Long-Term Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Post-Stroke Spasticity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Search Strategy for PubMed/MEDLINE
References
- Guzik, A.; Bushnell, C. Stroke Epidemiology and Risk Factor Management. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2017, 23, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.S. Stroke in the 21st Century: A Snapshot of the Burden, Epidemiology, and Quality of Life. Stroke Res. Treat. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.; Onuma, O.; Owolabi, M.; Sachdev, S. Stroke: A global response is needed. Bull. World Health Organ. 2016, 94, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.A.; Gaverth, J.; Yeung, E.; Marilyn, M.L. Assessment of spasticity after stroke using clinical measures: A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, J.P.; Choi, D.; Grotta, J.; Wolf, P. Stroke: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management, 4th ed.; Churchill Livingstone Hardcover: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 62–101. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.; Harvey, R.L.; Macko, R.F.; Winstein, C.J.; Zorowitz, R.D. Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation, 1st ed.; Demos Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 51–93. ISBN 978-1933864129. [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann, R.G.; Young, R.R.; Koella, W.P. Spasticity, Disordered Motor Control; Symposia Specialists: Miami, FL, USA, 1980; pp. 485–495. ISBN 9780883721285. [Google Scholar]
- Trompetto, C.; Marinelli, L.; Mori, L.; Pelosin, E.; Curra, A.; Molfetta, L.; Abbruzzese, G. Pathophysiology of spasticity: Implications for neurorehabilitation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorowitz, R.D.; Gillard, P.J.; Brainin, M. Poststroke spasticity: Sequelae and burden on stroke survivors and caregivers. Neurology 2013, 80 (Suppl. S2), 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opheim, A.; Danielsson, A.; Murphy, A.M.; Persson, H.C.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Upper-limb spasticity during the first year after stroke: Stroke arm longitudinal study at the University of Gothenburg. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 93, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Sunnerhagen, K.S.; Goldstein, L.B.; Cramer, S.C.; Donnan, G.A.; Duncan, P.W.; Francisco, G.; Good, D.; Graham, G.; et al. International PSS Disability Study Group. Poststroke chronic disease management: Towards improved identification and interventions for poststroke spasticity-related complications. Int. J. Stroke 2011, 6, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillard, P.J.; Sucharew, H.; Kleindorfer, D.; Belagaje, S.; Varon, S.; Alwell, K.; Moomaw, C.J.; Woo, D.; Khatri, P.; Flaherty, M.L.; et al. The negative impact of spasticity on the health-related quality of life of stroke survivors: A longitudinal cohort study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanas, V.R.; Calvo, S.J.; Urrutia, G.; Serra, L.P.; Perez, B.A.; German, R.A. The effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy to reduce lower limb spasticity in stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 27, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, D.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Jia, L.; Cheng, L. Long-term Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Poststroke Spasticity: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaut, A.; Chatelle, C.; Ziegler, E.; Bruno, M.A.; Laureys, S.; Gosseries, O. Spasticity after stroke: Physiology, assessment and treatment. Brain Inj. 2013, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, A.P.; Pinto, C.; Ruschel, M.J.V.; Figueiro, B.; Lukrafka, J.L.; Pagnussat, A.S. Effectiveness of static stretching positioning on post-stroke upper-limb spasticity and mobility: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, C.; Galuppo, L.; Romiti, D. Short-term effect of local muscle vibration treatment versus sham therapy on upper limb in chronic post-stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, P.W.; Ng, G.Y.; Chung, R.C.; Ng, S.S. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation improves walking capacity and reduces spasticity in stroke survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 32, 1203–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, A.; Lee, T.; Janzen, S.; Mays, R.; Mehta, S.; Teasell, R. Systematic review of the effectiveness of pharmacological interventions in the treatment of spasticity of the hemiparetic lower extremity more than six months post stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2012, 19, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerbeek, J.M.; van Wegen, E.; van Peppen, R.; van der Wees, P.J.; Hendriks, E.; Rietberg, M.; Kwakkel, G. What is the evidence for physical therapy poststroke? A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracies, J.M.; Pradines, M.; Ghédira, M. Guided Self-rehabilitation Contract vs conventional therapy in chronic stroke-induced hemiparesis: Neurorestore, a multicenter randomized controlled trial. BMC Neurol. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, P.; Bury, M.; Gompertz, P.; Ebrahim, S. Views of survivors of stroke on benefits of physiotherapy. Qual. Health Care 1994, 3, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poltawski, L.; Boddy, K.; Forster, A.; Goodwin, V.A.; Pavey, A.C.; Dean, S. Motivators for uptake and maintenance of exercise: Perceptions of long-term stroke survivors and implications for design of exercise programmes. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Amatya, B.; Bensmail, D.; Yelnik, A. Non-pharmacological interventions for spasticity in adults: An overview of systematic reviews. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakheit, A.M. The pharmacological management of post-stroke muscle spasticity. Drugs Aging. 2012, 29, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montane, E.; Vallano, A.; Laporte, J.R. Oral antispastic drugs in nonprogressive neurologic diseases: A systematic review. Neurology 2004, 63, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, P.; Jansen, A.; Lee, J.I.; Moll, M.; Ringelstein, M.; Rosenthal, D.; Bigalke, H.; Aktas, O.; Hartung, H.P.; Hefter, H. High prevalence of neutralizing antibodies after long-term botulinum neurotoxin therapy. Neurology 2019, 92, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M.; Leodori, G.; Fernandes, R.M.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Marti, M.J.; Colosimo, M.; Ferreira, J.J. Neutralizing Antibody and Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 29, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brin, M.F.; Comella, C.L.; Jankovic, J.; Lai, F.; Naumann, M. Long-term treatment with botulinum toxin type A in cervical dystonia has low immunogenicity by mouse protection assay. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethoux, F. Spasticity Management After Stroke. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 26, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.P.; Marsden, J. The management of spasticity in adults. BMJ 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chang, C.N.; Chen, Y.M.; Hu, G.C. Comparison of the effect of focused and radial extracorporeal shock waves on spastic equinus in patients with stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radinmehr, H.; Ansari, N.N.; Naghdi, S.; Tabatabaei, A.; Moghimi, E. Comparison of Therapeutic Ultrasound and Radial Shock Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Plantar Flexor Spasticity After Stroke: A Prospective, Single-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manganotti, P.; Amelio, E. Long-term effect of shock wave therapy on upper limb hypertonia in patients affected by stroke. Stroke 2005, 36, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.K.; Kailash. Shock wave treatment in medicine. J. Biosci. 2005, 30, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymarek, R.; Taradaj, J.; Rosinczuk, J. The Effect of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Stimulation on Upper Limb Spasticity in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Single-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1862–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.O.; Chitnis, P.V.; McClure, S.R. Acoustic field of a ballistic shock wave therapy device. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldager, C.B.; Kearney, C.; Spector, M. Clinical application of extracorpo- real shock wave therapy in orthopedics: Focused versus unfocused shock waves. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speed, C. A systematic review of shockwave therapies in soft tissue con- ditions: Focusing on the evidence. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaussy, C.; Brendel, W.; Schmiedt, E. Extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock waves. Lancet 1980, 2, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanic, S.L.; Dobrović, A.V.; Sosa, I.; Cvijanovic, O.; Bobinac, D. Effect of radial shock wave therapy on long bone fracture repair. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 875–879. [Google Scholar]
- Frassanito, P.; Cavalieri, C.; Maestri, R.; Felicetti, G. Effectiveness of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and kinesio taping in calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stania, M.; Juras, G.; Chmielewska, D.; Polak, A.; Kucio, C.; Krol, P. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Achilles Tendinopathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3086910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Wang, W.; Jiang, W.; Qian, Q. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on spasticity in post-stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Gao, F.; Zhao, T.; Sun, W.; Wang, B.; Li, Z. Positive Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Spasticity in Poststroke Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 2470–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henarejos, M.A.B.; Meca, J.; Pina, L.J.A.; Hernandez, C.R. Inter- and intra-rater reliability of the modified Ashworth scale: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymarek, R.; Ptaszkowski, K.; Ptaszkowska, L.; Kowal, M.; Sopel, M.; Taradaj, J.; Rosinczuk, J. Shock Waves as a Treatment Modality for Spasticity Reduction and Recovery Improvement in Post-Stroke Adults—Current Evidence and Qualitative Systematic Review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version, 2nd ed.John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, N.A. The PEDro scale is a valid measure of the methodological quality of clinical trials: A demographic study. Aust. J. Physiother. 2009, 55, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirbisch, L. Effets des ondes de choc radiales sur la spasticite du triceps sural de patients hemiplegiques en phase subaigue: Un essai controle randomise. Kinesither Rev. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Vahdatpour, B.; Mellat, M.; Ashtari, F.; Akbari, M. Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Spasticity in Stroke Patients. Arch. Iran. Med. 2017, 20, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.H.; Shin, M.K.; Choi, E.J.; Kang, H.J. Effective Site for the Application of Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Therapy on Spasticity in Chronic Stroke: Muscle Belly or Myotendinous Junction. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radinmehr, H.; Nakhostin, A.N.; Naghdi, S.; Olyaei, G.; Tabatabaei, A. Effects of one session radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy on post-stroke plantarflexor spasticity: A single-blind clinical trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, J.I.; Lee, S.U. Ultrasonographic Evaluation for the Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Gastrocnemius Muscle Spasticity in Patients With Chronic Stroke. PM&R 2019, 11, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Park, H.D.; Han, S.H.; Shim, G.Y.; Choi, K.Y. Duration of Treatment Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave on Spasticity and Subgroup-Analysis According to Number of Shocks and Application Site: A Meta-Analysis. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 43, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, S. Which clinical studies provide the best evidence? The best RCT still trumps the best observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flansbjer, U.B.; Holmbback, A.M.; Downham, D.; Patten, C.; Lexell, J. Reli- ability of gait performance tests in men and women with hemiparesis after stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 2005, 37, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Q.; Ma, K.; Zheng, H.; Xie, L. A Novel Quantitative Spasticity Evaluation Method Based on Surface Electromyogram Signals and Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandyan, A.D.; Gregoric, M.; Barnes, M.P.; Wood, D.; Wijck, V.F.; Burridge, J.; Hermens, H.; Johnson, G.R. Spasticity: Clinical perceptions, neurological realities and meaningful measurement. Disabil. Rehabil. 2005, 27, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, B.P. Spasticity Measurement. Arch. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 55 (Suppl. S1), 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numanoglu, A.; Gunel, M.K. Intraobserver reliability of modified Ashworth scale and modified Tardieu scale in the assessment of spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2012, 46, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, J.H.; Wood, D.E.; Hermens, H.J.; Voerman, G.E.; Johnson, G.R.; Wijck, F.; Platz, T.; Gregoric, M.; Hitchcock, R.; Pandyan, A.D. Theoretical and methodological considerations in the measurement of spasticity. Disabil. Rehabil. 2005, 27, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, S.; Prati, A.C.; Cavalieri, E.; Amelio, E.; Marlinghaus, E.; Suzuki, H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: Molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, S.; Cavalieri, E.; Amelio, E.; Ciampa, A.R.; Prati, A.C.; Marlinghaus, E.; Russo, S.; Suzuki, H. Extracorporeal shock waves: From lithotripsy to anti-inflammatory action by NO production. Nitric Oxide 2005, 12, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, J.A.; Kukulka, C.G. Effects of tendon pressure on alpha motoneuron excitability in patients with stroke. Phys. Ther. 1988, 68, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamato, A.; Micello, M.F.; Panza, F.; Fortunato, F.; Logroscino, G.; Picelli, A.; Manganotti, P.; Smania, N.; Fiore, P.; Ranieri, M. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of poststroke plantar-flexor muscles spasticity: A prospective open-label study. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2014, 21, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, H.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.M. The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on spasticity in chronic stroke patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 34, 663–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.K.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Hwang, S.L. Spasticity and electrophysiologic changes after extracorporeal shock wave therapy on gastrocnemius. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 35, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, M.J.; Son, S.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, H.; Lee, E.H.; Yoon, C.H.; Oh, M.K. The Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Spasticity in Subacute Stroke Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 37, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, S.S.; Forogh, B.; Razavi, S.; Ahadi, T.; Madjlesi, F.; Ansari, N.N. A single blind, clinical trial to investigate the effects of a single session extracorporeal shock wave therapy on wrist flexor spasticity after stroke. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 36, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Du, L.; Shan, L.; Dong, H.; Feng, J.; Kiessling, M.C.; Angstman, B.A.; Schmitz, C.; Jia, F. A Prospective Case-Control Study of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Spastic Plantar Flexor Muscles in Very Young Children With Cerebral Palsy. Medicine 2016, 95, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, E.; Ekker, M.S.; Putaala, J.; Kittner, S.; De Leeuw, F.E.; Tuladhar, A.M. Ischaemic stroke in young adults: A global perspective. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
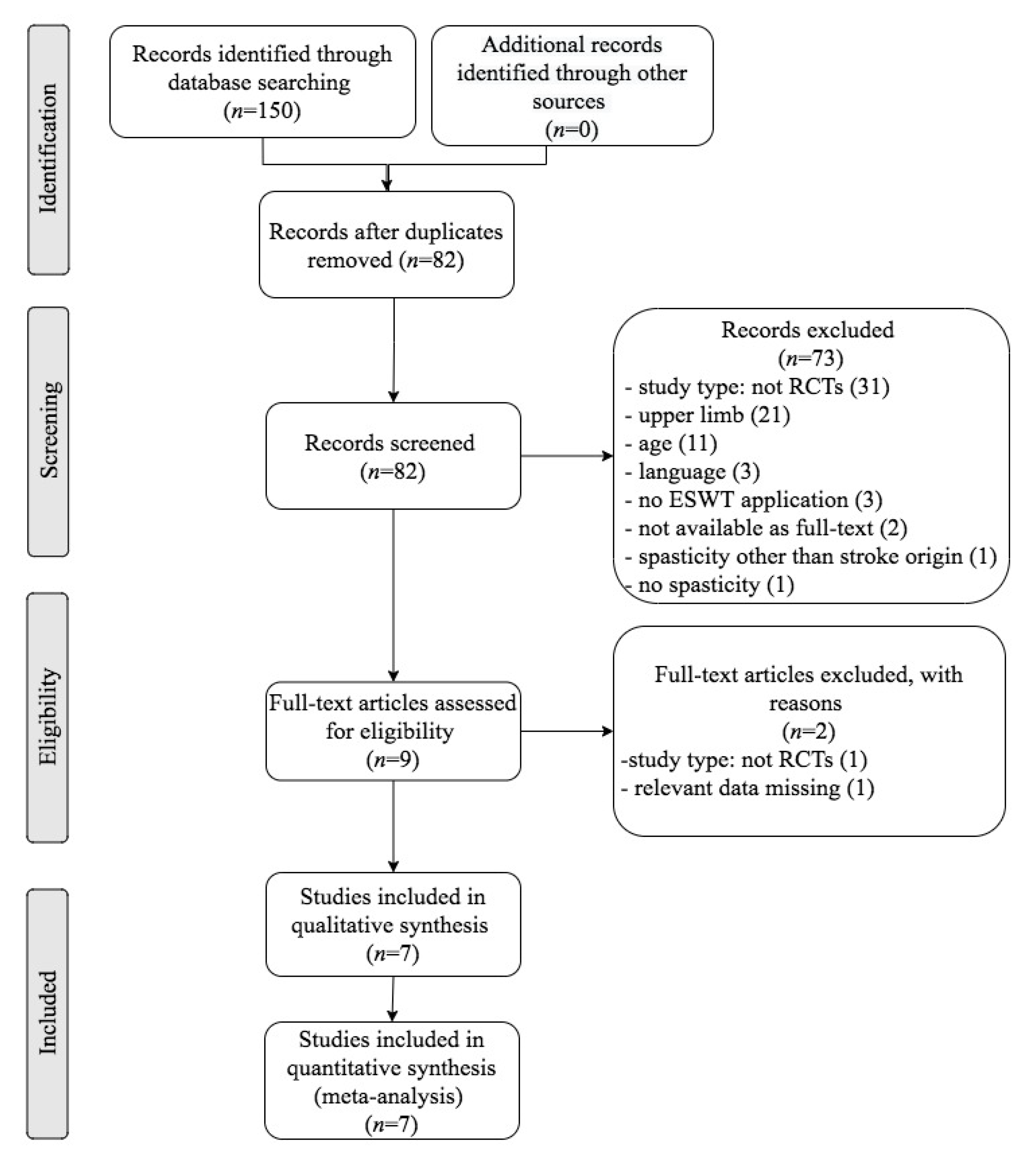
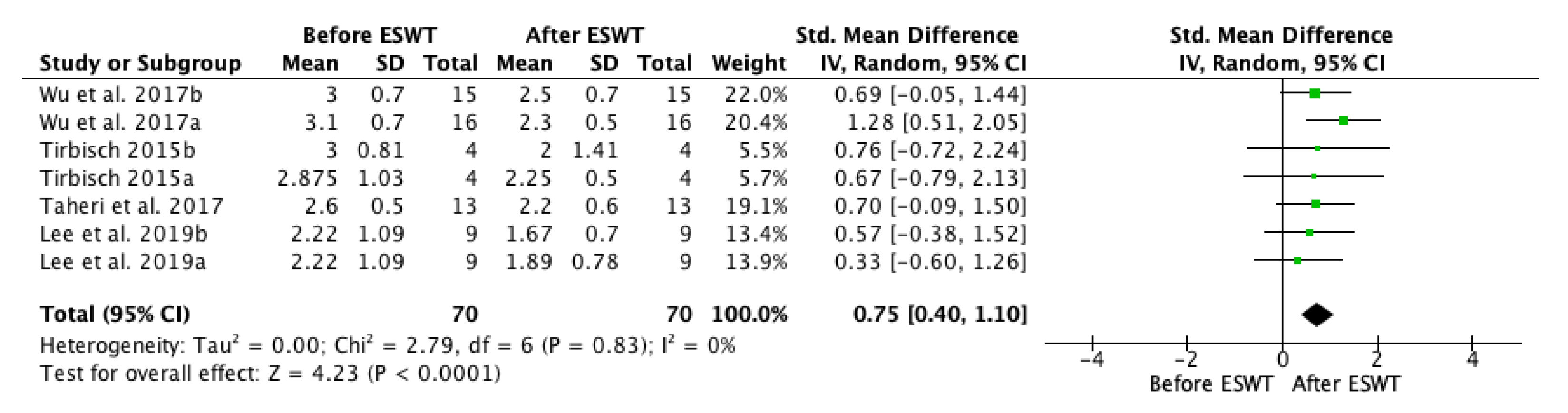
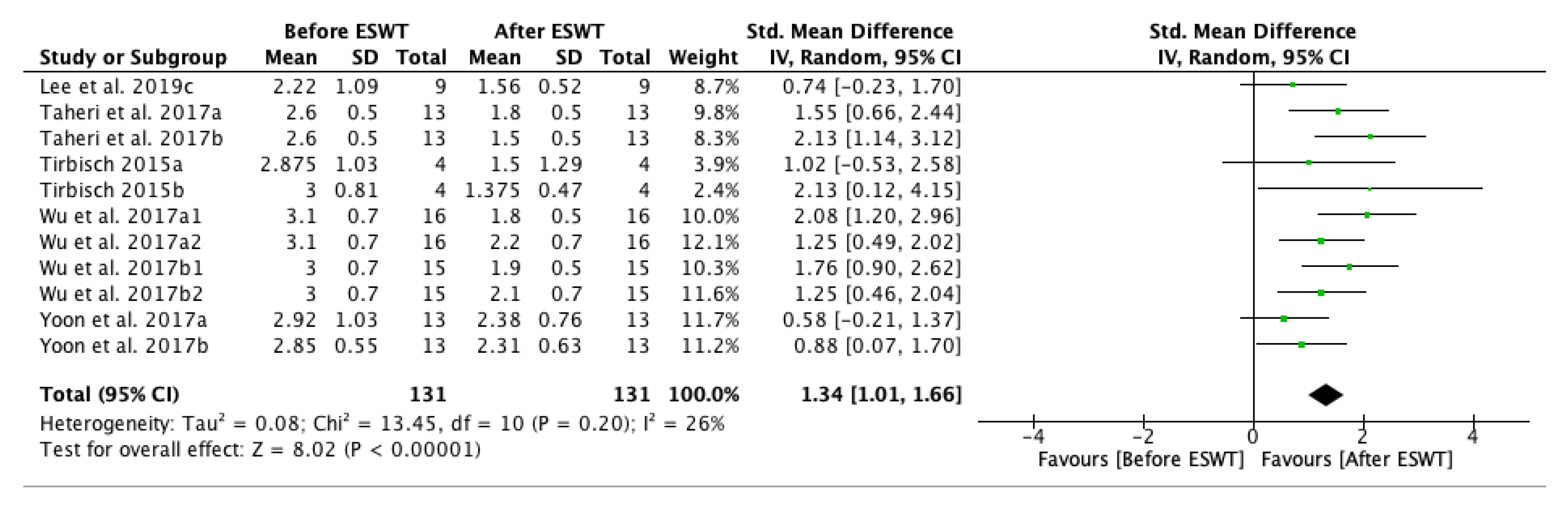
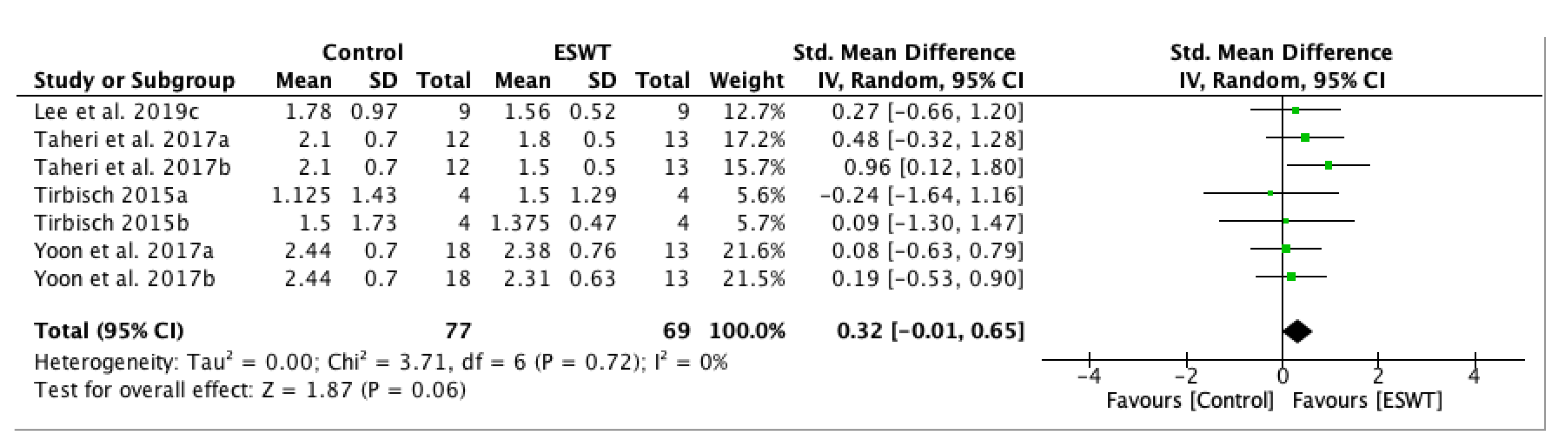
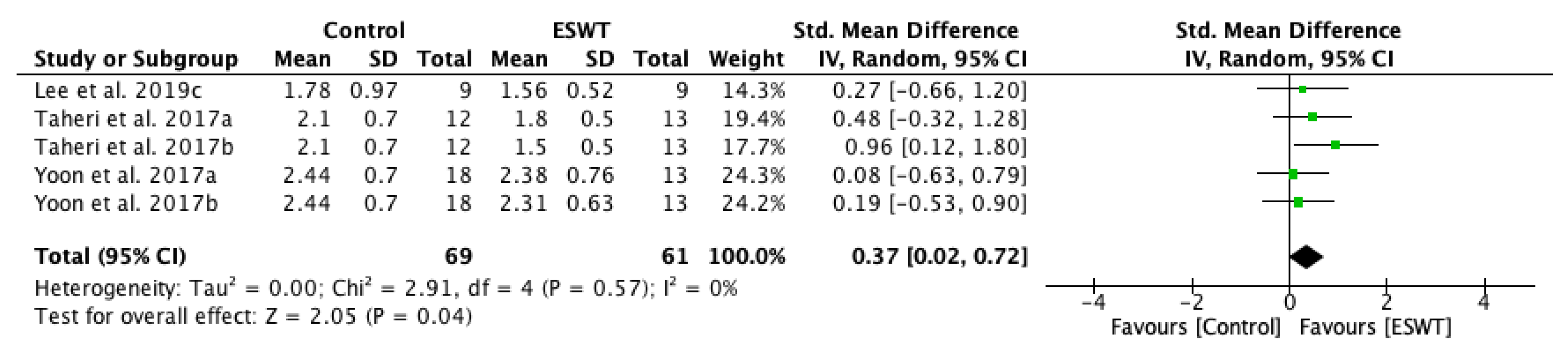
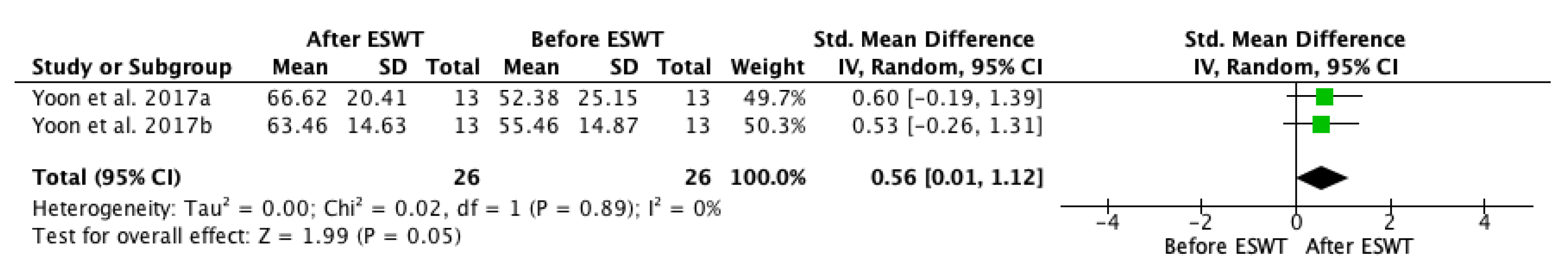
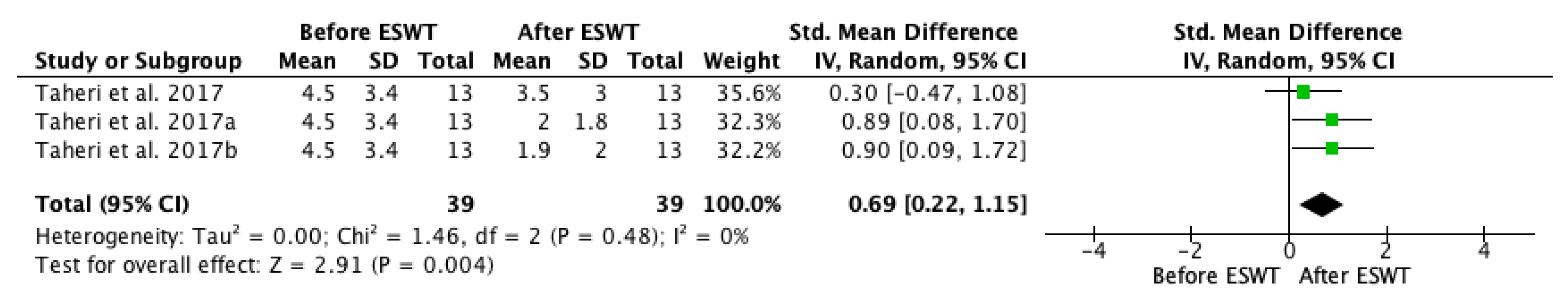
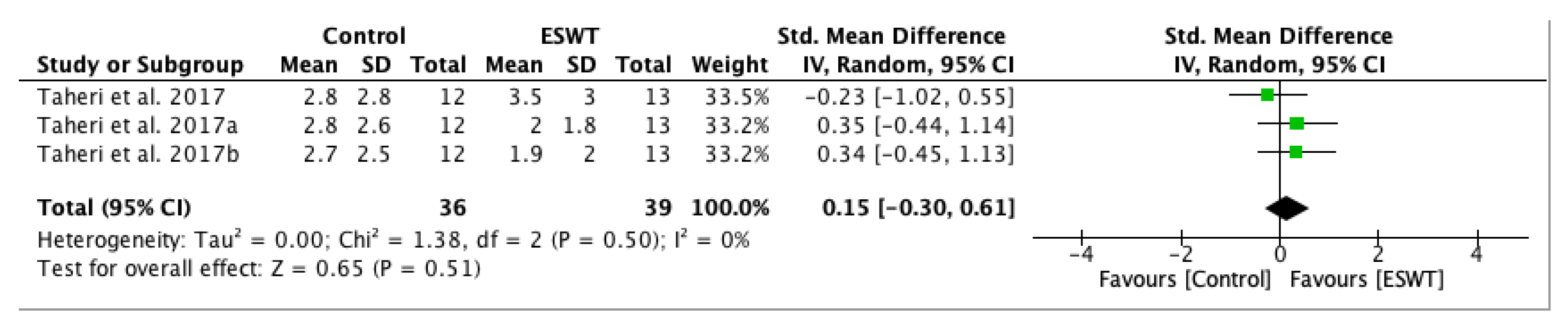
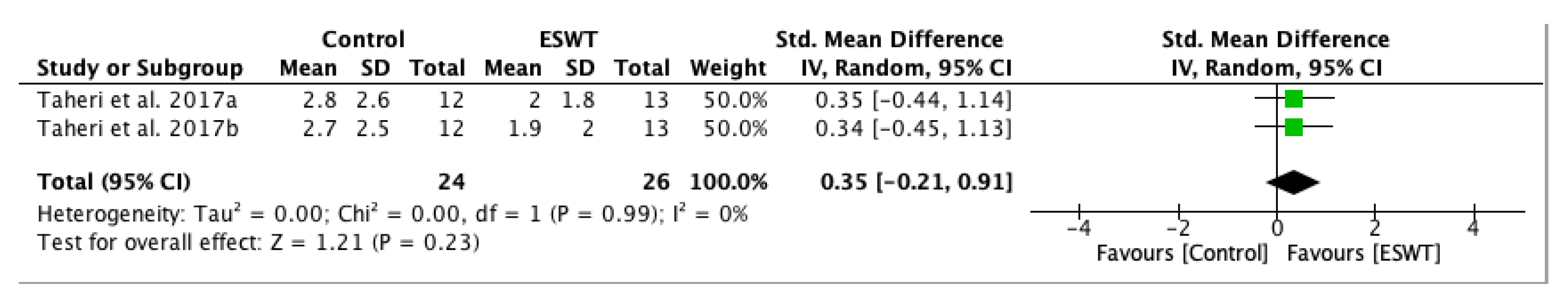

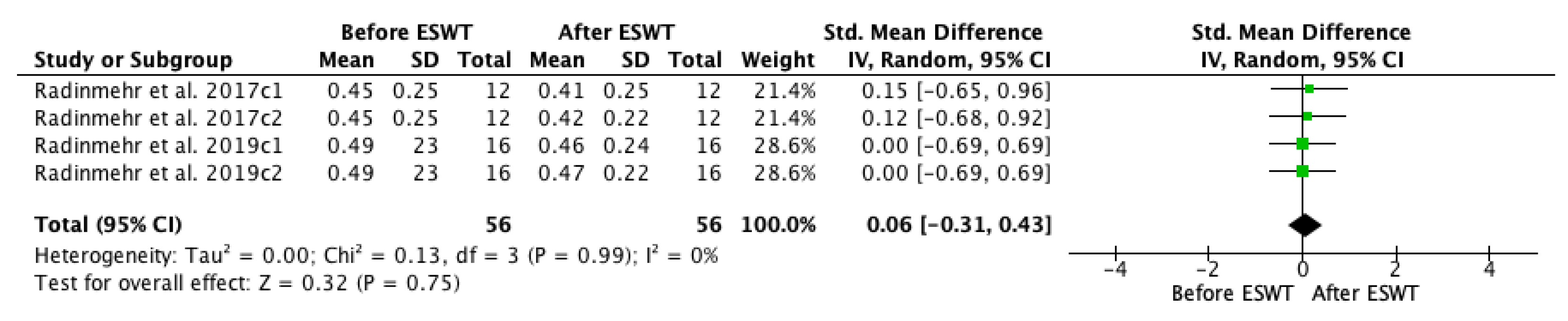
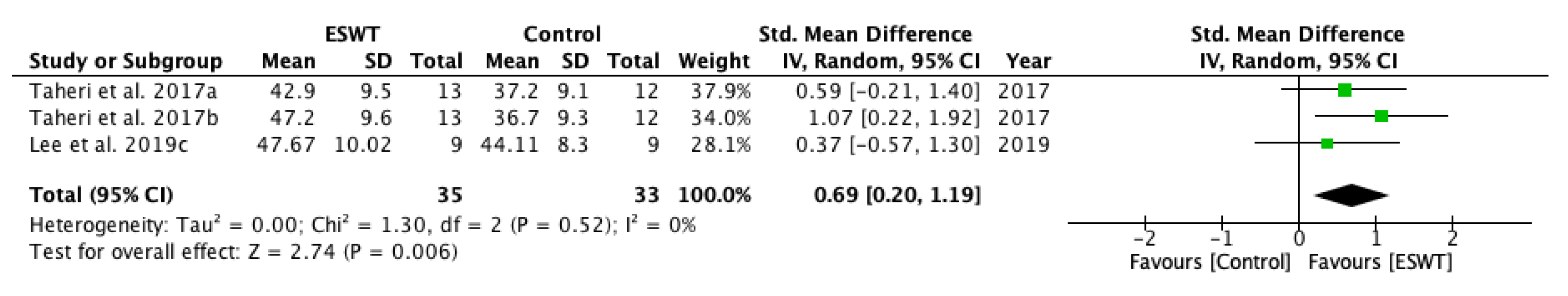
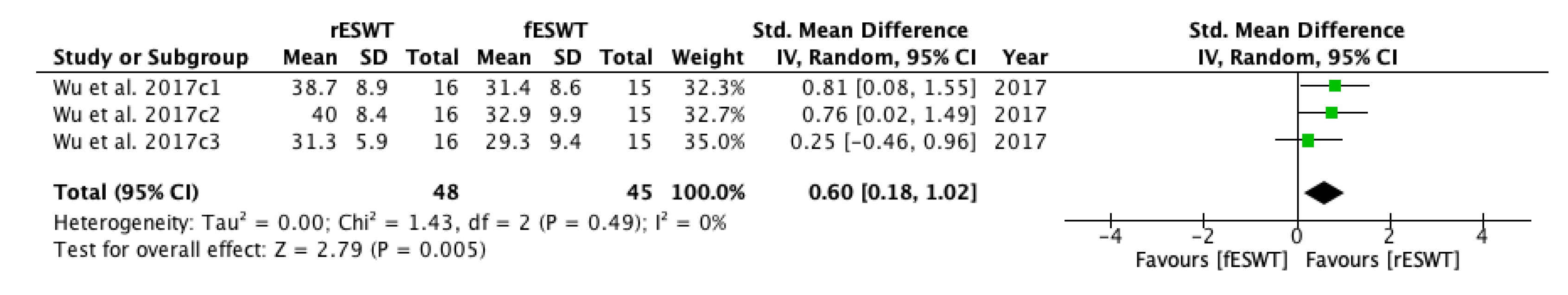
| Study | Country | Participants n (M/F) | Mean Age (Year) | Type of Stroke (Ischemic/Hemorrhagic) | Interventions | Time Since Onset Mean ± SD (Months) | Treated Muscle | Therapy Site | Sessions | Tested Muscles | Outcome Measures | Side Effects | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tirbisch [51] | France | 8 (3/5) | 49.5 ± 8.736 61.25 ± 11.116 | 3/1 3/1 | EG: rESWT+CP CG: CP | 3.97 ± 0.83 3.43 ± 1.63 | gastrocnemius muscle | myotendinous junction | 9 | soleus muscle gastrocnemius muscle | MAS, MTS | Pain | (initial) (after the 1st session) (at the end of the 9th session, week 3) |
| Taheri et al. [52] | Iran | 25 (17/8) | 56.5 ± 11.6 54.9 ± 9.4 | 11/2 11/1 | EG: fESWT+anti-spastic medications + stretching exercises CG: Anti-spastic medications + stretching exercises | 33 ± 21.4 25.8 ± 9.9 | gastrocnemius muscle | myotendinous junction | 3 | ankle plantar flexor | MAS, PROM, VAS Clonus score, 3-MWD, LEFS | NA | (baseline) (one week after treatment) (3 weeks after treatment) (12 weeks after treatment) |
| Yoon et al. [53] | Korea | 44 (42/2) | 61.0 ± 12.2 66.9 ± 4.9 59.5 ± 16.9 | NR | EG: Active ESWT muscle belly group active ESWT myotendinous junction group CG: sham ESWT, only sound over the muscle without any transducer contact | 99.1 ± 85.1 51.1 ± 36.0 38.7 ± 30.2 | semitendinosus muscle | muscle belly myotendinous junction | 3 | knee flexor | MAS, MTS | NA | (baseline) (1 week) (2 weeks) (3 weeks) |
| Wu et al. [32] | Taiwan | 31 (18/13) | 60.3 ± 9.9 59.6 ± 11.3 | 10/5 10/6 | EG: fESWT rESWT CG: NA | 53.2 ± 26.7 55.7 ± 26.1 | triceps surae muscle | muscle belly | 3 | gastrocnemius muscle | MAS, MTS, PROM, dynamic foot contact area, gait speed, AE | None | (prior to treatment) (one week after treatment) (4 weeks after treatment) (8 weeks after treatment) |
| Radinmehr et al. [54] | Iran | 12 (7/5) | 59.0 ± 13 | NR | EG: rESWT CG: NA | 34.3 ± 20.6 | plantar flexor muscle | gastrocnemius bulk | 1 | gastrocnemius muscle soleus muscle | ratio, H-reflex latency, Persian MMAS, AROM, PROM, PPFT, TUG Test | None | (baseline) (immediately after treatment) (one hour after the end of the treatment) |
| Lee et al. [55] | Korea | 18 (16/2) | 50.89 ± 8.81 44.11 ± 4.07 | 4/5 2/7 | EG: fESWT CG: sham stimulation | 12.89 ± 8.99 10.44 ± 9.11 | gastrocnemius muscle | medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle | 1 | gastrocnemius muscle | MAS, PROM, FMA, US measures: ATL, MFL, MT, PA | NA | (prior to treatment) (30 min after treatment) (1 week after treatment) (4 weeks after treatment) |
| Radinmehr et al. [33] | Iran | 32 (19/13) | 56.0 ± 12.3 56.2 ± 8.4 | NR | EG: rESWT US group: continuous ultrasound | 34.4 ± 20.5 36.8 ± 15.1 | gastrocnemius muscle | gastrocnemius bulk | 1 | knee flexors and knee extensors | Persian MMAS, AROM, PROM, PPFT, TUG Test, H-reflex test, ratio | NA | (baseline) (immediately after treatment) (1 h after the end of the treatment) |
| Items | Tirbisch (2015) | Taheri et al. (2017) | Yoon et al. (2017) | Wu et al. (2017) | Radinmehr et al. (2017) | Lee et al. (2019) | Radinmehr et al. (2019) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eligibility criteria were specified 1 | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Subjects were randomly allocated to groups | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Allocation concealment | yes | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no |
| Baseline comparability | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Blinding of all subjects | no | no | no | yes | no | yes | no |
| Blinding of all therapists | no | no | no | no | no | yes | no |
| Blinding of all assessors | yes | no | no | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Adequate outcome measures and follow-up | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Intention to treat analysis | yes | no | no | no | no | no | yes |
| Between-group statistical comparisons | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Point estimates and variability measures | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| PEDro score | 8 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 7 |
| Study | Number of Pulses/Shots | Energy/Pressure | Frequency (Hz) | Duration of Session |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tirbisch [51] | 2000 | 0.03 mJ/mm; 2.5 bar | 10 Hz | 15 min |
| Taheri et al. [52] | 1500 | 0.1 mJ/mm | 4 Hz | NA |
| Yoon et al. [53] | 1500 | 0.068–0.093 mJ/mm | 5 Hz | NA |
| Wu et al. [32] | 1500 | 0.10 mJ/mm; 2 bar | 5 Hz | NA |
| Radinmehr et al. [54] | 2000 | 0.34 mJ/mm; 60 mJ (1 bar) | 5 Hz | 7 min |
| Lee et al. [55] | 2000 | 0.1 mJ/mm | 4 Hz | NA |
| Radinmehr et al. [33] | 2000 | 0.34 mJ/mm; 60 mJ (1 bar) | 5 Hz | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihai, E.E.; Dumitru, L.; Mihai, I.V.; Berteanu, M. Long-Term Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Post-Stroke Spasticity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010086
Mihai EE, Dumitru L, Mihai IV, Berteanu M. Long-Term Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Post-Stroke Spasticity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(1):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010086
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihai, Emanuela Elena, Luminita Dumitru, Ilie Valentin Mihai, and Mihai Berteanu. 2021. "Long-Term Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Post-Stroke Spasticity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 1: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010086
APA StyleMihai, E. E., Dumitru, L., Mihai, I. V., & Berteanu, M. (2021). Long-Term Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Post-Stroke Spasticity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(1), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10010086





