Diagonal Earlobe Crease (Frank’s Sign) for Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
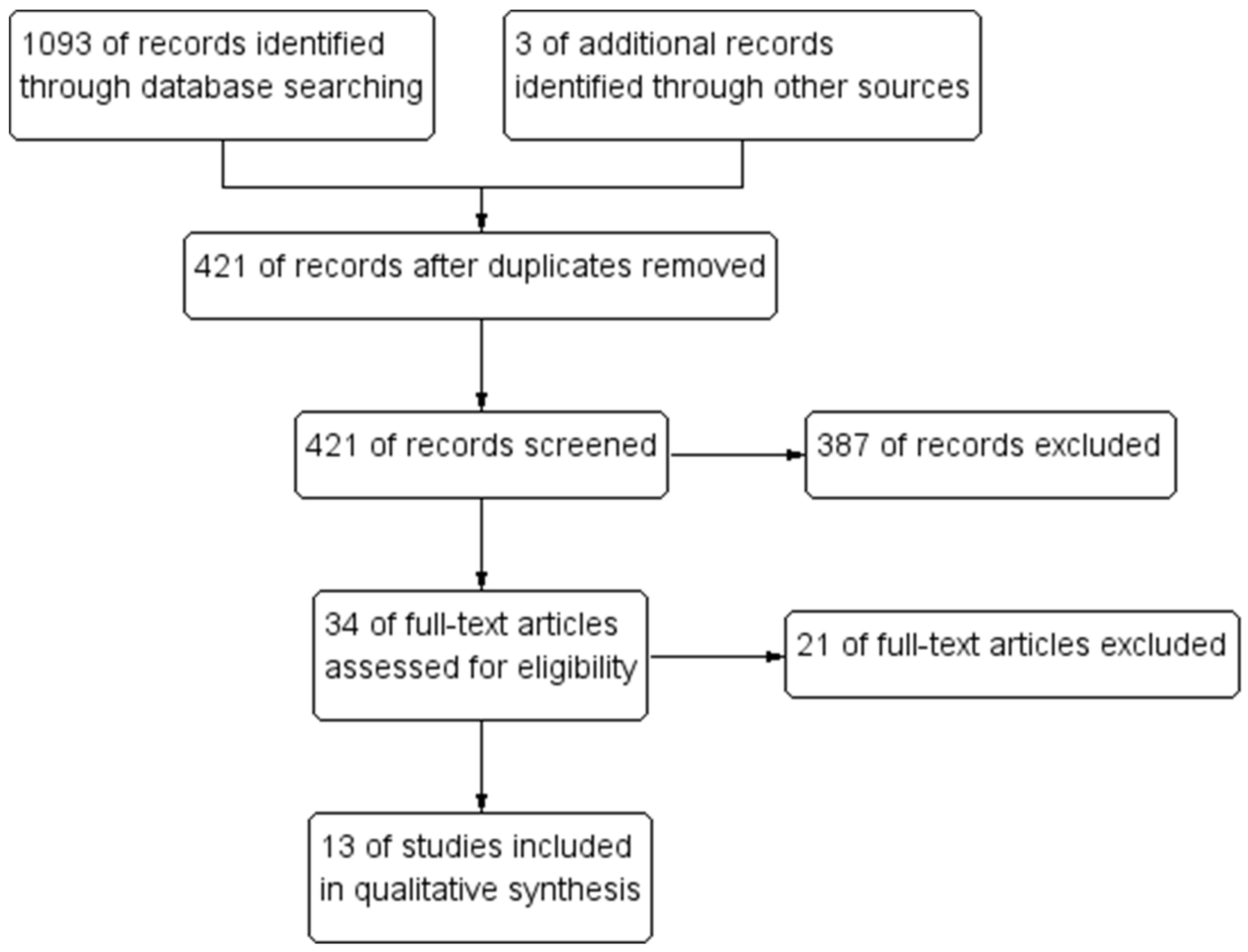
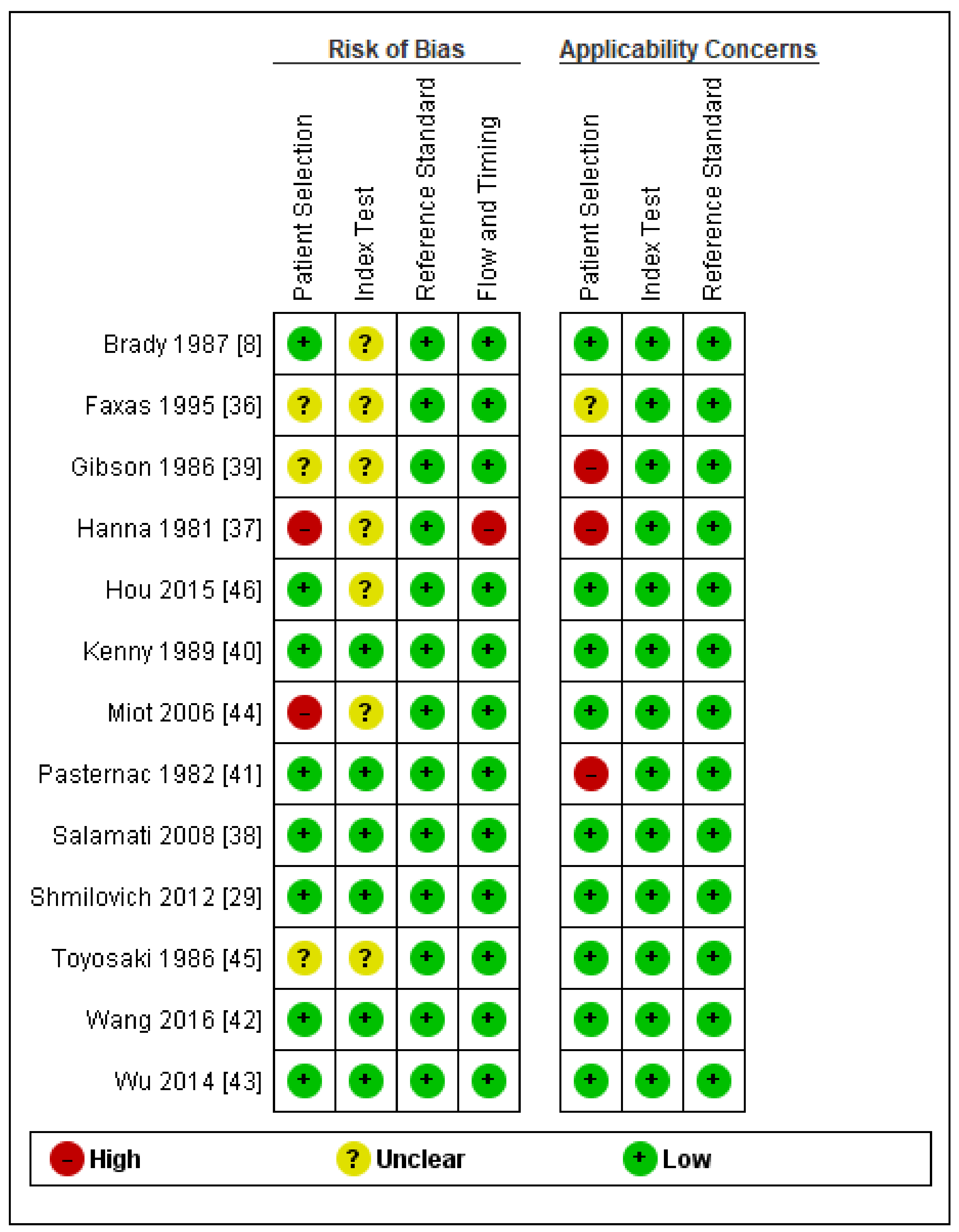
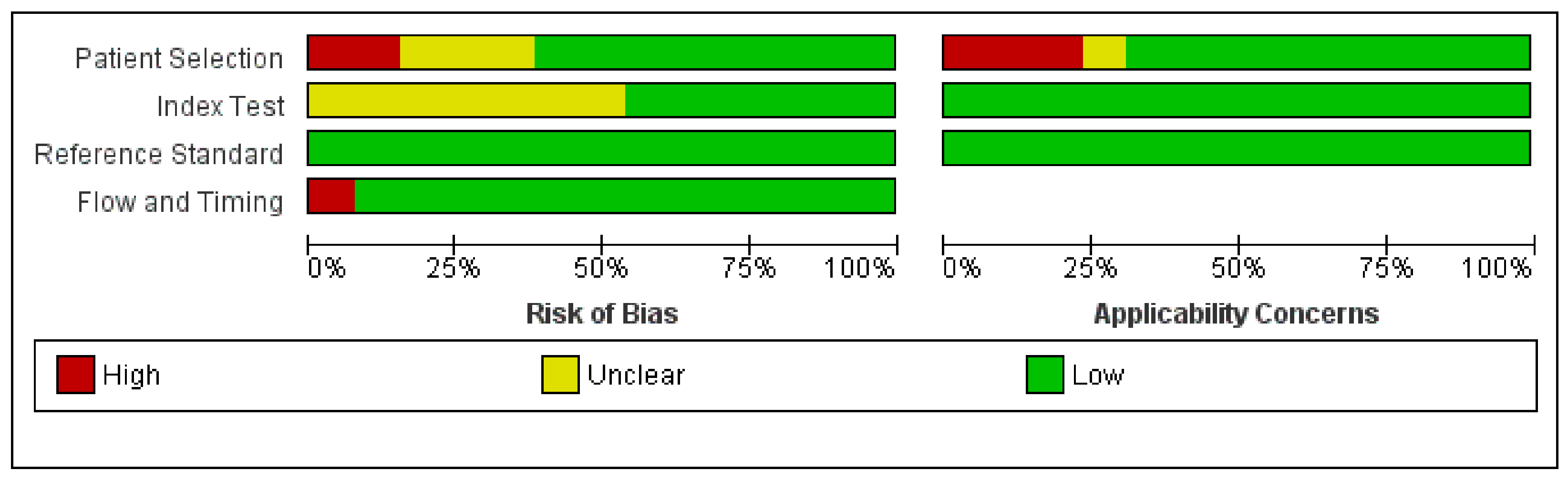
2. Materials and Methods
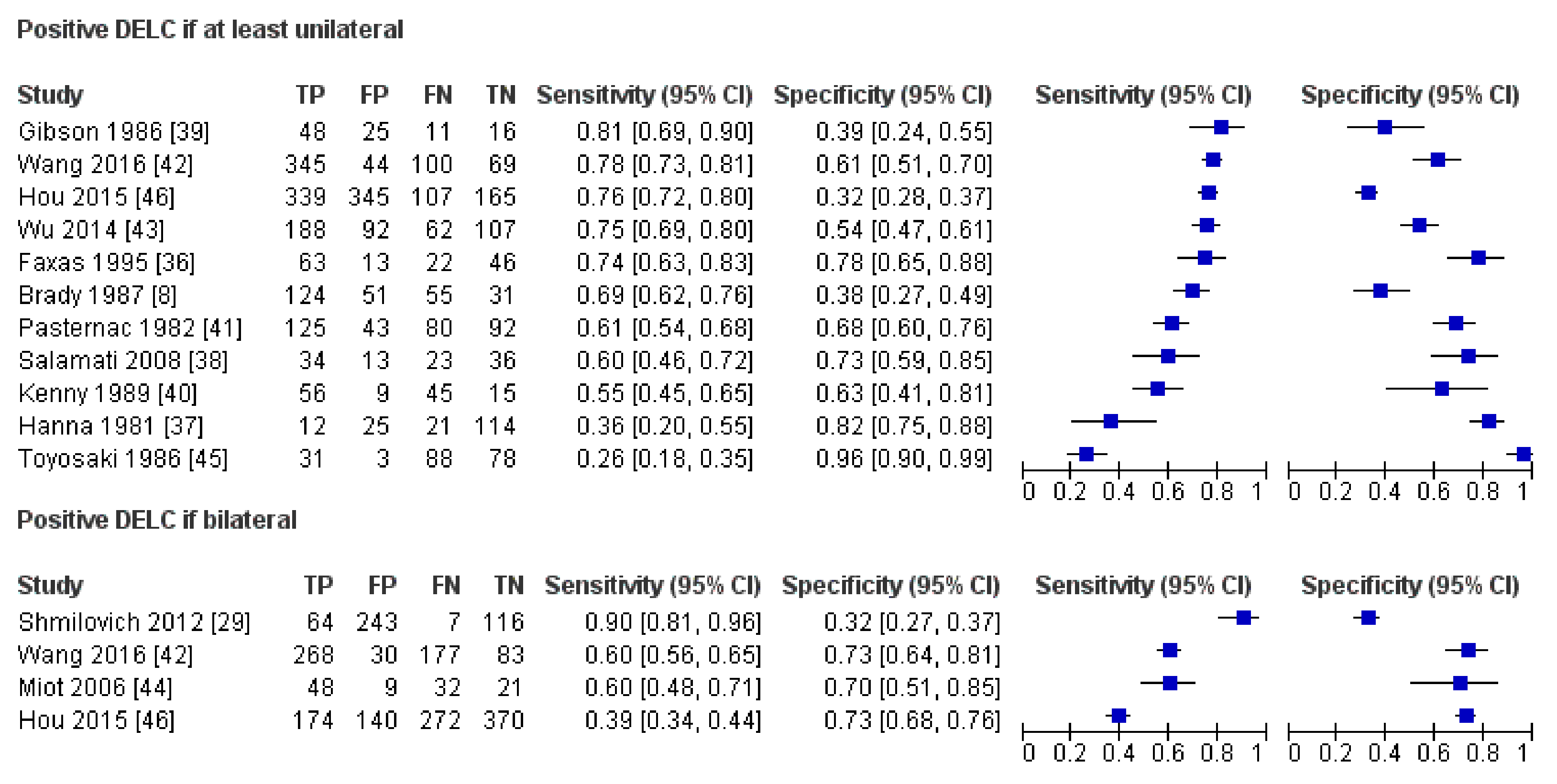
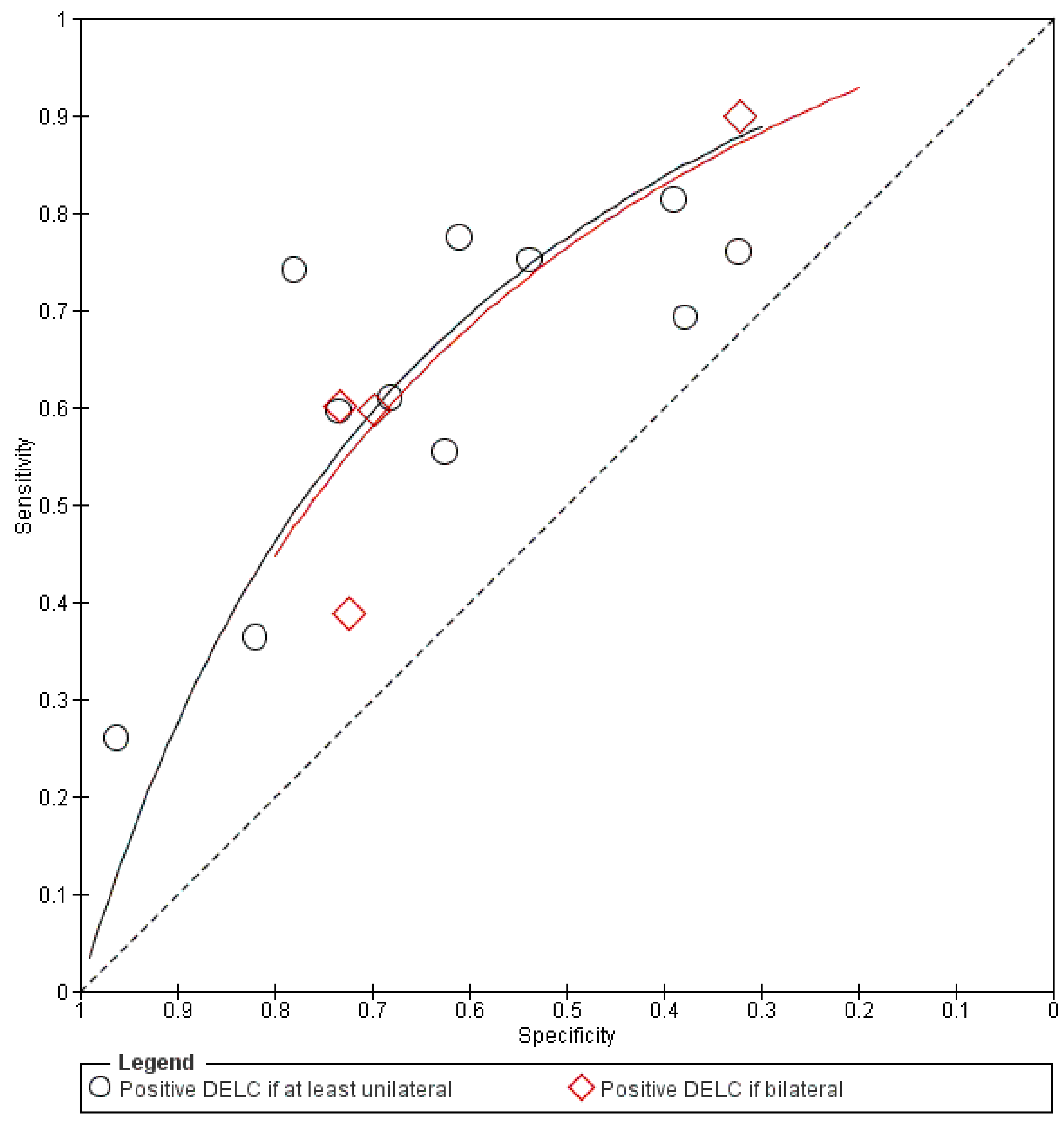
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Perez-Quilis, C.; Leischik, R.; Lucia, A. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease and acute coronary syndrome. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libby, P.; Theroux, P. Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2005, 111, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudoulas, K.D.; Triposkiadis, F.; Geleris, P.; Boudoulas, H. Coronary Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiologic Basis for Diagnosis and Management. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 58, 676–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.T. Aural Sign of Coronary-Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1973, 289, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellen, J.-C. Frank’s Sign and Manifestations of Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review of Literature. Master’s Thesis, Université Paris Diderot, Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stoyanov, G.S.; Dzhenkov, D.; Petkova, L.; Sapundzhiev, N.; Georgiev, S. The histological basis of Frank’s sign. Head Neck Pathol. 2020, 15, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, P.M.; Zive, M.A.; Goldberg, R.J.; Gore, J.M.; Dalen, J.E. A New Wrinkle to the Earlobe Crease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1987, 147, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukola, S. The diagonal ear-lobe crease, a physical sign associated with coronary heart disease. Acta Med. Scand. Suppl. 1978, 619, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, Y.; Maeda, T.; Guan, J.-Z.; Oyama, J.; Sugano, M.; Makino, N. Diagonal Earlobe Crease are Associated With Shorter Telomere in Male Japanese Patients With Metabolic Syndrome A Pilot Study. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McInnes, M.D.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.D.; McGrath, T.A.; PRISMA-DTA Group. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies: The PRISMA-DTA statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, J.; Bossuyt, P.; Gatsonis, C. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, A.D.; White, H.D.; Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC); American College of Cardiology (ACC); American Heart Association (AHA); et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 40, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.; Sterne, J.; Bossuyt, P.M. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrengül, H.; Dursunoğlu, D.; Kaftan, A.; Zoghi, M.; Tanrıverdi, H.; Zungur, M.; Kılıç, M. Bilateral diagonal earlobe crease and coronary artery disease: A significant association. Dermatology 2004, 209, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesbre, J.P.; Castier, B.; Tribouilloy, C.; Labeille, B.; Isorni, C. Frank’s sign and coronary disease. Ann. Cardiol. d’Angéiologie 1987, 36, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kuon, E.; Pfahlbusch, K.; Lang, E. The diagonal ear lobe crease for evaluating coronary risk. Z. Kardiol. 1995, 84, 512–519. [Google Scholar]
- Dytfeld, M.; Leśna, J.; Protasewicz, A.; Sarnowski, W.; Dyszkiewicz, W.; Paradowski, S. Ear lobe crease as a factor of potential risk for coronary artery disease?—World news review and own research. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 108, 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, T.; Mizuno, K.; Sugahara, H.; Arakawa, K.; Satomura, K.; Isojima, K.; Osuzu, F.; Aosaki, N.; Kurita, A.; Hosono, K.; et al. Significance of ear-lobe crease. Shinzo 1983, 15, 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, W.J. Ear lobe crease and coronary artery disease. Am. J. Med. 1983, 75, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, D.; McCormack, P.; Tyrrell, J.; Feely, J. Ear lobe crease and coronary heart disease. Ir. Med. J. 1992, 85, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gral, T.; Thornburg, M. Earlobe Creases in a Cohort of Elderly Veterans. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1983, 31, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blodgett, G. The Presence of a Diagonal Ear-Lobe Crease as an Indicator of Coronary Artery Disease. Master’s Thesis, The Univeristy of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, R.P.; Gilchrist, A.M. Diagonal ear-lobe crease: An independent risk factor in coronary heart disease? Ulst. Med. J. 1980, 49, 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lichstein, E.; Chadda, K.D.; Naik, D.; Gupta, P.K. Diagonal Ear-Lobe Crease: Prevalence and Implications as a Coronary Risk Factor. N. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 290, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawaskar, H.S.; Bawaskar, P.H.; Bawaskar, P.H. Diagonal ear lobe crease: A premonitory diagnostic sign of impeding ischemic heart disease. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2018, 7, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichstein, E.; Chapman, I.; Gupta, P.K.; Chadda, K.D.; Smith, H.; Schwartz, I.; Naik, D. Diagonal Ear-Lobe Crease and Coronary Artery Sclerosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1976, 85, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, R.R.; Taberna, M.D.; Quilis, C.T. Frank’s sign and chest pain. Med. Clín. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 154, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmilovich, H.; Cheng, V.Y.; Rajani, R.; Dey, D.; Tamarappoo, B.K.; Nakazato, R.; Smith, T.W.; Otaki, Y.; Nakanishi, R.; Gransar, H.; et al. Relation of Diagonal Ear Lobe Crease to the Presence, Extent, and Severity of Coronary Artery Disease Determined by Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 109, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmilovich, H.; Cheng, V.Y.; Nakazato, R.; Smith, T.W.; Otaki, Y.; Nakanishi, R.; Paz, W.; Pimentel, R.T.; Berman, D.S.; Rajani, R. Incremental Value of Diagonal Earlobe Crease to the Diamond-Forrester Classification in Estimating the Probability of Significant Coronary Artery Disease Determined by Computed Tomographic Angiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, H. Investigations of the diagonal earlobe crease in coronary heart disease. Herz Kreislauf. 1986, 18, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Mirić, D.; Rumboldt, Z.; Pavić, M.; Kuzmanić, A.; Bagatin, J. The role of the diagonal ear lobe crease in the clinical evaluation of coronary risk. Liječnički Vjesn. 1990, 112, 206–207. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabo, J.; Rentschler, P.; Pedemonte, N. Diagonal ear-lobe crease and vascular arteriosclerotic disease. Prensa Med. Argent 1983, 70, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Wermut, W.; Jaszczenko, S.; Ruszel, A. Ear lobe crease as a risk factor in coronary disease. Wiad. Lek. 1980, 33, 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Haft, J.I.; Gonnella, G.R.; Kirtane, J.S.; Anastasiades, A. Correlation of ear crease sign with coronary arteriographic findings. Cardiovasc. Med. 1979, 4, 861–863. [Google Scholar]
- Faxas, E.; Vigoa, A.; Chuckram, A.; Valdés, R.; Fariñas, H. Earlobe crease and ischemic heart disease. Rev. Cubana Med. 1995, 34, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, H.; Lancaster, M.; Tolan, G.; Jackson, W., Jr. Earlobe Crease and Coronary Artery Disease; USAF School of Aerospace Medicine, Aerospace Medical Division, Brooks Air Force Base: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Salamati, P.; Nazeri, I.; Alehossein, M.; Sotoudeh, K.; Rezaee, A. Earlobe crease and coronary artery disease. Pakistan J. Med. Sci. 2008, 24, 600–603. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, T.C.; Ashikaga, T. The ear lobe crease sign and coronary artery disease in aortic stenosis. Clin. Cardiol. 1986, 9, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, D.J.; Gilligan, D. Ear Lobe Crease and Coronary Artery Disease in Patients Undergoing Coronary Arteriography. Cardiology 1989, 76, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternac, A.; Sami, M. Predictive value of the ear-crease sign in coronary artery disease. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1982, 126, 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, L.-H.; Jia, E.-Z.; Li, Z.-Y.; Ding, X.-Q.; Ge, P.-C.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, T.-B.; Wang, L.-S.; Li, C.-J.; et al. Relationship between diagonal earlobe creases and coronary artery disease as determined via angiography. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e008558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.-L.; Yang, D.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-S.; Chai, W.-H.; Jin, M.-L. Diagonal earlobe crease and coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miot, H.A.; Medeiros, L.M.; Siqueira, C.R.; Cardoso, L.D.; Gumieiro, J.H.; Pandini Filho, M.A.; Miot, L.D. Association between coronary artery disease and the diagonal earlobe and preauricular creases in men. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2006, 81, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyosaki, N.; Tsuchiya, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Kawasaki, K.-I.; Shiina, A.; Toyooka, T.; Noda, T.; Terao, N.; Takeda, K.; Ishibashi, A.; et al. Earlobe crease and coronary heart disease in Japanese. Heart Vessels 1986, 2, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhou, L. The Combined Effect of Ear Lobe Crease and Conventional Risk Factor in the Diagnosis of Angiographically Diagnosed Coronary Artery Disease and the Short-Term Prognosis in Patients Who Underwent Coronary Stents. Medicine 2015, 94, e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, S. Simplifying likelihood ratios. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2002, 17, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knuuti, J.; Ballo, H.; Juarez-Orozco, L.E.; Saraste, A.; Kolh, P.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Jüni, P.; Windecker, S.; Bax, J.J.; Wijns, W. The performance of non-invasive tests to rule-in and rule-out significant coronary artery stenosis in patients with stable angina: A meta-analysis focused on post-test disease probability. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3322–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucenteforte, E.; Romoli, M.; Zagli, G.; Gensini, G.F.; Mugelli, A.; Vannacci, A. Ear lobe crease as a marker of coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 175, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.; Walford, S. Why we should be looking for ear lobe creases. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagonal ear lobe crease and coronary artery disease. Authorea 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonino, P.A.L.; Fearon, W.F.; De Bruyne, B.; Oldroyd, K.G.; Leesar, M.A.; Ver Lee, P.N.; Maccarthy, P.A.; Van’t Veer, M.; Pijls, N.H. Angiographic versus functional severity of coronary artery stenoses in the FAME study fractional flow reserve versus angiography in multivessel evaluation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2816–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Author (Year) | Country | Sample Size (n) | Males | Age 1 | DELC Prevalence | CAD Prevalence | DELC Definition | Reference Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brady (1987) [8] | USA | 261 | 100% | DELC+ 60 | 67% | 69% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| DELC− 52 | ||||||||
| Gibson (1986) [39] | USA | 100 | 68% | Males 65 | 73% | 59% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| Females 70 | ||||||||
| Faxas (1995) [36] | Cuba | 144 | NA | NA | 53% | 59% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| Hanna (1981) [37] | USA | 172 | 100% | 94% below 50 | 22% | 19% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| Hou (2015) [46] | China | 956 | 57% | CAD+ 55 ± 9 | 72%, 33% | 47% | At least unilateral, bilateral | ICA |
| CAD− 51 ± 8 | ||||||||
| Kenny (1989) [40] | Ireland | 125 | 90% | Range 35–90 | 52% | 81% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| Miot (2006) [44] | Brazil | 110 | 100% | 58 ± 12 | 52% | 73% | Bilateral | ICA |
| Pasternac (1982) [41] | Canada | 340 | 74% | 50 ± 8 | 49% | 60% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| Salamati (2008) [38] | Iran | 106 | 66% | 50 ± 14 | 44% | 54% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| Shmilovich (2012) [29] | USA | 430 | 61% | 61 ± 13 | 71% | 17% | Bilateral | CTA |
| Toyosaki (1986) [45] | Japan | 200 | 76% | 72% above 50 | 17% | 60% | At least unilateral | ICA |
| Wang (2016) [42] | China | 558 | 72% | 64 | 70%, 53% | 80% | At least unilateral, bilateral | ICA |
| Wu (2014) [43] | China | 449 | 62% | 63 ± 12 | 62% | 56% | At least unilateral | ICA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Więckowski, K.; Gallina, T.; Surdacki, A.; Chyrchel, B. Diagonal Earlobe Crease (Frank’s Sign) for Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132799
Więckowski K, Gallina T, Surdacki A, Chyrchel B. Diagonal Earlobe Crease (Frank’s Sign) for Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(13):2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132799
Chicago/Turabian StyleWięckowski, Krzysztof, Tomasz Gallina, Andrzej Surdacki, and Bernadeta Chyrchel. 2021. "Diagonal Earlobe Crease (Frank’s Sign) for Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 13: 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132799
APA StyleWięckowski, K., Gallina, T., Surdacki, A., & Chyrchel, B. (2021). Diagonal Earlobe Crease (Frank’s Sign) for Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132799






