Short-Term Outcomes of Switching to Ranibizumab in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Resistant to Aflibercept Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
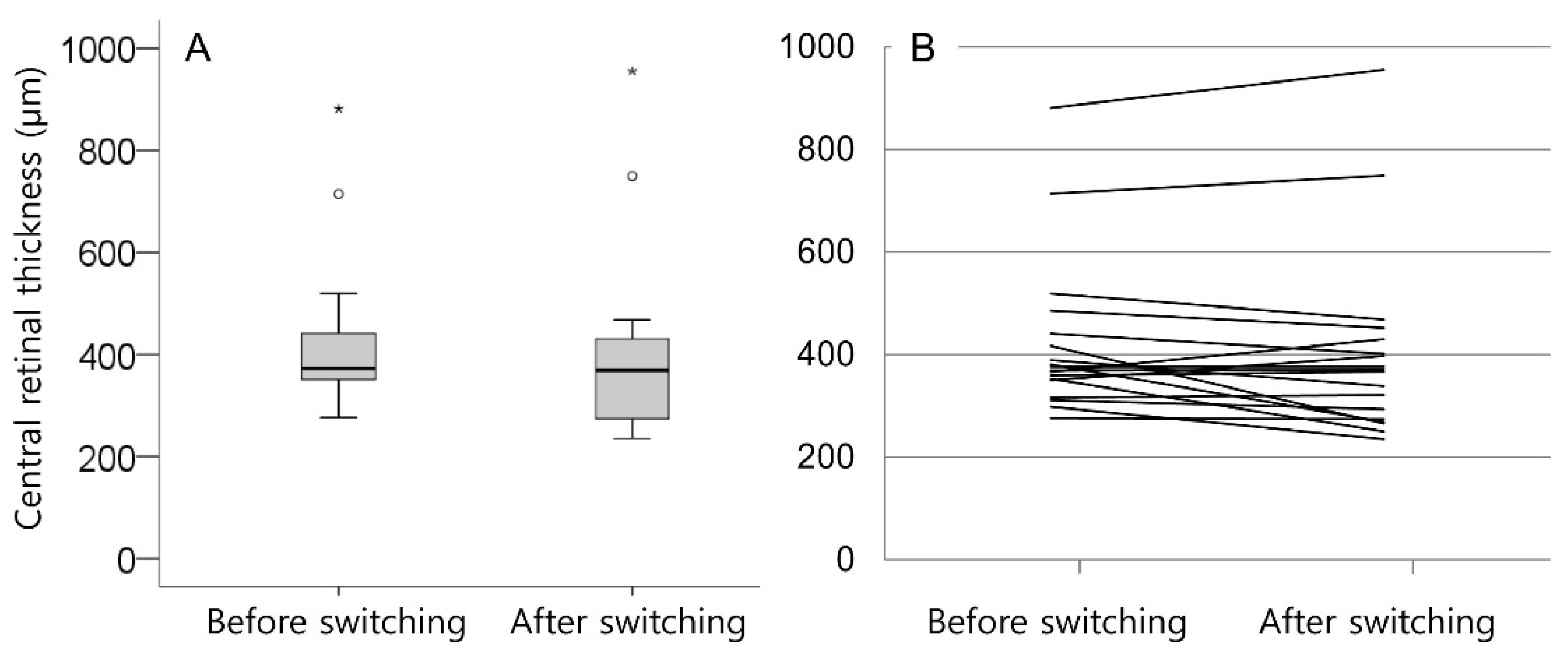
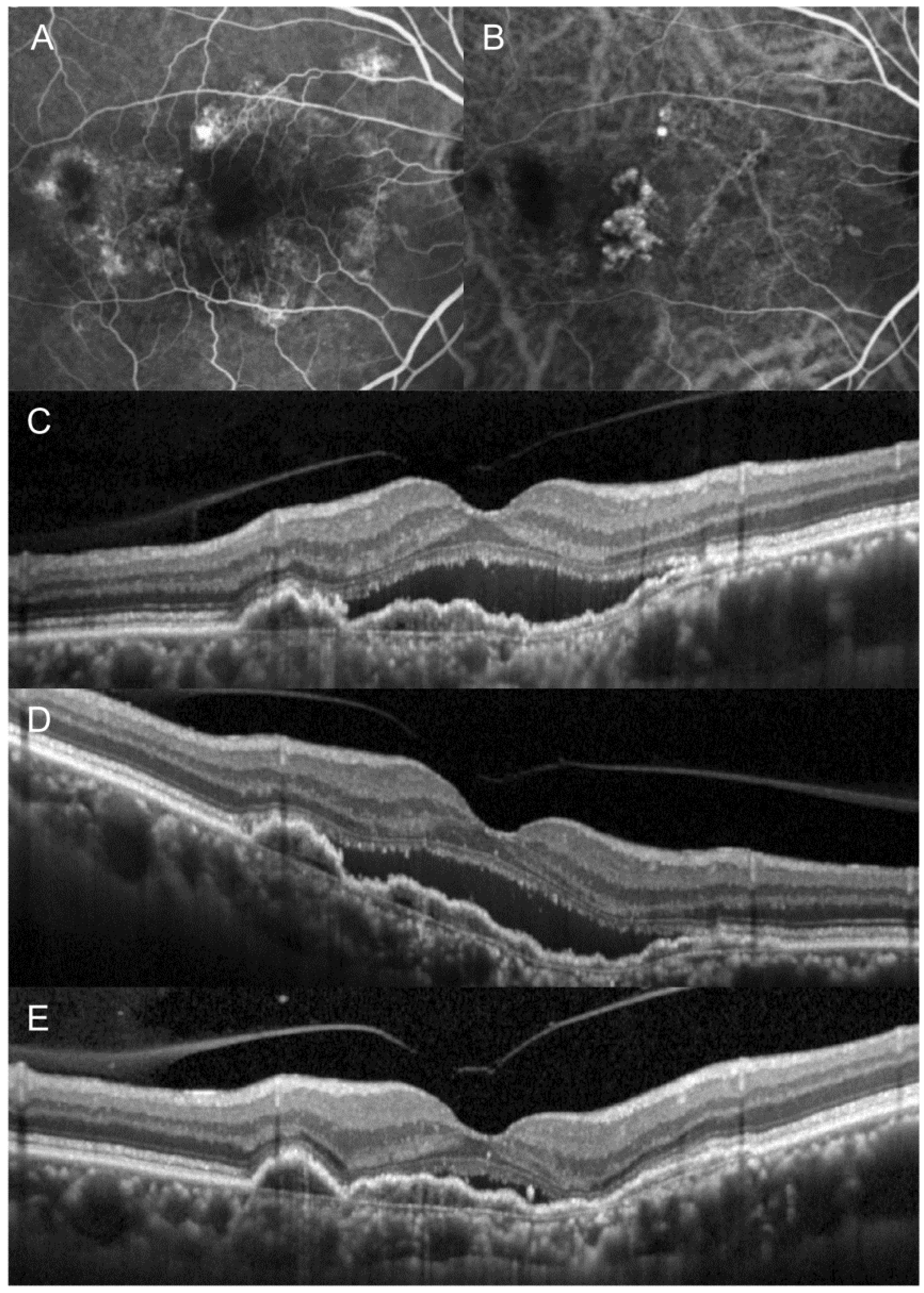
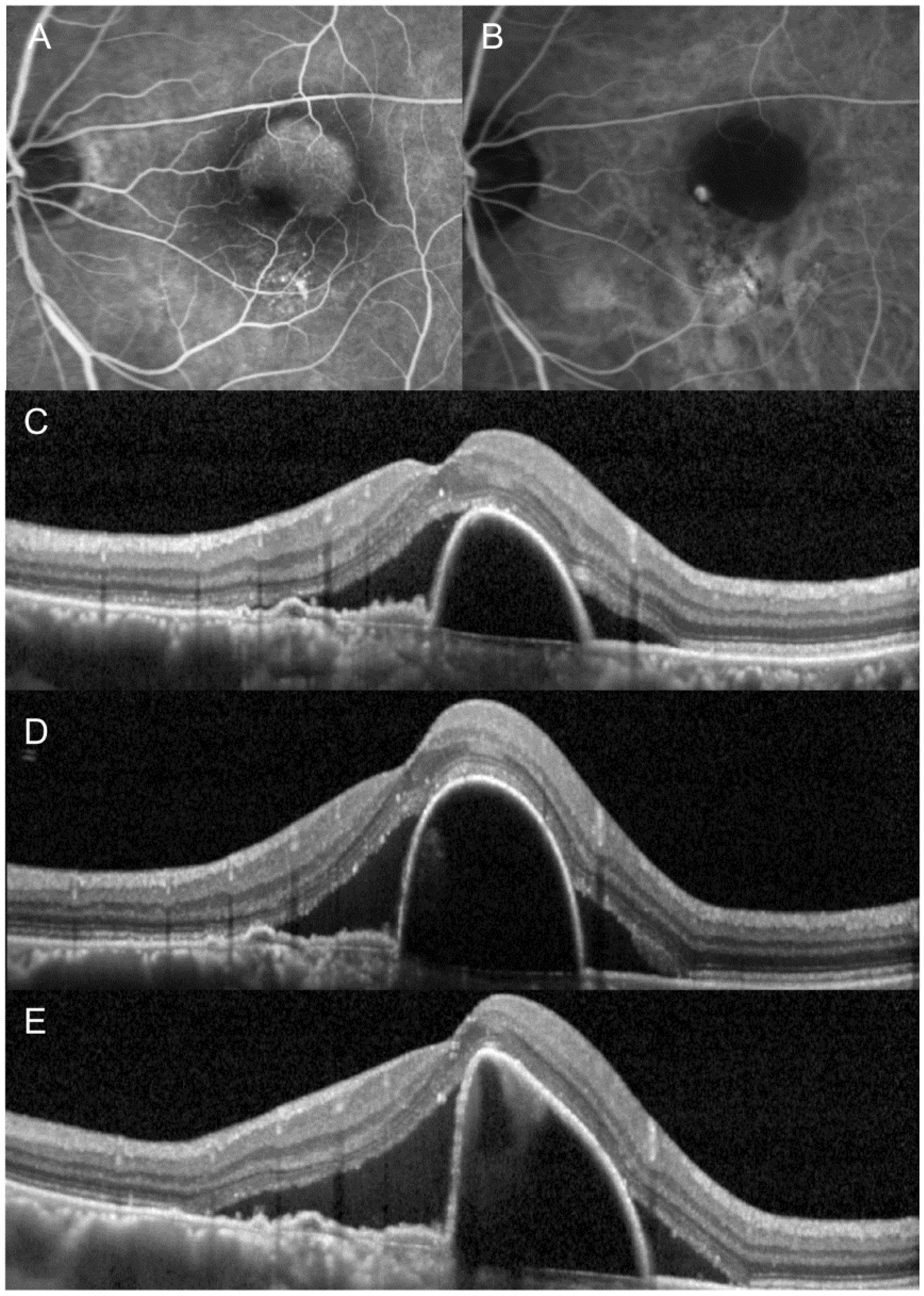
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spaide, R.F.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Slakter, J.S.; Sorenson, J.; Orlach, D.A. Indocyanine Green Videoangiography of Idiopathic Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. Retina 1995, 15, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.M.G.; Lai, T.Y.Y.; Ruamviboonsuk, P.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, Y.; Freund, K.B.; Gomi, F.; Koh, A.H.; Lee, W.-K.; Wong, T.Y. Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy: Definition, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, C.G. Investigation of the Trend of Selecting Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Agents for the Initial Treatment of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, D.J.; Kaiser, P.K.; Rosenfeld, P.J.; Stewart, M.W. Aflibercept for age-related macular degeneration: A game-changer or quiet addition? Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauser, S.; Muether, P.S. Clinical correlation to differences in ranibizumab and aflibercept vascular endothelial growth factor suppression times. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Okada, A.A.; Kano, M.; Koizumi, H.; Saito, M.; Maruko, I.; Sekiryu, T.; Iida, T. One-Year Results of Intravitreal Aflibercept for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, H.S.; Han, J.I.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, J.W. Intravitreal Aflibercept and Ranibizumab Injections for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 165, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Barbazetto, I.A.; Freund, K.B. Refractory Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration Secondary to Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 148, 70–78.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Kano, M.; Itagaki, K.; Oguchi, Y.; Sekiryu, T. Switching to Intravitreal Aflibercept Injection for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Refractory to Ranibizumab. Retina 2014, 34, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, C.; Wakabayashi, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Sayanagi, K.; Kawasaki, R.; Sato, S.; Sakaguchi, H.; Nishida, K. Tachyphylaxis during treatment of exudative age-related macular degeneration with aflibercept. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 2559–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorentzen, T.D.; Subhi, Y.; Sørensen, T.L. Prevalence of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy in White Patients with Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Retina 2018, 38, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhablani, J.; Shaikh, A.; Goud, A.; Kawasaki, R.; Kwon, O.W.; Chang, A.; Lam, D.; Das, T. Asia-Pacific Technology and Trend Survey 2016–2017. Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong Teo, K.Y.; Squirrell, D.M.; Nguyen, V.; Banerjee, G.; Cohn, A.; Barthelmes, D.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Gillies, M. A Multicountry Comparison of Real-World Management and Outcomes of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy: Fight Retinal Blindness! Cohort. Ophthalmol. Retina 2019, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.H.; Expert PCV Panel; Chen, L.J.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, Y.; Giridhar, A.; Iida, T.; Kim, H.; Lai, T.Y.Y.; Lee, W.K.; et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: Evidence-based guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment. Retina 2013, 33, 686–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, K.; Kaneko, H.; Kataoka, K.; Hattori, K.; Ra, E.; Tsunekawa, T.; Fukukita, H.; Haga, F.; Ito, Y.; Terasaki, H. Comparison between 1-year outcomes of aflibercept with and without photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: Retrospective observation study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Ogura, Y.; Lee, W.K.; Iida, T.; Chen, S.-J.; Mitchell, P.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Zhang, Z.; Leal, S.; Ishibashi, T. Efficacy and Safety of Intravitreal Aflibercept for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy: Two-Year Results of the Aflibercept in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 204, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, U.C.; Kim, B.H.; Choe, H.R.; Yeon, D.Y.; Yu, H.G. Long-term results of rescue photodynamic therapy for type 1 neovascularization refractory to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 99, e899–e907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.M.; Chen, E.; Mariani, A.; Major, J.C., Jr.; SAVE Study Group. Super-dose anti-VEGF (SAVE) trial: 2.0 mg intravitreal ranibizumab for recalcitrant neovascular macular degeneration-primary end point. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugel, P.U.; Singh, R.P.; Koh, A.; Ogura, Y.; Weissgerber, G.; Gedif, K.; Jaffe, G.J.; Tadayoni, R.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Holz, F.G. HAWK and HARRIER: Ninety-Six-Week Outcomes from the Phase 3 Trials of Brolucizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, N.; Parachuri, N.; Sadda, S.R.; Corradetti, G.; Heier, J.; Chin, A.T.; Boyer, D.; Dayani, P.; Arepalli, S.; et al. Brolucizumab—early real-world experience: BREW study. Eye 2020, 35, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Hoshino, J.; Mukai, R.; Nakamura, K.; Akiyama, H. Short-term outcomes of intravitreal brolucizumab for treatment-naïve neovascular age-related macular degeneration with type 1 choroidal neovascularization including polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, D.W. Submacular hemorrhage and grape-like polyp clusters: Factors associated with reactivation of the lesion in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Eye 2017, 31, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Son, W.Y.; Kim, R.Y.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.G.; Park, Y.-H. Recurrence and visual prognostic factors of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: 5-year results. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Koh, H.J.; Lee, S.C. Baseline polyp size as a potential predictive factor for recurrence of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujikawa, A.; Sasahara, M.; Otani, A.; Gotoh, N.; Kameda, T.; Iwama, D.; Yodoi, Y.; Tamura, H.; Mandai, M.; Yoshimura, N. Pigment epithelial detachment in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.W.; Eldeeb, M.; Lingam, G.; Thomas, D.; Bhargava, M.; Chee, C.K. Quantitative changes in pigment epithelial detachment area and volume predict retreatment in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 117, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, E.H.; Chen, J.J.; Lee, K.; Niemeijer, M.; Sonka, M.; Abramoff, M.D. Reproducibility of diabetic macular edema estimates from SD-OCT is affected by the choice of image analysis algorithm. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 4184–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Yamashiro, K.; Miyake, M.; Yoshikawa, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Oishi, A.; Tamura, H.; Ooto, S.; Tsujikawa, A.; Yoshimura, N. Factors associated with recurrence of age-related macular degeneration after anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment: A retrospective cohort study. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.8 ± 6.9 |
| Sex (male:female) | 13 (72.2%): 5 (27.8%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (27.8%) |
| Hypertension | 10 (55.6%) |
| Lens status (phakia:pseudophakia) | 13 (72.2%):5 (27.8%) |
| Duration between the diagnosis and the switching (months) | 11.7 ± 9.1 |
| No. of aflibercept injections before the switching | 5.7 ± 3.3 |
| Type of fluid when the switching was performed | |
| Subretinal fluid | 18 (100.0%) |
| Intraretinal fluid | 0 |
| Change in Best-Corrected Visual Acuity | No. of Eyes (%) |
|---|---|
| Improved ≥ 2 lines | 0 |
| Improved < 2 lines | 6 (33.3%) |
| Stationary | 8 (44.4%) |
| Deteriorated < 2 lines | 3 (11.1%) |
| Deteriorated ≥ 2 lines | 1 (5.6%) |
| Central retinal thickness | |
| Decreased ≥ 100 µm | 3 (16.7%) |
| Decreased < 100 µm, >50 µm | 3 (16.7%) |
| Stationary | 10 (55.6%) |
| Increased < 100 µm, >50 µm | 2 (11.1%) |
| Increased ≥ 100 µm | 0 |
| Characteristics | Responder Group (n = 6) | Non-Responder Group (n = 12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63.0 ± 7.6 | 67.2 ± 6.3 | 0.213 * |
| Sex | 1.000 † | ||
| Male | 4 (66.7%) | 9 (75.0%) | |
| Female | 2 (33.3%) | 3 (25.0%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2 (33.3%) | 3 (25.0%) | 1.000 † |
| Hypertension | 2 (33.3%) | 8 (66.7%) | 0.321 † |
| Lens status | 0.615 † | ||
| Phakia | 5 (83.3%) | 8 (66.7%) | |
| Pseudophakia | 1 (16.7%) | 4 (33.3%) | |
| Duration between the diagnosis and the switching (months) | 12.2 ± 10.4 | 11.5 ± 8.9 | 0.964 * |
| No. of aflibercept injections before the switching | 6.5 ± 4.7 | 5.3 ± 2.5 | 0.616 * |
| Best-corrected visual acuity (logMAR) | 0.39 ± 0.23 (20/49 ‡) | 0.41 ± 0.29 (20/51 ‡) | 0.964 * |
| Central retinal thickness (µm) | 392.5 ± 73.9 | 437.0 ± 180.8 | 0.820 * |
| No. of consecutive ranibizumab injections | 2.7 ± 5.2 | 2.8 ± 7.2 | 0.750 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, C.-G. Short-Term Outcomes of Switching to Ranibizumab in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Resistant to Aflibercept Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245739
Jeon Y-J, Kim J-H, Kim J-W, Kim C-G. Short-Term Outcomes of Switching to Ranibizumab in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Resistant to Aflibercept Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(24):5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245739
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Young-Joon, Jae-Hui Kim, Jong-Woo Kim, and Chul-Gu Kim. 2021. "Short-Term Outcomes of Switching to Ranibizumab in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Resistant to Aflibercept Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 24: 5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245739
APA StyleJeon, Y.-J., Kim, J.-H., Kim, J.-W., & Kim, C.-G. (2021). Short-Term Outcomes of Switching to Ranibizumab in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Resistant to Aflibercept Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(24), 5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245739






