The Correlation between Lower Extremity Fracture and Subsequent Arterial Embolism and Thrombosis—A National Population Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Survey of Confounding Factors of SAET
2.4. Statistical Analysis
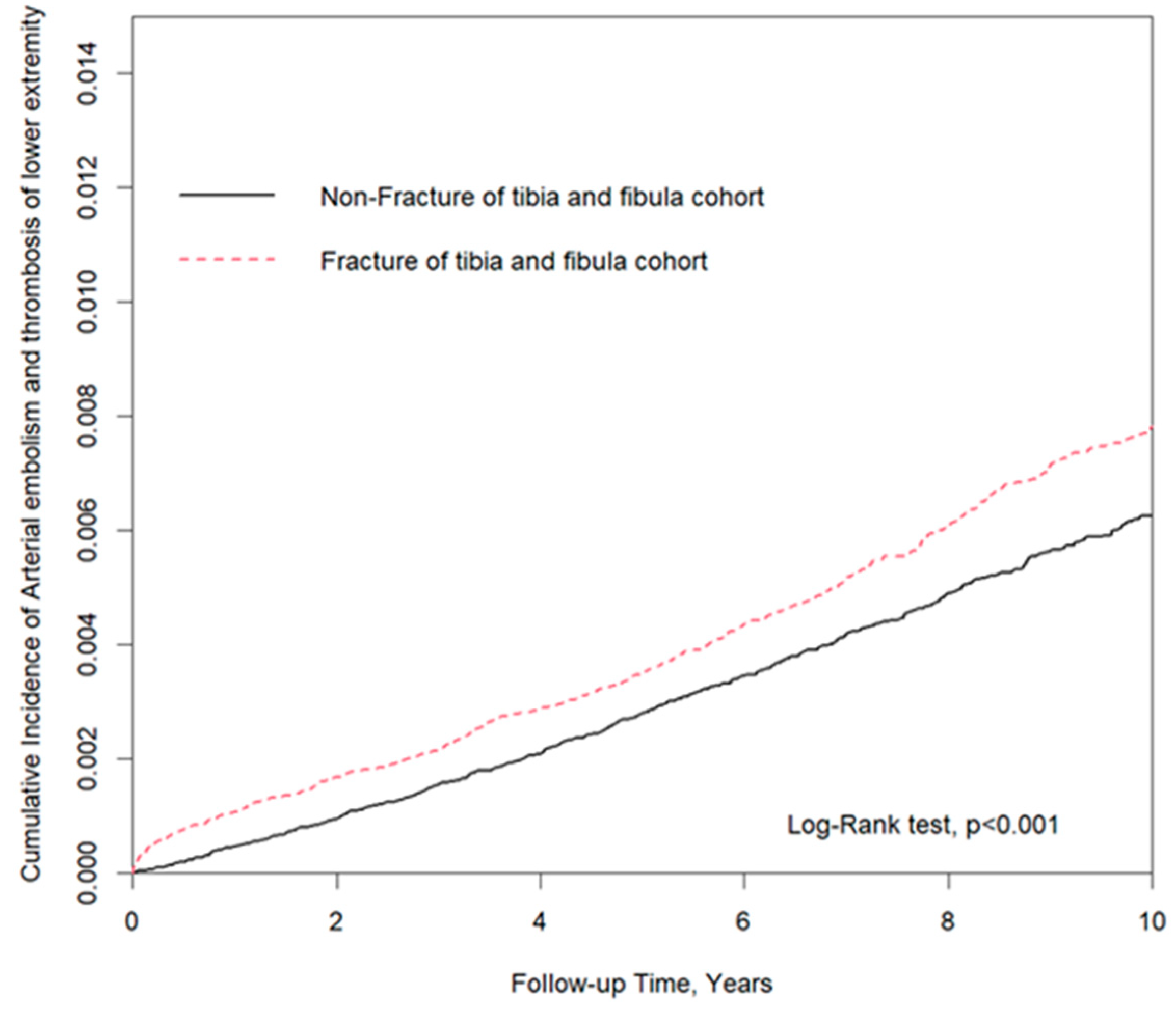
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evangelista, P.J.; Evangelista, L.M.; Evangelista, G.T.; Ruth, J.T.; Mills, J.L. Delayed complete limb ischemia following a closed tibial shaft fracture. Am. J. Orthop. 2013, 42, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Guled, U.; Gopinathan, N.R.; Goni, V.G.; Rhh, A.; John, R.; Behera, P. Proximal tibial and fibular physeal fracture causing popliteal artery injury and peroneal nerve injury: A case report and review of literature. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2015, 18, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-S.; Lin, K.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Tarng, Y.-W.; Chang, W.-N. Popliteal artery occlusion concomitant with a tibial plateau fracture and posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 48, 0300060519869073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcia, L.; Kim, D.Y. Predictors of Peripheral Vascular Injury in Patients with Blunt Lower Extremity Fractures. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.; Nosratinia, H.; Goldust, M.; Raghifar, R. Arterial Injuries in Extremities Trauma, Angiographic Findings. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinomiya, R.; Sunagawa, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakabayashi, A.; Makitsubo, M.; Adachi, N. Slow progressive popliteal artery insufficiency after neglected proximal tibial physeal fracture: A case report. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2018, 27, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss, C.; Koshty, A.; Niemann, B.; Boening, A.; Roth, P. Posttraumatic Arteriovenous Fistula of the Distal Posterior Tibial Artery as Cause of Delayed Wound Healing in an Unrecognized Arterial Injury. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. Rep. 2013, 3, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Salazar, J.; Tovar-López, J.; Hernández-Rodríguez, G.; De La Concha-Ureta, H. Post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery secondary to tibial shaft fracture. Case report. Acta Ortop. Mex. 2016, 30, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Toyota, T.; Horiuchi, H.; Takizawa, T.; Yamazaki, I.; Matsunaga, D.; Nakamura, Y.; Akizuki, S. A case of femoral pseudoaneurysm after surgery for intertrochanteric fracture. J. Orthop. Sci. 2017, 22, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walenga, J.M.; Kaiser, P.C.; Prechel, M.M.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Jeske, W.P.; Misselwitz, F.; Bacher, P.; Lassen, M.R.; Fareed, J. Sustained Release of Tissue Factor Following Thrombosis of Lower Limb Trauma. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2014, 20, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.J.; Zhang, C.L.; Zeng, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Li, Y. Analysis of the effects of different medicines on hypercoagulability state variations of femoral shaft fracture and after its operation. Zhong Yao Cai 2010, 33, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, W.; Tang, P. Dose-dependent roles of aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in abnormal bone remodeling and skeletal regeneration. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungprasert, P.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Peripheral arterial disease and risk of hip fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Postgrad. Med. 2018, 64, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, T.C.; Ewing, S.K.; Diem, S.J.; Taylor, B.; Orwoll, E.; Cummings, S.R.; Strotmeyer, E.; Ensrud, K. Peripheral Arterial Disease Is Associated with Higher Rates of Hip Bone Loss and Increased Fracture Risk in Older Men. Circulation 2009, 119, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firnhaber, J.M.; Powell, C.S. Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Phys. 2019, 99, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fowkes, F.G.R.; Rudan, D.; Rudan, I.; Aboyans, V.; Denenberg, J.O.; McDermott, M.M.; Norman, P.E.; Sampson, U.K.; Williams, L.J.; Mensah, G.A.; et al. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: A systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, T.; Richette, P. Impact of comorbidities on gout and hyperuricaemia: An update on prevalence and treatment options. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Chuang, Y.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, J.S.; Liang, K.Y. Incorporating development stratification of Taiwan townships into sampling design of large scale health interview survey. J. Health Manag. 2006, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- O’Malley, O.; Trompeter, A.J.; Krishnanandan, S.; Vesely, M.; Holt, P.; Goh, G.; Papadakos, N.; Bhatia, V.; Hing, C.B. How common are vascular injuries in open tibial fractures? A prospective longitudinal cohort study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2019, 29, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Sayed, H.; Berger, D.L. Blunt lower-extremity trauma and popliteal artery injuries: Revisiting the case for selective arteriography. Arch. Surg. 2002, 137, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngunde, P.J.; Akongnwi, A.C.N.; Mefire, C.A.; Puis, F.; Gounou, E.; Nkfusai, N.C.; Nwarie, U.G.; Cumber, S.N. Prevalence and pattern of lower extremity injuries due to road traffic crashes in Fako Division, Cameroon. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 32, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, F.; Lv, H.; Ji, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Epidemiology of low-energy lower extremity fracture in Chinese populations aged 50 years and above. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschitsch, E.P.; Durchschlag, E.; Dimai, H.P. Age-related prevalence of osteoporosis and fragility fractures: Real-world data from an Austrian Menopause and Osteoporosis Clinic. Climacteric 2017, 20, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewallen, L.; Theissen, A.; Sucato, D.J. Partial Tibial Nonunion due to Entrapment of Anterior Tibial Artery: A Case Report. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2019, 9, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyan, J.P.; Kordzadeh, A.; Hanif, M.A.; Griffiths, M.; Lyall, H.; Prionidis, I. Nonunion of the tibial facture as a consequence of posterior tibial artery pseudoaneurysm. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2015, 2015, rjv138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dickson, K.; Katzman, S.; Delgado, E.; Contreras, D. Delayed unions and nonunions of open tibial fractures. Correlation with arteriography results. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 302, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, H. Local thrombolysis in peripheral arterial occlusion. Herz 1989, 14, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Murrant, C.L. Structural and functional limitations of the collateral circulation in peripheral artery disease. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total | Fracture of Tibia and Fibula | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No n = 134,844 | Yes n = 134,844 | |||
| Gender | 0.98 | |||
| Female | 111,724 | 55,859 (41.4) | 55,865 (41.4) | |
| Male | 157,964 | 78,985 (58.6) | 78,979 (58.6) | |
| Age | >0.99 | |||
| <40 | 93,997 | 46,995 (34.9) | 47,002 (34.9) | |
| 40-64 | 124,507 | 62,251 (46.2) | 62,256 (46.2) | |
| ≥65 | 51,184 | 25,598 (19) | 25,586 (19) | |
| Mean (SD) a | 48.2 (17.1) | 48.2 (17.1) | >0.99 | |
| Baseline Comorbidity | ||||
| Hypertension | 23,526 | 11,765 (8.7) | 11,761 (8.7) | 0.98 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 17,180 | 8583 (6.4) | 8597 (6.4) | 0.91 |
| Gout | 4733 | 2362 (1.8) | 2371 (1.8) | 0.90 |
| Characteristics | Event | Crude | Adjusted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 1360) | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Fracture of Tibia and Fibula | |||||
| No | 593 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 767 | 1.32 (1.19–1.47) | <0.001 | 1.39 (1.24–1.54) | <0.001 |
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 559 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Male | 801 | 1.00 (0.90–1.11) | 1.000 | 1.53 (1.37–1.71) | <0.001 |
| Age at Baseline | |||||
| <45 | 77 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 45–64 | 516 | 5.48 (4.31–6.96) | <0.001 | 3.97 (3.11–5.06) | <0.001 |
| ≥65 | 767 | 25.49 (20.16–32.23) | <0.001 | 10.96 (8.53–14.07) | <0.001 |
| Baseline Comorbidity | |||||
| Hypertension | 480 | 8.67 (7.75–9.71) | <0.001 | 1.78 (1.55–2.03) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 522 | 13.87 (12.42–15.49) | <0.001 | 5.57 (4.90–6.32) | <0.001 |
| Gout | 78 | 4.64 (3.69–5.83) | <0.001 | 1.43 (1.13–1.81) | 0.003 |
| Variables | Matched Cohort | Fracture of Tibia and Fibula | HR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 134,844 | n = 134,844 | Crude | p-Value | Adjusted | p-Value | |||||
| Event | Person Years | IR | Event | Person Years | IR | (95% CI) | (95% CI) | |||
| Overall | 593 | 964,777 | 6.15 | 767 | 945,131 | 8.12 | 1.32 (1.19–1.47) | <0.001 | 1.39 (1.24–1.54) | <0.001 |
| Gender | ||||||||||
| Female | 249 | 396,001 | 6.29 | 310 | 389,968 | 7.95 | 1.27 (1.07–1.50) | 0.006 | 1.37 (1.16–1.62) | 0.0002 |
| Male | 344 | 568,776 | 6.05 | 457 | 555,164 | 8.23 | 1.36 (1.19–1.57) | <0.001 | 1.40 (1.22–1.61) | <0.001 |
| Age at Baseline | ||||||||||
| <40 | 19 | 359,942 | 0.53 | 58 | 359,025 | 1.62 | 3.07 (1.83–5.15) | <0.001 | 3.08 (1.83–5.17) | <0.001 |
| 40–64 | 213 | 451,823 | 4.71 | 303 | 442,063 | 6.85 | 1.46 (1.23–1.74) | <0.001 | 1.51 (1.26–1.79) | <0.001 |
| ≥65 | 361 | 153,012 | 23.59 | 406 | 144,044 | 28.19 | 1.20 (1.04–1.38) | 0.011 | 1.22 (1.05–1.40) | 0.007 |
| Baseline Comorbidity | ||||||||||
| Hypertension | 226 | 61,834 | 36.55 | 254 | 58,386 | 43.50 | 1.19 (1.00–1.43) | 0.055 | 1.22 (1.02–1.46) | 0.031 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 245 | 45,501.9 | 53.84 | 277 | 42,334 | 65.43 | 1.23 (1.04–1.46) | 0.019 | 1.24 (1.05–1.48) | 0.013 |
| Gout | 31 | 13,022.4 | 23.81 | 47 | 12,515 | 37.55 | 1.59 (1.01–2.49) | 0.047 | 1.65 (1.05–2.60) | 0.030 |
| Variables | Matched Cohort | Fracture of Tibia and Fibula | HR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 134,844 | n = 134,844 | Crude | p-Value | Adjusted | p-Value | |||||
| Event | Person Years | IR | Event | Person Years | IR | (95% CI) | (95% CI) | |||
| Female | ||||||||||
| Follow-up Years | ||||||||||
| <2 | 53 | 107,846 | 4.91 | 92 | 106,826 | 8.61 | 1.75 (1.25–2.46) | 0.001 | 1.82 (1.30–2.55) | 0.001 |
| 2–5 | 86 | 129,404 | 6.65 | 106 | 184,431 | 5.75 | 0.86 (0.63–1.18) | 0.345 | 0.93 (0.68–1.28) | 0.664 |
| ≥5 | 110 | 158,751 | 6.93 | 145 | 155,450 | 9.33 | 1.35 (0.97–1.73) | 0.078 | 1.50 (0.92–1.93) | 0.101 |
| Male | ||||||||||
| Follow-up Years | ||||||||||
| <2 | 70 | 152,339 | 4.60 | 125 | 150,228 | 8.32 | 1.81 (1.35–2.42) | <0.001 | 1.84 (1.38–2.47) | <0.001 |
| 2–5 | 73 | 127,692 | 5.72 | 114 | 180,974 | 6.30 | 1.10 (0.84–1.43) | 0.495 | 1.12 (0.86–1.45) | 0.421 |
| ≥5 | 168 | 232,007 | 7.24 | 218 | 223,962 | 9.73 | 1.35 (0.98–1.65) | 0.094 | 1.50 (1.00–1.93) | 0.051 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-X.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lin, M.-C.; Shih, P.-K. The Correlation between Lower Extremity Fracture and Subsequent Arterial Embolism and Thrombosis—A National Population Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225312
Chen J-X, Hsu S-Y, Lin M-C, Shih P-K. The Correlation between Lower Extremity Fracture and Subsequent Arterial Embolism and Thrombosis—A National Population Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(22):5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225312
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jian-Xun, Shao-Yun Hsu, Mei-Chen Lin, and Pin-Keng Shih. 2021. "The Correlation between Lower Extremity Fracture and Subsequent Arterial Embolism and Thrombosis—A National Population Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 22: 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225312
APA StyleChen, J.-X., Hsu, S.-Y., Lin, M.-C., & Shih, P.-K. (2021). The Correlation between Lower Extremity Fracture and Subsequent Arterial Embolism and Thrombosis—A National Population Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(22), 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225312






