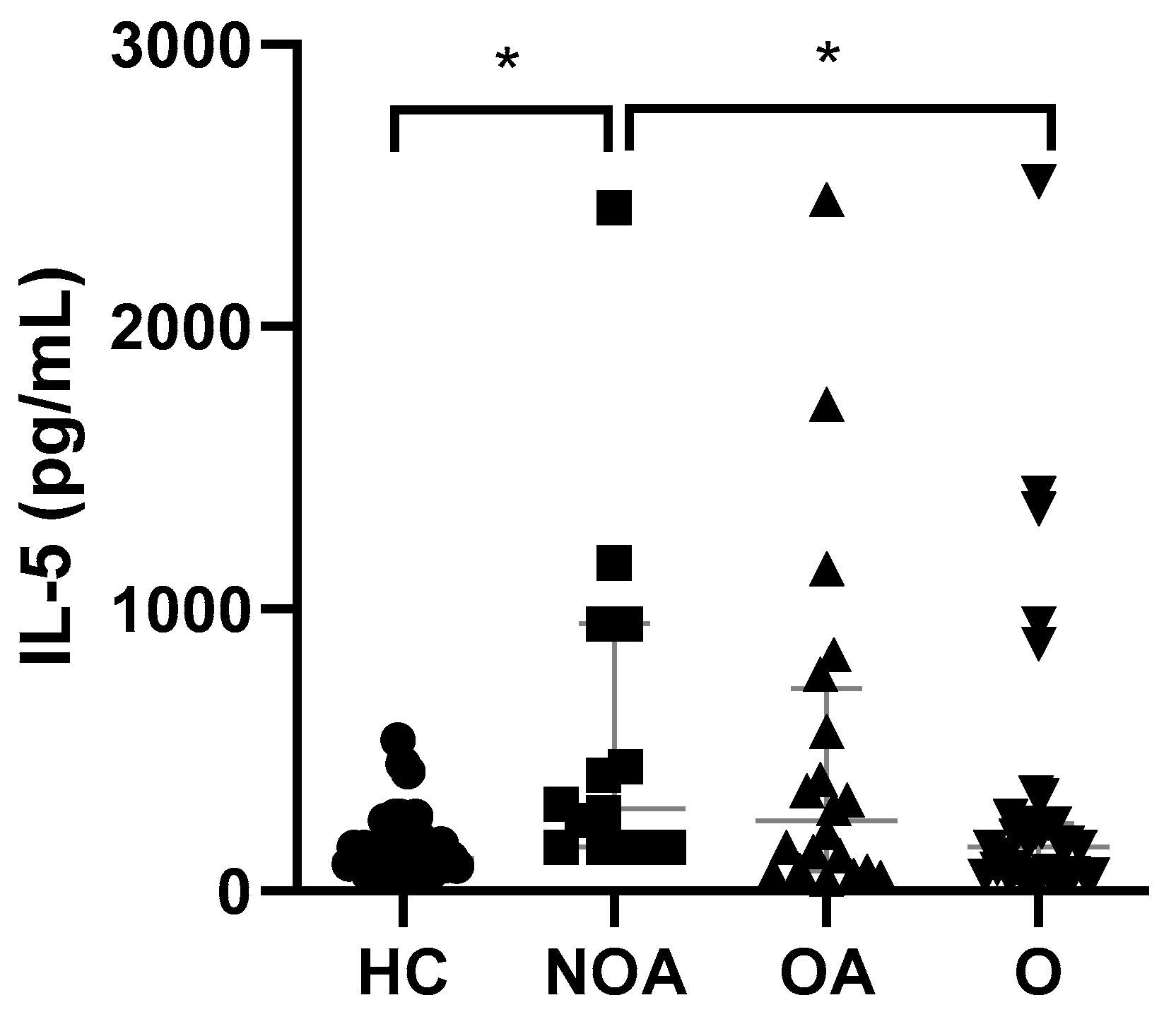
4.4. IL-5 Levels Were Only Found to Be Significantly Elevated in NOA Patients with Respect to HC
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bantulà, M.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Arismendi, E.; Picado, C. Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, L.; Kang, D.Y.; Wood, L.G.; Wang, G. Systemic Inflammation Mediates the Detrimental Effects of Obesity on Asthma Control. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018, 39, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arismendi, E.; Rivas, E.; Agustí, A.; Ríos, J.; Barreiro, E.; Vidal, J.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. The Systemic Inflammome of Severe Obesity before and after Bariatric Surgery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arismendi, E.; Bantulà, M.; Perpiñá, M.; Picado, C. Effects of Obesity and Asthma on Lung Function and Airway Dysanapsis in Adults and Children. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huisstede, A.; Rudolphus, A.; Cabezas, M.C.; Biter, L.U.; Van De Geijn, G.J.; Taube, C.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Braunstahl, G.J. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Asthma Control, Lung Function and Bronchial and Systemic Inflammation in Morbidly Obese Subjects with Asthma. Thorax 2015, 70, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forno, E.; Weiner, D.J.; Mullen, J.; Sawicki, G.; Kurland, G.; Han, Y.Y.; Cloutier, M.M.; Canino, G.; Weiss, S.T.; Litonjua, A.A.; et al. Obesity and Airway Dysanapsis in Children with and without Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit Care Med. 2017, 195, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, S.T.; Kuo, H.P.; Delclaux, C.; Jensen, M.E.; Wood, L.G.; Costa, D.; Nowakowski, D.; Wronka, I.; Oliveira, P.D.; et al. Effects of Obesity on Pulmonary Function Considering the Transition from Obstructive to Restrictive Pattern from Childhood to Young Adulthood. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Ford, E.S.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Association between Leptin and Asthma in Adults. Thorax 2006, 61, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, Y.W.; Sun, H.L.; Ng, Y.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Yang, S.F.; Ku, M.S.; Lu, K.H.; Sheu, J.N.; Lue, K.H. Associations of Serum Leptin with Atopic Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis in Children. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2010, 24, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozde, C.; Dogru, M.; Erdogan, F.; Ipek, I.O.; Ozde, S.; Karakaya, O. The Relationship between Adiponectin Levels and Epicardial Adipose Tissue Thickness in Non-Obese Children with Asthma. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 33, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Van Bever, H.P.S.; Lim, T.K.; Kuan, W.; Goh, D.Y.T.; Mahadevan, M.; Sim, T.B.; Ho, R.; Larbi, A.; Ng, T.P. Obesity, Asthma Prevalence and IL-4: Roles of Inflammatory Cytokines, Adiponectin and Neuropeptide Y. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 26, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashikawa, Y.; Iwata, M.; Inomata, M.; Kawagishi, Y.; Tokui, K.; Taka, C.; Kambara, K.; Okazawa, S.; Yamada, T.; Hayashi, R.; et al. Association of Serum Adiponectin with Asthma and Pulmonary Function in the Japanese Population. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezir, E.; Civelek, E.; Dibek Misirlioglu, E.; Toyran, M.; Capanoglu, M.; Karakus, E.; Kahraman, T.; Ozguner, M.; Demirel, F.; Gursel, I.; et al. Effects of Obesity on Airway and Systemic Inflammation in Asthmatic Children. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltieri, L.; Cazzo, E.; de Souza, A.L.; Alegre, S.M.; de Paula Vieira, R.; Antunes, E.; de Mello, G.C.; Claudio Martins, L.; Chaim, E.A. Influence of Weight Loss on Pulmonary Function and Levels of Adipokines among Asthmatic Individuals with Obesity: One-Year Follow-Up. Respir. Med. 2018, 145, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sideleva, O.; Suratt, B.T.; Black, K.E.; Tharp, W.G.; Pratley, R.E.; Forgione, P.; Dienz, O.; Irvin, C.G.; Dixon, A.E. Obesity and Asthma: An Inflammatory Disease of Adipose Tissue Not the Airway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of Spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddel, H.K.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bateman, E.D.; Brightling, C.E.; Brusselle, G.G.; Buhl, R.; Cruz, A.A.; Duijts, L.; Drazen, J.M.; FitzGerald, J.M.; et al. Global Initiative for Asthma Strategy 2021 Executive Summary and Rationale for Key Changes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzaki, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Sagawa, N.; Hosoda, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Mise, H.; Nishimura, H.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Tanaka, I.; Mori, T.; et al. Nonadipose Tissue Production of Leptin: Leptin as a Novel Placenta-Derived Hormone in Humans. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Correa, A.A.; Estrada, J.A.; Contreras, I. Leptin Signaling in the Control of Metabolism and Appetite: Lessons from Animal Models. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 66, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Carbone, F.; Cassano, S.; Greco, D.; Qian, K.; Auvinen, P.; Calì, G.; Stallone, G.; et al. Leptin-Induced MTOR Activation Defines a Specific Molecular and Transcriptional Signature Controlling CD4 + Effector T Cell Responses. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, P.; Canetti, C.; Gottschalk, A.; Tithof, P.K.; Peters-Golden, M.; Peters, M. Leptin Augments Alveolar Macrophage Leukotriene Synthesis by Increasing Phospholipase Activity and Enhancing Group IVC IPLA 2 (CPLA 2) Protein Expression. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastien Conus, S.; Bruno, A.; Simon, H.-U. Leptin Is an Eosinophil Survival Factor. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Cheung, P.F.-Y.; Lam, C.W.K. Leptin-Mediated Cytokine Release and Migration of Eosinophils: Implications for Immunopathophysiology of Allergic Inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Ueki, S.; Kamada, R.; Kihara, J.; Yamauchi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Takeda, M.; Itoga, M.; Chihara, M.; Ito, W.; et al. Leptin Has a Priming Effect on Eotaxin-Induced Human Eosinophil Chemotaxis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 155, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Castillo, E.F.; Luo, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, X.O. Leptin Enhances TH2 and ILC2 Responses in Allergic Airway Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22043–22052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, D.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, Y.; Yang, X.; Chock, C.J.; Liu, M.; Yang, X.O. Leptin Promotes Allergic Airway Inflammation through Targeting the Unfolded Protein Response Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, M.; Cai, S. A Systemic Inflammatory Endotype of Asthma with More Severe Disease Identified by Unbiased Clustering of the Serum Cytokine Profile. Medicine 2016, 95, 3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruxandra Otelea, M.; Arghir, O.C.; Zugravu, C.; Rascu, A. Molecular Sciences Adiponectin and Asthma: Knowns, Unknowns and Controversies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuwon, K.M.; Spurlock, M.E. Adiponectin Inhibits LPS-Induced NF-ΚB Activation and IL-6 Production and Increases PPARγ2 Expression in Adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 2005, 288, R1220–R1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Folco, E.J.; Minami, M.; Wara, A.K.; Feinberg, M.W.; Sukhova, G.K.; Colvin, R.A.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Luster, A.D.; et al. Adiponectin Inhibits the Production of CXC Receptor 3 Chemokine Ligands in Macrophages and Reduces T-Lymphocyte Recruitment in Atherogenesis. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Baliga, M.S.; Ponemone, V.; Kaur, K.; Larsen, B.; Fletcher, E.; Greene, J.; Fayad, R. Mucus and Adiponectin Deficiency: Role in Chronic Inflammation-Induced Colon Cancer. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2013, 28, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Hahm, D.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Sur, B.; Lee, H.M.; Ryu, C.J.; Yang, H.I.; Kim, K.S. Potential Therapeutic Antibodies Targeting Specific Adiponectin Isoforms in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Drai, J.; Fouque, D. Adiponectin and Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Koca, C.; Ozol, D.; Uysal, S.; Yildirim, Z.; Kavakli, H.S.; Yigitoglu, M.R. Interaction of Metabolic Syndrome with Asthma in Postmenopausal Women: Role of Adipokines. Inflammation 2013, 36, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrone, T.; Simone, M.; Altamura, M.; Munno, I. Characterization of the Immune Inflammatory Profile in Obese Asthmatic Children. Endocr. Metab. Immune. Disord. Targets 2014, 14, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.E.; Gibson, P.G.; Collins, C.E.; Wood, L.G. Airway and Systemic Inflammation in Obese Children with Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Azambuja, R.; da Costa Santos Azambuja, L.S.E.; Costa, C.; Rufino, R. Adiponectin in Asthma and Obesity: Protective Agent or Risk Factor for More Severe Disease? Lung 2015, 193, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogru, M.; Ozde, S.; Aktas, A.; Yuksel Karatoprak, E. The Adiponectin Levels and Asthma Control in Non-Obese Children with Asthma. J. Asthma 2015, 52, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelo, A.V.; da Fonseca, V.M.; Peixoto, M.V.M.; de Carvalho, S.R.; Azevedo, C.M.; Elsas, M.I.G.; Marques, B. Visceral Adiposity Is Associated with Cytokines and Decrease in Lung Function in Women with Persistent Asthma. Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2016, 22, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, M. Correlations of Severity of Asthma in Children with Body Mass Index, Adiponectin and Leptin. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaroucha, A.; Daniil, Z.; Malli, F.; Georgoulias, P.; Minas, M.; Kostikas, K.; Bargiota, A.; Zintzaras, E.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Leptin, Adiponectin, and Ghrelin Levels in Female Patients with Asthma during Stable and Exacerbation Periods. J. Asthma 2013, 50, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessi, M.C.; Bastelica, D.; Morange, P.; Berthet, B.; Leduc, I.; Verdier, M.; Geel, O.; Juhan-Vague, I. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1, Transforming Growth Factor-Beta1, and BMI Are Closely Associated in Human Adipose Tissue during Morbid Obesity. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J. Transforming Growth Factor Beta Superfamily Regulation of Adipose Tissue Biology in Obesity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.H.; Oh, E.Y.; Han, H.; Yang, M.; Park, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.-W. Insulin Resistance Mediates High-Fat Diet-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis and Airway Hyperresponsiveness through the TGF-Β1 Pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Huang, C.D.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, K.Y.; Lin, S.M.; Liu, C.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Ko, Y.S.; Kian, F.C.; Kuo, H.P. Increased Circulating Fibrocytes in Asthma with Chronic Airflow Obstruction. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 178, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshall, E.M.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Martin, R.J.; Song, Y.L.; Cameron, L.; Ernst, P.; Hamid, Q. Eosinophil-Associated TGF-1 MRNA Expression and Airways Fibrosis in Bronchial Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 17, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrego, A.; Hew, M.; Oates, T.; Sukkar, M.; Kian, F.C. Expression and Activation of TGF-β Isoforms in Acute Allergen-induced Remodelling in Asthma. Thorax 2007, 62, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.W.; Trudeau, J.B.; Balzar, S.; Wenzel, S.E. Peripheral Blood and Airway Tissue Expression of Transforming Growth Factor β by Neutrophils in Asthmatic Subjects and Normal Control Subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, I.; Nitta, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Hoshi, H.; Honma, M.; Woolley, K.; O’Byrne, P.; Tamura, G.; Jordana, M.; Shirato, K. Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 (TGF Beta 1) Gene Expression by Eosinophils in Asthmatic Airway Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 15, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, J.; Fabisiak, J.P.; Hawes, K.; Absher, M. Cytokine Signaling in Lung: Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Secretion by Lung Fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1991, 260, L123–L128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, W.I.; Van Schadewijk, A.; Sont, J.K.; Sharma, H.S.; Stolk, J.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Van Krieken, J.H.J.M. Transforming Growth Factor Β1 and Recruitment of Macrophages and Mast Cells in Airways in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 158, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, C.Y.; Pang, L.; Holland, E.; Knox, A.J.; Yi, C.; Knox TGF-, A.J. TGF-1 Stimulates IL-8 Release, COX-2 Expression, and PGE 2 Release in Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L201–L207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostert, C.; Grusdat, M.; Letellier, E.; Brenner, D. The TNF Family of Ligands and Receptors: Communication Modules in the Immune System and Beyond. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 115–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabal-Hierro, L.; Lazo, P.S. Signal Transduction by Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslick, S.; Williams, E.J.; Berthon, B.S.; Wright, T.; Karihaloo, C.; Gately, M.; Wood, L.G. Chain Fatty Acids Reduce Systemic Inflammation in Monocytes and Adipose Tissue Macrophages from Obese Subjects. Nutrients 2022, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golikova, E.A.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Kovalevskaya-Kucheryavenko, T.V.; Nepomnyashih, V.M.; Sennikov, S.V. Levels of TNF, TNF Autoantibodies and Soluble TNF Receptors in Patients with Bronchial Asthma. J. Asthma 2013, 50, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, B.P.; Galle-Treger, L.; Jahani, P.S.; Howard, E.; Helou, D.G.; Banie, H.; Soroosh, P.; Akbari, O. TNFR2 Signaling Enhances ILC2 Survival, Function, and Induction of Airway Hyperreactivity. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.E.; Pratley, R.E.; Forgione, P.M.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Whittaker-Leclair, L.A.; Griffes, L.A.; Garudathri, J.; Raymond, D.; Poynter, M.E.; Bunn, J.Y.; et al. Effects of Obesity and Bariatric Surgery on Airway Hyperresponsiveness, Asthma Control, and Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 508–515.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Dinarello, C.A.; Molgora, M.; Garlanda, C. IL-1 and Related Cytokines in Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Novick, D.; Kim, S.; Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18 and IL-18 Binding Protein. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedimbi, S.K.; Hägglöf, T.; Karlsson, M.C.I. IL-18 in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4795–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caligiuri, M.A.; Suzuki, K.; Wechser, M.; Goodsaid, F.; VanDeusen, J.B.; Whitman, S.P.; Fehniger, T.A.; Cooper, M.A.; Shah, M.H.; Turner, M.J. Innate Immune Response Combination with IL-12: Implications for the Activation with IL-18 or IL-15 in Expression by Human NK Cells Following Differential Cytokine and Chemokine Gene. J. Immunol. Ref. 1999, 4511, 4511–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Eisenstein, M.; Reznikov, L.; Fantuzzi, G.; Novick, D.; Rubinstein, M.; Dinarello, C.A. Structural Requirements of Six Naturally Occurring Isoforms of the IL-18 Binding Protein to Inhibit IL-18. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, D.; Schwartsburd, B.; Pinkus, R.; Suissa, D.; Belzer, I.; Sthoeger, Z.; Keane, W.F.; Chvatchko, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Fantuzzi, G.; et al. A novel IL-18BP ELISA shows elevated serum IL-19BP in sepsis and extensive decrease of free IL-18. Cytokine 2001, 14, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard-Guyonvarch, C.; Harel, M.; Gabay, C. The Role of Interleukin 18/Interleukin 18-Binding Protein in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease and Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Pontillo, A.; Ciotola, M.; Di Palo, C.; Grella, E.; Nicoletti, G.; Giugliano, D. Weight Loss Reduces Interleukin-18 Levels in Obese Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3864–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Wisnivesky, J.P.; Busse, P.J.; Halm, E.A.; Li, X.-M. Detection of Immunological Biomarkers Correlated with Asthma Control and Quality of Life Measurements in Sera from Chronic Asthmatic Patients. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 106, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Miyazaki, N.; Oashi, K.; Teramoto, S.; Shiratori, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Ohmichi, M.; Abe, S. IL-18 Might Reflect Disease Activity in Mild and Moderate Asthma Exacerbation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camiolo, M.J.; Zhou, X.; Wei, Q.; Bittar, H.E.T.; Kaminski, N.; Ray, A.; Wenzel, S.E. Machine Learning Implicates the IL-18 Signaling Axis in Severe Asthma. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e149945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.R.; Lane, S.J.; Nakhosteen, J.A.; Yoshimura, T.; Lee, T.H.; Poston, R.N. Increased Expression of the Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Bronchial Tissue from Asthmatic Subjects. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 10, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, E.M.; Charo, I.F.; Kunkel, S.L.; Strieter, R.M.; Boring, L.; Gosling, J.; Lukacs, N.W. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Mediates Cockroach Allergen-Induced Bronchial Hyperreactivity in Normal but Not CCR2-/- Mice: The Role of Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurashima, K.; Mukaida, N.; Fujimura, M.; Schröder, J.M.; Matsuda, T.; Matsushima, K. Increase of Chemokine Levels in Sputum Precedes Exacerbation of Acute Asthma Attacks. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 59, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, J.A.; Lloyd, C.M.; Wen, D.; Albar, J.P.; Wells, T.N.C.; Proudfoot, A.; Martinez-A., C.; Dorf, M.; Bjerke, T.; Coyle, A.J.; et al. The Coordinated Action of CC Chemokines in the Lung Orchestrates Allergic Inflammation and Airway Hyperresponsiveness. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolattukudy, P.E.; Niu, J. Inflammation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Autophagy, and the Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1/CCR2 Pathway. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, A.; Singh, A.; Shukla, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Mir, I.; Yadav, R. An Immediate Post Op and Follow up Assessment of Circulating Adipo-Cytokines after Bariatric Surgery in Morbid Obesity. Metab. Open 2022, 13, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The IL-33/ST2 Pathway: Therapeutic Target and Novel Biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C. IL-33, an Alarmin of the IL-1 Family Involved in Allergic and Non Allergic Inflammation: Focus on the Mechanisms of Regulation of Its Activity. Cells 2021, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, G.; Beaven, M.A.; Olivera, A.; Gilfillan, A.M.; Metcalfe, D.D. Activated Mast Cells Synthesize and Release Soluble ST2-a Decoy Receptor for IL-33. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 3034–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, H.; Hayakawa, M.; Kume, A.; Tominaga, S.I. Soluble ST2 Blocks Interleukin-33 Signaling in Allergic Airway Inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26369–26380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sajee, D.; Sehmi, R.; Hawke, T.J.; El-Gammal, A.; Howie, K.J.; Watson, R.M.; Londei, M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’Byrne, P.M. Expression of IL-33 and TSLP and Their Receptors in Asthmatic Airways after Inhaled Allergen Challenge. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Préfontaine, D.; Nadigel, J.; Chouiali, F.; Audusseau, S.; Semlali, A.; Chakir, J.; Martin, J.G.; Hamid, Q. Increased IL-33 Expression by Epithelial Cells in Bronchial Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamekura, R.; Kojima, T.; Takano, K.; Go, M.; Sawada, N.; Himi, T. The Role of IL-33 and Its Receptor ST2 in Human Nasal Epithelium with Allergic Rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Spallanzani, R.G.; Mathis, D. Visceral Adipose Tissue Tregs and the Cells That Nurture Them. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Asano, S. Pathophysiological Roles of Actin-Binding Scaffold Protein, Ezrin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 2022, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinauskaite-Zukauske, V.; Januskevicius, A.; Janulaityte, I.; Miliauskas, S.; Malakauskas, K.; Katsaounou, P.A. Serum Levels of Epithelial-Derived Cytokines as Interleukin-25 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin after a Single Dose of Mepolizumab in Patients with Severe Non-Allergic Eosinophilic Asthma: A Short Report. Scand. J. Immunol. 2019, 90, e12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Yan, X.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Meng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shan, X.; Zhang, X.; Mao, S.; et al. Ezrin, a Membrane Cytoskeleton Cross-Linker Protein, as a Marker of Epithelial Damage in Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.P.; Turner, J.R.; Philipson, L.H. Glucose-Induced ERM Protein Activation and Translocation Regulates Insulin Secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chupp, G.L.; Lee, C.G.; Jarjour, N.; Shim, Y.M.; Holm, C.T.; He, S.; Dziura, J.D.; Reed, J.; Coyle, A.J.; Kiener, P.; et al. A Chitinase-like Protein in the Lung and Circulation of Patients with Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Shimizu, K.; Tanabe, N.; Makita, H.; Taniguchi, N.; Kimura, H.; Suzuki, M.; Abe, Y.; Matsumoto-Sasaki, M.; Oguma, A.; et al. Further Evidence for Association of YKL-40 with Severe Asthma Airway Remodeling. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 24, S1081–S1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, J.L.; Yan, X.; Holm, C.T.; Grant, N.; Liu, Q.; Cohn, L.; Nezgovorova, V.; Meyers, D.A.; Bleecker, E.R.; Crisafi, G.M.; et al. Characterisation of Asthma Subgroups Associated with Circulating YKL-40 Levels. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilmarinen, P.; Tuomisto, L.E.; Niemelä, O.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, E.; Kankaanranta, H. YKL-40 and Adult-Onset Asthma: Elevated Levels in Clusters with Poorest Outcome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2466–2468.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konradsen, J.R.; James, A.; Nordlund, B.; Reinius, L.E.; Söderhäll, C.; Melén, E.; Wheelock, Å.; Lödrup Carlsen, K.C.; Lidegran, M.; Verhoek, M.; et al. The Chitinase-like Protein YKL-40: A Possible Biomarker of Inflammation and Airway Remodeling in Severe Pediatric Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 328–335.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specjalski, K.; Chełmińska, M.; Jassem, E. YKL-40 Protein Correlates with the Phenotype of Asthma. Lung 2015, 193, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, S.B.; Rathcke, C.N.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Madsbad, S.; Vestergaard, H. Effects of Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass on Fasting and Postprandial Levels of the Inflammatory Markers YKL-40 and MCP-1 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Glucose Tolerant Subjects. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 361781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempen, M.; Kopp, H.P.; Elhenicky, M.; Höbaus, C.; Brix, J.M.; Koppensteiner, R.; Schernthaner, G.; Schernthaner, G.H. YKL-40 Is Elevated in Morbidly Obese Patients and Declines After Weight Loss. Obes. Surg. 2009, 19, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgios, I.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A.; Stylianou, C.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Arvanitidou, M.; Haidich, A.B. Elevated Circulating Levels of the Serum Acute-Phase Protein YKL-40 (Chitinase 3-like Protein 1) Are a Marker of Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Prepubertal Children. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2012, 61, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Rotellar, F.; Valentí, V.; Silva, C.; Gil, M.J.; Salvador, J.; Frühbeck, G. Increased Circulating and Visceral Adipose Tissue Expression Levels of YKL-40 in Obesity-Associated Type 2 Diabetes Are Related to Inflammation: Impact of Conventional Weight Loss and Gastric Bypass. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhoen, M.; Uyttenhove, C.; van Snick, J.; Helmby, H.; Westendorf, A.; Buer, J.; Martin, B.; Wilhelm, C.; Stockinger, B. Transforming Growth Factor-β “reprograms” the Differentiation of T Helper 2 Cells and Promotes an Interleukin 9–Producing Subset. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardalhon, V.; Awasthi, A.; Kwon, H.; Galileos, G.; Gao, W.; Sobel, R.A.; Mitsdoerffer, M.; Strom, T.B.; Elyaman, W.; Ho, I.C.; et al. Interleukin 4 Inhibits TGF-β-Induced-Foxp3+T Cells and Generates, in Combination with TGF-β, Foxp3− Effector T Cells That Produce Interleukins 9 and 10. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Lu, L.; Lau, C.S.; Lu, Q. Th9 Cells and IL-9 in Autoimmune Disorders: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Potentials. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Ferrante, A.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R.; Triolo, G. Interleukin-9 and T Helper Type 9 Cells in Rheumatic Diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elyaman, W.; Bradshaw, E.M.; Uyttenhove, C.; Dardalhon, V.; Awasthi, A.; Imitola, J.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; Van Snick, J.; Renauld, J.C.; et al. IL-9 Induces Differentiation of TH17 Cells and Enhances Function of FoxP3+ Natural Regulatory T Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12885–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Tan, W.; Wu, C. Detection of IL-9 Producing T Cells in the PBMCs of Allergic Asthmatic Patients. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdaviani, S.A.; Eskian, M.; Khorasanizadeh, M.; Bashardoost, B.; Nejad, S.T.; Jamaati, H.; Rezaei, A.; Sadr, M.; Aryan, Z.; Rezaei, N. Interleukin 9 Serum Level and Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Patients with Asthma. Acta Bio. Med. Atenei Parm. 2021, 92, 2021206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpenbeck, V.J.; Hohlfeld, J.M.; Volkmann, B.; Hagenberg, A.; Geldmacher, H.; Braun, A.; Krug, N. Segmental Allergen Challenge in Patients with Atopic Asthma Leads to Increased IL-9 Expression in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Lymphocytes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Tepper, R.S.; Kaplan, M.H. Predisposition to the Development of IL-9-Secreting T Cells in Atopic Infants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1357–1360.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Dong, J. Critical Roles of Balanced T Helper 9 Cells and Regulatory T Cells in Allergic Airway Inflammation and Tumor Immunity. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 8816055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehra, S.; Yao, W.; Nguyen, E.T.; Glosson-Byers, N.L.; Akhtar, N.; Zhou, B.; Kaplan, M.H. TH9 Cells Are Required for Tissue Mast Cell Accumulation during Allergic Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 433–440.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanraj, P.; Van Heerden, M.B.; Pepper, M.S.; Ambele, M.A. Sexual Dimorphism in Changes That Occur in Tissues, Organs and Plasma during the Early Stages of Obesity Development. Biology 2021, 28, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Pathophysiol. Sev. Asthma Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Barcala, F.J.; San-Jose, M.E.; Nieto-Fontarigo, J.J.; Carreira, J.M.; Calvo-Alvarez, U.; Cruz, M.J.; Facal, D.; Garcia-Sanz, M.T.; Valdes-Cuadrado, L.; Salgado, F.J. Association between Blood Eosinophil Count with Asthma Hospital Readmissions. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 53, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Barcala, F.J.; Nieto-Fontarigo, J.J.; Lourido-Cebreiro, T.; Rodríguez-García, C.; San-Jose, M.E.; Carreira, J.M.; Calvo-Alvarez, U.; Cruz, M.J.; Facal, D.; Garcia-Sanz, M.T.; et al. Obesity Does Not Increase the Risk of Asthma Readmissions. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallah, N.; Rodriguez-Segade, S.; Gonzalez-Barcala, F.J.; Takkouche, B. Blood Eosinophil Count as Predictor of Asthma Exacerbation. A Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marijsse, G.S.; Seys, S.F.; Schelpe, A.S.; Dilissen, E.; Goeminne, P.; Dupont, L.J.; Ceuppens, J.L.; Bullens, D.M.A. Obese Individualswith Asthma Preferentially Have a High IL-5/IL-17A/IL-25 Sputum Inflammatory Pattern. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| HC (n, 33) | NOA (n, 14) | OA (n, 21) | O (n, 35) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 43 (37–50) | 52 (43–59) | 56 (50–61) * | 49 (45–58) |
| Female, n (%) | 24 (72) | 12 (86) | 16 (76) | 29 (83) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.5 (21.6–25.0) | 23.2 (22.3–24.9) | 38.4 (34.9–44.1) *,# | 43.4 (39.3–46.9) *,# |
| Mild asthma, n (%) | - | 0 (0) | 4 (19.1) | - |
| Moderate asthma, n (%) | - | 6 (42.9) | 5 (23.8) | - |
| Severe asthma, n (%) | - | 8 (57.1) | 12 (57.1) | - |
| FVC, % pred | 126.6 (122.2–136.3) | 132.1 (116.7–141.3) | 110.4 (94.0–122.5) *,# | 116.0 (102.4–127.0) *,# |
| FEV1, % pred | 101.0 (93.5–109.0) | 86.5 (75.2–103.8) | 85.0 (61.0–95.5) * | 90.5 (84.0–101.0) |
| FEV1/FVC | 79.0 (76.0–83.0) | 71.0 (57.0–75.0) * | 77.0 (69.5–82.0) | 82.0 (79.0–84.0) #,† |
| ICS §, n (%) | - | 13 (92.9) | 19 (82.6) | - |
| Atopia, n (%) | - | 8 (57.1) | 10 (43.5) | - |
| IgE, kU/L | 26.9 (16.5–80.2) | 95.5 (34.8–306.0) | 63.7 (14.4–273.0) | 48.3 (18.9–110.0) |
| Eosinophils, % | 2.0 (1.3–3.2) # | 4.7 (3.6–6.3) | 3.3 (2.3–5.0) | 2.4 (1.6–3.2) # |
| Eosinophils, cells/mm3 | 100 (100–200) | 300 (200–425) * | 200 (125–300) * | 200 (100–200) # |
| Neutrophils, % | 60.5 (55.2–65.6) | 54.8 (51.4–61.0) | 56.7 (51.6–64.6) | 63.2 (56.4–66.2) # |
| Neutrophils, cells/mm3 | 3.5 (3.0–4.3) | 3.6 (3.2–4.2) | 3.7 (3.0–4.9) | 4.5 (3.7–5.1) * |
| Obese Asthmatics (n, 10) | Obese (n, 31) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | V2 | V1 | V2 | |
| Age, years | 53 (47–58) | 54 (49–59) | 49 (45–59) | 50 (47–59) |
| Female, n (%) | 10 (100) | 10 (100) | 26 (84) | 26 (84) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 44.1 (38.7–47.1) | 29.9 (26.4–34.8) * | 42.7 (38.7–45.9) | 29.0 (27.4–30.8) # |
| Mild asthma, n (%) | 4 (40) | 9 (90) | - | - |
| Moderate asthma, n (%) | 4 (40) | 1 (10) | - | - |
| Severe asthma, n (%) | 2 (20) | 0 (0) | - | - |
| ACT | 18 (18–24) | 25 (25–25) * | - | - |
| FVC, % pred | 110.6 (96.9–121.5) | 119.0 (111.9–136.3) | 116.5 (104.3–129.2) | 130.4 (116.7–141.7) # |
| FEV1, % pred | 89.0 (79.5–97.2) | 96.5 (92.5–104.8) | 93.5 (84.7–101.0) | 102.0 (89.0–109.0) # |
| FEV1/FVC | 80.5 (76.5–82.5) | 81.5 (77.5–83.0) | 82.0 (79.0–84.0) | 81.0 (75.0–83.0) # |
| ICS §, n (%) | 6 (60) | 2 (20) | - | - |
| IgE, kU/L | 35.4 (17.3–117.5) | 35.7 (20.3–64.0) | 51.7 (16.8–115.0) | 28.3 (14.4–62.8) |
| Eosinophils, % | 2.9 (1.9–3.7) | 2.5 (1.4–3.3) | 2.4 (1.6–3.4) | 2.2 (1.6–2.8) |
| Eosinophils, cells/mm3 | 200 (100–225) | 200 (75–225) | 200 (100–200) | 100 (100–200) # |
| Neutrophils, % | 56.7 (53.5–64.3) | 56.2 (54.7–58.5) | 62.5 (55.5–65.3) | 56.9 (52.3–64.4) |
| Neutrophils, cells/mm3 | 3.6 (2.9–4.4) | 3.3 (2.9–4.2) | 4.4 (3.7–5.1) | 3.1 (2.6–4.2) # |
| HC | NOA | OA | O | HC vs. NOA | HC vs. OA | HC vs. O | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | ||||||
| TGF-β1 | N, | 33 | 14 | 21 | 35 | |||
| ng/mL | 361.2 | 349.1 | 348.6 | 495.4 | 0.9725 | 0.7382 | 0.0155 | |
| 25th–75th | (158.2–516.4) | (255.1–442.0) | (239.2–416.1) | (288.0–746.0) | ||||
| TNFR2 | N, | 32 | 14 | 21 | 34 | |||
| ng/mL | 32.4 | 45.5 | 45.1 | 70.0 | 0.0792 | 0.1163 | <0.0001 | |
| 25th–75th | (8.8–56.2) | (25.0–99.2) | (22.4–65.8) | (45.8–96.7) | ||||
| MCP-1 | N, | 28 | 14 | 21 | 34 | |||
| ng/mL | 8.6 | 9.7 | 14.5 | 21.3 | 0.5388 | 0.0441 | 0.0003 | |
| 25th–75th | (6.5–17.8) | (8.1–14.7) | (10.6–28.1) | (11.5–75.7) | ||||
| Ezrin | N, | 33 | 14 | 21 | 35 | |||
| ng/mL | 216.9 | 325.5 | 322.5 | 341.7 | 0.0025 | 0.0005 | <0.0001 | |
| 25th–75th | (160.4–285.4) | (217.2–361.0) | (232.1–471.1) | (251.1–414.0) | ||||
| YKL-40 | N, | 33 | 14 | 21 | 34 | |||
| ng/mL | 23,440 | 58,428 | 60,240 | 59,151 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| 25th–75th | (13,720–39,958) | (47,346–103,219) | (44,494–171,396) | (41,590–86,112) | ||||
| ST2 | N, | 32 | 14 | 21 | 35 | |||
| ng/mL | 999.1 | 931.2 | 1009.0 | 1570.0 | 0.6667 | 0.7903 | 0.0238 | |
| 25th–75th | (676.5–1456.0) | (576.0–1308.0) | (486.2–2229.0) | (820.8–3207.0) | ||||
| IL-5 | N, | 33 | 14 | 20 | 35 | |||
| ng/mL | 116.6 | 294.2 | 252.1 | 155.5 | 0.0004 | 0.1443 | 0.7442 | |
| 25th–75th | (93.6–191.1) | (155.5–949.6) | (72.3–718.2) | (58.1–240.7) | ||||
| IL-9 | N, | 28 | 8 | 14 | 28 | |||
| ng/mL | 3.2 | 4.9 | 12.8 | 3.4 | 0.3530 | 0.0171 | 0.7666 | |
| 25th–75th | (2.0–7.5) | (1.8–16.4) | (2.2–19.3) | (1.9–7.1) | ||||
| IL-18 | N, | 27 | 14 | 21 | 32 | |||
| ng/mL | 40.7 | 57.8 | 69.3 | 56.9 | 0.0207 | 0.0118 | 0.0648 | |
| 25th–75th | (22.3–81.0) | (30.4–152.6) | (40.9–102.9) | (34.0–99.4) |
| OA | O | OA vs. O | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | ||||
| TGF-β1 | N, | 21 | 35 | |
| ng/mL | 348.6 | 495.4 | 0.0103 | |
| 25th–75th | (239.2–416.1) | (288.0–746.0) | ||
| TNFR2 | N, | 21 | 34 | |
| ng/mL | 45.1 | 70.0 | 0.018 | |
| 25th–75th | (22.4–65.8) | (45.8–96.7) | ||
| MCP-1 | N, | 21 | 34 | |
| ng/mL | 14.5 | 21.3 | 0.1528 | |
| 25th–75th | (10.6–28.1) | (11.5–75.7) | ||
| Ezrin | N, | 21 | 35 | |
| ng/mL | 322.5 | 341.7 | 0.8273 | |
| 25th–75th | (232.1–471.1) | (251.1–414.0) | ||
| YKL-40 | N, | 21 | 34 | |
| ng/mL | 60,240 | 59,151 | 0.6002 | |
| 25th–75th | (44,494–171,396) | (41,590–86,112) | ||
| ST2 | N, | 21 | 35 | |
| ng/mL | 1009.0 | 1570.0 | 0.1502 | |
| 25th–75th | (486.2–2229.0) | (820.8–3207.0) | ||
| IL-5 | N, | 20 | 35 | |
| ng/mL | 252.1 | 155.5 | 0.221 | |
| 25th–75th | (72.3–718.2) | (58.1–240.7) | ||
| IL-9 | N, | 14 | 28 | |
| ng/mL | 12.8 | 3.4 | 0.0299 | |
| 25th–75th | (2.2–19.3) | (1.9–7.1) | ||
| IL-18 | N, | 21 | 32 | |
| ng/mL | 69.3 | 56.9 | 0.3049 | |
| 25th–75th | (40.9–102.9) | (34.0–99.4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bantulà, M.; Tubita, V.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Mullol, J.; Valero, A.; Bobolea, I.; Pascal, M.; de Hollanda, A.; Vidal, J.; Picado, C.; et al. Differences in Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Obesity-Associated Asthma: Effects of Weight Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133782
Bantulà M, Tubita V, Roca-Ferrer J, Mullol J, Valero A, Bobolea I, Pascal M, de Hollanda A, Vidal J, Picado C, et al. Differences in Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Obesity-Associated Asthma: Effects of Weight Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(13):3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133782
Chicago/Turabian StyleBantulà, Marina, Valeria Tubita, Jordi Roca-Ferrer, Joaquim Mullol, Antonio Valero, Irina Bobolea, Mariona Pascal, Ana de Hollanda, Josep Vidal, César Picado, and et al. 2022. "Differences in Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Obesity-Associated Asthma: Effects of Weight Loss" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 13: 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133782
APA StyleBantulà, M., Tubita, V., Roca-Ferrer, J., Mullol, J., Valero, A., Bobolea, I., Pascal, M., de Hollanda, A., Vidal, J., Picado, C., & Arismendi, E. (2022). Differences in Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Obesity-Associated Asthma: Effects of Weight Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(13), 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133782








