Highly Conductive and Flexible Gel Polymer Electrolyte with Bis(Fluorosulfonyl)imide Lithium Salt via UV Curing for Li-Ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
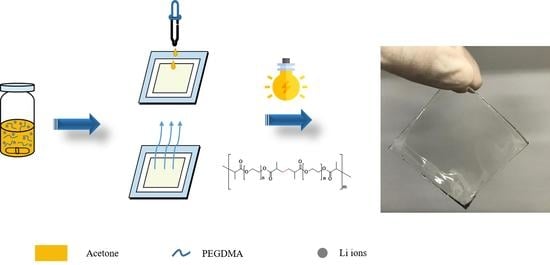
2.2. Fabrication of Self-Standing Gel Polymer Electrolytes
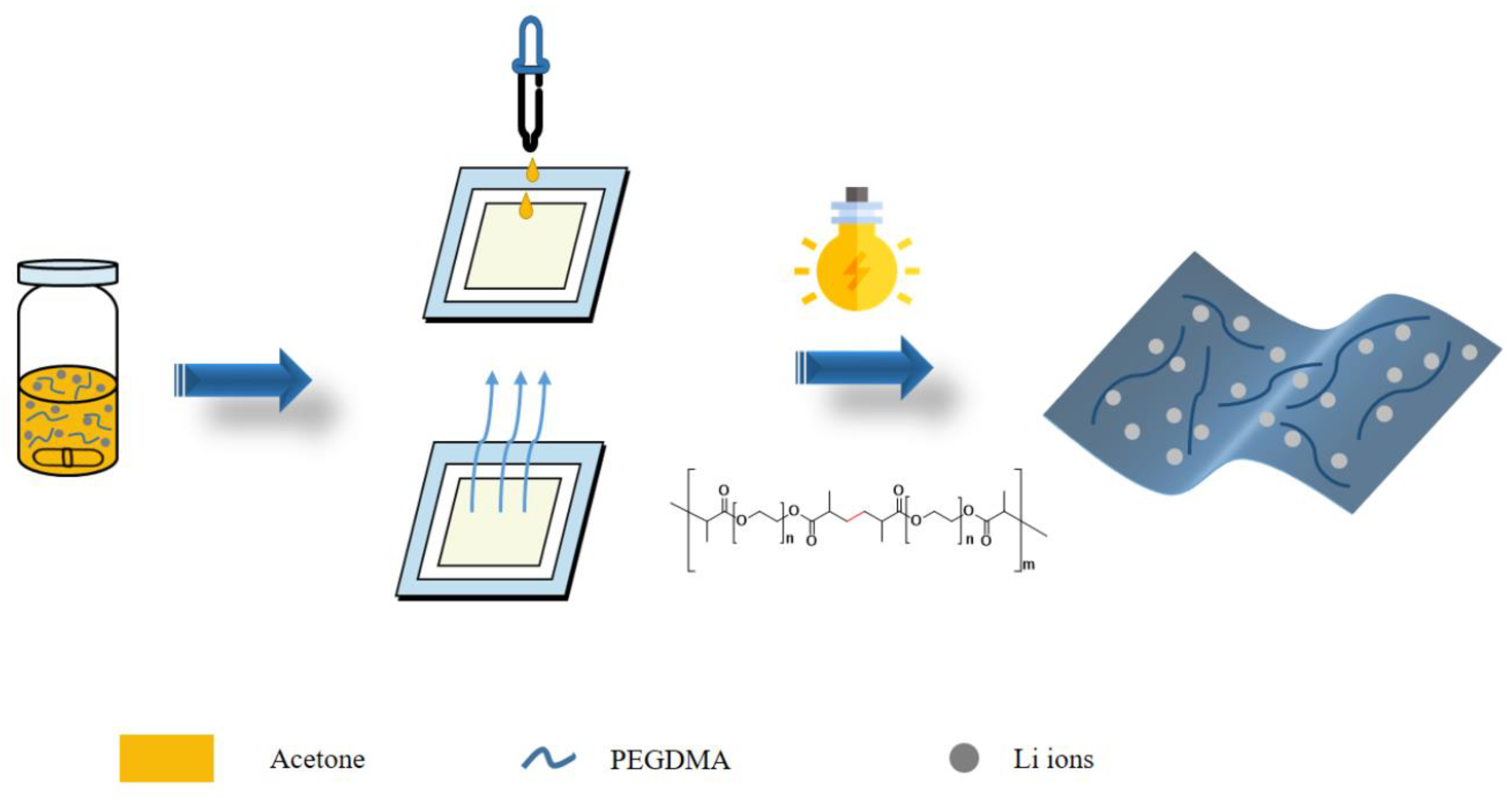
2.3. Characterization of Self-Standing Gel Polymer Electrolytes
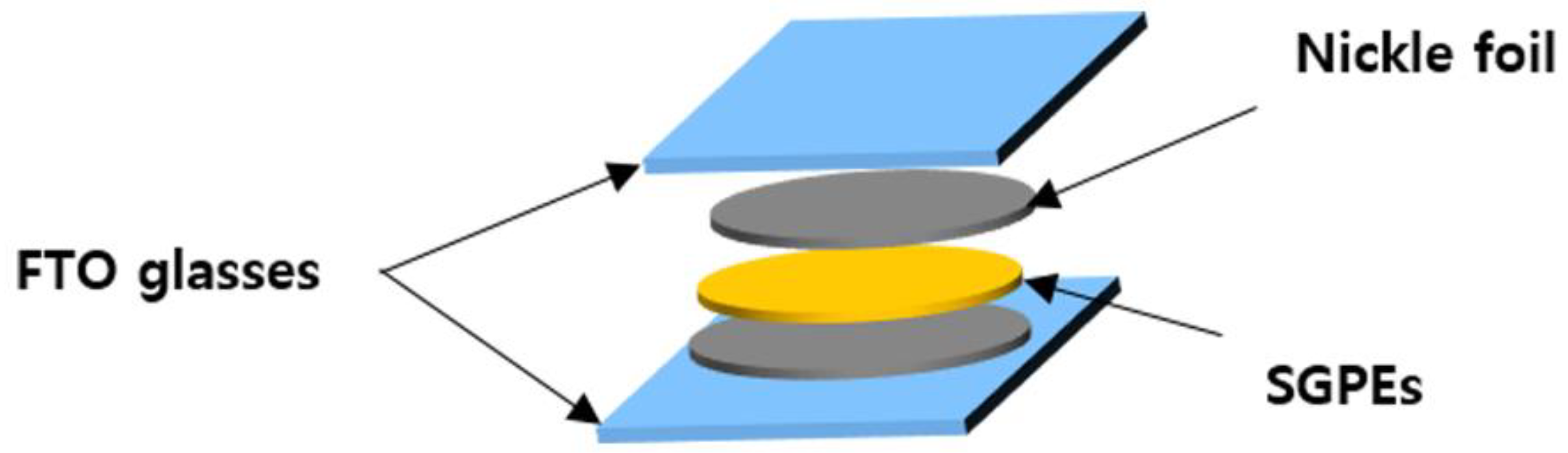
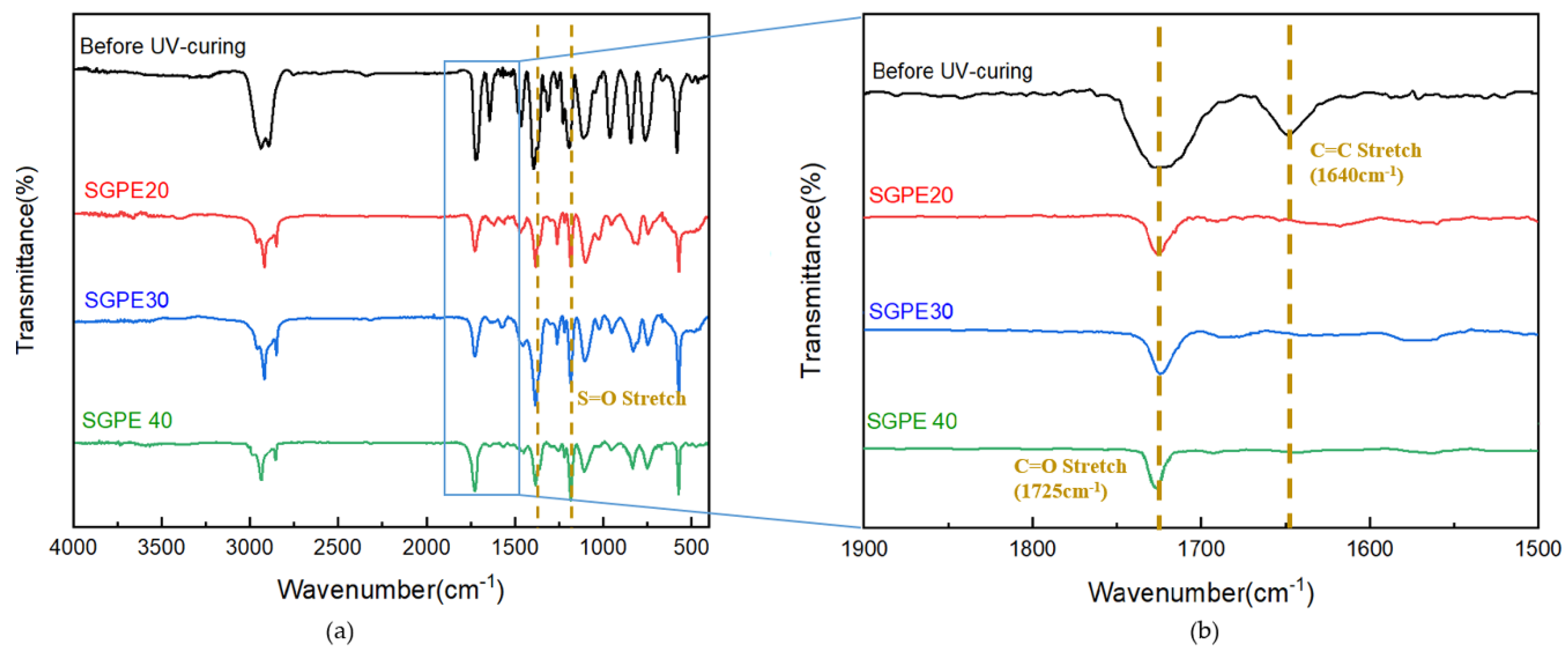
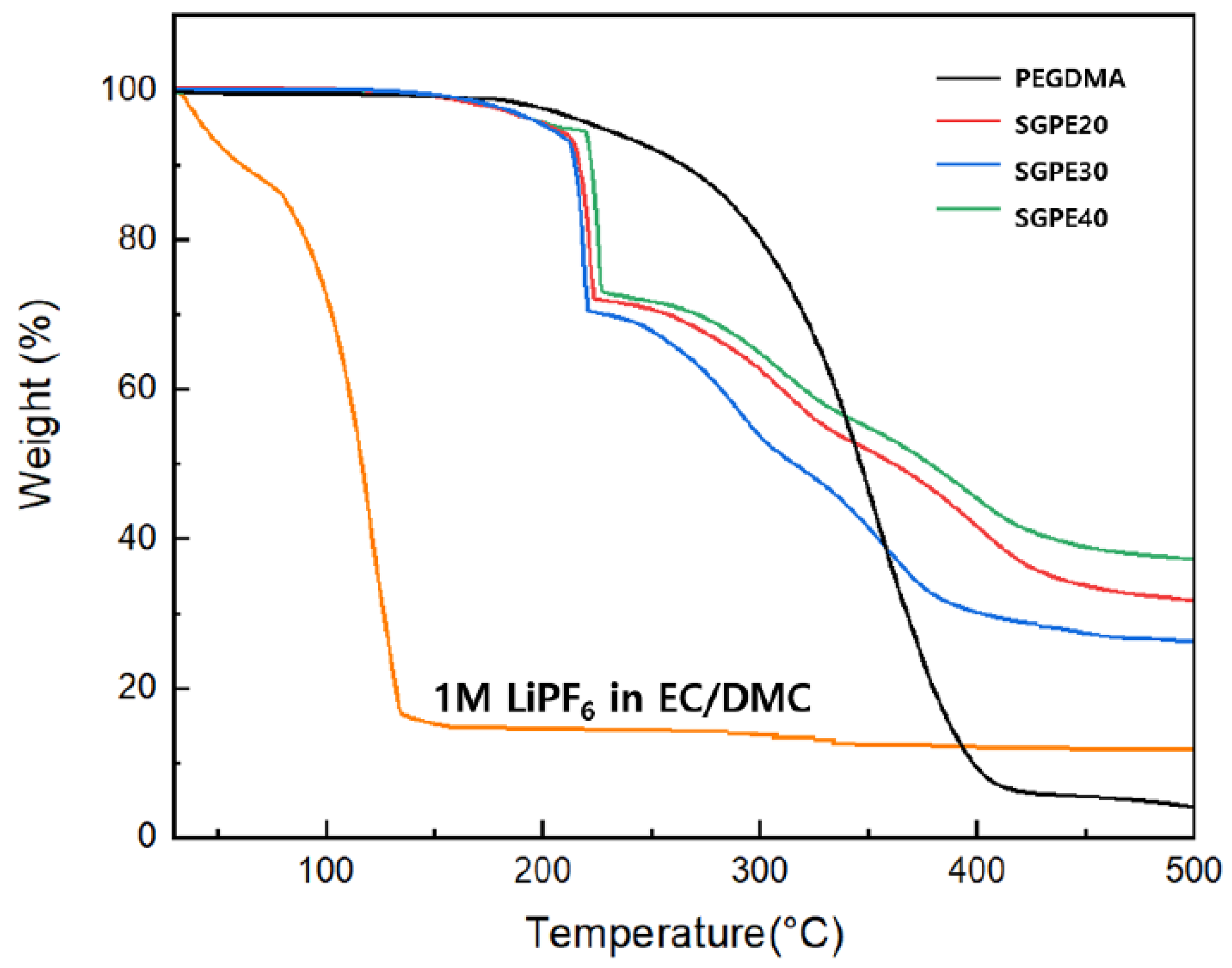
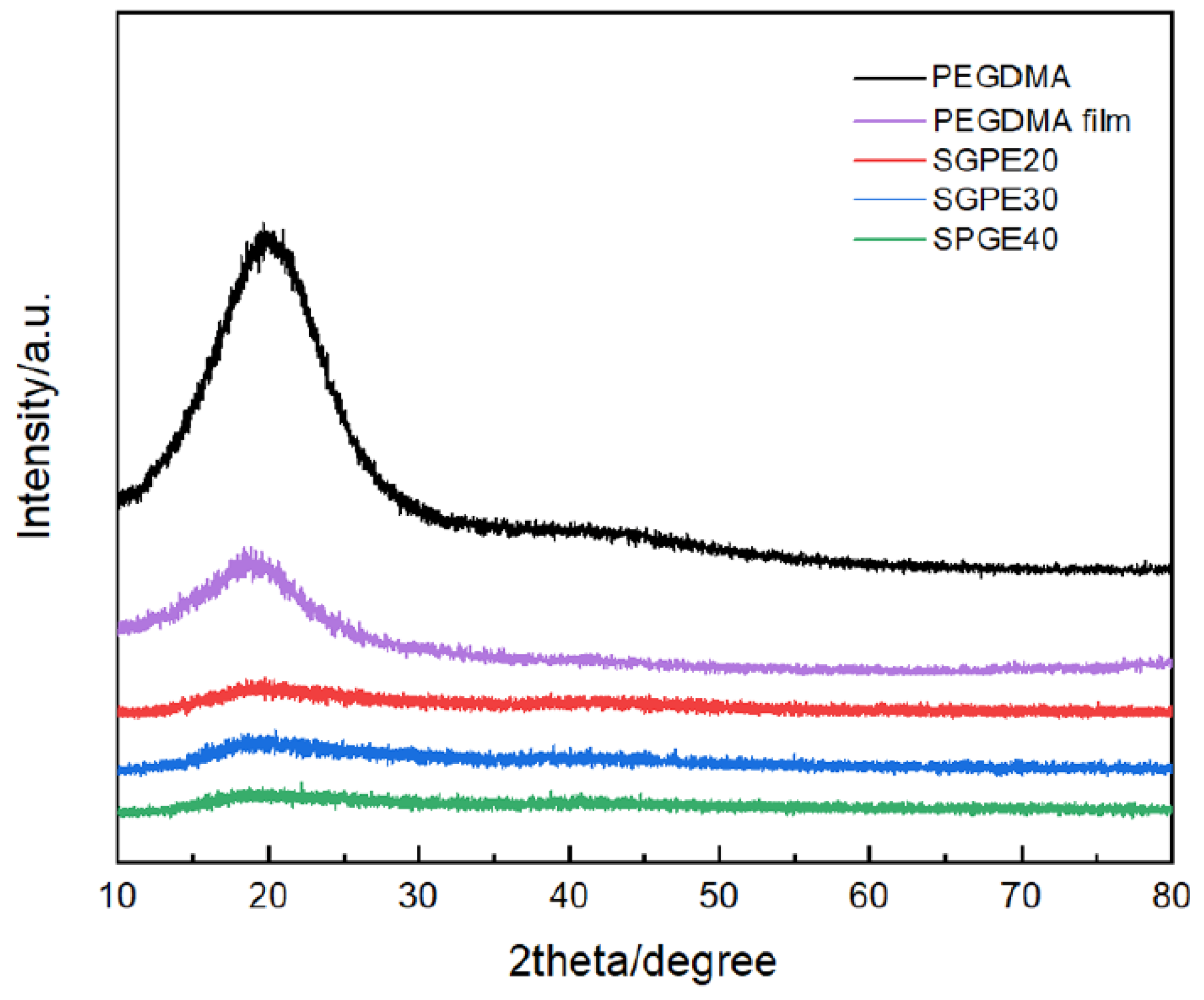
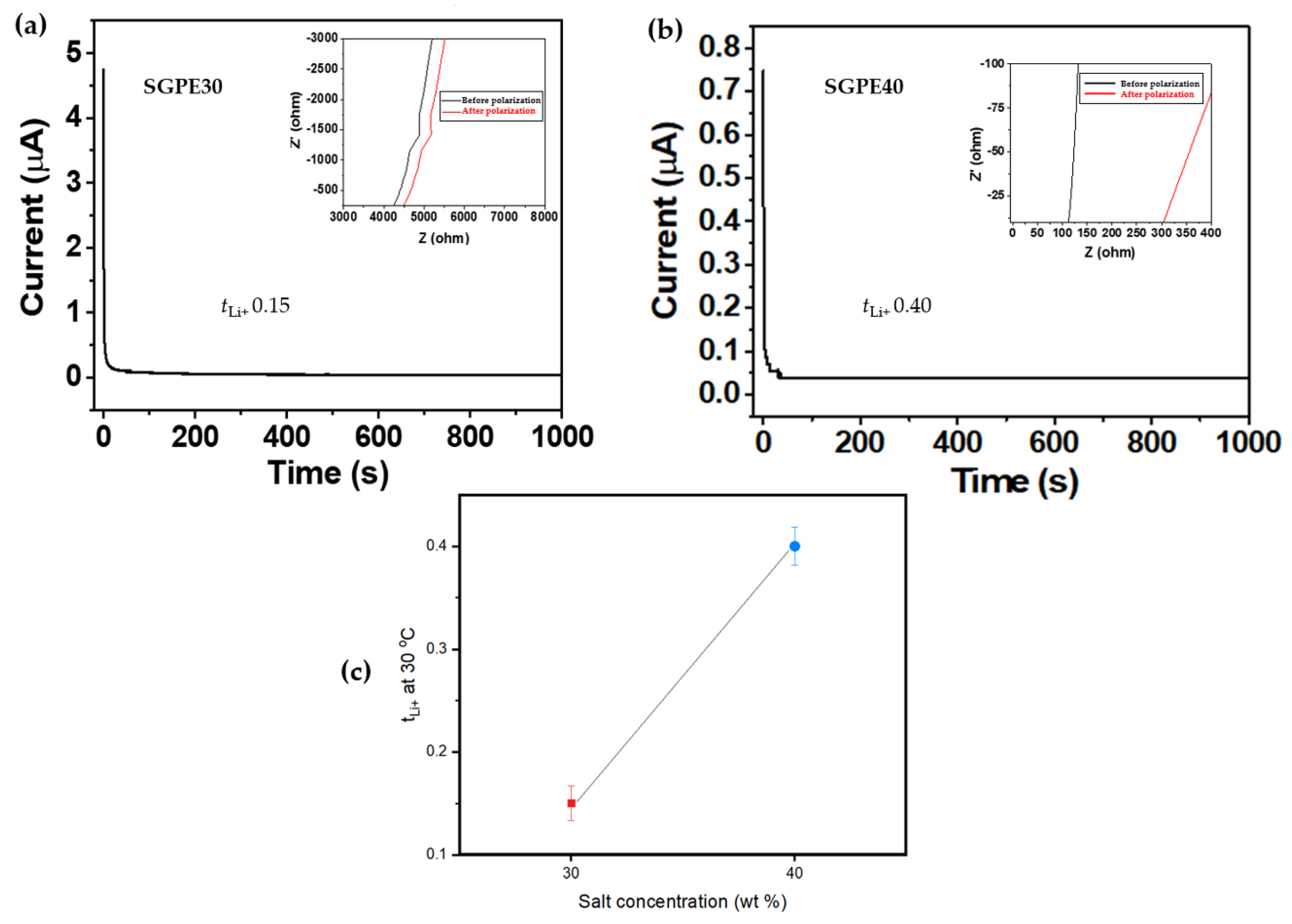
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Hussain, A.; Mohamed, A. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery State of Charge Estimation and Management System in Electric Vehicle Applications: Challenges and Recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Hua, J.; Ouyang, M. A Review on the Key Issues for Lithium-Ion Battery Management in Electric Vehicles. J. Power Sources 2013, 226, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, L.H.; Ye, Y.; Tay, A.A.O. Integration Issues of Lithium-Ion Battery into Electric Vehicles Battery Pack. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomgren, G.E. The Development and Future of Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A5019–A5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Nonaqueous Liquid Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Rechargeable Batteries Nonaqueous Liquid Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Rechargeable Batteries. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4303–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarascon, J.-M.; Armand, M. Issues and Challenges Facing Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Nature 2001, 414, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Thomas, M.L.; Zhang, S.; Ueno, K.; Yasuda, T.; Dokko, K. Application of Ionic Liquids to Energy Storage and Conversion Materials and Devices. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7190–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Qi, X.; He, Y.-B.; Li, B.; Yang, Q.-H.; Hu, Y.-S.; Kang, F. In Situ Synthesis of Hierarchical Poly(Ionic Liquid)-Based Solid Electrolytes for High-Safety Lithium-Ion and Sodium-Ion Batteries. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, H.W.; Harrup, M.K.; Dufek, E.J.; Jamison, D.K.; Sazhin, S.V.; Gering, K.L.; Daubaras, D.L. Fluorinated Phosphazene Co-Solvents for Improved Thermal and Safety Performance in Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2014, 263, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-H.; Su, H.-M.; Huang, H.-T.; Kuo, P.-L.; Teng, H. Immobilized Cation Functional Gel Polymer Electrolytes with High Lithium Transference Number for Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 572, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthiram, A.; Yu, X.; Wang, S. Lithium Battery Chemistries Enabled by Solid-State Electrolytes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16103:1–16103:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.K.; Gong, Y.; Dai, J.; Gong, A.; Han, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yan, C.; et al. Flexible, Solid-State, Ion-Conducting Membrane with 3D Garnet Nanofiber Networks for Lithium Batteries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7094–7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, R.; Schaefer, J.L.; Archer, L.A.; Coates, G.W. Suppression of Lithium Dendrite Growth Using Cross-Linked Polyethylene/Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Electrolytes: A New Approach for Practical Lithium-Metal Polymer Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7395–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wu, Z.; He, P.; Fan, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. A Self-Standing, UV-Cured Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Reinforced Composite Gel Electrolytes for Dendrite-Suppressing Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Mater. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, H.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z.; Shao, H.; Ding, F. Suppression of Lithium Dendrite Formation by Using LAGP-PEO (LiTFSI) Composite Solid Electrolyte and Lithium Metal Anode Modified by PEO (LiTFSI) in All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13694–13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, X.; Chai, J.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Q.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Feng, J. High Performance Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Rechargeable Batteries: A Self-Catalyzed Strategy toward Facile Synthesis. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel Stephan, A. Review on Gel Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher Bachman, J.; Muy, S.; Grimaud, A.; Chang, H.-H.; Pour, N.; Lux, S.F.; Paschos, O.; Maglia, F.; Lupart, S.; Lamp, P.; et al. Inorganic Solid-State Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries: Mechanisms and Properties Governing Ion Conduction. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mita, Y.; Seki, S.; Ohno, Y.; Miyashiro, H. Comparative Study of Lithium Secondary Batteries Using Nonvolatile Safety Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A677–A681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacin, M.R. Recent Advances in Rechargeable Battery Materials: A Chemist’s Perspective. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. All Solid-State Polymer Electrolytes for High-Performance Lithium Ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 5, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wan, C.C. Review of Gel-Type Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 1999, 77, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Gu, N.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, E.; Dong, S. Plasticizer Effect on the Ionic Conductivity of PEO-Based Polymer Electrolyte. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 74, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Echeverri, M.; Ward, D.; Zhu, Y.; Kyu, T. Highly Conductive Solvent-Free Polymer Electrolyte Membrane for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Effect of Prepolymer Molecular Weight. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 498, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, C. Kinetic Study and New Applications of UV Radiation Curing. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2002, 23, 1067–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.S. Photoinitiators for UV and Visible Curing of Coatings: Mechanisms and Properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1996, 100, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, D.; Xie, X. Poly(Ethylene Oxide)-Based Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19218–19253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, D.; Bouchet, R.; Glé, D.; Denoyel, R. Mechanism of Ion Transport in PEO/LiTFSI Complexes: Effect of Temperature, Molecular Weight and End Groups. Solid State Ionics 2012, 227, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-B.; Zhou, S.-S.; Zhang, D.-J.; Feng, S.-W.; Li, L.-F.; Liu, K.; Feng, W.-F.; Nie, J.; Li, H.; Huang, X.-J.; et al. Lithium Bis (Fluorosulfonyl) Imide (LiFSI) as Conducting Salt for Nonaqueous Liquid Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Physicochemical and Electrochemical Properties. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.J.; Long, G.K.; Liu, S.; Li, G.R.; Gao, X.P. A LiFSI-LiTFSI Binary-Salt Electrolyte to Achieve High Capacity and Cycle Stability for a Li-S Battery. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14647–14650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.; Park, K.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, H. Unraveling the Role of LiFSI Electrolyte in the Superior Performance of Graphite Anodes for Li-Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, B.; Dedryvère, R.; Gorgoi, M.; Rensmo, H.; Gonbeau, D.; Edström, K. Improved Performances of Nanosilicon Electrodes Using the Salt LiFSI: A Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9829–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L.; Xu, F.; Feng, W.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Armand, M.; Nie, J.; Zhou, Z. Lithium Bis (Fluorosulfonyl) Imide/Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Polymer Electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 133, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judez, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; González-Marcos, J.A.; Zhou, Z.; Armand, M.; Rodriguez-Martinez, L.M. Lithium Bis (Fluorosulfonyl) Imide/Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Polymer Electrolyte for All Solid-State Li-S Cell. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1956–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khateeb, S.A.; Amiruddin, S.; Farid, M.; Selman, J.R.; Al-Hallaj, S. Thermal Management of Li-Ion Battery with Phase Change Material for Electric Scooters: Experimental Validation. J. Power Sources 2005, 142, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizzani, C.; Gabrielli, G.; Mastragostino, M. Thermal Stability and Flammability of Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 4801–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Kyu, T. Effect of Plasticization on Ionic Conductivity Enhancement in Relation to Glass Transition Temperature of Crosslinked Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 5637–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Chai, J.; Duan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. Progress in Nitrile-Based Polymer Electrolytes for High Performance Lithium Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10070–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y. Ion-conductive polymer electrolytes based on poly (ethylene carbonate) and its derivatives. Polym. J. 2017, 49, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



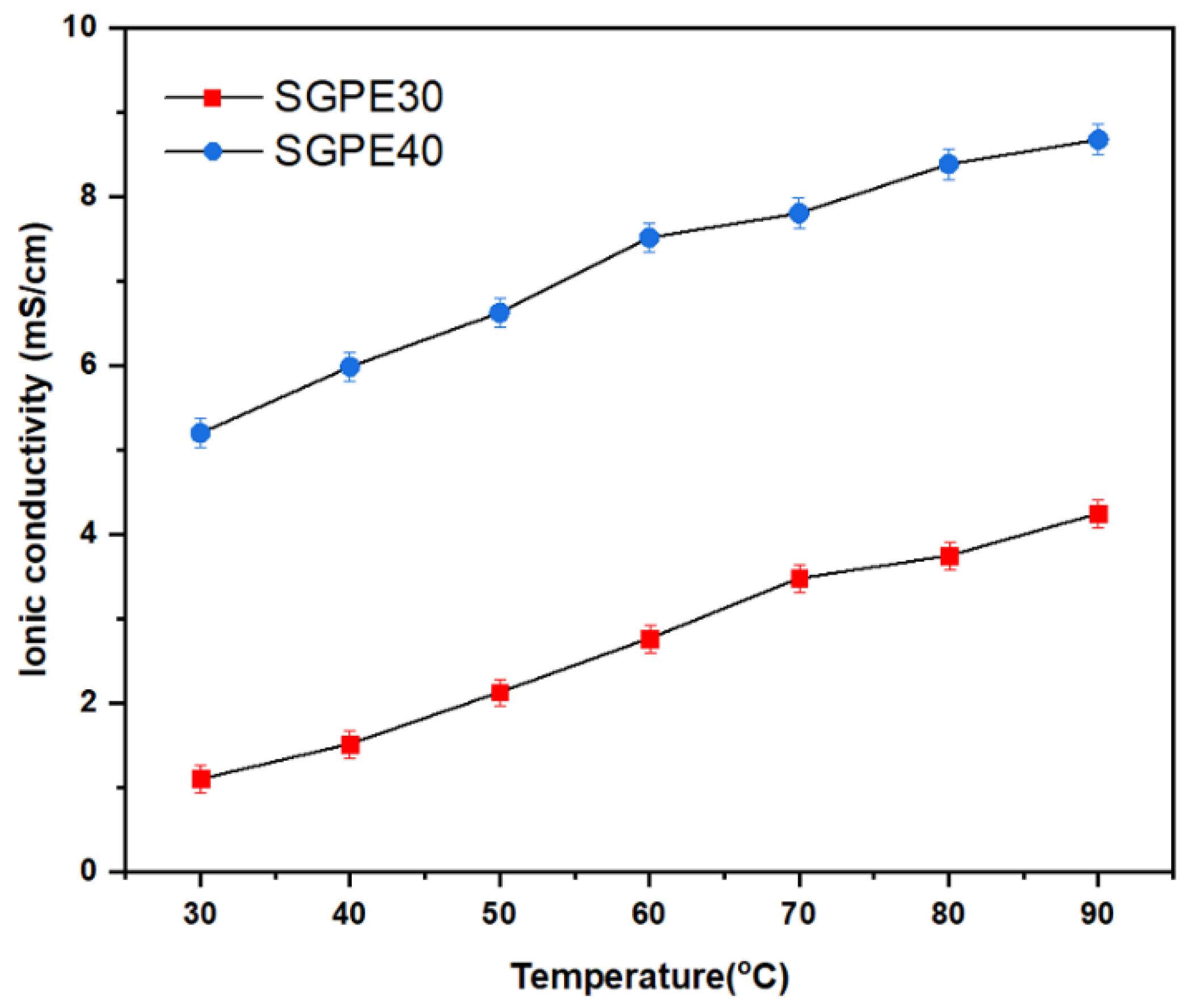
| Sample | 30 °C | 40 °C | 50 °C | 60 °C | 70 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGPE30 | 1.111 | 1.52 | 2.13 | 2.77 | 3.48 | 3.75 | 4.25 |
| SGPE40 | 5.21 | 5.99 | 6.63 | 7.52 | 7.81 | 8.39 | 8.38 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, L.; Ahmed, F.; Ryu, T.; Yoon, S.; Zhang, W.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Jang, H.; Kim, W. Highly Conductive and Flexible Gel Polymer Electrolyte with Bis(Fluorosulfonyl)imide Lithium Salt via UV Curing for Li-Ion Batteries. Membranes 2019, 9, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110139
Jin L, Ahmed F, Ryu T, Yoon S, Zhang W, Lee Y, Kim D, Jang H, Kim W. Highly Conductive and Flexible Gel Polymer Electrolyte with Bis(Fluorosulfonyl)imide Lithium Salt via UV Curing for Li-Ion Batteries. Membranes. 2019; 9(11):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110139
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Lei, Faiz Ahmed, Taewook Ryu, Sujin Yoon, Wei Zhang, Yonghoon Lee, Daeho Kim, Hohyoun Jang, and Whangi Kim. 2019. "Highly Conductive and Flexible Gel Polymer Electrolyte with Bis(Fluorosulfonyl)imide Lithium Salt via UV Curing for Li-Ion Batteries" Membranes 9, no. 11: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110139
APA StyleJin, L., Ahmed, F., Ryu, T., Yoon, S., Zhang, W., Lee, Y., Kim, D., Jang, H., & Kim, W. (2019). Highly Conductive and Flexible Gel Polymer Electrolyte with Bis(Fluorosulfonyl)imide Lithium Salt via UV Curing for Li-Ion Batteries. Membranes, 9(11), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110139