Changes in Tongue Area, Pharyngeal Area, and Pharyngeal Airway Velocity after Correction of Mandibular Prognathism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
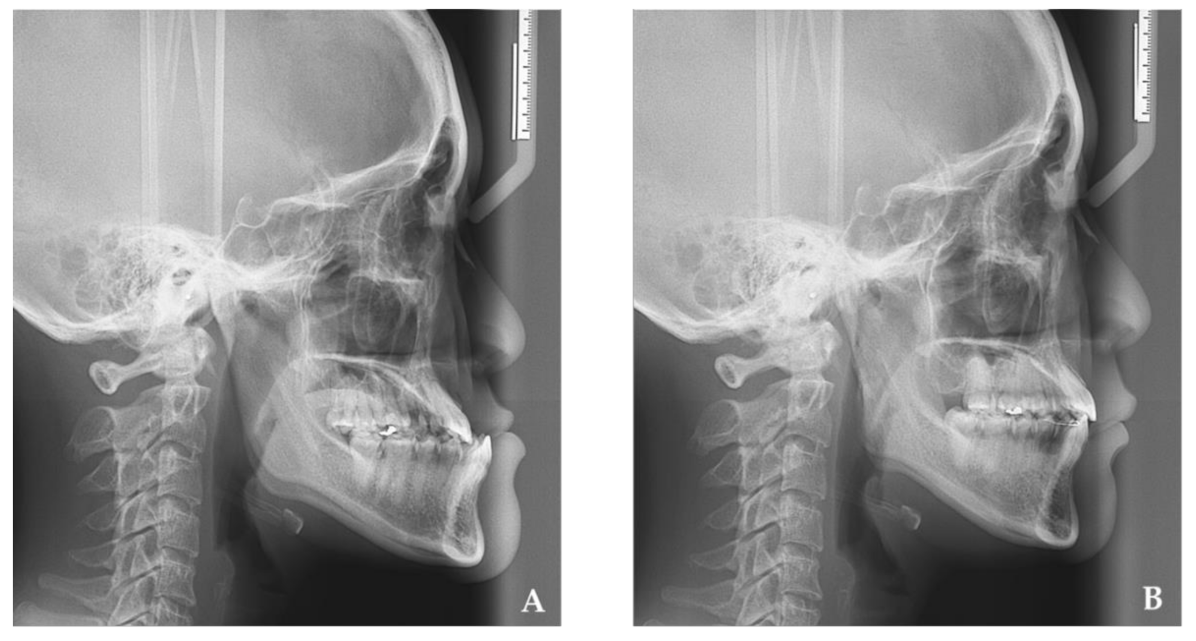
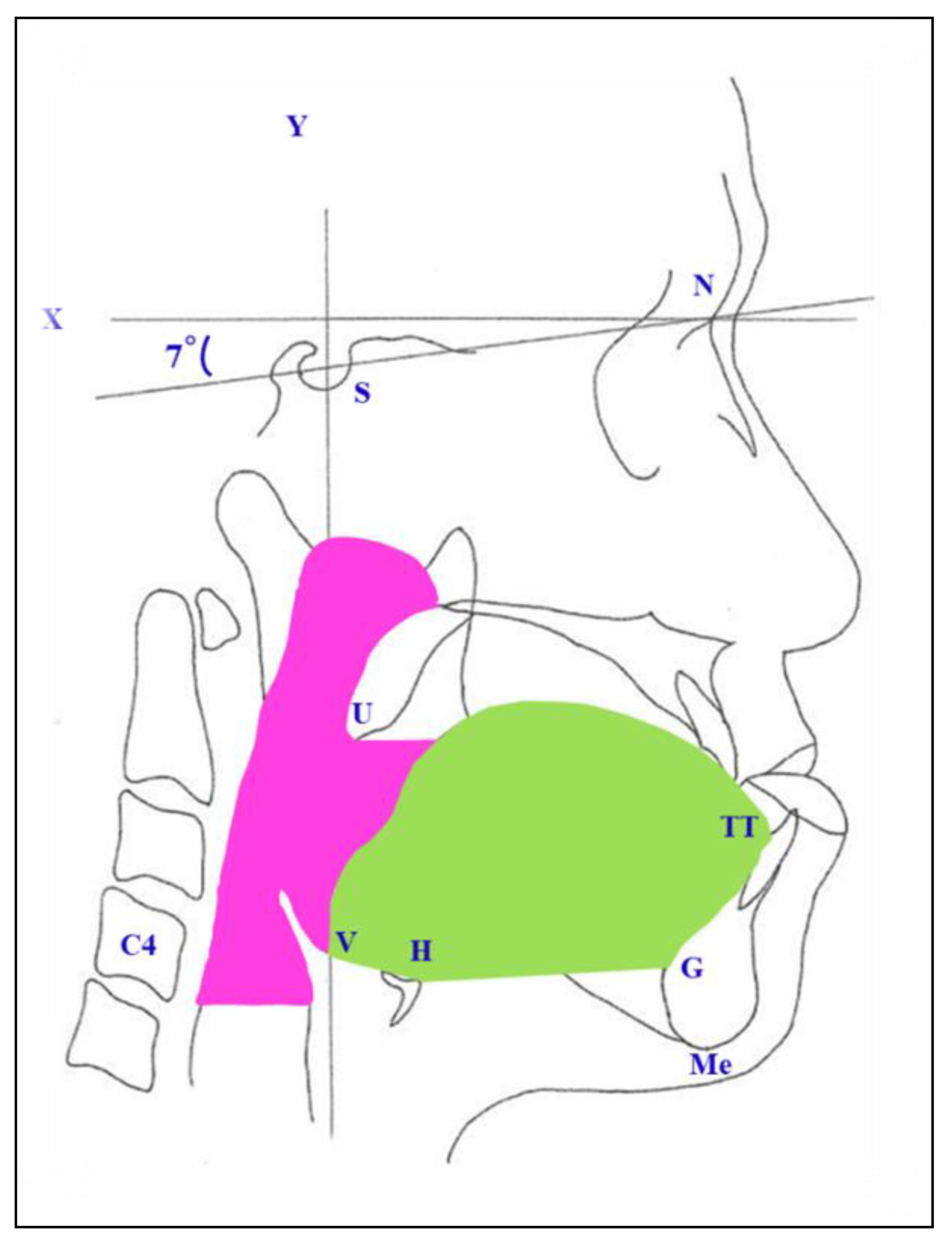
2. Materials and Methods
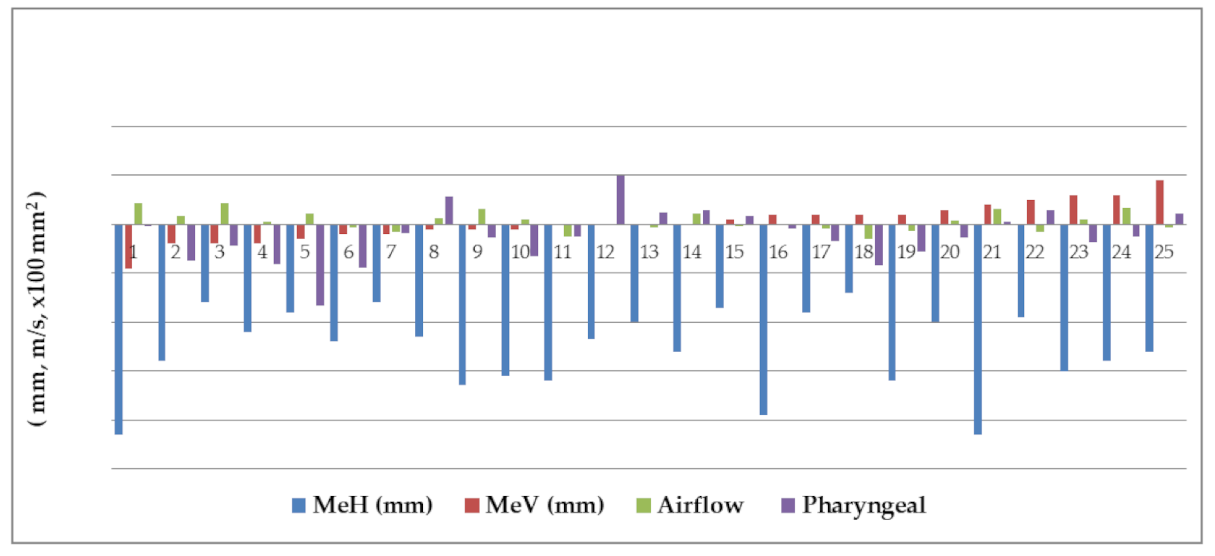
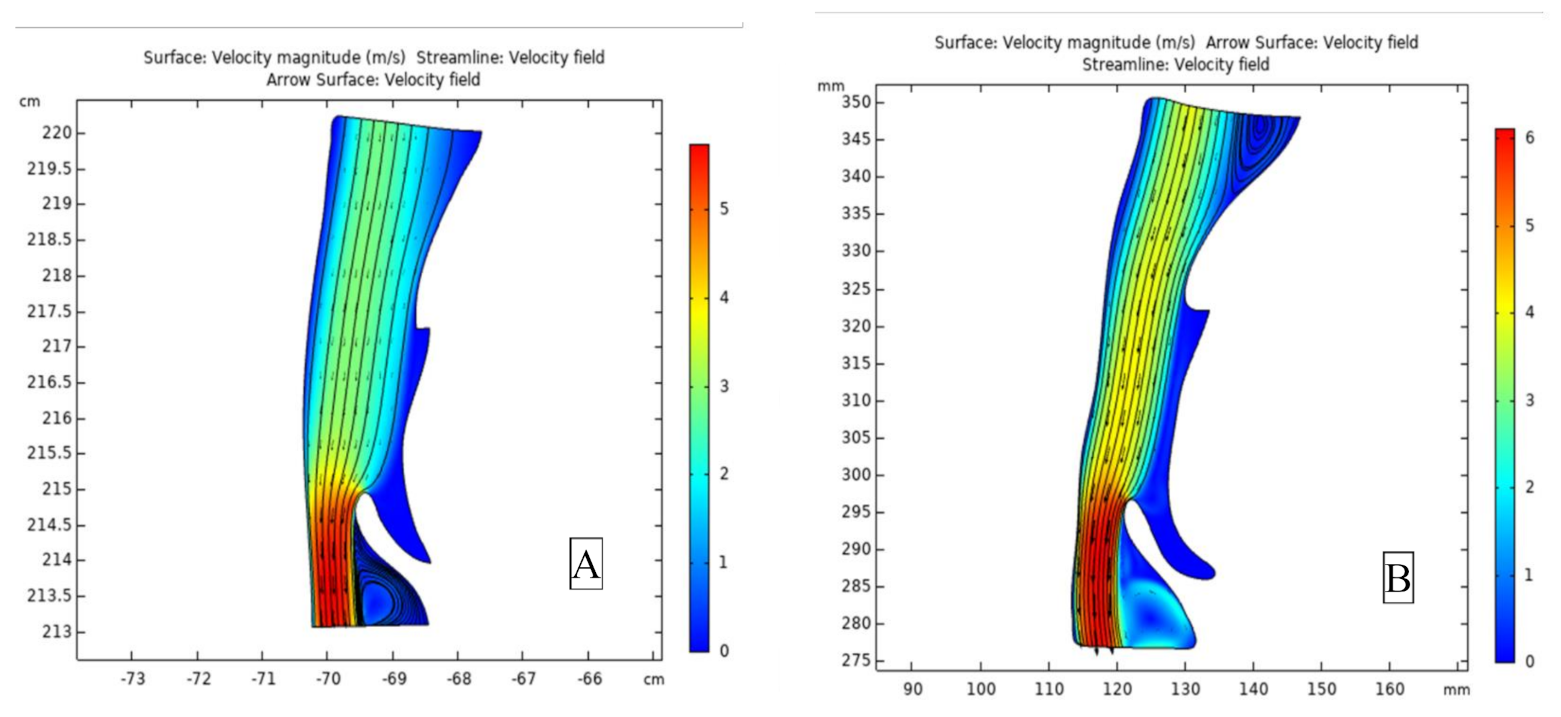
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berkovitz, B.K.B.; Moxham, B.J. The Mouth, Palate and Pharynx: A Textbook of Head and Neck Anatomy; Wolfe Medical: London, UK, 1988; pp. 272–331. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, L.D.; Vogl, A.W.; Mitchell, A.W.M. Head and Neck: Gray’s Anatomy for Students, 2nd ed.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2010; pp. 796–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Aittokallio, T.; Saaresranta, T.; PoloKantola, P.; Nevalainen, O.; Polo, O. Analysis of inspiratory flow shapes in patients with partial upper-airway obstruction during sleep. Chest 2001, 119, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genta, P.R.; Sands, S.A.; Butler, J.P.; Loring, S.H.; Katz, E.S.; Demko, B.G.; Kezirian, E.J.; White, D.P.; Wellman, A. Airflow Shape Is Associated with the Pharyngeal Structure Causing OSA. Chest 2017, 152, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamata, A.; Fujishita, M.; Ariji, Y.; Ariji, E. Three-dimensional computed tomographic evaluation of morphologic airway changes after mandibular setback osteotomy for prognathism. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2000, 89, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, T.; Yamazaki, A.; Takeda, S.; Sato, Y. Effect of bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy setback on the soft palate and pharyngeal airway space. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselnik, M.; Pogrel, M.A. Assessment of the pharyngeal airway space after mandibular setback surgery. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2000, 58, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, A.; Williams, S.; Ritzau, M. Relationships of changes in craniofacial morphology, head posture, and nasopharyngeal airway size following mandibular osteotomy. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial. Orthop. 1989, 96, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Gu, G.; Nagata, J.; Suto, M.; Anraku, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Kuroe, K.; Ito, G. Hyoid position, pharyngeal airway and head posture in relation to relapse after the mandibular setback in skeletal Class III. Clin. Orthod. Res. 2000, 3, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudara, C.; Nielsen, I.; Huang, J.C.; Maki, K.; Miller, A.J.; Hatcher, D. Comparison of airway space with conventional lateral headfilms and 3-dimensional reconstruction from cone-beam computed tomography. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial. Orthop. 2009, 135, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronoosh, P.; Khojastepour, L. Analysis of Pharyngeal Airway Using Lateral Cephalogram vs CBCT Images: A Cross-sectional Retrospective Study. Open. Dent. J. 2015, 9, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoumi, N.; Framanzad, F.; Zamanian, B.; Seddighi, A.S.; Moosavi, M.H.; Najarian, S.; Bastani, D. 2D Computational Fluid Dynamic Modeling of Human Ventricle System Based on Fluid-Solid Interaction and Pulsatile Flow. Basic. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Na, J.S.; Jung, H.D.; Cho, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.S. Computational analysis of airflow dynamics for predicting collapsible sites in the upper airways: A preliminary study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalewski, B.; Kamińska, A.; Syrico, A.; Kałduńska, A.; Pałka, Ł.; Sobolewska, E. The usefulness of modified Mallampati score and CT upper airway volume measurements in diagnosing OSA among patients with breathing-related sleep disorders. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, N.; Inoshita, A.; Suda, S.; Shiota, S.; Shiroshita, N.; Kawana, F.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsumoto, F.; Ikeda, K.; Kasai, T. Clinical, polysomnographic, and cephalometric features of obstructive sleep apnea with AHI over 100. Sleep Breath. 2021, 25, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of changes in the morphology and airflow dynamics of the upper airways in OSAHS patients after treatment with oral appliances. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, J.M.; Frohberg, U.; Van Sickels, J.E. Long-term airway space changes after mandibular setback using bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1990, 19, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Lai, S.; Chen, K.K.; Lee, H.E. Correlation between the pharyngeal airway space and head posture after surgery for mandibular prognathism. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 251021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarakati, S.F.; Kula, K.S.; Ghoneima, A.A. The reliability and reproducibility of cephalometric measurements: A comparison of conventional and digital methods. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2012, 41, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, X.D.; Mao, L.X.; Xia, Y.H.; Yuan, L.J.; Cai, M.; Liu, J.Q.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; et al. Influence of temporomandibular joint disc displacement on mandibular advancement in patients without pre-treatment condylar resorption. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Hamdan, A.M.; Fakhouri, W.D. Skeletal malocclusion: A developmental disorder with a life-long morbidity. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2014, 6, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altemus, L.A. Frequency of the incidence of malocclusion in American negro children aged twelve to sixteen. Angle. Orthod. 1959, 29, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.G.; Kang, D.S. Prevalence of malocclusion among Latino adolescents. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2001, 119, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, E.L. The prevalence of malocclusion amongst Hong Kong male dental students. Br. J. Orthod. 1994, 21, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, W.S.; Balbach, D.R.; Lamphiear, D.E. The heritability of attained growth in the human face. Am. J. Orthod. 1970, 58, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakasima, A.; Ichinose, M.; Nakata, S.; Takahama, Y. Hereditary factors in the craniofacial morphology of Angle’s Class II and Class III malocclusion. Am. J. Orthod. 1982, 82, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.W.; Powell, N.B.; Guilleminault, C.; Ware, W. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome following surgery for mandibular prognathism. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1987, 45, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, N.R.; Battagel, J.M. The effects of orthognathic surgery on pharyngeal airway dimensions and quality of sleep. J. Orthod. 2000, 27, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, S.M.; Gorgulu, S.; Gokce, H.; Bengi, O.; Sabuncuoglu, F.; Ozgen, F.; Bilgic, H. Changes in posterior airway space, pulmonary function and sleep quality, following bimaxillary orthognathic surgery. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, Y.; Oshima, M.; Iwai, T.; Kitajima, H.; Omura, S.; Tohnai, I. Computational fluid dynamics study of the pharyngeal airway space before and after mandibular setback surgery in patients with mandibular prognathism. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazawa, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Ooi, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yanagisawa-Minami, A.; Oku, Y.; Yokura, A.; Ban, Y.; Suga, H.; Kawashiri, S.; et al. Relationship between pharyngeal airway depth and ventilation condition in mandibular setback surgery: A computational fluid dynamics study. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Chen, C.M.; Chen, P.H.; Chou, S.T.; Pan, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.C. Comparison of Pharyngeal Airway between Mandibular Setback Surgery Patients (Skeletal Class III) and Nonsurgery Patients (Skeletal Classes I and II). Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Me (mm) | Mean | SD | p Value | Significant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal change | |||||
| Clockwise Rotation | −13.0 | 4.71 | <0.001 | * | |
| Counterclockwise Rotation | −12.7 | 4.27 | <0.001 | * | |
| No Rotation | −12.7 | 2.53 | 0.002 | * | |
| Total | −12.8 | 4.03 | <0.001 | * | |
| Vertical change | |||||
| Clockwise Rotation | 1.9 | 1.22 | <0.001 | * | |
| Counterclockwise Rotation | −1.6 | 1.21 | 0.003 | * | |
| No Rotation | 0.0 | 0.00 | 0.364 | NS | |
| Total | 0.2 | 1.91 | 0.578 | NS | |
| Variables | Mean | SD | p Value | Significant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airflow velocity (m/s) | |||||
| Clockwise Rotation | 0.0 | 0.96 | 0.939 | NS | |
| Counterclockwise Rotation | 0.8 | 0.98 | 0.026 | * | |
| No Rotation | −0.1 | 0.93 | 0.780 | NS | |
| Total | 0.3 | 1.01 | 0.133 | NS | |
| Pharyngeal airway area (mm2) | |||||
| Clockwise Rotation | −88.4 | 174.38 | 0.124 | NS | |
| Counterclockwise Rotation | −255.5 | 297.96 | 0.024 | * | |
| No Rotation | 160.4 | 254.71 | 0.297 | NS | |
| Total | −115.5 | 274.34 | 0.046 | * | |
| Tongue area (mm2) | |||||
| Clockwise Rotation | 5.1 | 277.97 | 0.953 | NS | |
| Counterclockwise Rotation | −88.1 | 133.13 | 0.066 | NS | |
| No Rotation | −63.4 | 113.19 | 0.344 | NS | |
| Total | −43.2 | 205.96 | 0.305 | NS | |
| Variable | MeT21H | MeT21V | Tongue Area | Pharyngeal Area | Airflow Velocity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p Value | r | p Value | r | p Value | r | p Value | r | p Value | |
| MeT21H | 1 | 0.029 | 0.891 | −0.127 | 0.545 | 0.018 | 0.932 | −0.384 | 0.058 | |
| MeT21V | 0.029 | 0.891 | 1 | 0.273 | 0.186 | 0.364 | 0.074 | −0.329 | 0.108 | |
| Pharyngeal area | −0.127 | 0.545 | 0.273 | 0.186 | 1 | 0.106 | 0.614 | −0.041 | 0.846 | |
| Tongue area | 0.018 | 0.932 | 0.364 | 0.074 | 0.106 | 0.614 | 1 | −0.201 | 0.335 | |
| Airflow velocity | −0.384 | 0.058 | −0.329 | 0.108 | −0.041 | 0.846 | −0.201 | 0.335 | 1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-M.; Yu, T.-Y.; Chou, S.-T.; Cheng, J.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Pan, C.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-C. Changes in Tongue Area, Pharyngeal Area, and Pharyngeal Airway Velocity after Correction of Mandibular Prognathism. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194560
Chen C-M, Yu T-Y, Chou S-T, Cheng J-H, Chen S-C, Pan C-Y, Tseng Y-C. Changes in Tongue Area, Pharyngeal Area, and Pharyngeal Airway Velocity after Correction of Mandibular Prognathism. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194560
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chun-Ming, Ting-Ying Yu, Szu-Ting Chou, Jung-Hsuan Cheng, Shih-Chieh Chen, Chin-Yun Pan, and Yu-Chuan Tseng. 2021. "Changes in Tongue Area, Pharyngeal Area, and Pharyngeal Airway Velocity after Correction of Mandibular Prognathism" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194560
APA StyleChen, C.-M., Yu, T.-Y., Chou, S.-T., Cheng, J.-H., Chen, S.-C., Pan, C.-Y., & Tseng, Y.-C. (2021). Changes in Tongue Area, Pharyngeal Area, and Pharyngeal Airway Velocity after Correction of Mandibular Prognathism. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194560






