Arguments against the Requirement of a Biological License Application for Human Pancreatic Islets: The Position Statement of the Islets for US Collaborative Presented during the FDA Advisory Committee Meeting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Position against Regulation of Human Islets as Drugs and BLA Approval
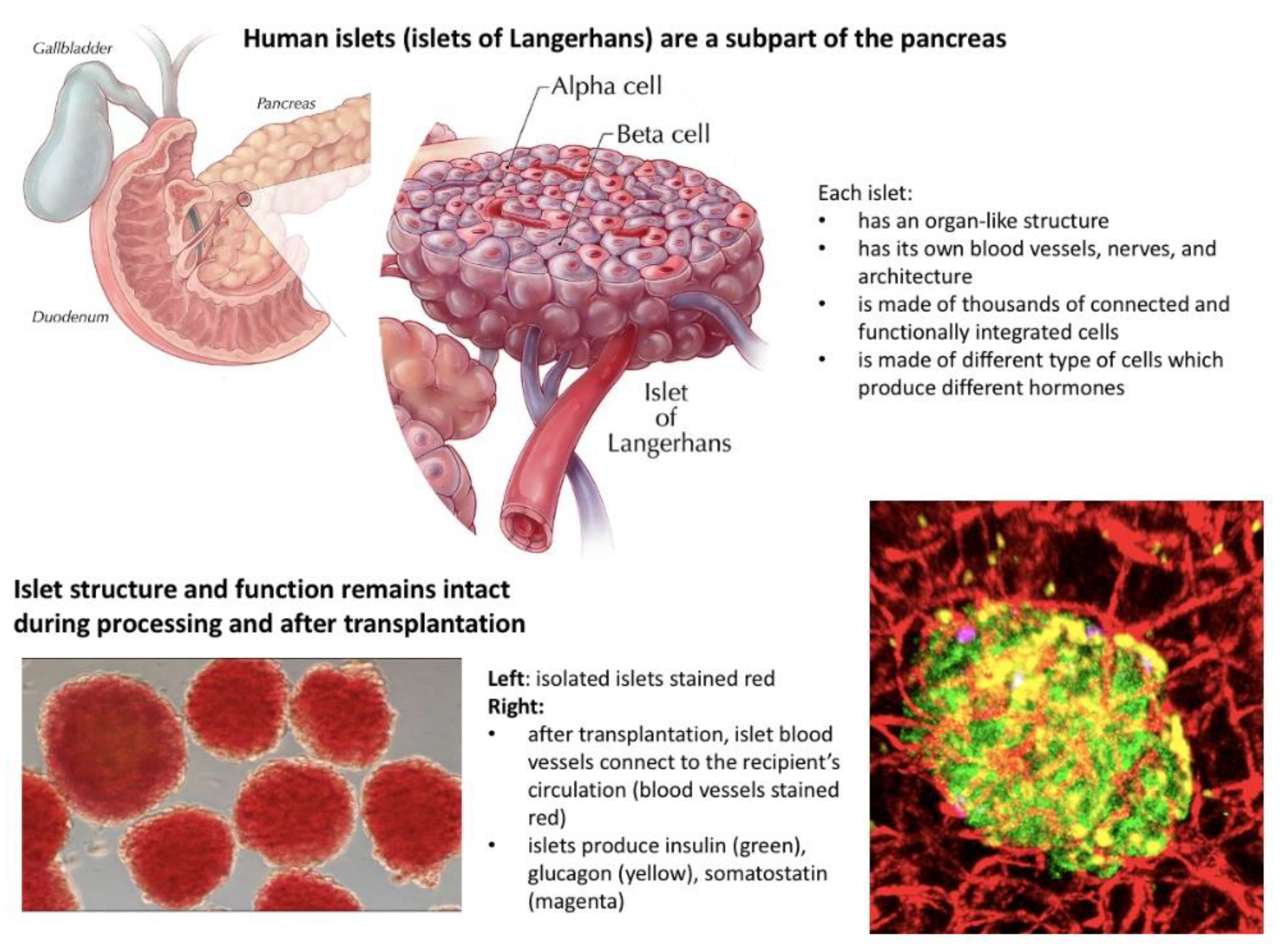
2.1. Islets as Organs
- Exist naturally in the human body and are not artificially manufactured;
- Consist of many different types of cells with unique and well-integrated functions;
- Have their own internal blood vessel and neural network;
- Maintain their own morphology and structure during processing and after transplantation;
- Connect their own vasculature to the recipient blood vessel network after transplantation;
- Do not tolerate below zero temperatures and can be preserved in room temperature for only a short period of time;
- Most importantly, in contrast to drugs, the potency of islets as with any other organ for transplantation cannot be reassured by a single test prior to transplantation but can be reassured only by the continuous assessment by the transplant team of complex parameters and constant supervision from the moment of donor selection through pancreas recovery, processing, preservation, transplantation, and, finally, post-transplant patient care in order to provide safe, effective, and appropriate clinical care.
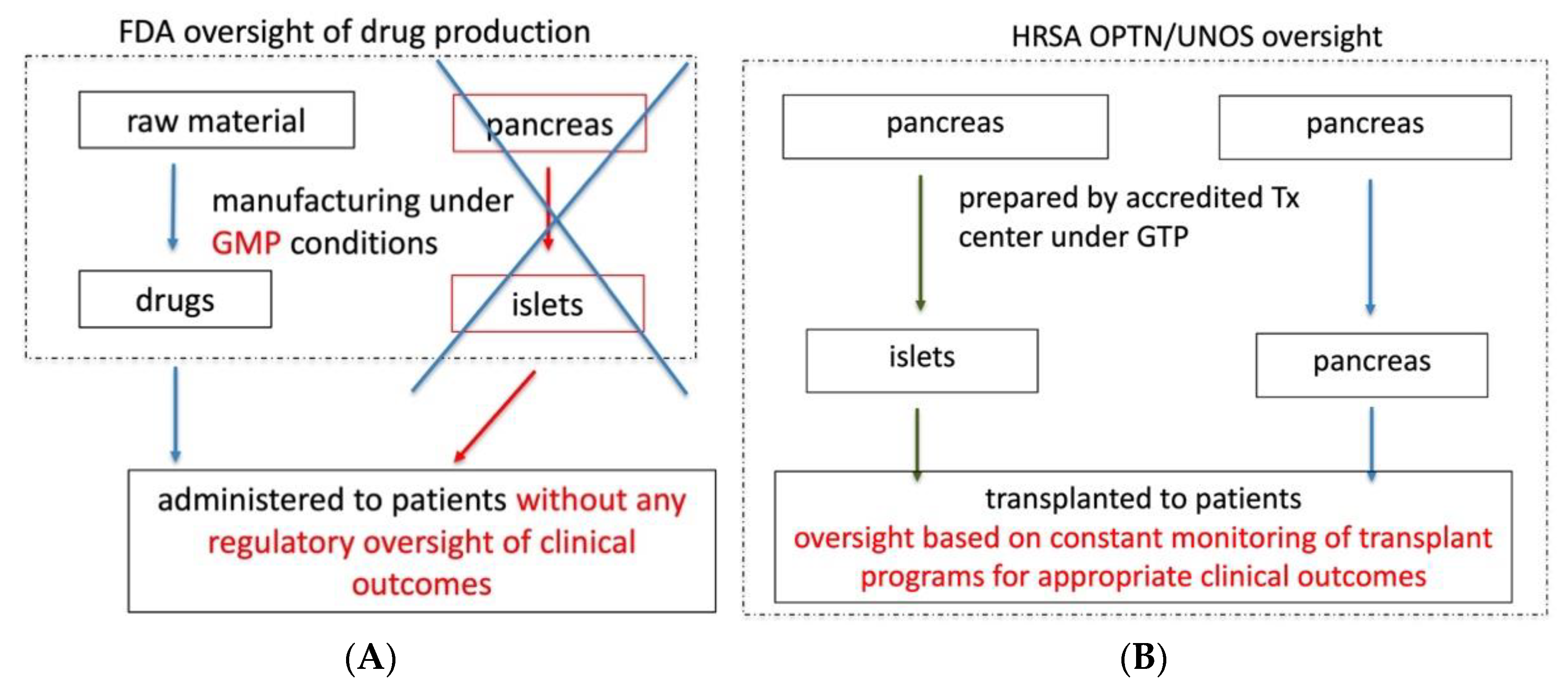
2.2. The FDA’s Position That Allogeneic Islets Are Drugs and Require a BLA Has Prevented Islet Transplantation from Becoming a Standard of Care Procedure in the US, in Contrast to Other Countries
2.3. Granting a BLA to a Private, For-Profit Company Will Not Solve the Problem of Islet Transplantation in the US But Will Lead to Its Further Demise
- A right to commercialize human islets as a biological drug for use in transplantation. This is inconsistent with the federal prohibition on commercialization of human organs [3];
- 7 years of marketing exclusivity under the Orphan Drug Act;
- Significant leverage in terms of the contract with any transplant center to provide islets for transplantation, including the price for islets;
- Unprecedented influence over which transplant centers are able to offer their patients islet transplantation.
- As such, we foresee the following downstream consequences:
- Transplant centers will have no alternative source of islets for clinical use;
- Transplant centers will have no control over the quality of islets for their patients;
- Access to islet transplantation will be limited due to increased costs and decreased availability of islets compared to a situation where islets are regulated as organs and are exempt from BLA.
2.4. Granting This BLA May Compromise Patient Safety
2.5. Proposed Solution
- Legally, it would conform with the statutory definition of human organs under the National Organ Transplantation Act (NOTA);
- Provide OPTN/UNOS with legal authority for holistic, systematic clinical oversight over islet transplantation. Thus, protecting patients by ensuring the safety and effectiveness of islet transplantation therapy;
- Prevent imminent commercialization of human islets, which is prohibited under NOTA, by preventing the FDA from granting a BLA for human islets to a commercial entity.
2.6. FDA’s Position That a BLA Is Required for Unrelated Allogeneic Islets Is Inconsistent with the Agency’s Approach to Autologous Islets
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, D.J. Selected Food and Drug Administration Review Issues for Regulation of Allogeneic Islets of Langerhans as Somatic Cell Therapy. Transplantation 2002, 74, 1816–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.J. FDA regulation of allogeneic islets as a biological product. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 40, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.; Gottlieb, S. Balancing Safety and Innovation for Cell-Based Regenerative Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidance for Industry. Considerations for Allogeneic Pancreatic Islet Cell Products; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research: District of Columbia, WA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, P.; Philipson, L.; Kaufman, D.B.; Philipson, L.H.; Kaufman, D.B.; Ratner, L.E.; Abouljoud, M.S.; Bellin, M.D.; Buse, J.B.; Kandeel, F.; et al. The Islets for US Collaborative. The Demise of Islet Allotransplantation in the US: A Call for an Urgent Regulatory Update. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 21, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowski, P.; Barth, R.N.; Japour, A.; Javitt, G.; Pyda, J.S.; Bachul, P.J.; Nowicki, E.; Ricordi, C.; on behalf of the Islets for US Collaborative. Regulatory updates are needed to prevent the commercialization of islet transplantation in the US. Am. J. Transplant. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulreda, M.H.; Berggren, P.O. The pancreatic islet: A micro-organ in control. CellR4 2021, 9, e3093. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, G.C.; Bonner-Weir, S. Why pancreatic islets should be regarded and regulated like organs. CellR4 2021, 9, e3083. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, A.; Bradbury, L.; Johnson, R.; Fuggle, S.V.; Shaw, J.A.M.; Casey, J.J.; Friend, P.J.; Watson, C.J.E. The UK Pancreas Allocation Scheme for Whole Organ and Islet Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 2443–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Witkowski, P.; Odorico, J.; Pyda, J.; Anteby, R.; Stratta, R.J.; Schrope, B.A.; Hardy, M.A.; Buse, J.; Leventhal, J.R.; Cui, W.; et al. Arguments against the Requirement of a Biological License Application for Human Pancreatic Islets: The Position Statement of the Islets for US Collaborative Presented during the FDA Advisory Committee Meeting. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132878
Witkowski P, Odorico J, Pyda J, Anteby R, Stratta RJ, Schrope BA, Hardy MA, Buse J, Leventhal JR, Cui W, et al. Arguments against the Requirement of a Biological License Application for Human Pancreatic Islets: The Position Statement of the Islets for US Collaborative Presented during the FDA Advisory Committee Meeting. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(13):2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132878
Chicago/Turabian StyleWitkowski, Piotr, Jon Odorico, Jordan Pyda, Roi Anteby, Robert J. Stratta, Beth A. Schrope, Mark A. Hardy, John Buse, Joseph R. Leventhal, Wanxing Cui, and et al. 2021. "Arguments against the Requirement of a Biological License Application for Human Pancreatic Islets: The Position Statement of the Islets for US Collaborative Presented during the FDA Advisory Committee Meeting" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 13: 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132878
APA StyleWitkowski, P., Odorico, J., Pyda, J., Anteby, R., Stratta, R. J., Schrope, B. A., Hardy, M. A., Buse, J., Leventhal, J. R., Cui, W., Hussein, S., Niederhaus, S., Gaglia, J., Desai, C. S., Wijkstrom, M., Kandeel, F., Bachul, P. J., Becker, Y. T., Wang, L.-J., ... on behalf of the Islets for US Collaborative. (2021). Arguments against the Requirement of a Biological License Application for Human Pancreatic Islets: The Position Statement of the Islets for US Collaborative Presented during the FDA Advisory Committee Meeting. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132878







