Hollow Fiber Membranes of Blends of Polyethersulfone and Sulfonated Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Sulfonation of PESU
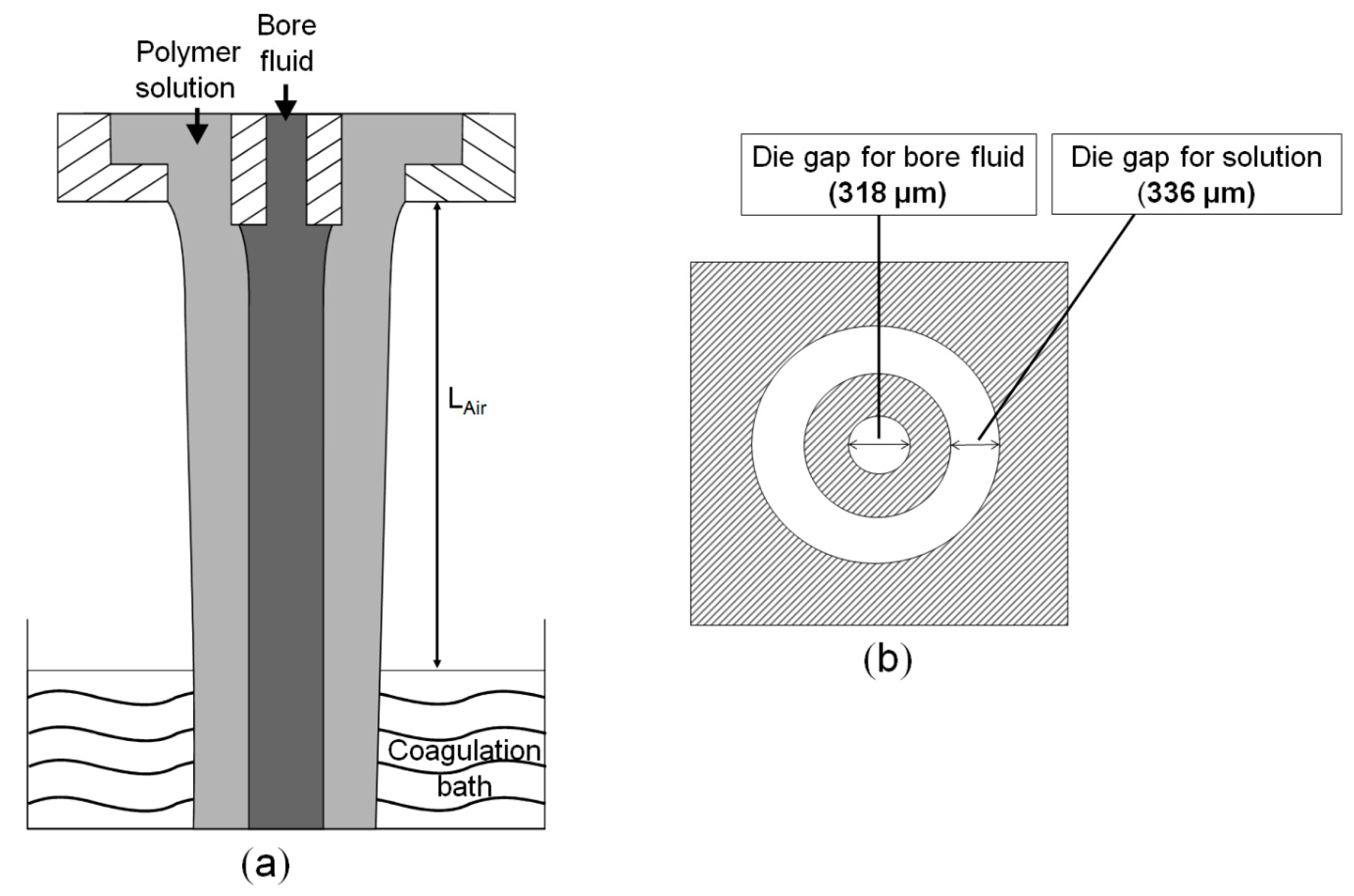
2.3. Hollow Fiber Membranes
2.3.1. Fabrication of the Hollow Fiber Membranes
2.3.2. Compositions of the Solutions for Hollow Fiber Spinning
2.4. Characterization of the Polymers and Hollow Fibers
2.4.1. Thermal Characterization
2.4.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.4.5. Water Flux Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
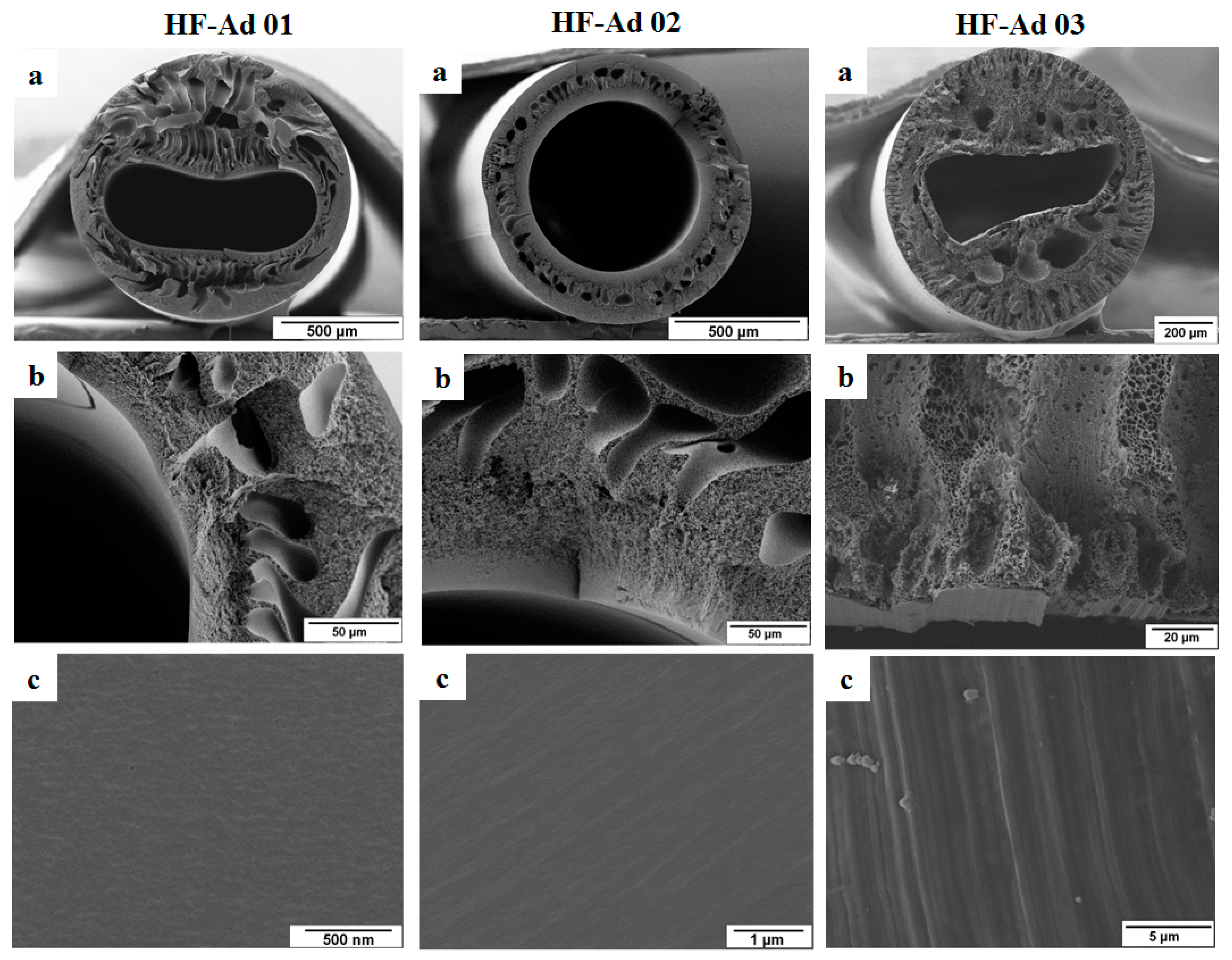
3.1. Dope Solution with Common Additives
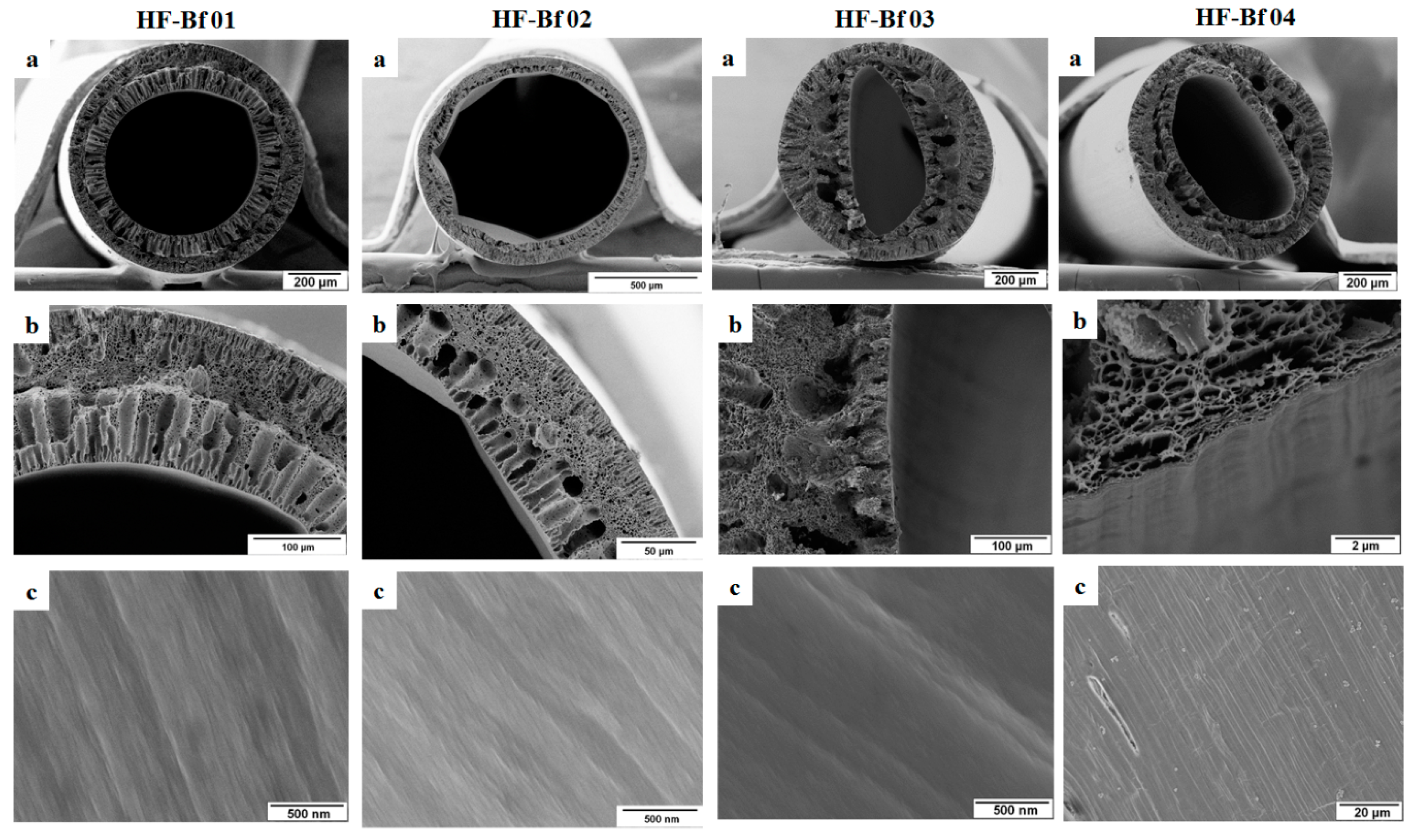
3.2. Spinning with Different Bore Fluids
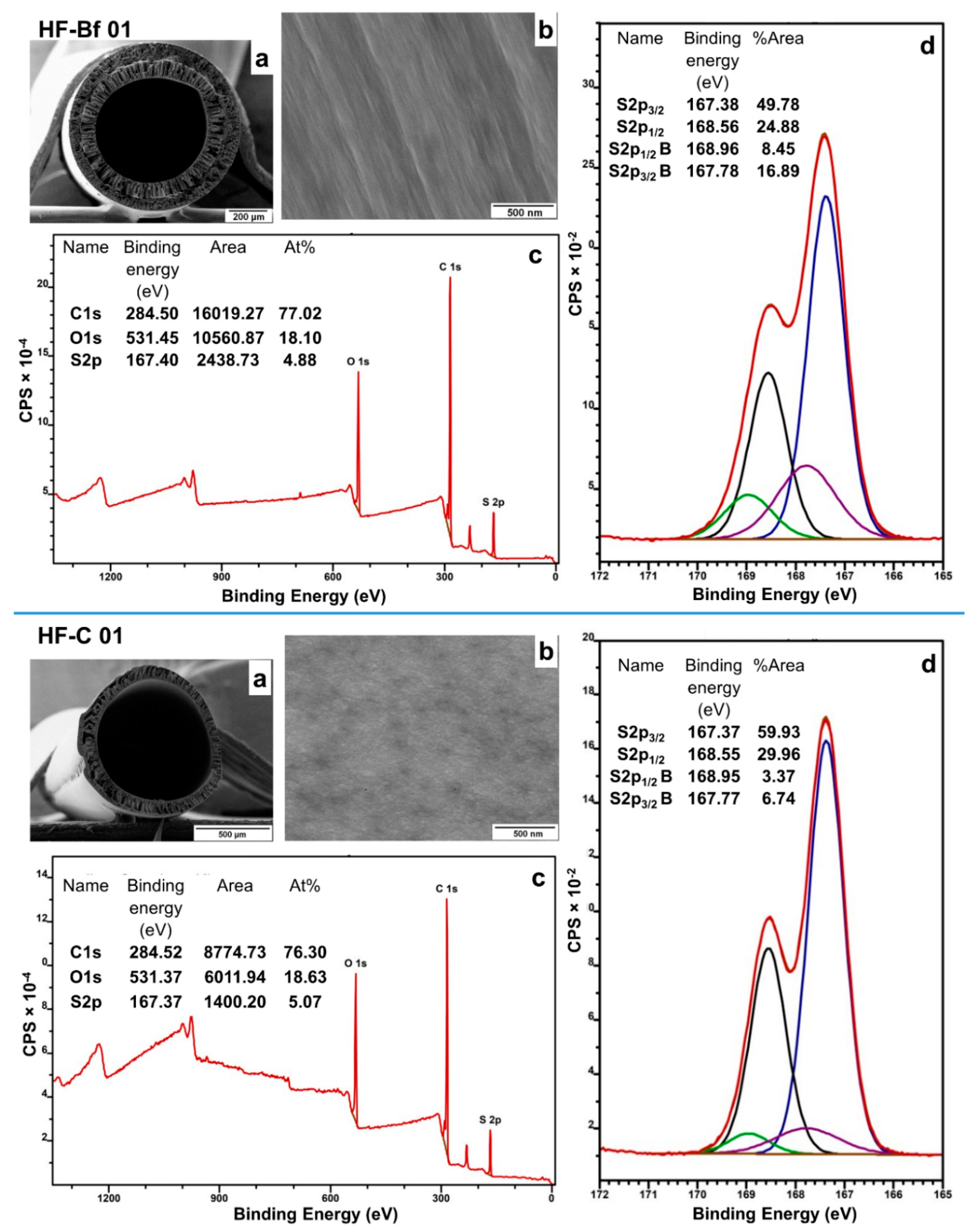
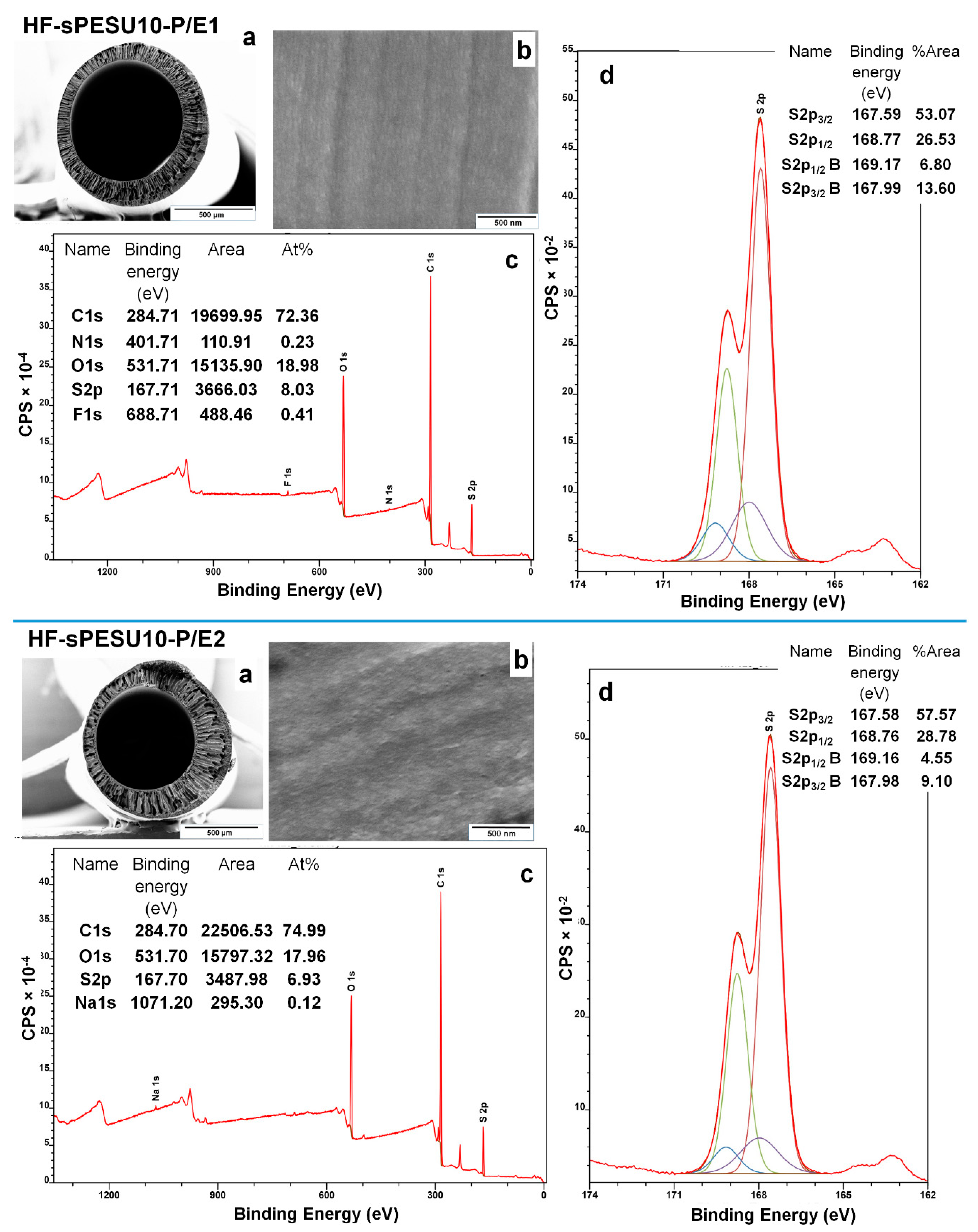
3.3. Analysis of the Inner Surface of the Hollow Fibers by XPS
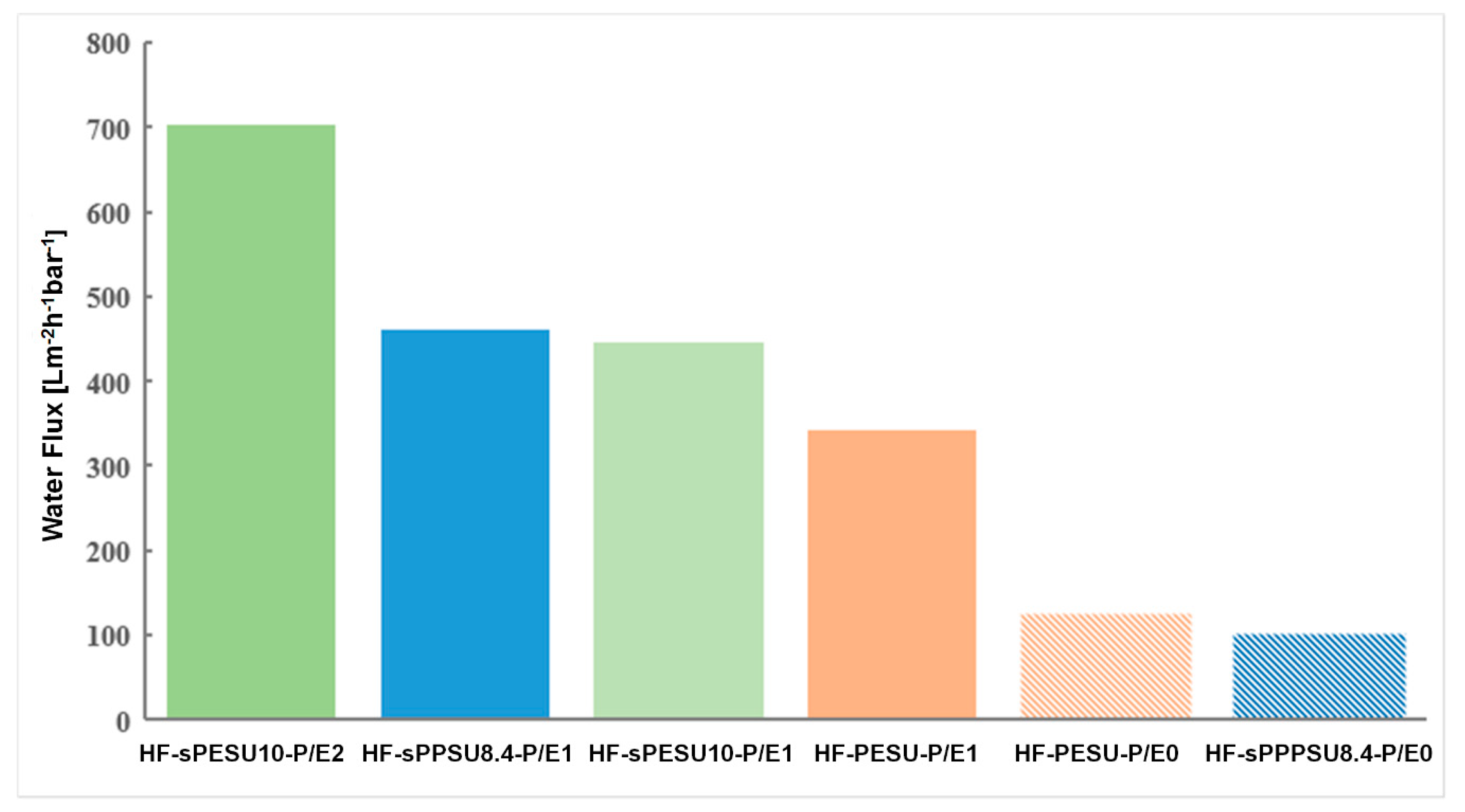
3.4. Characterization and Performance of Hollow Fiber Membranes Prepared with PSSNa/EG in the Dope Solution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahimpour, A.; Madaeni, S.S.; Ghorbani, S.; Shockravi, A.; Mansourpanah, Y. The influence of sulfonated polyethersulfone (SPES) on surface nano-morphology and performance of polyethersulfone (PES) membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.Y.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F. Recent progresses in polymeric hollow fiber membrane preparation, characterization and applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 111, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.-F.; Yang, H.-Y.; Cheng, L.; Kato, N.; Jeon, S.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. Effect of molecular weight of sulfonated poly(ether sulfone) (SPES) on the mechanical strength and antifouling properties of poly(ether sulfone)/SPES blend membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 11302–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. The effects of mechanical and chemical modification of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface chemistry, structure and fouling performance of PES ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.-B.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Rheology and phase inversion behavior of polyphenylenesulfone (PPSU) and sulfonated PPSU for membrane formation. Polymer 2016, 99, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Exploration of highly sulfonated polyethersulfone (SPES) as a membrane material with the aid of dual-layer hollow fiber fabrication technology for protein separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 309, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Chung, T.-S.; Amy, G. Developing thin-film-composite forward osmosis membranes on the PES/SPSF substrate through interfacial polymerization. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjojo, N.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C.; Warzelhan, V. A sulfonated polyphenylenesulfone (SPPSU) as the supporting substrate in thin film composite (TFC) membranes with enhanced performance for forward osmosis (FO). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Shen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X. Chitosan/sulfonated polyethersulfone–polyethersulfone (CS/SPES-PES) composite membranes for pervaporative dehydration of ethanol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 5772–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.; Koll, J.; Radjabian, M.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. A facile method to prepare double-layer isoporous hollow fiber membrane by in situ hydrogen bond formation in the spinning line. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Ye, H.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Ding, X.-L.; Lin, L.-G.; Zhao, L.; Li, H. The effect of polymer concentration and additives of cast solution on performance of polyethersulfone/sulfonated polysulfone blend nanofiltration membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Krantz, W.B.; Chung, T.-S. A novel primer to prevent nanoparticle agglomeration in mixed matrix membranes. AIChE J. 2007, 53, 2470–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Koops, G.H.; Strathmann, H. Characterization of morphology controlled polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes by the addition of polyethylene glycol to the dope and bore liquid solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 223, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, K.-H. Effect of peg additive on membrane formation by phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 138, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Han, G.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Widjojo, N.; Maletzko, C. Effects of polyethylene glycol on membrane formation and properties of hydrophilic sulfonated polyphenylenesulfone (SPPSU) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Maki, T.; Teramoto, M.; Kobayashi, K. Effect of PVP additive on porous polysulfone membrane formation by immersion precipitation method. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 3449–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jho, J.Y.; Won, J.; Kang, Y.S. Influence of the addition of PVP on the morphology of asymmetric polyimide phase inversion membranes: Effect of PVP molecular weight. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 236, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In-Chul, K.; Kew-Ho, L. Effect of various additives on pore size of polysulfone membrane by phase-inversion process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 2562–2566. [Google Scholar]
- Mulyati, S.; Takagi, R.; Fujii, A.; Ohmukai, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Improvement of the antifouling potential of an anion exchange membrane by surface modification with a polyelectrolyte for an electrodialysis process. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, C.; Dong, B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yu, S.; Gao, C. Enhancing the permselectivity of thin-film composite poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) nanofiltration membrane by incorporating poly(sodium-p-styrene-sulfonate) (PSSNA). J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.; Koll, J.; Abetz, C.; Notzke, H.; Abetz, V. Continuous production of macroporous films: An alternative to breath figure assembly. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albo, J.; Hagiwara, H.; Yanagishita, H.; Ito, K.; Tsuru, T. Structural characterization of thin-film polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Wang, J.; Tsuru, T. Gas transport properties of interfacially polymerized polyamide composite membranes under different pre-treatments and temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Wang, J.; Tsuru, T. Application of interfacially polymerized polyamide composite membranes to isopropanol dehydration: Effect of membrane pre-treatment and temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, K.; Teo, W.K. Preparation and characterization of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 163, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Matsuura, T.; Chung, T.-S.; Guo, W.F. The effects of flow angle and shear rate within the spinneret on the separation performance of poly(ethersulfone) (PES) ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 240, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.F.; Chung, T.-S.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y. Fabrication of fluoropolyimide/polyethersulfone (PES) dual-layer asymmetric hollow fiber membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 198, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Widjojo, N.; Sukitpaneenit, P.; Teoh, M.M.; Lipscomb, G.G.; Chung, T.-S.; Lai, J.-Y. Evolution of polymeric hollow fibers as sustainable technologies: Past, present, and future. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1401–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Hof, J.A.; Reuvers, A.J.; Boom, R.M.; Rolevink, H.H.M.; Smolders, C.A. Preparation of asymmetric gas separation membranes with high selectivity by a dual-bath coagulation method. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 70, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; He, T. Does more solvent in bore liquid create more open inner surface in hollow fiber membranes? Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerle, K.; Strathmann, H. Analysis of the structure-determining process of phase inversion membranes. Desalination 1990, 79, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienk, I.M.; Boom, R.M.; Beerlage, M.A.M.; Bulte, A.M.W.; Smolders, C.A.; Strathmann, H. Recent advances in the formation of phase inversion membranes made from amorphous or semi-crystalline polymers. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 113, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
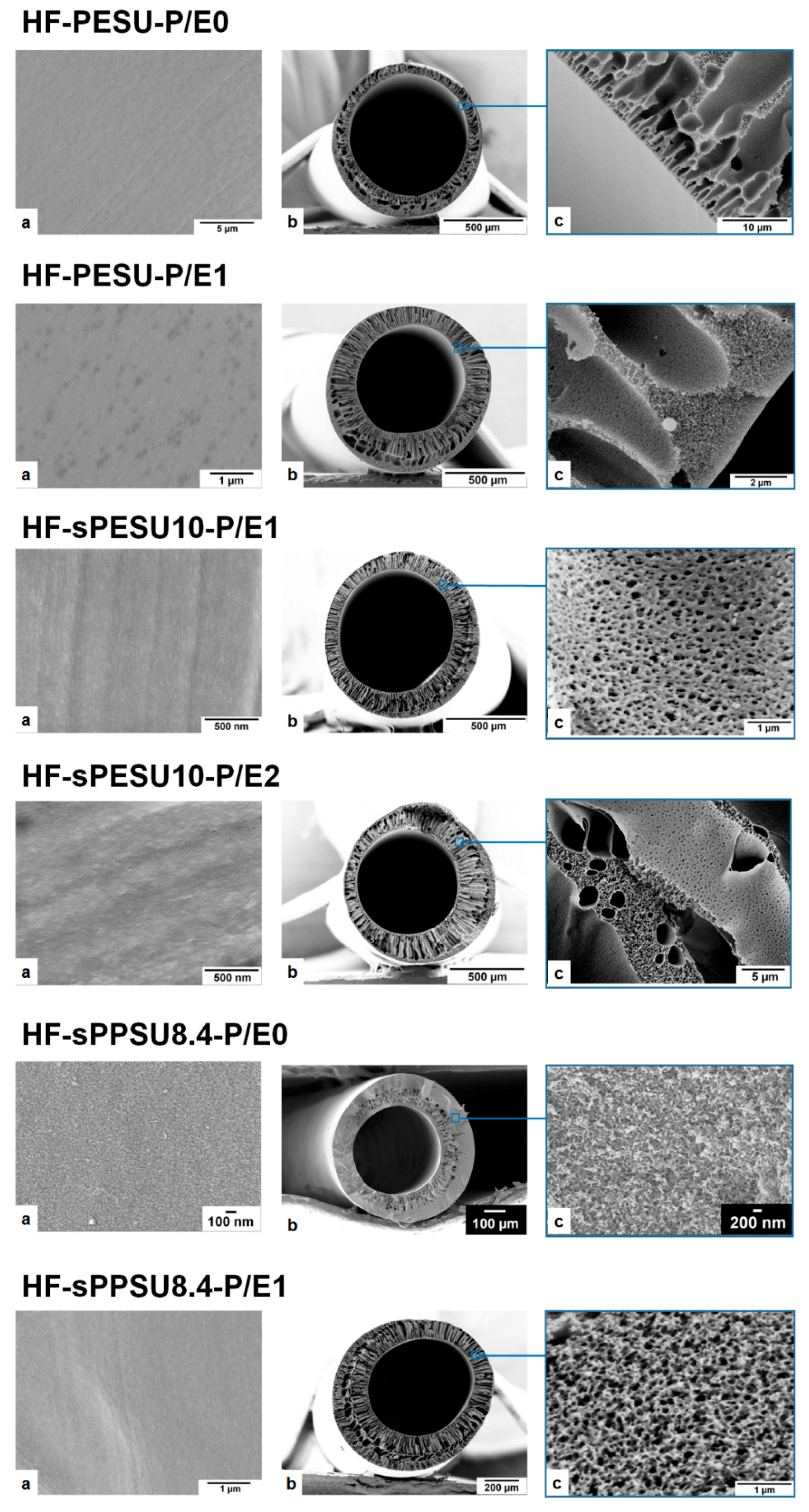
| Membrane Code | Polymer Concentration and Composition a | Solvent and Additive Concentration | Bore Fluid Composition b |
|---|---|---|---|
| HF-Ad 01 | 25% PESU/sPESU10 (60/40) | 54.75% NMP 20.25% GBL | Water/NMP (80/20) |
| HF-Ad 02 | 25% PESU/sPESU10 (60/40) | 45% NMP 22.5% GBL 7.5% PVP | Water/NMP (80/20) |
| HF-Ad 03 | 25% PESU/sPESU10 (60/40) | 67.5% NMP 7.5% PEG200 | Water/NMP (80/20) |
| Membrane Code | Polymer Concentration and Composition a | Solvent and Additive Concentration | Bore Fluid Composition b |
|---|---|---|---|
| HF-Bf 01 | 25% PESU/sPESU10 (90/10) | 75% NMP | Water (100) |
| HF-Bf 02 | 25% PESU/sPESU10 (90/10) | 75% NMP | Water/glycerol (50/50) |
| HF-Bf 03 | 25% PESU/sPESU10 (90/10) | 75% NMP | Water of pH 2 (100) |
| HF-Bf 04 | 25% PESU/sPESU10 (90/10) | 75% NMP | Water of pH 11 (100) |
| Membrane Code | Polymer Concentration and Composition a | Solvent and Additive Concentration | Bore Fluid Composition b |
|---|---|---|---|
| HF-C 01 | 20% PESU/sPPSU5 (90/10) | 80% DMAc | Water (100) |
| Membrane Code c | Polymer Concentration and Composition d | Solvent and Other Additives Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| HF-PESU-P/E0 | 18% PESU | 82% NMP |
| HF-PESU-P/E1 | 18% PESU | 67.9% NMP 13.4% EG 0.70% PSSNa |
| HF-sPESU10-P/E1 | 18% PESU/sPESU10 (60/40) | 67.9% NMP 13.4% EG 0.70% PSSNa |
| HF-sPESU10-P/E2 | 15% PESU/sPESU10 (90/10) | 59% NMP 24.7% EG 1.3% PSSNa |
| HF-sPPSU8.4-P/E0 | 25% PESU/sPPSU8.4 (60/40) | 75% NMP |
| HF-sPPSU8.4-P/E1 | 18% PESU/sPPSU8.4 (60/40) | 67.9% NMP 13.4% EG 0.70% PSSNa |
| Inner Surface of HF-Bf 01 | Inner Surface of HF-C 01 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 2p Region from (O=S=O) Groups | S 2p Region from (–SO3H) Groups | S 2p Region from (O=S=O) Groups | S 2p Region from (–SO3H) Groups | ||||||||
| Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % | Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % | Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % | Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % |
| S2p3/2 | 167.38 | 49.78 | S2p3/2 B | 167.78 | 16.89 | S2p3/2 | 167.37 | 59.93 | S2p3/2 B | 167.77 | 6.74 |
| S2p1/2 | 168.56 | 24.88 | S2p1/2 B | 168.96 | 8.45 | S2p1/2 | 168.55 | 29.96 | S2p1/2 B | 168.95 | 3.37 |
| Near-surface coverage of sPESU10 (% of Atoms) | ~34% | Near-surface coverage of sPPSU5 (% of Atoms) | ~11% | ||||||||
| Inner Surface of HF-sPESU10-P/E1 | Inner Surface of HF-sPESU10-P/E2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 2p Region from (O=S=O) Groups | S 2p Region from (–SO3H) Groups | S 2p Region from (O=S=O) Groups | S 2p Region from (–SO3H) Groups | ||||||||
| Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % | Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % | Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % | Peak | Binding Energy (eV) | Area % |
| S2p3/2 | 167.59 | 53.07 | S2p3/2 B | 167.99 | 13.60 | S2p3/2 | 167.58 | 57.57 | S2p3/2 B | 167.98 | 9.10 |
| S2p1/2 | 168.77 | 26.53 | S2p1/2 B | 169.17 | 6.80 | S2p1/2 | 168.76 | 28.78 | S2p1/2 B | 169.16 | 4.55 |
| Near-surface coverage of sPESU10 (% of atoms) | ~25.6% | Near-surface coverage of sPESU10 (% of atoms) | ~16% | ||||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, N.; Koll, J.; Scharnagl, N.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. Hollow Fiber Membranes of Blends of Polyethersulfone and Sulfonated Polymers. Membranes 2018, 8, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030054
Noor N, Koll J, Scharnagl N, Abetz C, Abetz V. Hollow Fiber Membranes of Blends of Polyethersulfone and Sulfonated Polymers. Membranes. 2018; 8(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Nazia, Joachim Koll, Nico Scharnagl, Clarissa Abetz, and Volker Abetz. 2018. "Hollow Fiber Membranes of Blends of Polyethersulfone and Sulfonated Polymers" Membranes 8, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030054
APA StyleNoor, N., Koll, J., Scharnagl, N., Abetz, C., & Abetz, V. (2018). Hollow Fiber Membranes of Blends of Polyethersulfone and Sulfonated Polymers. Membranes, 8(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030054






