Chronotype of Lung Fluid Levels in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participant Selection
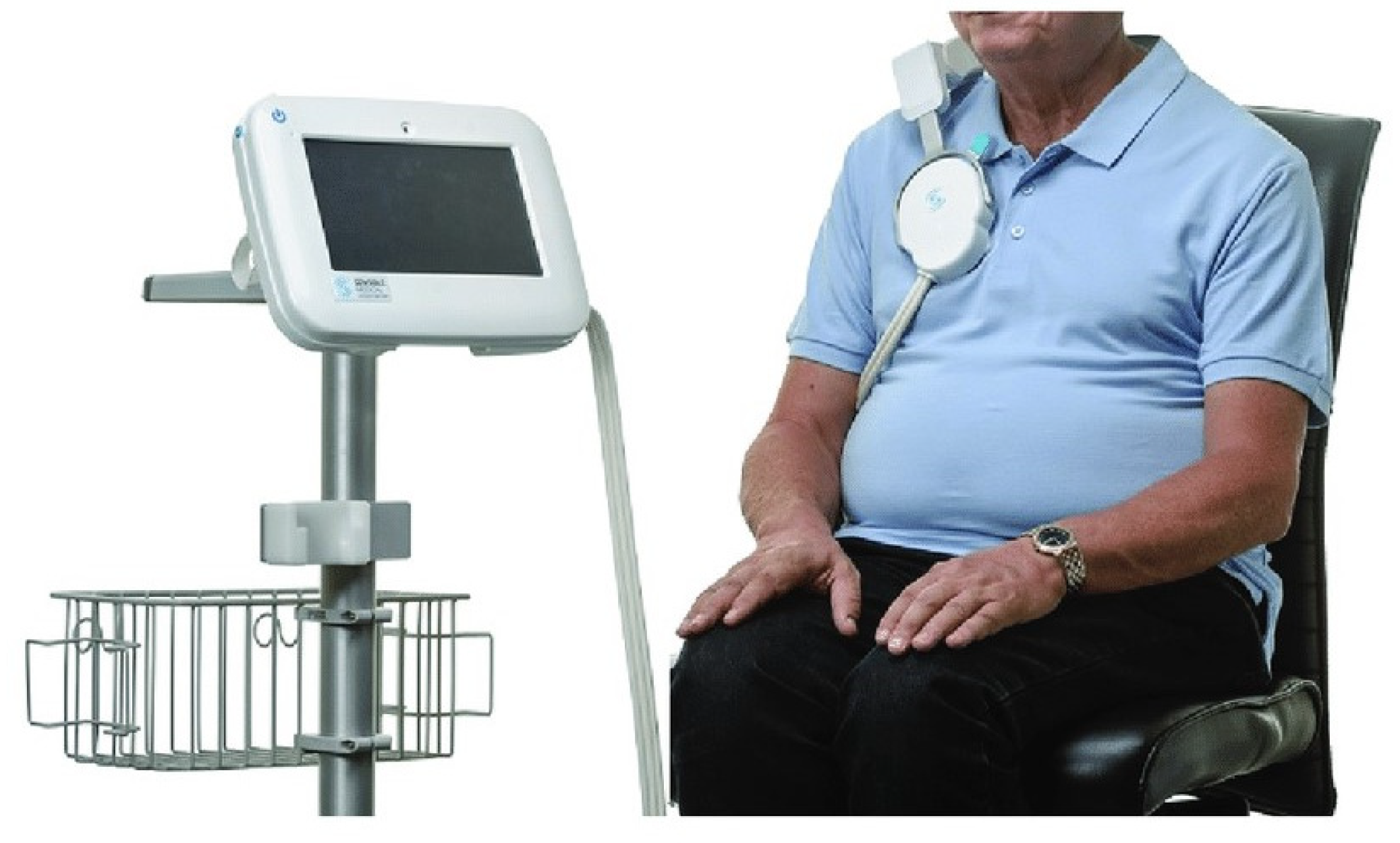
2.2. ReDS System
2.3. Statistical Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
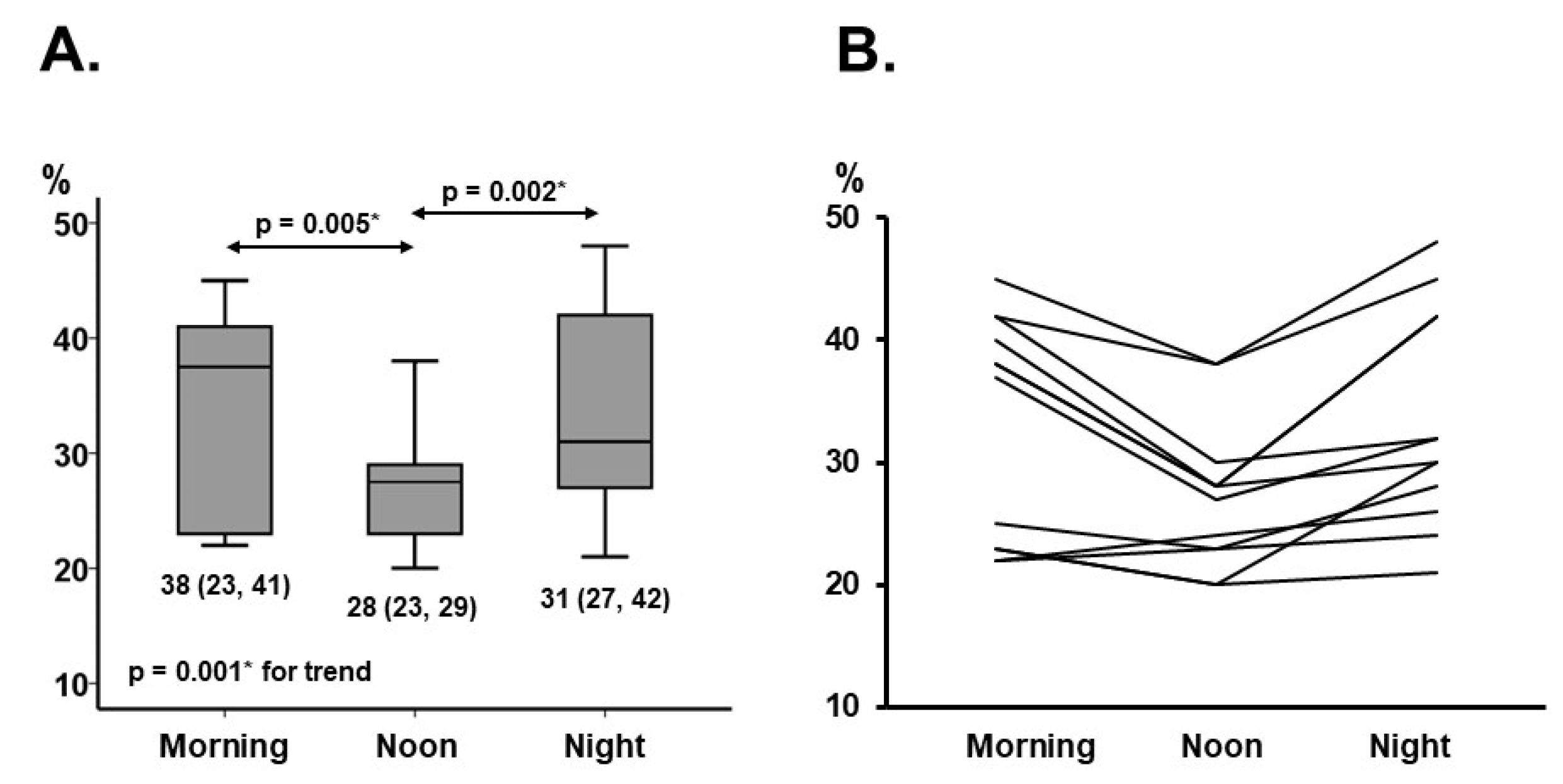
3.2. Chronotype of ReDS Values
4. Discussion
4.1. Chronotype of Cardiovascular Parameters
4.2. Other Factors Associated with Chronotype of Lung Fluid Levels
4.3. Study Limitations
4.4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crnko, S.; Du Pré, B.C.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Van Laake, L.W. Circadian rhythms and the molecular clock in cardiovascular biology and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, M.; Shirakabe, A.; Hata, N.; Shinada, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Tomita, K.; Tsurumi, M.; Shimura, T.; Okazaki, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Association between the admission time and the clinical findings in patients with acute heart failure. J. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uriel, N.; Sayer, G.; Imamura, T.; Rodgers, D.; Kim, G.; Raikhelkar, J.; Sarswat, N.; Kalantari, S.; Chung, B.; Nguyen, A.; et al. Relationship Between Noninvasive Assessment of Lung Fluid Volume and Invasively Measured Cardiac Hemodynamics. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amir, O.; Rappaport, D.; Zafrir, B.; Abraham, W.T. A Novel Approach to Monitoring Pulmonary Congestion in Heart Failure: Initial Animal and Clinical Experiences Using Remote Dielectric Sensing Technology. Congest. Heart Fail. 2013, 19, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, Y.; Zghouzi, M.; Suleiman, A.-R.M.; Sheikh, A.; Kupferman, J.; Sarfraz, A.; Arshad, J.; Mir, T.; Ullah, W.; Pacha, H.M.; et al. Efficacy of remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) in the prevention of heart failure rehospitalizations: A meta-analysis. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2021, 11, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, A.; Barghash, M.H.; Giustino, G.; Alvarez-Garcia, J.; Konje, S.; Parikh, A.; Ullman, J.; Keith, B.; Donehey, J.; Mitter, S.S.; et al. Early use of remote dielectric sensing after hospitalization to reduce heart failure readmissions. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T.; Gonoi, W.; Hori, M.; Ueno, Y.; Narang, N.; Onoda, H.; Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, M.; Kataoka, N.; Ushijima, R.; et al. Validation of Noninvasive Remote Dielectric Sensing System to Quantify Lung Fluid Levels. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T.; Hori, M.; Ueno, Y.; Narang, N.; Onoda, H.; Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, M.; Kataoka, N.; Sobajima, M.; Fukuda, N.; et al. Association between Lung Fluid Levels Estimated by Remote Dielectric Sensing Values and Invasive Hemodynamic Measurements. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portaluppi, F.; Montanari, L.; Ferlini, M.; Vergnani, L.; D’Ambrosi, A.; Cavallini, A.R.; Bagni, B.; degli Uberti, E. Consistent changes in the circadian rhythms of blood pressure and atrial natriuretic peptide in congestive heart failure. Chronobiol. Int. 1991, 8, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, R.; Gallerani, M.; Portaluppi, F.; Fersini, C. Relationships of the Circadian Rhythms of Thrombotic, Ischemic, Hemorrhagic, and Arrhythmic Events to Blood Pressure Rhythms. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 783, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Huang, C.; Cheng, H.; Yu, W.; Chiang, C.; Sung, S.; Chen, C. Nocturnal thoracic volume overload and post-discharge outcomes in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 2807–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T.; Hori, M.; Koi, T.; Fukui, T.; Oshima, A.; Fujioka, H.; Ueno, Y.; Onoda, H.; Tanaka, S.; Fukuda, N.; et al. Relationship Between Body Posture and Lung Fluid Volume Assessed Using a Novel Noninvasive Remote Dielectric Sensing System. Circ. Rep. 2022, 4, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N = 12 | |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Age, years | 84 (75, 90) |
| Men | 4 (33%) |
| Body mass index | 21.7 (20.2, 22.9) |
| Comorbidity | |
| Hypertension | 10 (83%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (42%) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3 (25%) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 0 (0%) |
| Ischemic heart disease | 6 (50%) |
| History of stroke | 2 (17%) |
| Peripheral artery disease | 0 (0%) |
| History of previous heart failure admission | 6 (50%) |
| Laboratory data | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.7 (10.4, 13.2) |
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 3.6 (3.2, 3.9) |
| Serum sodium, mEq/L | 139 (137, 141) |
| Serum potassium, mEq/L | 4.3 (3.8, 4.6) |
| Serum total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.5 (0.5, 0.7) |
| Estimated glomerular filtration ratio, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 47 (39, 62) |
| Serum C-reactive protein, mg/dL | 0.3 (0.1, 0.9) |
| Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide, pg/mL | 235 (178, 450) |
| Echocardiography | |
| Left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, mm | 51 (44, 53) |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % | 59 (56, 62) |
| Mild or greater mitral regurgitation | 3 (25%) |
| Mild or greater tricuspid regurgitation | 2 (17%) |
| E/A ratio | 0.74 (0.56, 1.15) |
| Inferior vena cava diameter expiratory/inspiratory, mm | 11 (8, 15)/6 (4, 7) |
| E/e’ ratio | 12.4 (10.1, 14.3) |
| Medication | |
| Beta-blocker | 9 (75%) |
| Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor | 7 (58%) |
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist | 4 (33%) |
| SGLT2 inhibitor | 4 (33%) |
| Diuretics | 6 (50%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueno, Y.; Imamura, T.; Narang, N.; Kinugawa, K. Chronotype of Lung Fluid Levels in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102714
Ueno Y, Imamura T, Narang N, Kinugawa K. Chronotype of Lung Fluid Levels in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(10):2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102714
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeno, Yohei, Teruhiko Imamura, Nikhil Narang, and Koichiro Kinugawa. 2022. "Chronotype of Lung Fluid Levels in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 10: 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102714
APA StyleUeno, Y., Imamura, T., Narang, N., & Kinugawa, K. (2022). Chronotype of Lung Fluid Levels in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(10), 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102714







