IL-17 Promotes Nitric Oxide Production in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Exhaled Breath Condensate Collection
2.4. Cytokine Assays
2.5. Pulmonary Function Tests
2.6. FeNO
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison between Th1, Th2 and Th17-Related Cytokines in Patients and Healthy Controls
3.2. Comparison between VEGF in Patients and Healthy Controls
3.3. Lung Function Tests and FeNO Levels in Patients and Controls
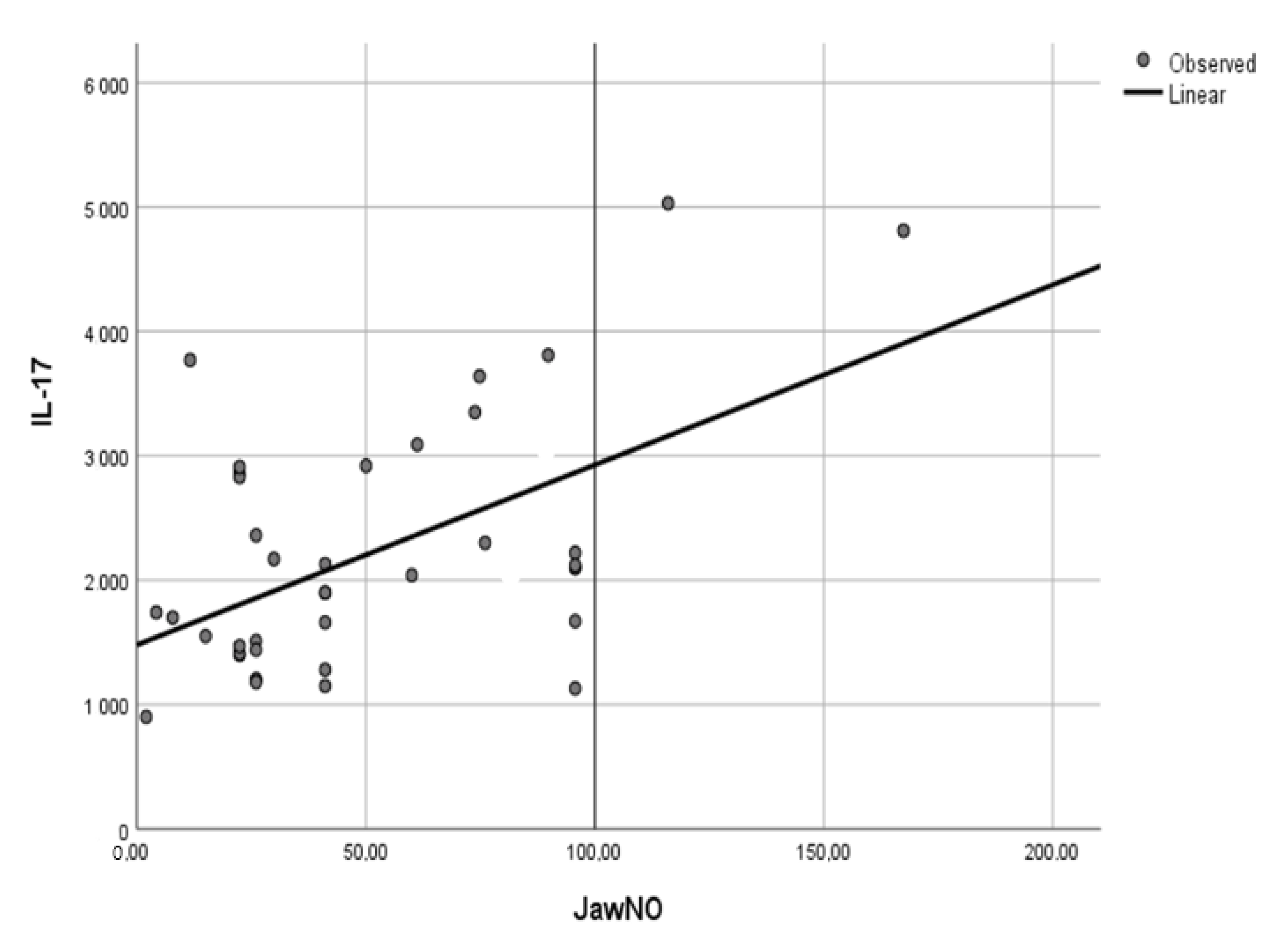
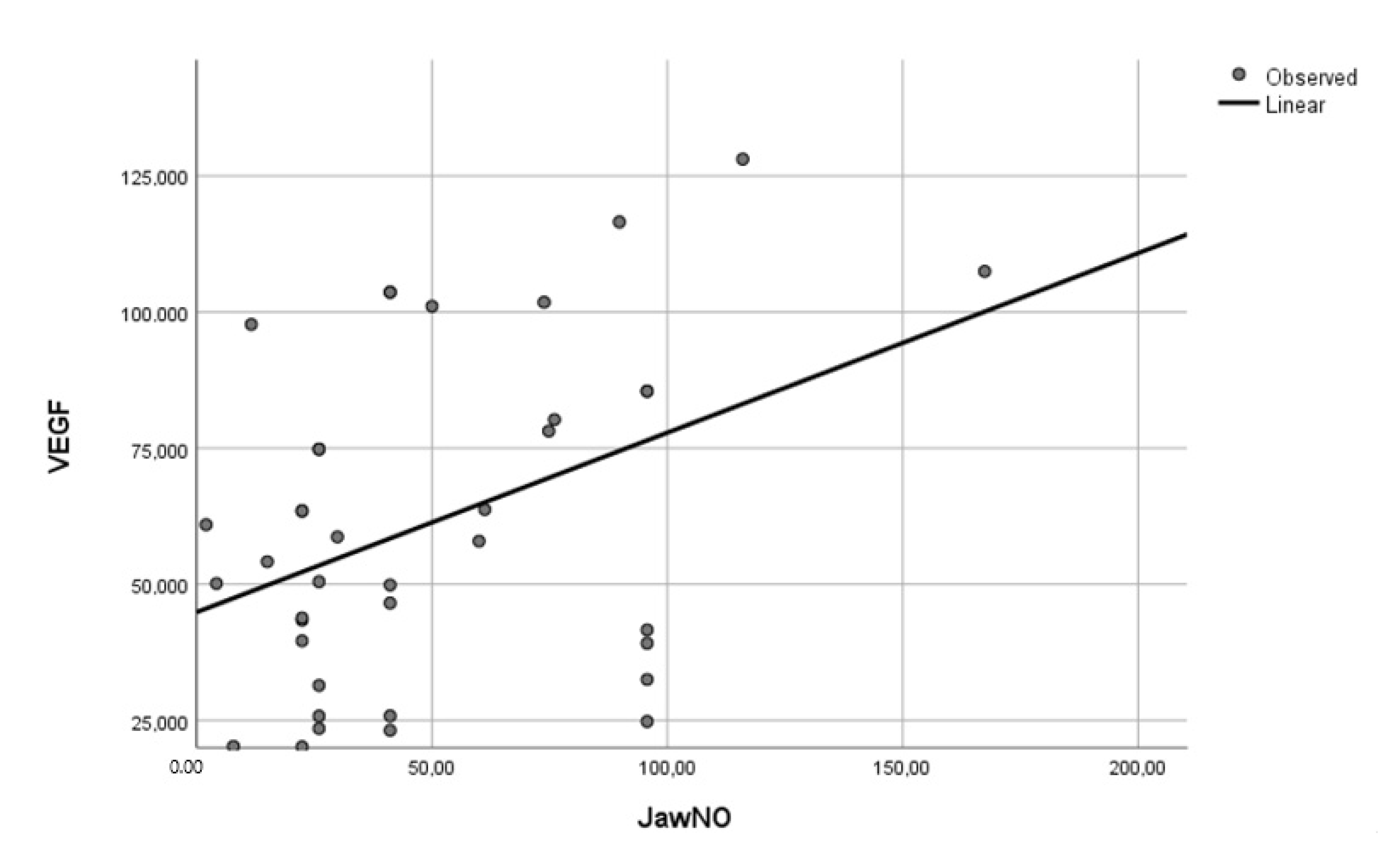
3.4. Correlations between Cytokines and FeNO in NSCLC Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Groot, P.M.; Wu, C.C.; Carter, B.W.; Munden, R.F. The epidemiology of lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walser, T.; Cui, X.; Yanagawa, J.; Lee, J.M.; Heinrich, E.; Lee, G.; Sharma, S.; Dubinett, S. The Role of Inflammation. Smoking and Lung Cancer. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. Genetic single-nucleotide polymorphisms of inflammation-related factors associated with risk of lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, P.; Wang, Y.; Vijayakrishnan, J.; Matakidou, A.; Spitz, M.R.; Eisen, T.; Amos, C.I.; Houlston, R.S. Deciphering the impact of common genetic variation on lung cancer risk: A genome-wide association study. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6633–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateu-Jimenez, M.; Curull, V.; Pijuan, L.; Sánchez-Font, A.; Rivera-Ramos, H.; Rodríguez-Fuster, A.; Aguiló, R.; Gea, J.; Barreiro, E. Systemic and Tumor Th1 and Th2 Inflammatory Profile and Macrophages in Lung Cancer: Influence of Underlying Chronic Respiratory Disease. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.C.; Zhong, X.N.; Liu, G.N.; Wei, J.R. The Treg/Th17 Paradigm in Lung Cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 730380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Che, D.; Cao, J.; Shen, J.; Jin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, F.; Gu, K.; Man, Y.; Shang, L.; et al. Interleukin-17 levels correlate with poor prognosis and vascular endothelial growth factor concentration in the serum of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Biomarkers 2015, 20, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, S.; Rolla, G.; Bucca, C.; Geronazzo, G.; Ridolfi, I.; Ferraris, A.; Fusaro, E.; Peroni, C.L.; Dughera, L.; Brussino, L. Gastric Juice Expression of Th-17 and T-Reg Related Cytokines in Scleroderma Esophageal Involvement. Cells 2020, 9, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolla, G.; Fusaro, E.; Nicola, S.; Bucca, C.; Peroni, C.; Parisi, S.; Cassinis, M.C.; Ferraris, A.; Angelino, F.; Heffler, E.; et al. Th-17 cytokines and interstitial lung involvement in systemic sclerosis. J. Breath Res. 2016, 10, 046013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, S.; Fornero, M.; Fusaro, E.; Peroni, C.; Priora, M.; Rolla, G.; Bucca, C.; Brussino, L. Th1- and Th17-Related Cytokines in Venous and Arterial Blood of Sclerodermic Patients with and without Digital Ulcers. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7908793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, S.; Rolla, G.; Monti, R.; Brussino, L. Treatment of psoriatic arthritis with secukinumab: A case series. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S1), 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Tan, Y.; Bajinka, O.; Wang, L.; Tang, Z. Th17/IL-17 Axis Regulated by Airway Microbes Get Involved in the Development of Asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitiello, G.A.; Miller, G. Targeting the interleukin-17 immune axis for cancer immunotherapy. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Hao, K.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X. Serum interleukin-17 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer. Biomarkers 2014, 19, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gao, F.H. Th17 Cells Paradoxical Roles in Melanoma and Potential Application in Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.J.P.; De Medeiros Fernandes, T.A.A.; De Araújo, J.M.G.; Cobucci, R.N.O.; Lanza, D.C.F.; Bezerra, F.L.; Andrade, V.S.; Fernandes, J.V. Th17 response in patients with cervical cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6215–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussino, L.; Culla, B.; Bucca, C.; Giobbe, R.; Boita, M.; Isaia, G.; Heffler, E.; Oliaro, A.; Filosso, P.; Rolla, G. Inflammatory cytokines and VEGF measured in exhaled breath condensate are correlated with tumor mass in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 027110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pan, B.; Shen, J.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shang, L.; Jin, S.; Cao, S.; Che, D.; Liu, F.; Yu, Y. Interleukin-17 promotes angiogenesis by stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells via the STAT3/GIV signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16053, reprinted in Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapila, V.; Sellke, F.W.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mesana, T.G.; Ruel, M. Nitric oxide and the angiogenic response: Can we improve the results of therapeutic angiogenesis? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 14, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Duan, L.; Qian, X.; Fan, J.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Wu, F.; Guo, M.; Hu, G.; et al. IL-17 Promotes Angiogenic Factors IL-6, IL-8, and Vegf Production via Stat1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36551, reprinted in Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Kang, H.; Fung, A.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, D. The role of interleukin 17 in tumour proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 623759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karetsi, E.; Ioannou, M.G.; Kerenidi, T.; Minas, M.; Molyvdas, P.A.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Paraskeva, E. Differential expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. Clinics 2012, 67, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demey, L.; Van Muylem, A.; Perez-Bogerd, S.; Haccuria, A.; Michils, A. Combined effects of type 2 inflammation and lung function on exhaled nitric oxide ability to reflect asthma control. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, PA2617. [Google Scholar]
- Donohue, J.F.; Jain, N. Exhaled nitric oxide to predict corticosteroid responsiveness and reduce asthma exacerbation rates. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, M.; Radovanovic, D.; Airoldi, A.; Cristiano, A.; Frassanito, F.; Gaboardi, P.; Saad, M.; Atzeni, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Santus, P. Rationale underlying the measurement of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S119), 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kubáň, P.; Foret, F. Exhaled breath condensate: Determination of non-volatile compounds and their potential for clinical diagnosis and monitoring. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 805, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J. Exhaled breath condensate—An overview. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2007, 27, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleil, J.D.; Hubbard, H.F.; Sobus, J.R.; Sawyer, K.; Madden, M.C. Volatile polar metabolites in exhaled breath condensate (EBC): Collection and analysis. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparri, R.; Sedda, G.; Spaggiari, L. Biomarkers in Early Diagnosis and Early Stage Lung Cancer: The Clinician’s Point of View. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Zhao, D.H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J.G.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, K.; Xie, L.X. The clinical value of exhaled nitric oxide in patients with lung cancer. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobin, L.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Wittekind, C. International Union against Cancer: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th ed.; West Sussex: Chichester, UK, 2009; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, I.; Hunt, J.; Barnes, P.J.; Alving, K.; Antczak, A.; Baraldi, E.; Becher, G.; van Beurden, W.J.; Corradi, M.; Dekhuijzen, R.; et al. ATS/ERS Task Force on Exhaled Breath Condensate. Exhaled breath condensate: Methodological recommendations and unresolved questions. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, P.J.; Ryder, R.R.; Todd, I.; Fairclough, L.C. ELISA in the multiplex era: Potentials and pitfalls. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, B. Bio-Rad’s Bio-Plex® suspension array system, xMAP technology overview. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 118, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastelijn, E.A.; Rijkers, G.T.; Van Moorsel, C.H.; Zanen, P.; Kwakkel-van Erp, J.M.; Van De Graaf, E.A.; Van Kessel, D.A.; Grutters, J.C.; Van Den Bosch, J.M. Systemic and exhaled cytokine and chemokine profiles are associated with the development of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2010, 29, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannot, G.; Tangrea, M.A.; Richardson, A.M.; Flaig, M.J.; Hewitt, S.M.; Marcus, E.M.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Chuaqui, R.F. Layered expression scanning: Multiplex molecular analysis of diverse life science platforms. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 376, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Standardized lung function testing: Report working party. Bull. Eur. Physiopathol. Respir. 1983, 19 (Suppl. S5), 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cotes, J.E.; Chinn, D.J.; Quanjer, H.; Roca, J.; Yernault, J.C. Standardization of the measurement of transfer factor (diffusing capacity). Eur. Respir. J. 1993, 6, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, H.C.; Yu, C.T.; Kuo, H.P. Increased level of exhaled nitric oxide and up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in patients with primary lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukias, N.M.; George, S.C. A two-compartment model of pulmonary nitric oxide exchange dynamics. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.S.; Freese, J. Regression Models for Categorical Dependent Variables Using Stata, 2nd ed.; Stata Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2006; pp. 223–292. [Google Scholar]
- Rabe-Hesketh, S.; Skrondal, A. Multilevel and Longitudinal Modeling Using Stata; Stata Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gour, N.; Wills-Karp, M. IL-4 and IL-13 signaling in allergic airway disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrogi, A.J.; Travis, W.D.; Welsh, J.A.; Khan, M.A.; Rahim, H.; Tazelaar, H.; Pairolero, P.; Trastek, V.; Jett, J.; Caporaso, N.E.; et al. Nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase 2, and vascular endothelial growth factor in the angiogenesis of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 4739–4744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, R.; Wakabayashi, I. HDGF enhances VEGF-dependent angiogenesis and FGF-2 is a VEGF-independent angiogenic factor in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.K.; Singhi, E.K.; Arroyo, J.P.; Ikizler, T.A.; Gould, E.R.; Brown, J.; Beckman, J.A.; Harrison, D.G.; Moslehi, J. Mechanisms of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) Inhibitor–Associated Hypertension and Vascular Disease. Hypertension 2018, 71, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapetropoulos, A.; García-Cardeña, G.; Madri, J.A.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide production contributes to the angiogenic properties of vascular endothelial growth factor in human endothelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 3131–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler-Jones, C.; Abu-Ghazaleh, R.; Cospedal, R.; Houliston, R.A.; Martin, J.; Zachary, I. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates prostacyclin production and activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in endothelial cells via p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1997, 420, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högman, M.; Drca, N.; Ehrstedt, C.; Meriläinen, P. Exhaled nitric oxide partitioned into alveolar, lower airways and nasal contributions. Respir. Med. 2000, 94, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann-Klee, P.G.; Lehtimäki, L.; Lindholm, T.; Malmberg, L.P.; Sovijärvi, A.R.A.; Piirilä, P.L. Converting FENO by different flows to standard flow FENO. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2019, 39, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NSCLC Patients | Controls | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yrs (range) | 63.8 (range 39–82) | 60.1 (range 41–79) | n.s. |
| Females, N (%) | 3 (20%) | 9 (30%) | n.s. |
| Lung cancer stages | |||
| IA, N (%) | 8 (53.33%) | N/A | |
| IB, N (%) | 4 (26.66%) | N/A | |
| IIA, N (%) | 3 (20%) | N/A |
| Patients | Healthy Controls | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Th1-related cytokines (pg/mL) | |||
| IL-1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.045 |
| IL-6 | 0.29 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | <0.001 |
| IL-12 | 0.70 ± 0.35 | 0.12 ± 0.10 | <0.001 |
| INF-g | 1.49 ± 0.80 | 1.64 ± 0.62 | n.s. |
| TNF-a | 0.75 ± 0.29 | 0.76 ± 0.13 | n.s. |
| Th17-related cytokines (pg/mL) | |||
| IL-17 | 2.85 ± 1.22 | 1.83 ± 0.57 | <0.001 |
| IL-23 | 1.15 ± 2.92 | 0.31 ± 0.67 | <0.001 |
| Th2-related cytokines (pg/mL) | |||
| IL-4 | 0.16 ± 0.15 | 0.16 ± 0.09 | n.s. |
| IL-5 | 0.19 ± 0.22 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | n.s. |
| IL-13 | 0.34 ± 0.55 | 0.12 ± 0.06 | n.s. |
| VEGF (pg/mL) | 78.45 ± 29.45 | 49.26 ± 26.55 | 0.002 |
| Patients | Controls | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| FEV1, % predicted ± SD | 95.24 ± 13.6 | 90.37 ± 6.9 | n.s. |
| FVC, % predicted ± SD | 106.97 ± 15.5 | 107.65 ± 7.1 | n.s. |
| FEV1/FVC, % ± SD | 75.46 ± 2.5 | 84.13 ± 6.7 | n.s. |
| FENO 50 mL/s, mean ± SD (ppb) | 22.42 ± 16.87 | 13.20 ± 2.74 | 0.001 |
| FENO 150 mL/s, mean ± SD (ppb) | 14.07 ± 7.95 | 13.03 ± 1.97 | n.s. |
| JawNO, mean ± SD | 55.96 ± 26.71 | 36.30 ± 21.39 | 0.038 |
| CalvNO, mean ± SD | 24.28 ± 13.05 | 8.42 ± 3.80 | 0.001 |
| IL-6 | IL-17 | IL-1 | VEGF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeNO 50 mL/s | r = 0.467, p = 0.049 | r = 0.841, p = 0.036 | r = 0.754, p = 0.044 | |
| JawNO | r = 0.502, p = 0.042 | r = 0.796, p < 0.001 | r = 0.761, p = 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicola, S.; Ridolfi, I.; Rolla, G.; Filosso, P.; Giobbe, R.; Boita, M.; Culla, B.; Bucca, C.; Solidoro, P.; Brussino, L. IL-17 Promotes Nitric Oxide Production in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194572
Nicola S, Ridolfi I, Rolla G, Filosso P, Giobbe R, Boita M, Culla B, Bucca C, Solidoro P, Brussino L. IL-17 Promotes Nitric Oxide Production in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194572
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicola, Stefania, Irene Ridolfi, Giovanni Rolla, Pierluigi Filosso, Roberto Giobbe, Monica Boita, Beatrice Culla, Caterina Bucca, Paolo Solidoro, and Luisa Brussino. 2021. "IL-17 Promotes Nitric Oxide Production in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194572
APA StyleNicola, S., Ridolfi, I., Rolla, G., Filosso, P., Giobbe, R., Boita, M., Culla, B., Bucca, C., Solidoro, P., & Brussino, L. (2021). IL-17 Promotes Nitric Oxide Production in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194572






