Fabrication and Evaluation of Trimethylmethoxysilane (TMMOS)-Derived Membranes for Gas Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
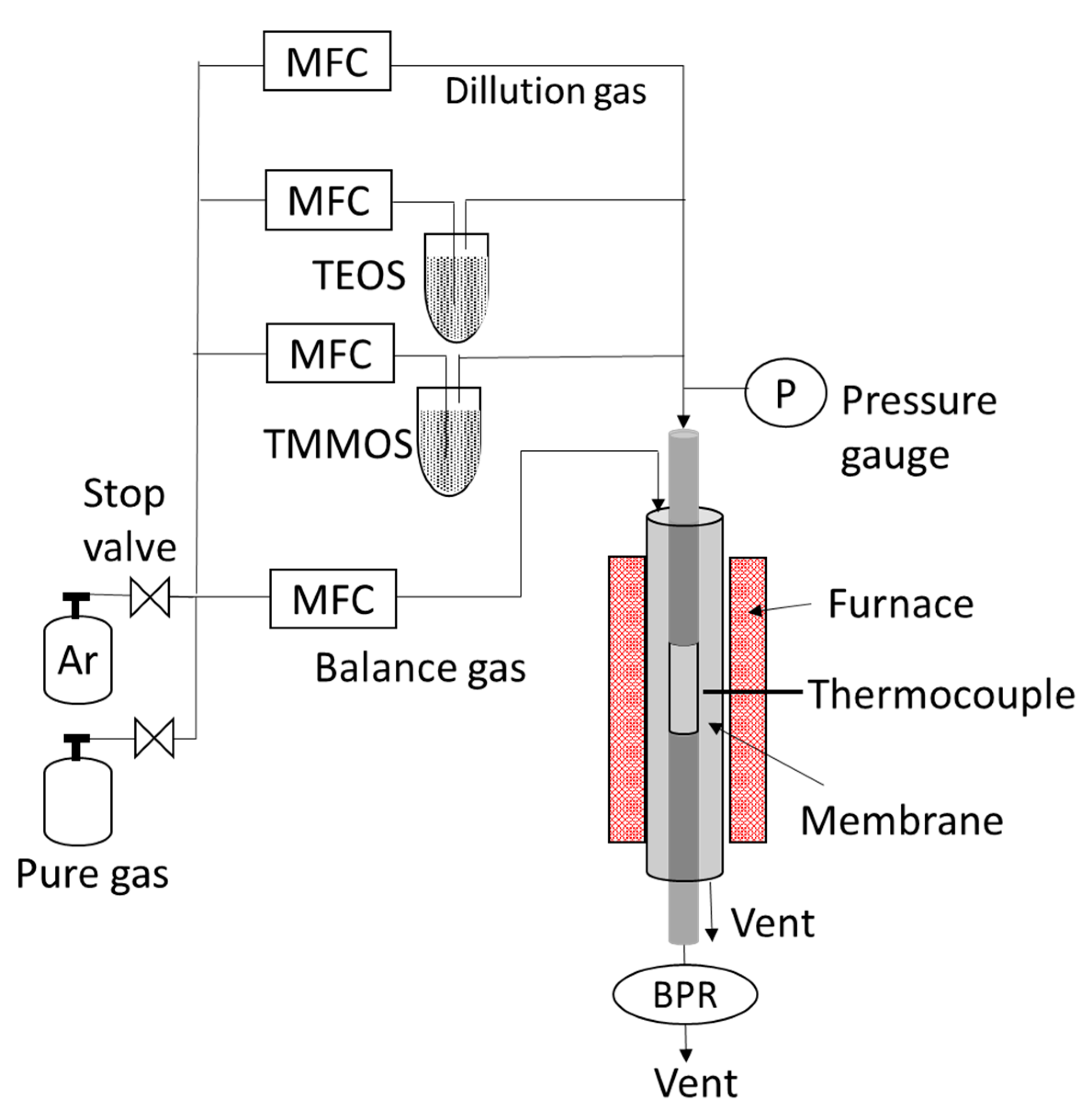
2.1. Preparation of Membranes
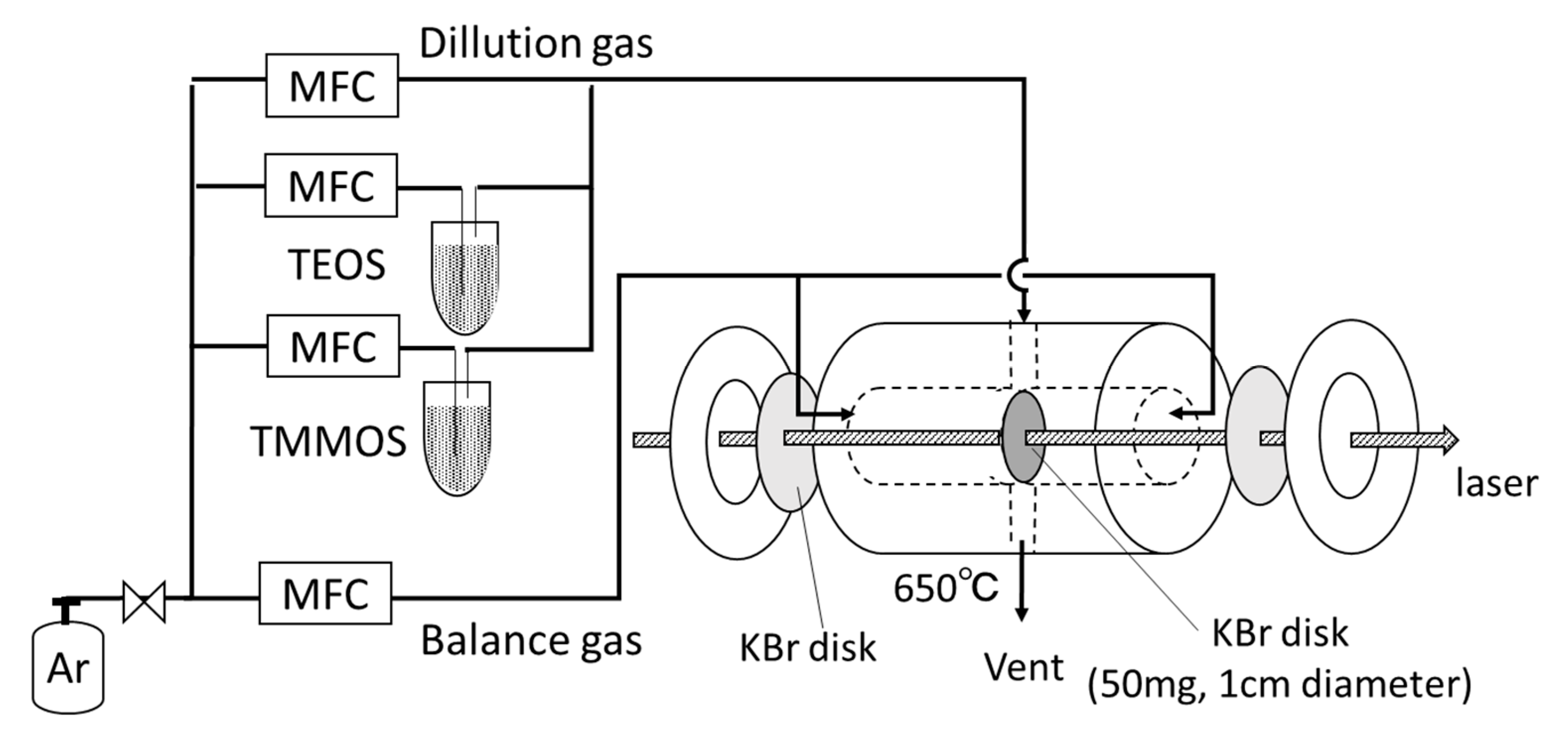
2.2. Characterizations
2.3. Permeance Measurements
2.4. Hydrothermal Stability Tests
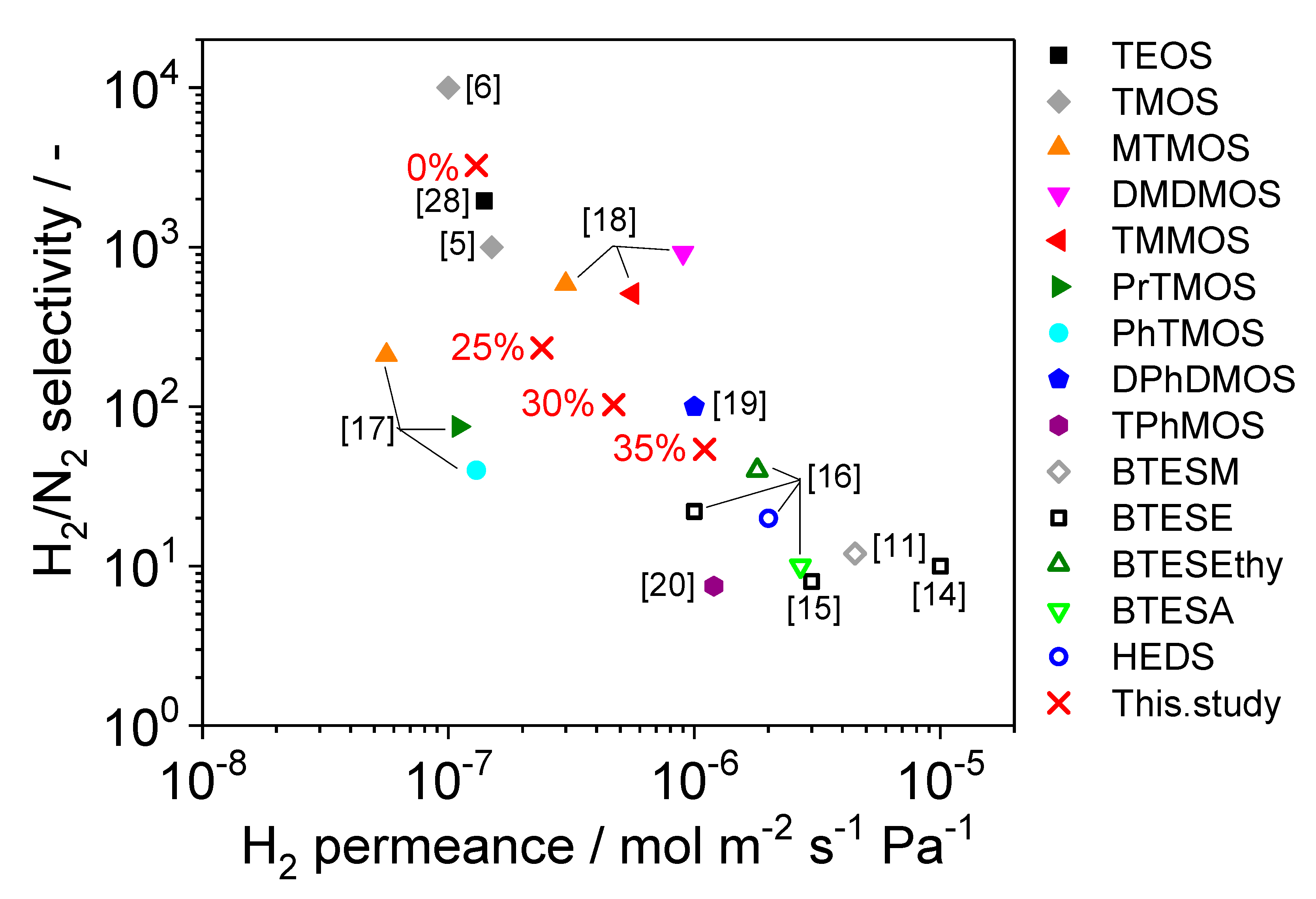
3. Results and Discussion
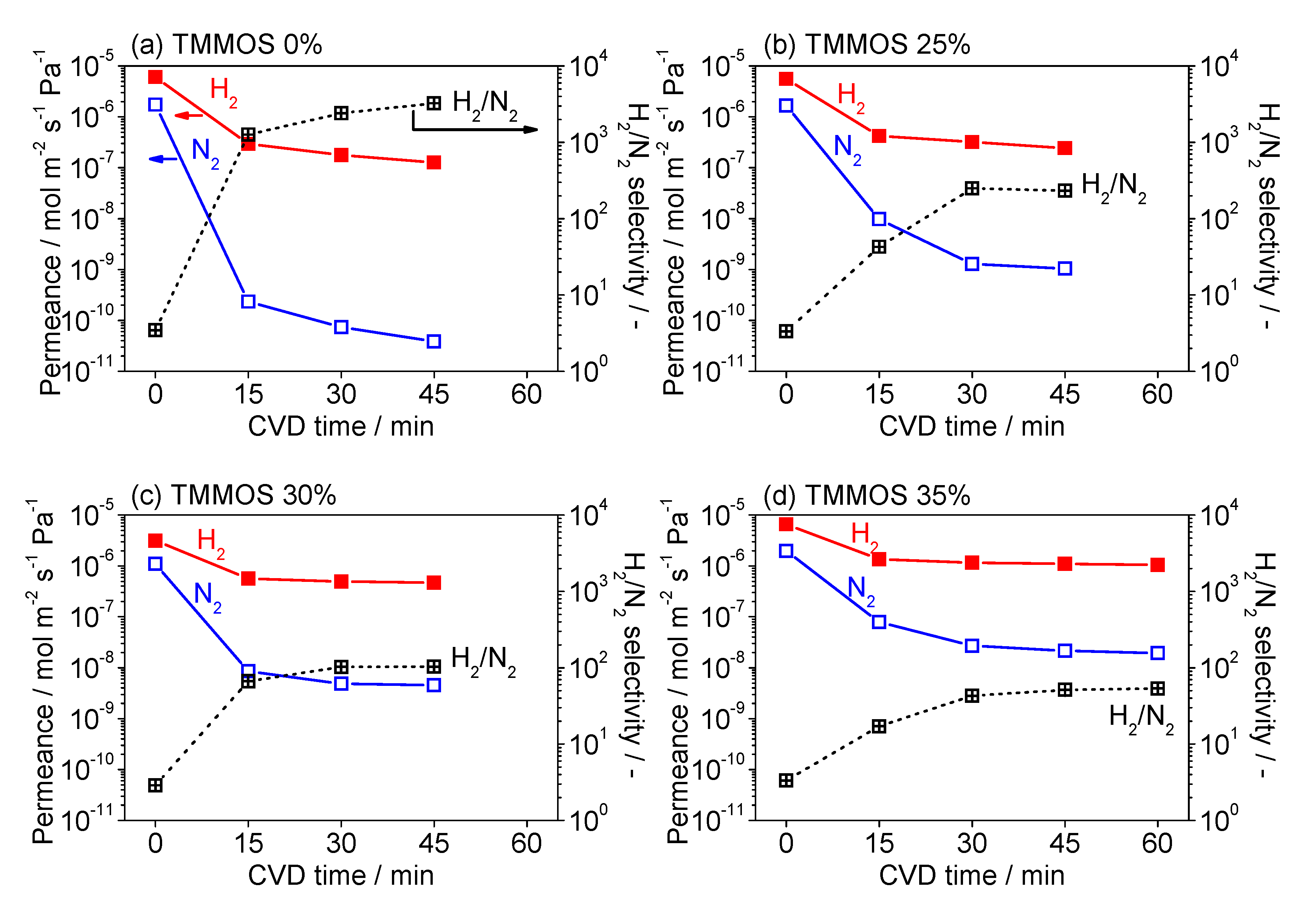
3.1. Fabrication of TMMOS-Derived Membranes
3.2. Characterization
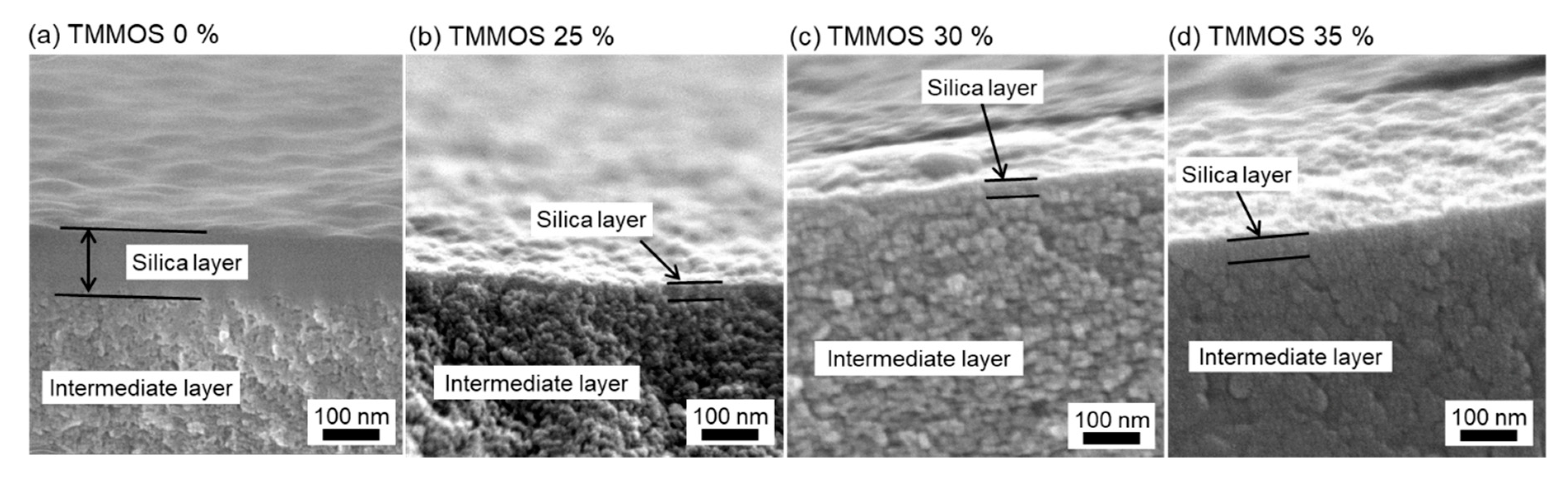
3.2.1. SEM Images
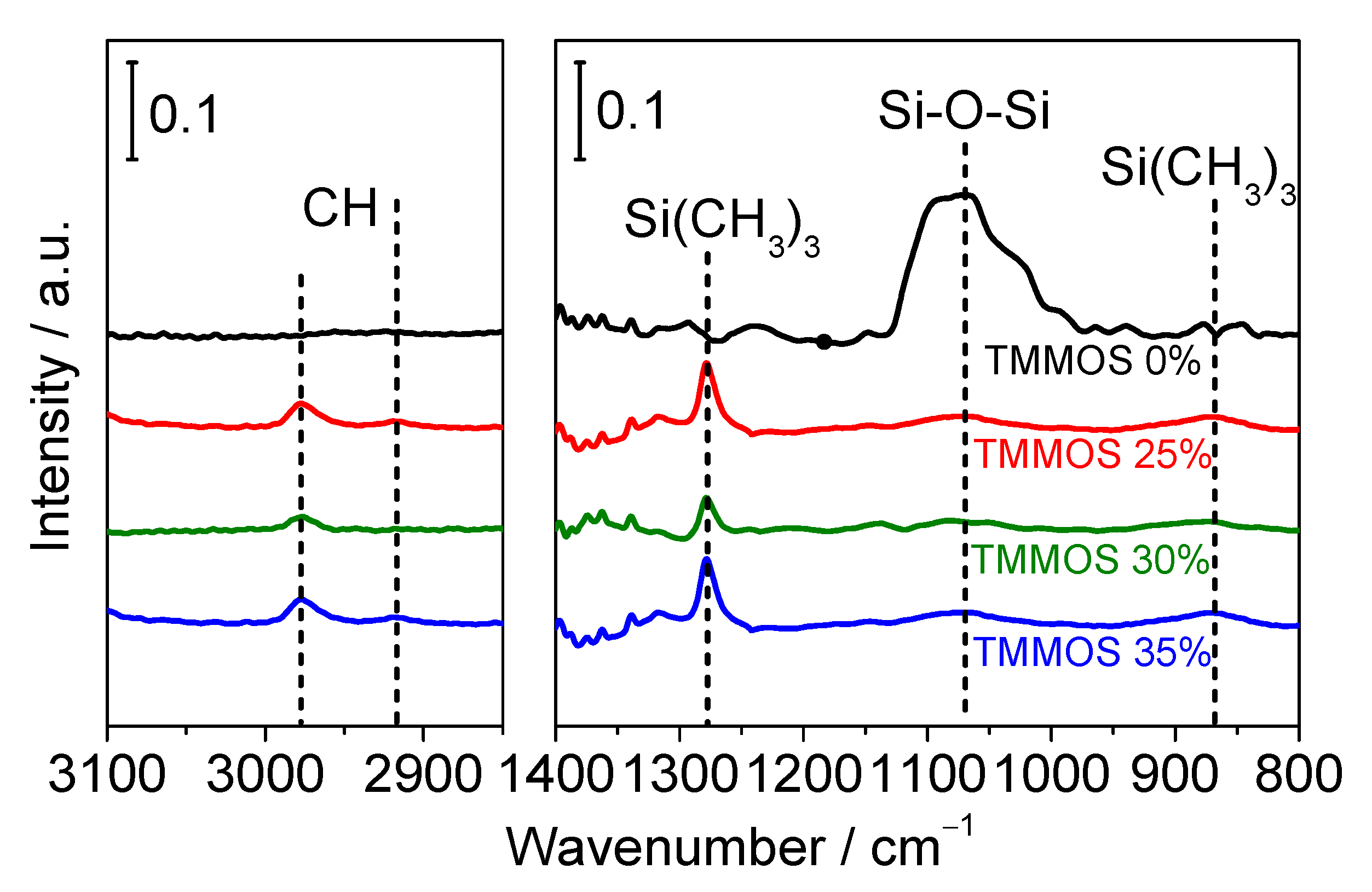
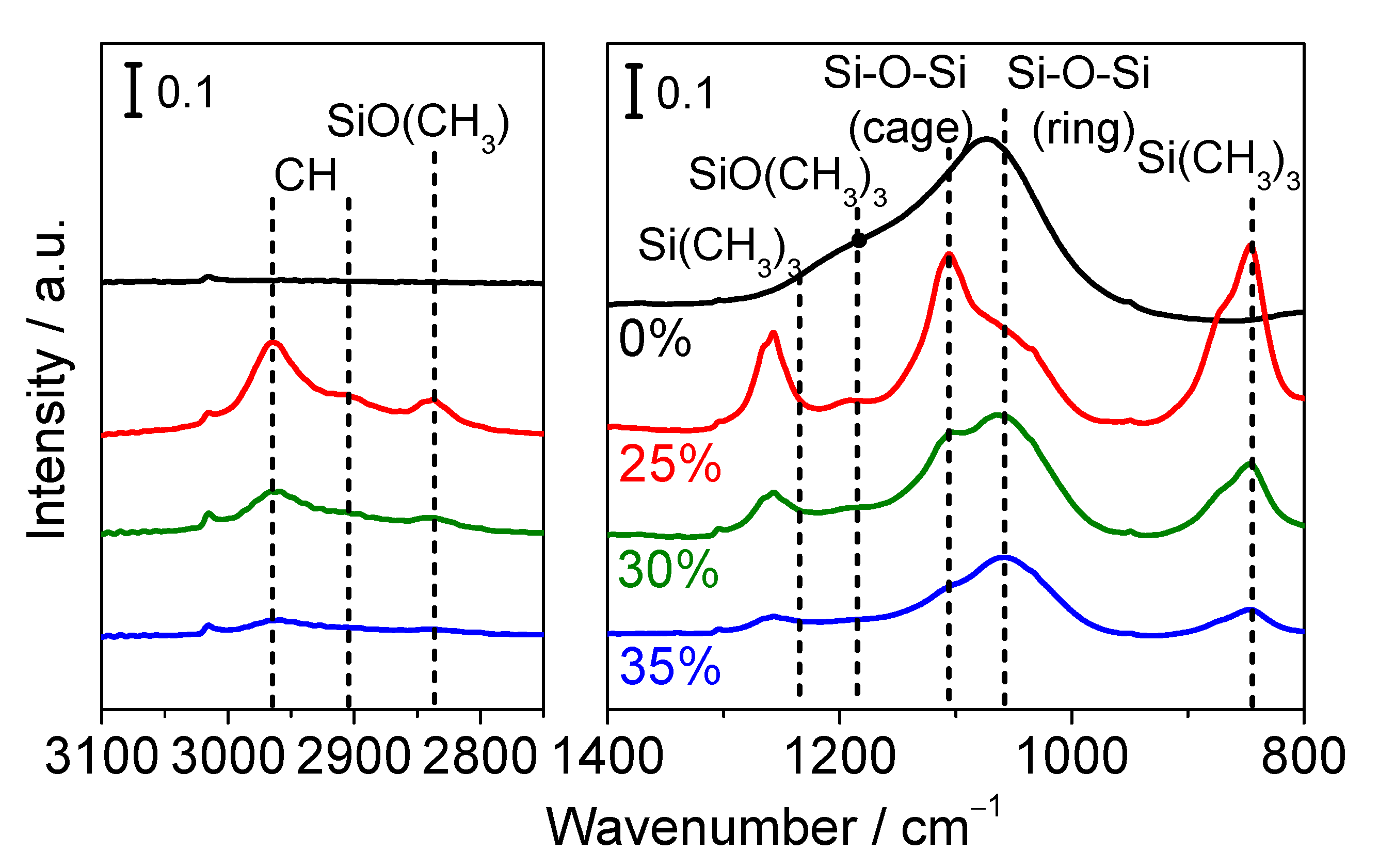
3.2.2. FTIR Measurements
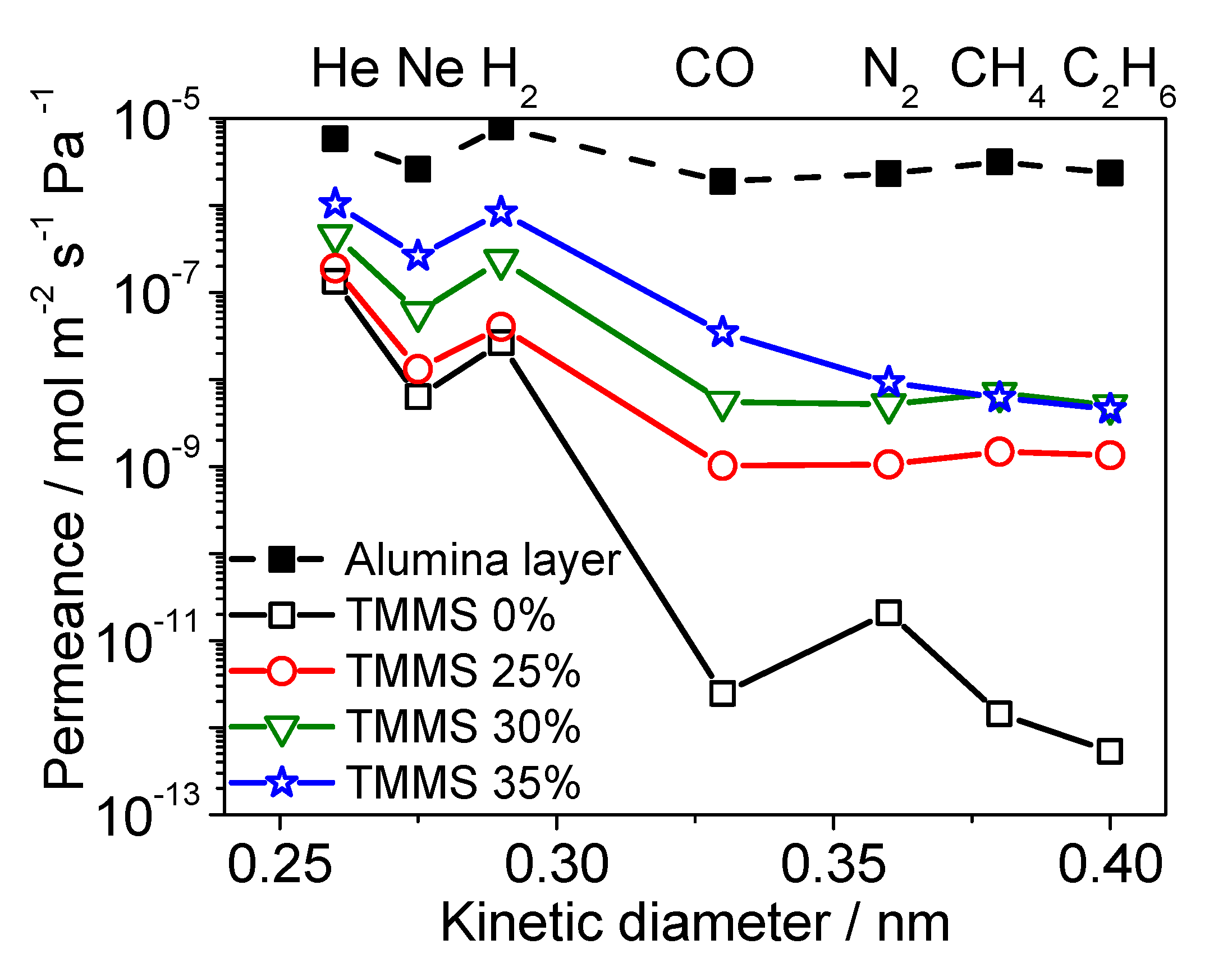
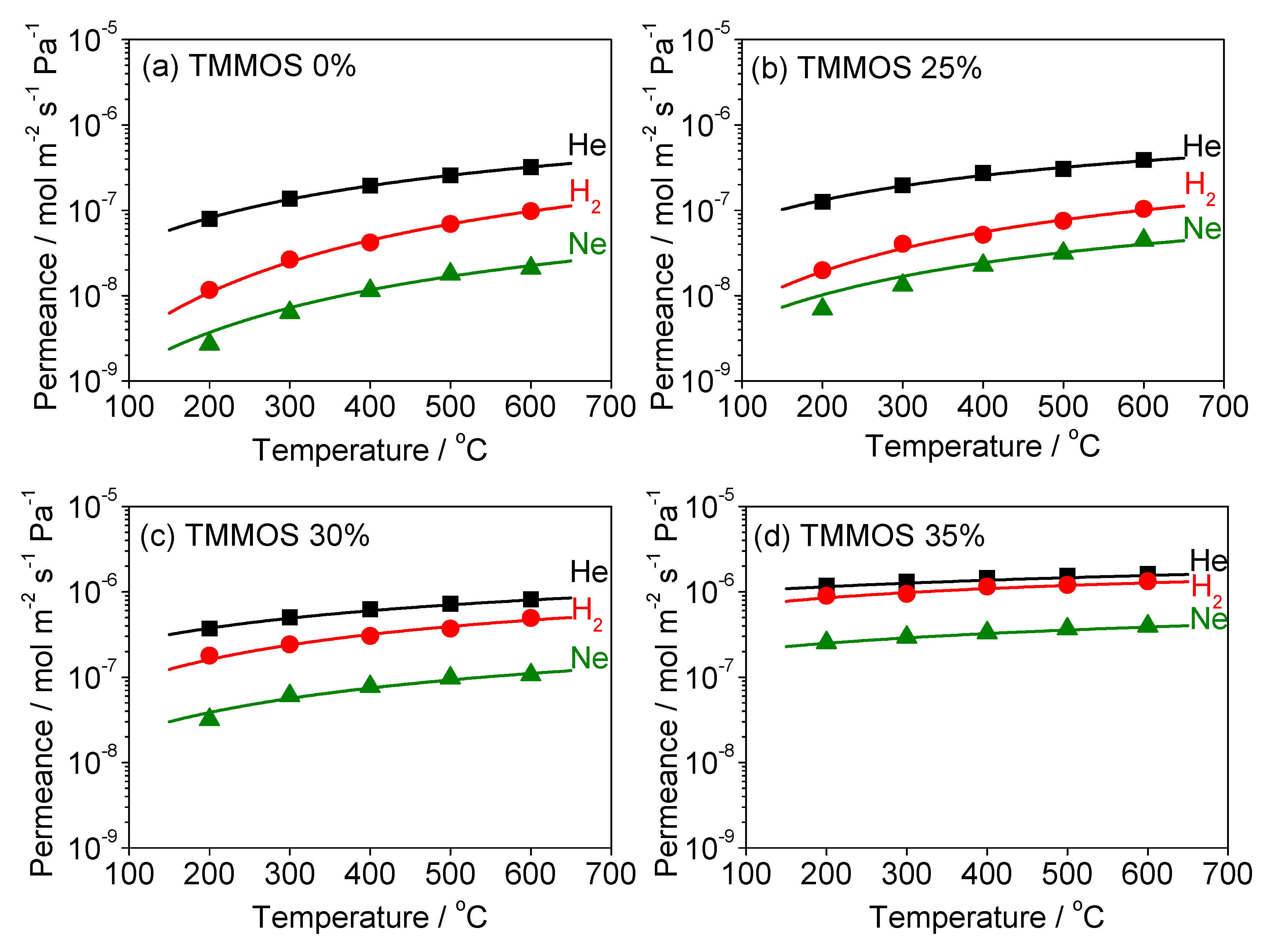
3.3. Diffusion Mechanism Analysis
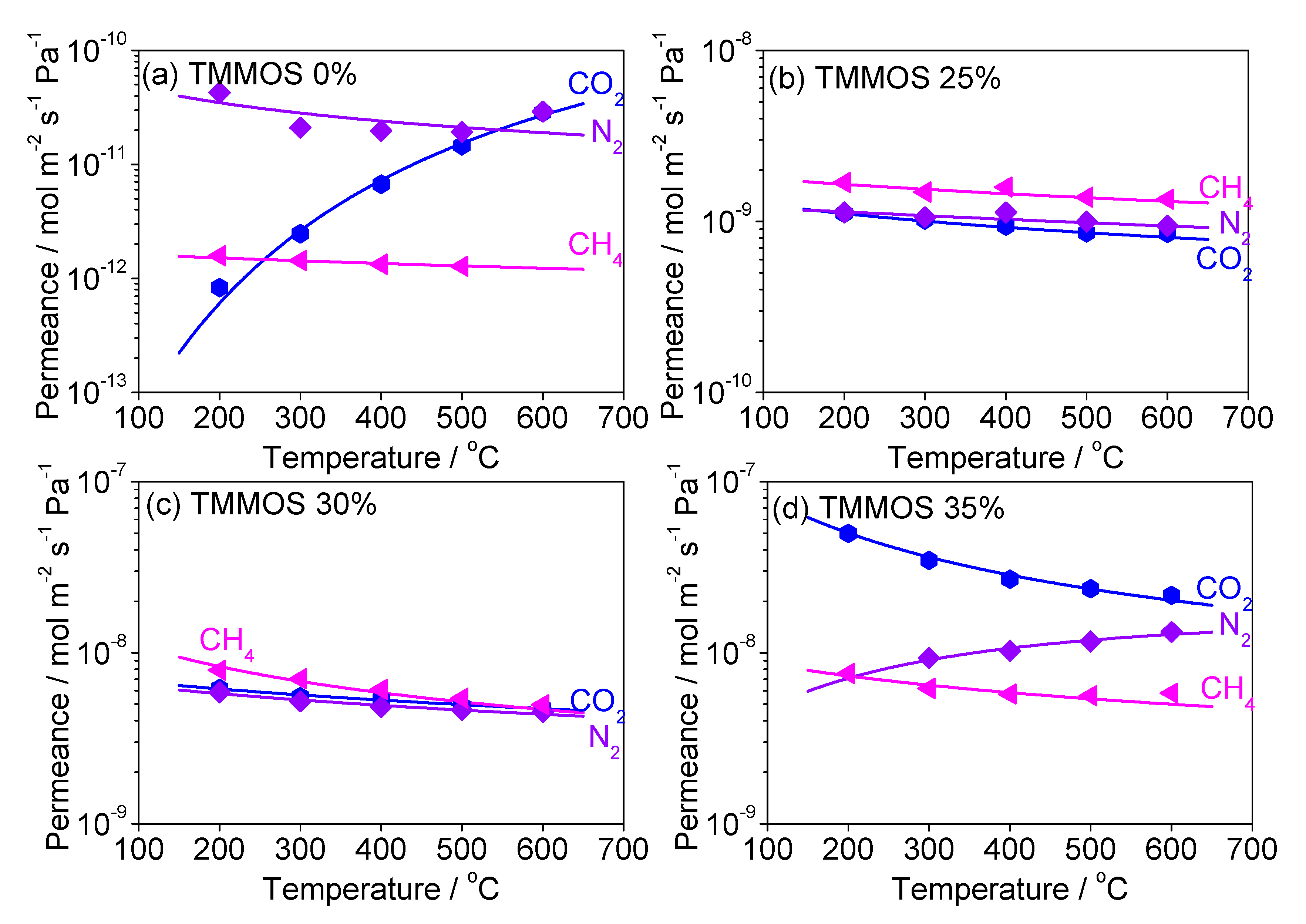
Diffusion Mechanism Analysis of Large Molecules (CO2, N2, CH4)
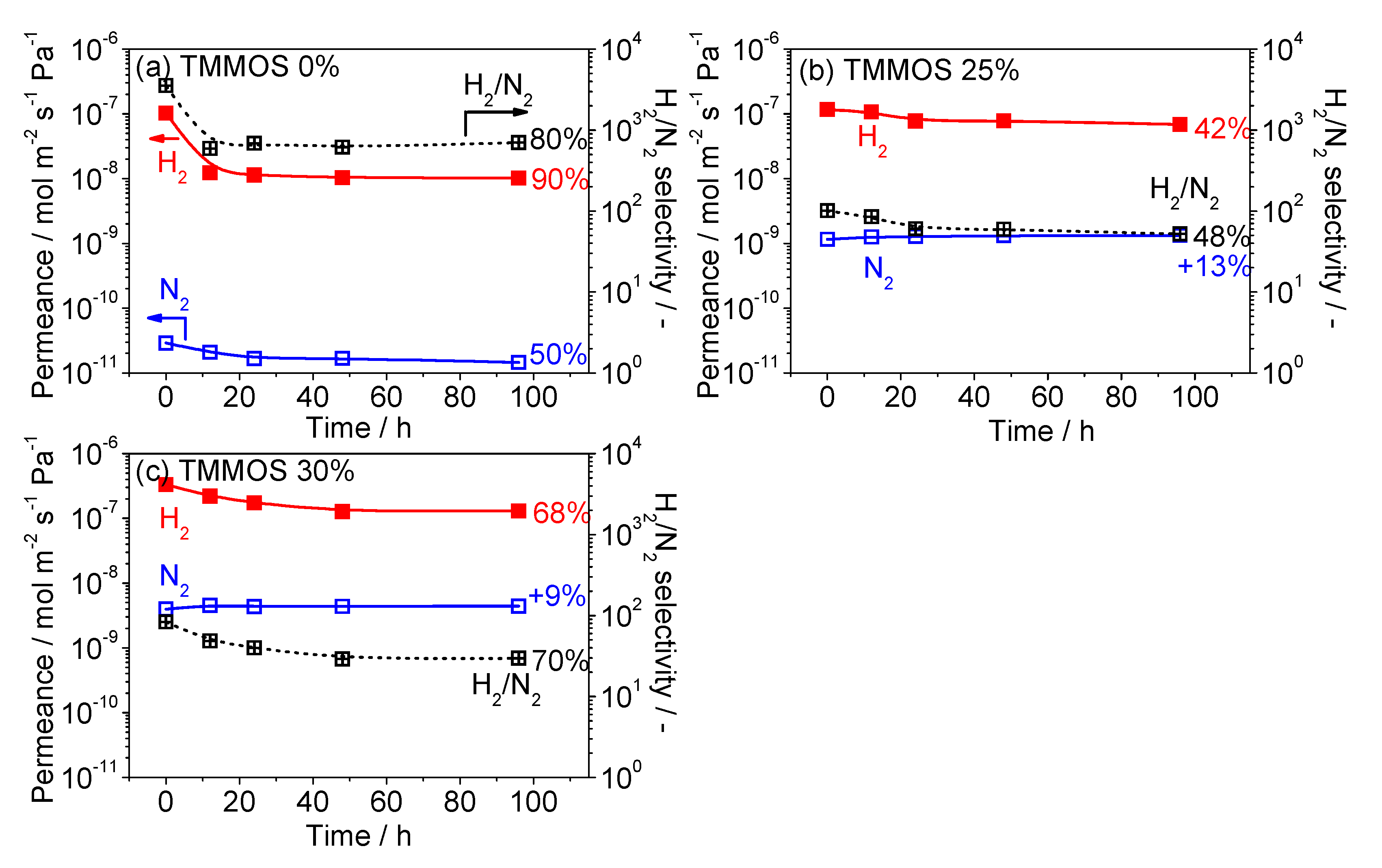
3.4. Hydrothermal Stability Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallucci, F.; Fernandez, E.; Corengia, P.; Annaland, M.S. Recent advances on membranes and membrane reactors for hydrogen production. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 92, 40–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, R.; Sahu, S.; James, O.O.; Maity, S. A review on development of industrial processes and emerging techniques for production of hydrogen from renewable and sustainable sources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, T.; Inoue, H. Single gas permeation through porous glass modified with tetraethoxysilane. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavalas, G.R.; Megiris, C.E.; Nam, S.W. Deposition of H2-permselective SiO2-films. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1989, 44, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Ono, K.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Sugawara, T.; Nakao, S. Preparation of a stable silica membrane by a counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition method. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Fujisaki, S.; Sato, K.; Hataya, K.; Iwamoto, Y.; Nomura, M.; Nakao, S. Relationship between the mesoporous intermediate layer structure and the gas permeation property of an amorphous silica membrane synthesized by counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 2008, 91, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, S.J.; Oyama, S.T. Silica membranes for hydrogen separation prepared by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 111, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Yun, G.N.; Takagaki, A.; Kikuchi, R.; Oyama, S.T. Effects of pressure contact time, permeance, and selectivity in membrane reactors: The case of the dehydrogenation of ethane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, S.T.; Lee, D.; Hacarlioglu, P.; Saraf, R.F. Theory of hydrogen permeability in nonporous silica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 244, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, S.T.; Yamada, M.; Sugawara, T.; Takagaki, A.; Kikuchi, R. Review on mechanisms of gas permeation through inorganic membranes. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2011, 54, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezashi, M.; Kawano, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Organic-inorganic hybrid silica membranes with controlled silica network size for propylene/propane separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezashi, M.; Shazwani, W.N.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Separation of propylene/propane binary mixtures by bis(triethoxysilyl)methane(BTESM)-derived silica membranes fabricated at different calcination temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezashi, M.; Yada, K.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Organic-inorganic hybrid silica membranes with controlled silica network size: Preparation and gas permeation characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezashi, M.; Kawano, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Design of silica networks for development of highly permeable hydrogen separation membranes with hydrothermal stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 131, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.R.; Shibata, T.; Kanezashi, M.; Mizuno, T.; Ohshita, J.; Tsuru, T. Pore-size-controlled silica membranes with disiloxane alkoxides for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Ito, K.; Ohshita, J.; Tsuru, T. New insights into the microstructure-separation properties of organosilica membranes with ethane ethylene, and acethylene bridges. ACS. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 9357–9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Nishi, Y.; Sakanishi, T.; Utsumi, K.; Nakamura, R. Preparation of thin LiSiO membranes by using a CVD method. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Nagayo, T.; Monma, K. Pore size control of a molecular sieve silica membrane prepared by a counter diffusion CVD method. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2007, 40, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Akamatsu, K.; Sugawara, T.; Miyoshi, A.; Nakao, S. Development of pore-size-controlled silica membranes for gas separation by chemical vapor deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yamada, H.; Saito, T.; Kai, T.; Murakami, K.; Nakashima, M.; Ohshita, J.; Akamatsu, K.; Nakao, S. Development of hydrogen-selective triphenylmethoxysilane-derived silica membranes with tailored pore size by chemical vapor deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, H.; Minamizawa, T.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Microporous organosilica membranes for gas separation prepared via PECVD using different O/Si ratio precursors. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 489, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Oyama, S.T. Ultrathin, hydrogen-selective silica membranes deposited on alumina-graded structures prepared from size-controlled boehmite sols. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 306, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, D.R. Vapor pressure of pure substances. Organic and inorganic compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1947, 39, 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sea, B.K.; Soewito, E.; Watanabe, M.; Kusakabe, K.; Morooka, S.; Kim, S.S. Hydrogen recovery from a H2–H2O–HBr mixture utilizing silica-based membranes at elevated temperatures. 1. Preparation of H2O- and H2-selective membranes. Ind. End. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 2502–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaeda, M.; Yamasaki, S. Separation of inorganic/organic gas mixtures by porous silica membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 25, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Hacarlioglu, P.; Oyama, S.T. Hydrothermally stable silica–alumina composite membranes for hydrogen separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Sato, K. Degradation mechanism of an H2-permselective amorphous silica membrane. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4115–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milella, A.; Palumbo, F.; Delattre, J.L.; Fracassi, F.; d’Agostino, R. Deposition and characterization of dielectric thin films from allyltrimethylsilane glow dischanges. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, F.; Martinez, E.; Esteve, J. Improvement of hardness in plasma polymerized hexamethyldisiloxane coatings by silica-like surface modification. Thin Solid Films 2000, 377–378, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamou, P.H.T.; Overbeek, J.P.; Kreiter, R.; van Veen, H.M.; Vente, J.F.; Wienk, I.M.; Cuperus, P.F.; Creatore, M. Plasma deposited hybrid silica membranes with a controlled retention of organic bridges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5567–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkiewicz-Pietrzykowska, A.; Cotrino, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R. Deposition of thin films of SiOxCyH in a surfatron microwave plasma reactor with hexamethyldisiloxane as precursor. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2005, 11, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kanezashi, M.; Tsuru, T. Preparation of organic-inorganic hybrid silica membranes using organoalkosilanes: The effect of pendent groups. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioya, Y.; Ohdaira, T.; Suzuki, R.; Seino, Y.; Omote, K. Effect of UV anneal on plasma CVD low-k film. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 2973–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, S. Polyurethane Networks Nanoreinforced by Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2005, 26, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sea, B.K.; Ando, K.; Kusakabe, K.; Morooka, S. Separation of hydrogen from steam using a Si-C based membrane formed by chemical vapor deposition of triisopropylsilane. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 146, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ciora, R.J.; Fayyaz, B.; Liu, P.K.T.; Suwanmethanond, V.; Mallada, R.; Sahimi, M.; Tsotsis, T.T. Preparation and reactive applications of nanoporous silicon carbide membranes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 4957–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
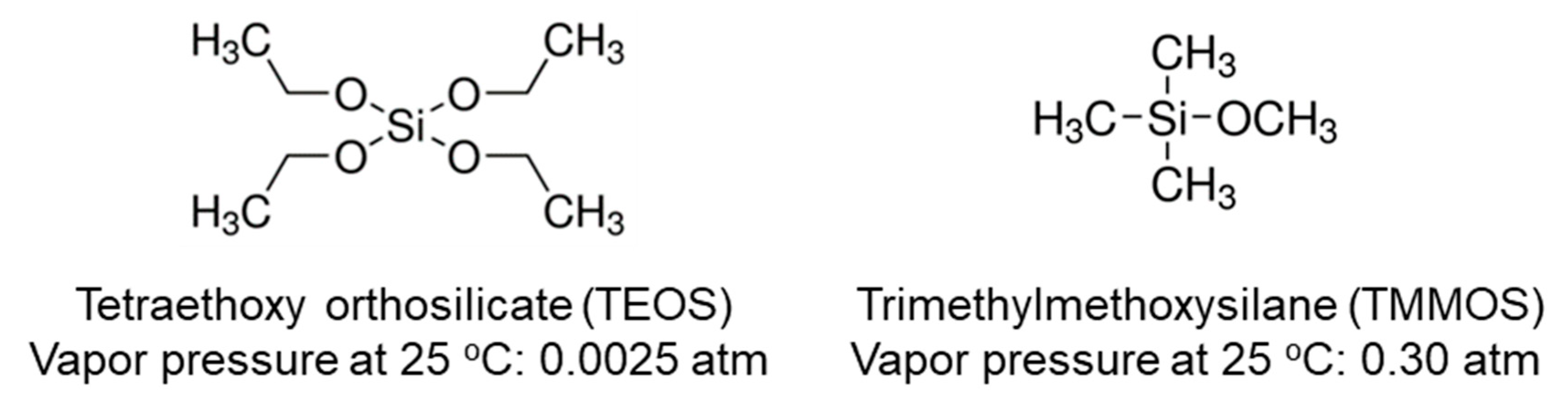
| Membrane | Bubbler Temperature (°C) | Volumetric Flow Rates of Ar Carrier (cm3 min−1) | Molar Flow Rates (μmol s−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEOS | TMMOS | TEOS | TMMOS | TEOS | TMMOS | |
| TMMOS 0% | 90 | - | 6 | - | 0.26 | - |
| TMMOS 25% | 98 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 0.35 | 0.12 |
| TMMOS 30% | 90 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 0.26 | 0.12 |
| TMMOS 35% | 85 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 0.21 | 0.12 |
| TMMOS Percentage | Gas | Ns (Site m−3) | ν* (s−1) | ∆ESS (kJ mol−1) | d (nm) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | He | 4.26 × 1026 | 2.81 × 1012 | 9.13 | 0.839 | 1.00 |
| Ne | 3.34 × 1026 | 2.16 × 1012 | 12.85 | 0.841 | 0.980 | |
| H2 | 2.52 × 1026 | 3.21 × 1012 | 17.19 | 0.842 | 0.998 | |
| 25% | He | 3.13 × 1026 | 5.37 × 1012 | 6.33 | 0.841 | 0.986 |
| Ne | 2.40 × 1026 | 3.57 × 1012 | 9.04 | 0.842 | 0.947 | |
| H2 | 1.84 × 1026 | 7.51 × 1012 | 12.35 | 0.843 | 0.987 | |
| 30% | He | 1.95 × 1026 | 3.48 × 1012 | 3.83 | 0.843 | 0.998 |
| Ne | 1.89 × 1026 | 2.30 × 1012 | 6.38 | 0.843 | 0.970 | |
| H2 | 1.73 × 1026 | 4.76 × 1012 | 7.44 | 0.843 | 0.970 | |
| 35% | He | 1.57 × 1026 | 2.94 × 1012 | −0.08 | 0.844 | 0.995 |
| Ne | 1.43 × 1026 | 1.54 × 1012 | 1.12 | 0.844 | 1.00 | |
| H2 | 0.87 × 1026 | 3.02 × 1012 | 1.86 | 0.845 | 0.952 |
| TMMOS Ratio | Gas | C | Ep (kJ mol−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | CO2 | 6.17 × 10−8 | 35.2 | 0.993 |
| N2 | 1.90 × 10−10 | −2.57 | 0.400 | |
| CH4 | 1.49 × 10−11 | 0.830 | 0.907 | |
| 25% | CO2 | 1.06 × 10−5 | 12.0 | 0.985 |
| N2 | 5.23 × 10−6 | 17.3 | 0.978 | |
| CH4 | 4.12 × 10−6 | 17.2 | 0.983 | |
| 30% | CO2 | 1.54 × 10−5 | 9.35 | 0.999 |
| N2 | 6.84 × 10−6 | 11.9 | 0.983 | |
| CH4 | 9.23 × 10−6 | 12.0 | 0.956 | |
| 35% | CO2 | 1.70 × 10−5 | 5.28 | 0.982 |
| N2 | 1.12 × 10−5 | 6.48 | 0.982 | |
| CH4 | 1.13 × 10−5 | 6.19 | 0.917 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mise, Y.; Ahn, S.-J.; Takagaki, A.; Kikuchi, R.; Oyama, S.T. Fabrication and Evaluation of Trimethylmethoxysilane (TMMOS)-Derived Membranes for Gas Separation. Membranes 2019, 9, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100123
Mise Y, Ahn S-J, Takagaki A, Kikuchi R, Oyama ST. Fabrication and Evaluation of Trimethylmethoxysilane (TMMOS)-Derived Membranes for Gas Separation. Membranes. 2019; 9(10):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100123
Chicago/Turabian StyleMise, Yoshihiro, So-Jin Ahn, Atsushi Takagaki, Ryuji Kikuchi, and Shigeo Ted Oyama. 2019. "Fabrication and Evaluation of Trimethylmethoxysilane (TMMOS)-Derived Membranes for Gas Separation" Membranes 9, no. 10: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100123
APA StyleMise, Y., Ahn, S.-J., Takagaki, A., Kikuchi, R., & Oyama, S. T. (2019). Fabrication and Evaluation of Trimethylmethoxysilane (TMMOS)-Derived Membranes for Gas Separation. Membranes, 9(10), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100123







