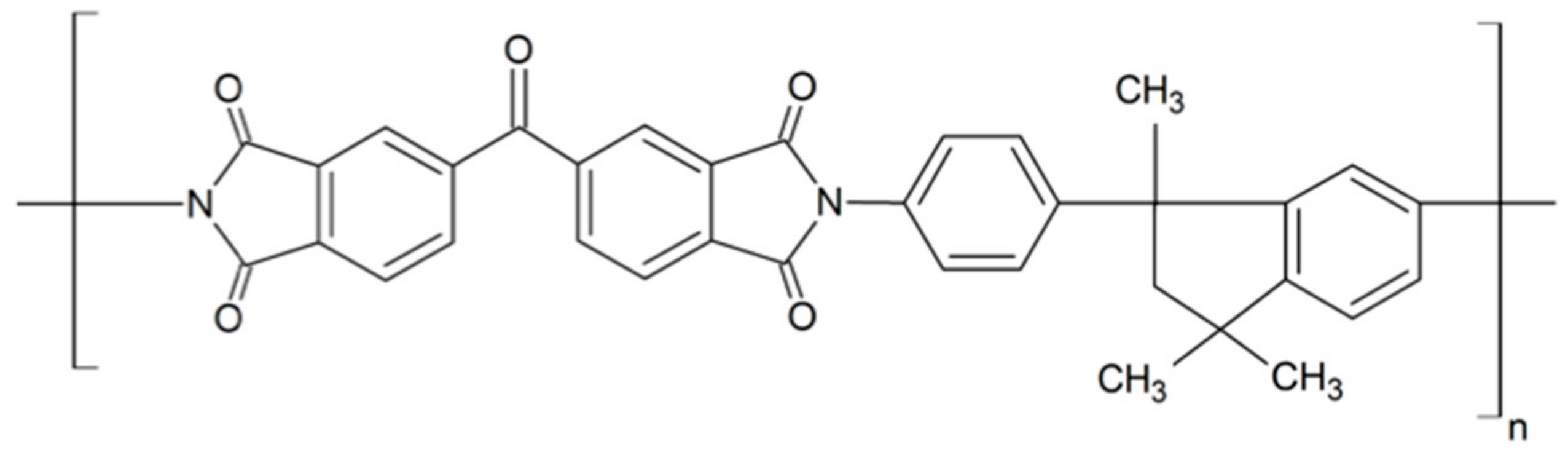
Progress on Incorporating Zeolites in Matrimid®5218 Mixed Matrix Membranes towards Gas Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
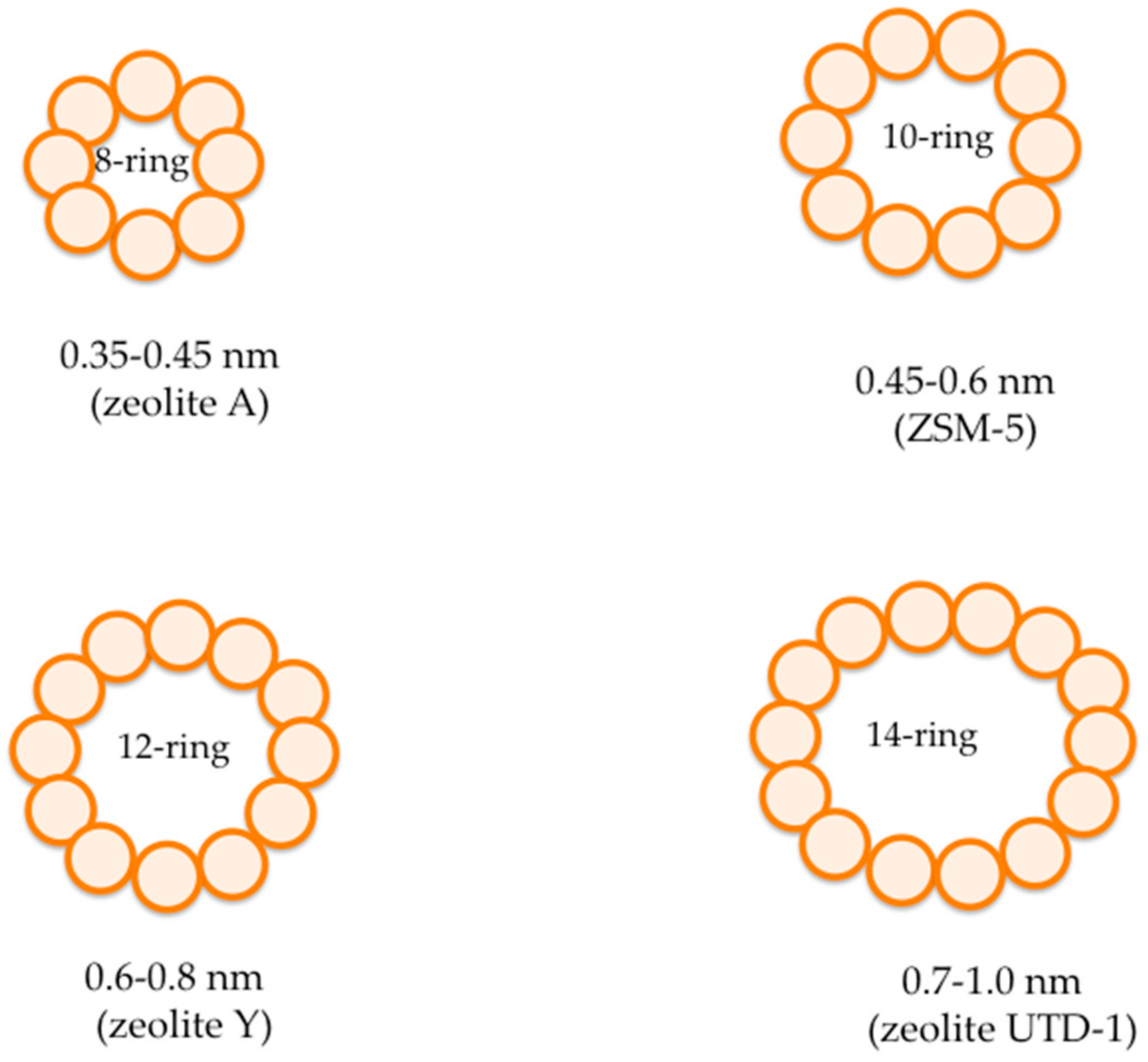
2. Fundamentals of Zeolites
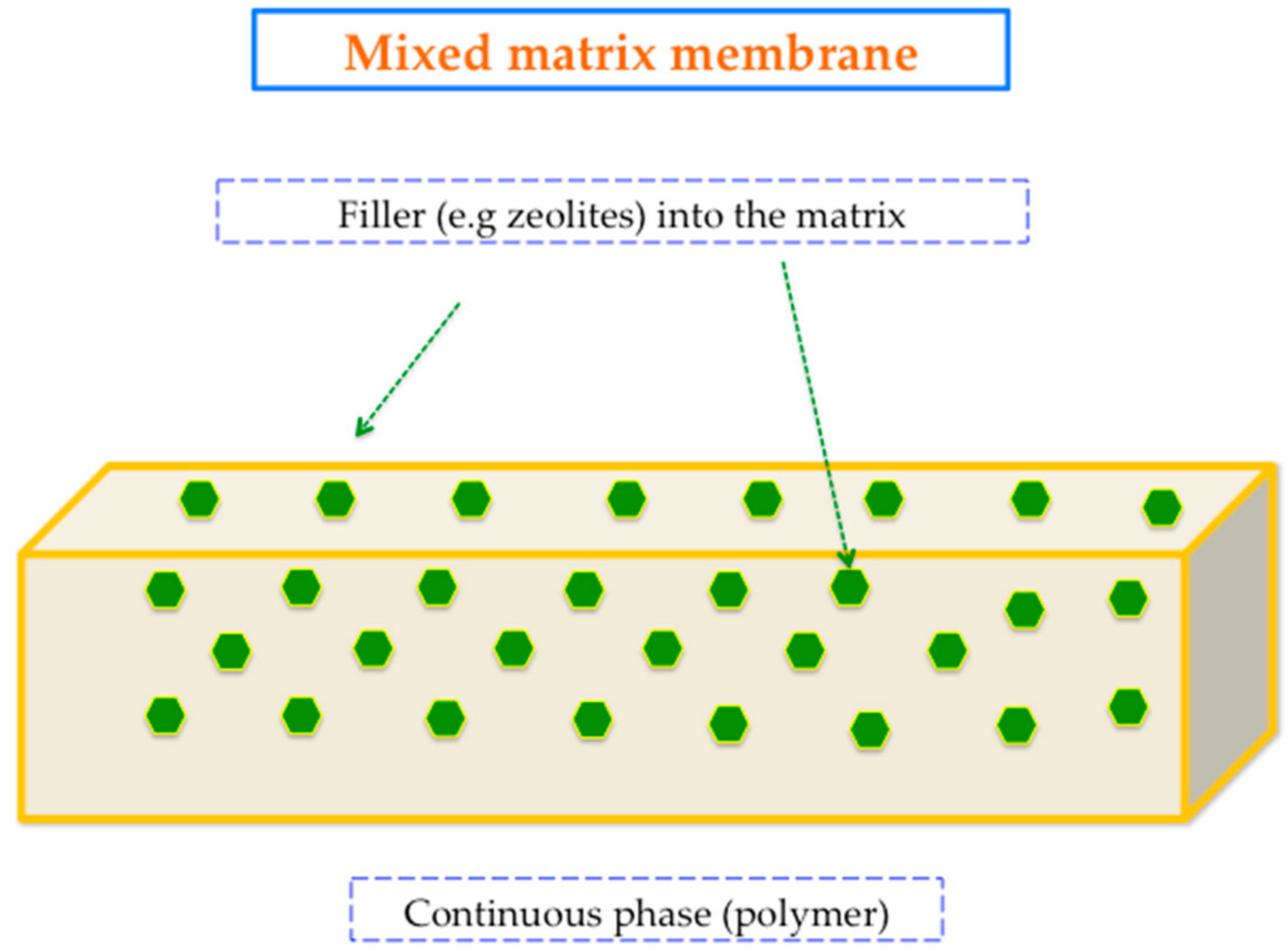
3. The Concept of Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs) Incorporating Zeolites
4. Gas Transport Mechanism in MMMs
4.1. Gas Transport in Dense Membranes
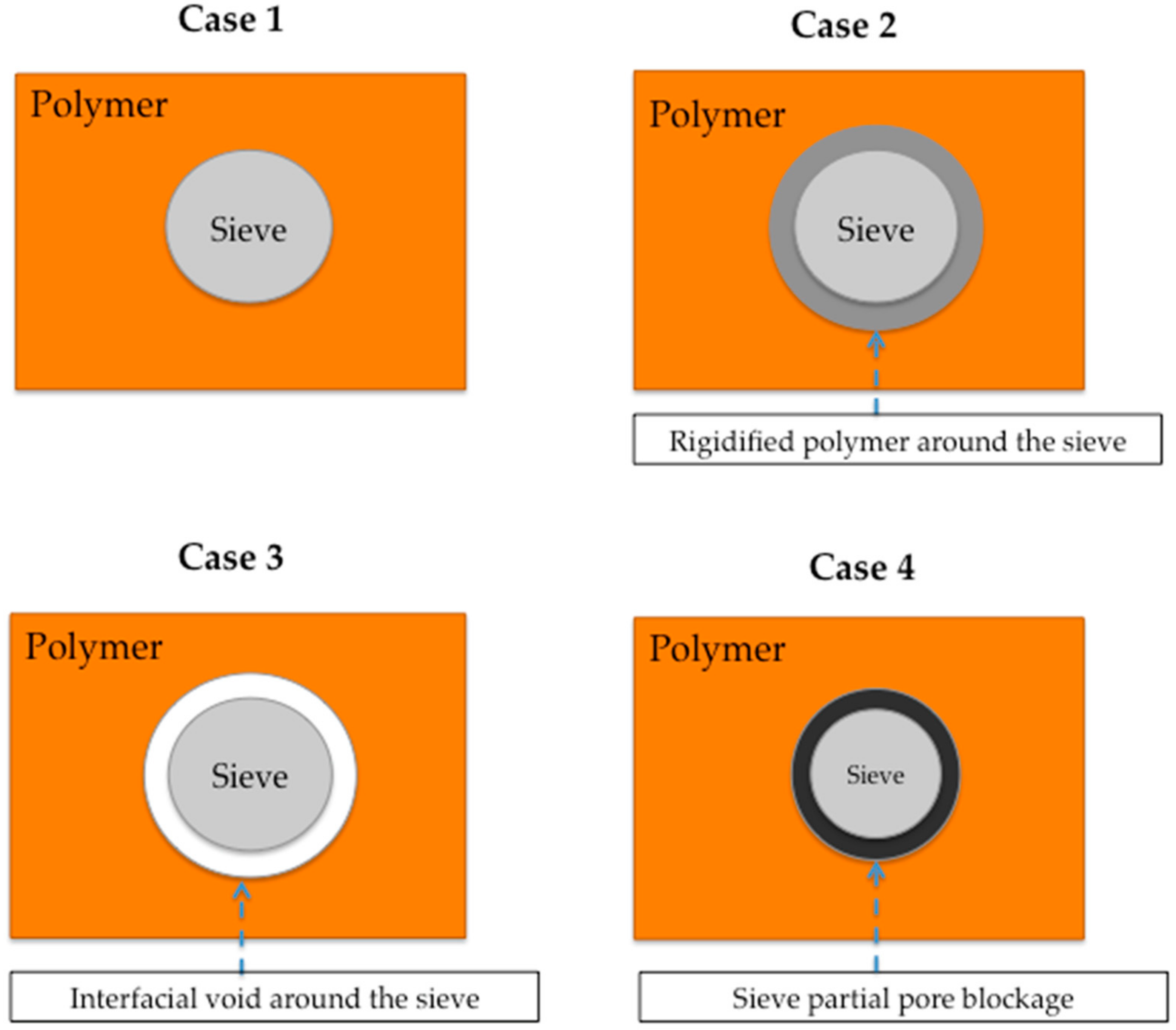
4.2. Strategies to Reach Optimal Interface Morphology
5. Zeolites as Filling Material in the Preparation of MMMs Based on Matrimid®5218
5.1. Beginnings of Incorporating Zeolites into Matrimid®
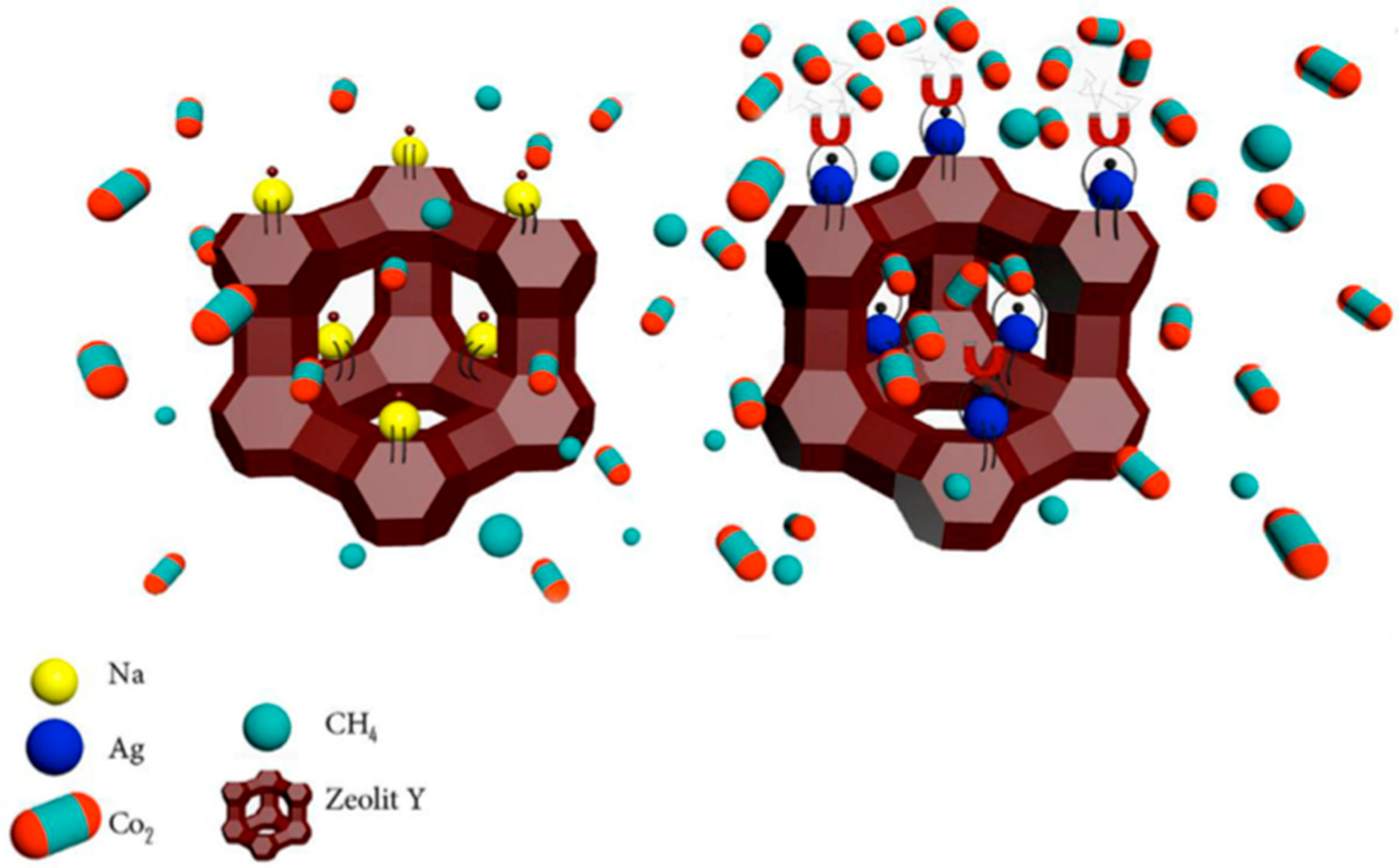
5.2. Recent Developments on Incorporating Zeolites into Matrimid®
6. Future Trends and Concluding Remarks
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guiver, M.D.; Robertson, G.P.; Dai, Y.; Bilodeau, F.; Kang, Y.S.; Lee, K.J.; Jho, J.Y.; Won, J. Structural characterization and gas-transport properties of brominated Matrimid polyimide. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2002, 40, 4193–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Matrimid® 5218 dense membrane for the separation of azeotropic MeOH-MTBE mixtures by pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Scura, F.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E. Membrane technologies for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 359, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Martin-Gil, V.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Fíla, V. Matrimid® 5218 in preparation of membranes for gas separation—Current state-of-the-art. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 205, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinov, N.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Hensen, E.J.M. Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroon, M.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Montazer-Rahmati, M.M. Performance studies of mixed matrix membranes for gas separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, C.; Tao, W.X.; Stevens, G.W.; Kentish, S. Sorption of methane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water in Matrimid 5218. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 2284–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
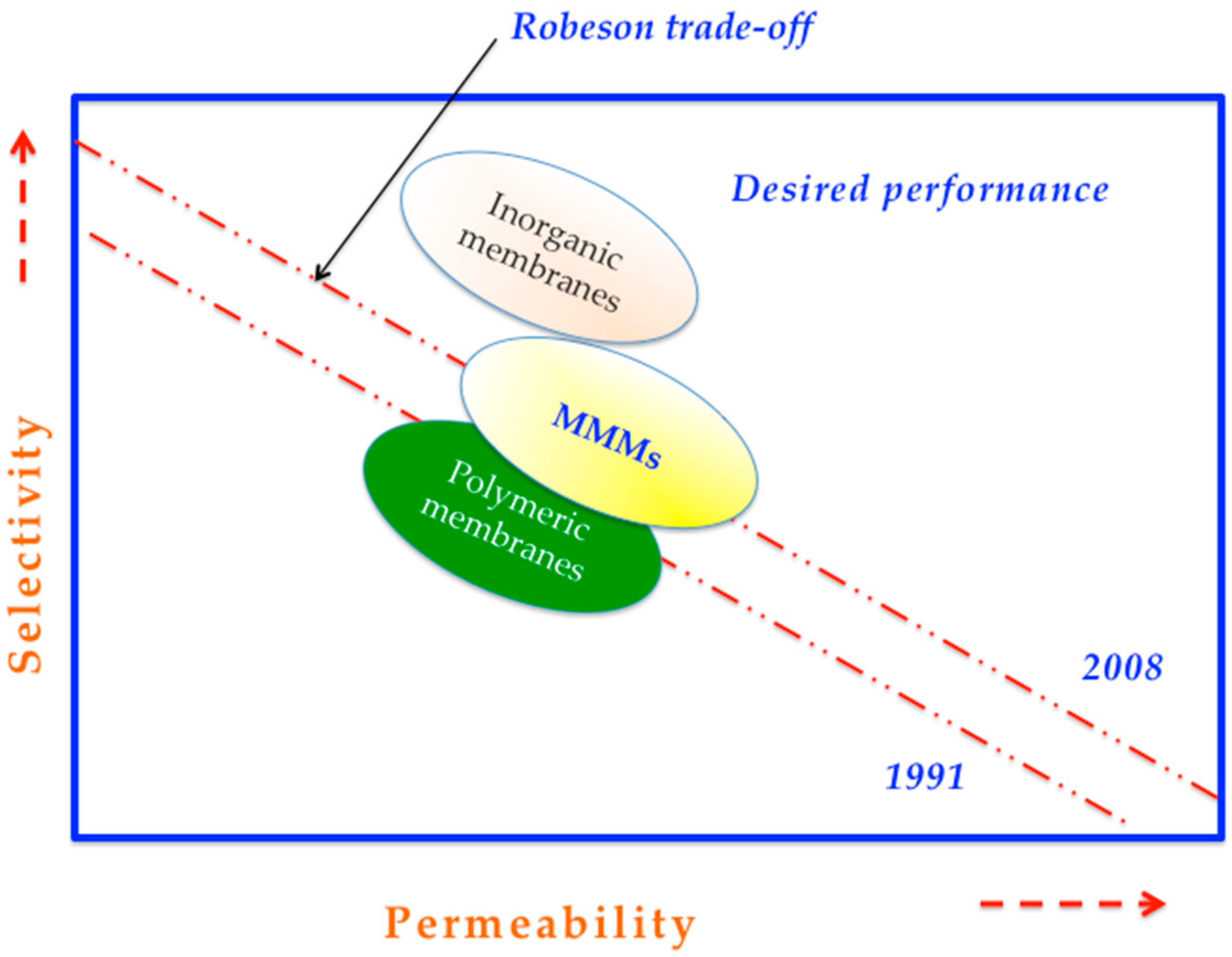
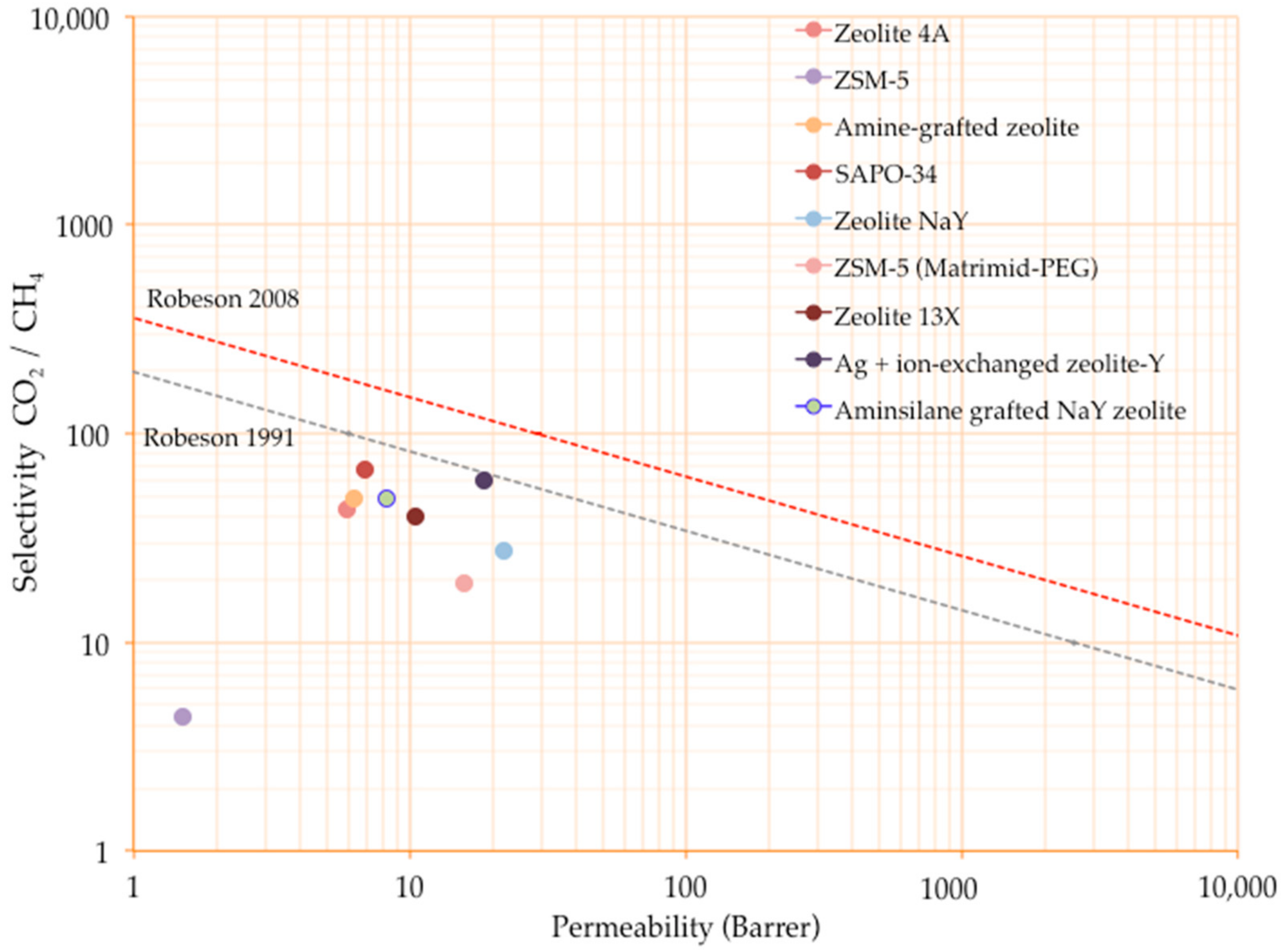
- Robeson, L.M. Correlation of separation factor versus permeability for polymeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 62, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, R.; Lozano, A.; Pradanos, P.; Marcos, A.; Tejerina, F.; Hernandez, A. Effect of fractional free volume and Tg on gas separation through membranes made with different glassy polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Fíla, V.; Dung, C.T. Mixed matrix membranes based on PIMs for gas permeation: Principles, synthesis, and current status. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechnik, J.; Sumby, C.J.; Janiak, C. Enhancing mixed-matrix membrane performance with metal-organic framework additives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 4467–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanh Jeazet, H.B.; Staudt, C.; Janiak, C. Metal-organic frameworks in mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Li, H.; Chen, V. Challenges and opportunities for mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Sanip, S.M.; Ng, B.C.; Aziz, M. Recent advances of inorganic fillers in mixed matrix membrane for gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, S.L.; Tye, C.T.; Bhatia, S. Membrane separation process-Pervaporation through zeolite membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wen, R.; Guo, Y.H.; Su, J.F.; Matsuura, T. Multilayer poly(vinyl alcohol)-zeolite 4A composite membranes for ethanol dehydration by means of pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) for ethanol purification through pervaporation: Current state of the art. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, Y.; Abbasi, M.; Hashemifard, S.A. Investigation of in-line coagulation-MF hybrid process for oily wastewater treatment by using novel ceramic membranes. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Xu, X.; Yao, X.; Liu, H.; Gu, X. Fabrication of novel hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite membranes with tunable mesopores for ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.X.; Huang, X.C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.M.; Tang, C.Y. A thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membrane prepared on a support with in situ embedded zeolite nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 166, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, X.; Sun, L.; Rong, H.; Zhu, G. A zeolite-like aluminophosphate membrane with molecular-sieving property for water desalination. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. A review on inorganic membranes for desalination and wastewater treatment. Desalination 2018, 434, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, M.; Lakhotia, S.R.; Ghosh, A.K.; Bindal, R.C.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Lakhotia, S.R.; Ghosh, A.K.; Bindal, R.C. Removal of arsenic from aqueous media using zeolite/chitosan nanocomposite membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, A.; Carnevale, M.C.; Donato, L.; Drioli, E.; Alharbi, O.; Aljlil, S.A.; Criscuoli, A.; Algieri, C. Scale-up of MFI zeolite membranes for desalination by vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 397, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, D.; Claudio, G.; Eames, P.C. An experimental investigation to assess the potential of using MgSO4 impregnation and Mg2+ ion exchange to enhance the performance of 13X molecular sieves for interseasonal domestic thermochemical energy storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.H.; Chen, L.; Sun, L.B.; Liu, X.Q. Adsorptive removal of thiophene by cu-modified mesoporous silica MCM-48 derived from direct synthesis. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, L.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Chebude, Y.; Diaz, I. Synthesis of zeolite A using kaolin from Ethiopia and its application in detergents. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3440–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čejka, J.; Centi, G.; Perez-Pariente, J.; Roth, W.J. Zeolite-based materials for novel catalytic applications: Opportunities, perspectives and open problems. Catal. Today 2012, 179, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zones, S.I. Translating new materials discoveries in zeolite research to commercial manufacture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E. Zeolites from a materials chemistry perspective. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigen, E.M. Chapter 2 zeolites and molecular sieves an historical perspective. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1991, 58, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millini, R.; Bellussi, G. Zeolite Science and Perspectives. In Zeolites in Catalysis; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 1–36. ISBN 9781788010610. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, A.D.J.M.; de León, G.C.; García Rodríguez, S.P.; Fuentes López, N.C.; Pérez Camacho, O.; Perera Mercado, Y.A. Na+/Ca2+aqueous ion exchange in natural clinoptilolite zeolite for polymer-zeolite composite membranes production and their CH4/CO2/N2 separation performance. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 54, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Leo, C.P.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ahmad, A.L. Interfacial sealing and functionalization of polysulfone/SAPO-34 mixed matrix membrane using acetate-based ionic liquid in post-impregnation for CO2capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, Z.; Ilyas, A.; Li, X.; Bilad, M.R.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Khan, A.L. Tuning the gas separation performance of fluorinated and sulfonated PEEK membranes by incorporation of zeolite 4A. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afarani, H.T.; Sadeghi, M.; Moheb, A. The gas separation performance of polyurethane-zeolite mixed matrix membranes. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2016, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, G.S.; Moreira, F.K.V.; Matsumoto, R.L.S.; Michelon, M.; Filho, F.M.; Hubinger, M.D. Influence of nanofiltration membrane features on enrichment of jussara ethanolic extract (Euterpe edulis) in anthocyanins. J. Food Eng. 2018, 226, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amooghin, A.E.; Omidkhah, M.; Kargari, A. Enhanced CO2 transport properties of membranes by embedding nano-porous zeolite particles into Matrimid[registered sign]5218 matrix. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 8552–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Barquín, A.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Valencia, S.; Irabien, A. Mixed matrix membranes for O2/N2 separation: The influence of temperature. Membranes 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavolaro, A.; Drioli, E. Zeolite membranes. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 975–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Nakayama, K.; Sakai, H. Gas separation characteristics of DDR type zeolite membrane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 68, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Bu, N.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, R. Preparation of steam-stable high-silica CHA (SSZ-13) membranes for CO2/CH4and C2H4/C2H6 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakhov, A.O.; Knyazeva, E.E.; Novitsky, E.G. Gas transport properties of LiA type zeolite-filled poly(trimethylsilylpropyne) membranes. Pet. Chem. 2015, 55, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.-D.; Peinemann, K.-V.; Behling, R.-D. Ceramic zeolite composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 82, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.H.; Park, H.C.; Kang, Y.S.; Won, J.; Kim, W.N. Zeolite-filled polyimide membrane containing 2,4,6-triaminopyrimidine. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 188, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 1991; ISBN 0792309782. [Google Scholar]
- Fick, A. Erwiderung auf einige Stellen der Abhandlung: ”Ueber die Diffusion von Flüssigkeiten; vonFr. Beilstein. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1857, 102, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012; ISBN 9781118359686. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, T.S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander Stern, S. Polymers for gas separations: The next decade. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 94, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastani, D.; Esmaeili, N.; Asadollahi, M. Polymeric mixed matrix membranes containing zeolites as a filler for gas separation applications: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Ebadi Amooghin, A.; Montazer-Rahmati, M.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. State-of-the-art membrane based CO2 separation using mixed matrix membranes (MMMs): An overview on current status and future directions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 817–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Mizushina, Y.; Mizukami, F.; Sakaguchi, K. Selective adsorption of biopolymers on zeolites. Chem. A Eur. J. 2001, 7, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chung, T.S.; Cao, C.; Kulprathipanja, S. The effects of polymer chain rigidification, zeolite pore size and pore blockage on polyethersulfone (PES)-zeolite A mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 260, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Burns, R.; Schaeffer, M.; Koros, W.J. Challenges in forming successful mixed matrix membranes with rigid polymeric materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechar, T.W.; Kim, S.; Vaughan, B.; Marand, E.; Baranauskas, V.; Riffle, J.; Jeong, H.K.; Tsapatsis, M. Preparation and characterization of a poly(imide siloxane) and zeolite L mixed matrix membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 277, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Nik, O.G.; Rodrigue, D.; Kaliaguine, S. Mixed matrix membranes of aminosilanes grafted FAU/EMT zeolite and cross-linked polyimide for CO2/CH4 separation. Polymer 2012, 53, 3269–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Husain, S.; Koros, W.J. A general strategy for adhesion enhancement in polymeric composites by formation of nanostructured particle surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorosti, F.; Omidkhah, M.R.; Pedram, M.Z.; Moghadam, F. Fabrication and characterization of polysulfone/polyimide-zeolite mixed matrix membrane for gas separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Cao, C.; Huang, Z.; Kulprathipanja, S. Fundamental understanding of nano-sized zeolite distribution in the formation of the mixed matrix single- and dual-layer asymmetric hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Kulprathipanja, S. An investigation to revitalize the separation performance of hollow fibers with a thin mixed matrix composite skin for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 276, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Rajagopalan, R. Dual-layer hollow carbon fiber membranes for gas separation consisting of carbon and mixed matrix layers. Carbon 2007, 45, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Kulprathipanja, S. Fabrication of Mixed Matrix Hollow Fibers with Intimate Polymer–Zeolite Interface for Gas Separation. AIChe J. 2006, 52, 2898–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Rahim, R.A.; Rahman, W.A.W.A. Characterization of polyethersulfone/Matrimid® 5218 miscible blend mixed matrix membranes for O2/N2 gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Balkus, K.J.; Musselman, I.H.; Ferraris, J.P. Mixed-matrix membranes composed of Matrimid® and mesoporous ZSM-5 nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Musselman, I.H.; Ferraris, J.P.; Balkus, K.J. Gas permeability properties of mixed-matrix matrimid membranes containing a carbon aerogel: A material with both micropores and mesopores. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 2794–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, O.; Mosleh, S.; Khosravi, T.; Mohammadi, T. Preparation, characterization and gas permeation of polyimide mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaidou, C.I.; Pantoleontos, G.; Koutsonikolas, D.E.; Kaldis, S.P.; Sakellaropoulos, G.P. Gas separation properties of polyimide-zeolite mixed matrix membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Hägg, M.B. Development of matrimid/zeolite 4A mixed matrix membranes using low boiling point solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 115, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Asarehpour, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Bakhtiari, O. Preparation and characterization of SAPO-34—Matrimid® 5218 mixed matrix membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loloei, M.; Omidkhah, M.; Moghadassi, A.; Amooghin, A.E. Preparation and characterization of Matrimid® 5218 based binary and ternary mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 39, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Kazemi, A.; Talebnia, F. Matrimid mixed matrix membranes for enhanced CO2/CH4 separation. J. Polym. Eng. 2016, 36, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Bakhtiari, O. Effective hydrogen purification from methane via polyimide Matrimid® 5218-Deca-dodecasil 3R type zeolite mixed matrix membrane. Energy 2017, 141, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D.; Tezel, F.H.; Kruczek, B.; Kalipcilar, H. Investigation and comparison of mixed matrix membranes composed of polyimide matrimid with ZIF-8, silicalite, and SAPO-34. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane gas separation: A review/state of the art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norahim, N.; Yaisanga, P.; Faungnawakij, K.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Klaysom, C. Recent membrane developments for CO2 separation and capture. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Navarro, M.T.; Pariente, J.P. Synthesis of an ultralarge pore titanium silicate isomorphous to MCM-41 and its application as a catalyst for selective oxidation of hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, A.; Stöcker, M.; Schmidt, R. Composites of micro- and mesoporous materials: Simultaneous syntheses of MFI/MCM-41 like phases by a mixed template approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 27, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.L.; Klaysom, C.; Gahlaut, A.; Khan, A.U.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Mixed matrix membranes comprising of Matrimid and -SO3H functionalized mesoporous MCM-41 for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi Amooghin, A.; Omidkhah, M.; Sanaeepur, H.; Kargari, A. Preparation and characterization of Ag+ ion-exchanged zeolite-Matrimid® 5218 mixed matrix membrane for CO2/CH4 separation. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundstock, A.; Friebe, S.; Caro, J. On comparing permeation through Matrimid®-based mixed matrix and multilayer sandwich FAU membranes: H2/CO2 separation, support functionalization and ion exchange. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Lee, S.S.; Bae, T.H. Mixed-matrix membranes containing inorganically surface-modified 5A zeolite for enhanced CO2/CH4 separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 237, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amooghin, A.E.; Sanaeepur, H.; Omidkhah, M.; Kargari, A. “Ship-in-a-bottle”, a new synthesis strategy for preparing novel hybrid host-guest nano-composites for highly selective membrane gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1751–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.D.; Fout, T.; Plasynski, S.; McIlvried, H.; Srivastava, R.D. Advances in CO2 capture technology-The U.S. Department of Energy—s Carbon Sequestration Program. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2008, 2, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Moral-Vico, J.; Abo Markeb, A.; Busquets-Fité, M.; Komilis, D.; Puntes, V.; Sánchez, A.; Font, X. Critical review of existing nanomaterial adsorbents to capture carbon dioxide and methane. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Li, F.; Yuan, Q. Adsorption separation of CO2/CH4 gas mixture on the commercial zeolites at atmospheric pressure. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Bao, Z. Adsorption of CO2, CH4, N2O, and N2 on MOF-5, MOF-177, and Zeolite 5A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavenati, S.; Grande, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E. Adsorption equilibrium of methane, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen on zeolite 13X at high pressures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talesh, S.S.A.; Fatemi, S.; Hashemi, S.J.; Ghasemi, M. Effect of Si/Al ratio on CO2-CH4 adsorption and selectivity in synthesized SAPO-34. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangnekar, N.; Mittal, N.; Elyassi, B.; Caro, J.; Tsapatsis, M. Zeolite membranes—A review and comparison with MOFs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7128–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Zeolites | MOFs | Silicas | Carbon Molecular Sieves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed pore size | Cations interconnected by organic anions | Directly alter the molecular packing of the polymer chains | High adsorptivity capacity |
| High temperature stability | Rather flexible and dynamic frameworks | Increase the free volume of polymers | Relatively wide opening with constricted apertures |
| High stability in humidity | Coordinative bonds | Nonpermeability of the nonporous silica particles | Better affinity to glassy polymers |
| Limitations for modification | Flexible pore size, soft structure | Probable weak interaction silica–polymer | Good adhesion at interfaces |
| Pore size crystallographically controlled | Not well-defined molecular sieving | High possibility to produce interfacial voids | High productivity with excellent separation |
| Great potential as supported thin film | Low temperature stability | Possibilities for surface modification (e.g., silane coupling) | Well-defined molecular sieving |
| Not thermodynamically most stable but dense structures | Poor stability in humidity | - | Great potential for MMMs |
| Well-defined molecular sieving | Thermodynamically unstable | - | - |
| Good sorption and diffusion properties | A variety of possibilities for modification | - | - |
| - | Offer accessible open metals | - | - |
| - | Great potential for MMMs | - | - |
| Polymer | Tg (°C) | Permeability (Barrer) | Selectivity | FV | ρ (g/cm3) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | H2 | N2 | CO2 | CH4 | O2/N2 | CO2/N2 | CO2/CH4 | H2/CO2 | H2/N2 | H2/CH4 | ||||
| Matrimid® | 302–310 | 2.1 | 27.16 | 0.28 | 7.68 | 0.22 | 6.4 | 30 | 34.91 | 3.88 | 97 | 83.33 | 0.17 | 1.2 |
| Polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIM-1) | 399–415 | 370 | 1300 | 92 | 2300 | 125 | 4.0 | 25 | 18 | 0.57 | 14 | 10 | 0.24 | 0.94 |
| Polysulfone (PSF) | 185 | 1.2 | 16.4 * | 0.20 | 4.9 | 0.21 | 6.0 | 22.4 | 23.3 | 1.53 | 20 | 34.4 | 0.13 | 1.19 |
| Poly[1-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propyne] (PTMSP) | >250 | 7200 | 4200 | 6890 | 37,000 | 18,400 | 1.7 | 10.7 | 4.46 | 0.53 | 2.5 | 0.995 | 0.34 | 0.83 |
| Polybenzimidazole (PBI) | 435 | 0.009 | 0.6 | 0.0048 | 0.16 | 0.0018 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 88.88 | 3.75 | 125 | 333.3 | 0.11 | 1.311 |
| Molecule | Kinetic Diameter (Å) | Polarizability (Å3) | Dipole Moment (D) | Quadrupole Moment (D Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 3.30 | 2.650 | 0.000 | 4.30 |
| CH4 | 3.76 | 2.600 | 0.000 | 0.02 |
| H2 | 2.89 | 0.80 | 0.000 | 0.66 |
| O2 | 3.47 | 1.600 | 0.000 | 0.39 |
| CO | 3.69 | 1.95 | 0.112 | 2.50 |
| N2 | 3.64 | 1.760 | 0.000 | 1.52 |
| Type of Zeolite | Filler Loading | Evaluated Application | Conditions | Performance | Remark of the Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite 4A | 15 wt % | Separation CO2/CH4 | Single gas permeation, 10 bar, 30 °C. | CO2: 5.9 Barrer CH4: 0.1 Barrer CO2/CH4: 43 | Good interaction between zeolite and polymer, enhancing the separation performance. | [69] |
| ZSM-5 | 10 wt % | Separation CO2/CH4, O2/N2 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 2–5 bar, 35 °C. | N2: 0.2 Barrer O2: 0.7 Barrer CH4: 0.3 Barrer CO2: 1.5 Barrer CO2/CH4: 4.4 O2/N2: 3.0 | The MMMs displayed higher permeability than the pristine polymer. | [61] |
| Zeolite 4A | 30 wt % | Separation CO2/N2, He/N2, H2/He, H2/CO2 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 10 bar, 25 °C. | H2: 83 Barrer CO2: 262 Barrer N2: 140 Barrer He: 38 Barrer CO2/N2: 50.6 | Enhanced permeability for He, H2, CO2, and N2 increasing with zeolite loading. | [70] |
| ZSM-5 | 20 wt % | Separation CO2/N2 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 10 bar, 25 °C. | H2: 147 Barrer CO2: 423 Barrer N2: 180 Barrer He: 108 Barrer CO2/N2: 86.2 | Enhanced permeability for He, H2, CO2, and N2 increasing with zeolite loading. | [70] |
| Zeolite 13X | 30 wt % | Separation CO2/N2 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 10 bar, 25 °C. | H2: 178 Barrer CO2: 378 Barrer N2: 185 Barrer He: 111 Barrer | Enhanced permeability for He, H2, CO2, and N2 increasing with zeolite loading. | [70] |
| Amine-grafted zeolite | 25 wt % | Separation CO2/CH4 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 150 psi, 35 °C. | CO2: 6.3 Barrer CH4: 0.1 Barrer CO2/CH4: 48.5 | Cross-linked Matrimid® and modified zeolite displayed a considerable enhancement towards CO2/CH4 separation. | [59] |
| Zeolite 4A | 30 wt % | Separation CO2/N2, O2/N2, H2/N2 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 8 bar, 30 °C | H2: 101.6 Barrer CO2: 48.3 Barrer O2: 11.1 Barrer N2: 2.0 Barrer CO2/N2: 23.3 O2/N2: 5.3 H2/N2: 49.1 | The MMMs showed enhanced permeability for all gases. | [71] |
| SAPO-34 | 20 wt % | Separation CO2/CH4 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 10 bar, 25 °C | CO2: 6.9 Barrer CH4: 0.1 Barrer CO2/CH4: 67 | The MMMs displayed enhancements for both permeability and selectivity. | [72] |
| Zeolite NaY | 20 wt % | Separation CO2/CH4 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 2 bar, 35 °C. | CO2: 22 Barrer CH4: 0.8 Barrer CO2/CH4: 27.6 | The CO2 permeability was enhanced more than twofold by incorporating the zeolite | [39] |
| ZSM-5 | 5 wt % | Separation CO2/CH4 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 10 bar, 35 °C. | CO2: 15.7 Barrer CH4: 0.8 Barrer CO2/CH4: 19.2 | The MMMs displayed enhancements for both permeability and selectivity. | [73] |
| Zeolite 13X | 30 wt % | Separation CO2/CH4 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 12 bar, 25 °C. | CO2: 10.5 Barrer CH4: 0.2 Barrer CO2/CH4: 39.8 | The MMMs displayed enhanced separation performance over the pristine polymer. | [74] |
| Deca-dodecasil 3R (DDR) | 20 wt % | Separation H2/CH4 | Single gas permeation, conditions: 10 bar, 35 °C. | H2: 34.9 Barrer H2/CH4: 375.2 | The incorporation of the zeolite-type filler enhanced the hydrogen permeability more than 100%. | [75] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro-Muñoz, R.; Fíla, V. Progress on Incorporating Zeolites in Matrimid®5218 Mixed Matrix Membranes towards Gas Separation. Membranes 2018, 8, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8020030
Castro-Muñoz R, Fíla V. Progress on Incorporating Zeolites in Matrimid®5218 Mixed Matrix Membranes towards Gas Separation. Membranes. 2018; 8(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro-Muñoz, Roberto, and Vlastimil Fíla. 2018. "Progress on Incorporating Zeolites in Matrimid®5218 Mixed Matrix Membranes towards Gas Separation" Membranes 8, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8020030
APA StyleCastro-Muñoz, R., & Fíla, V. (2018). Progress on Incorporating Zeolites in Matrimid®5218 Mixed Matrix Membranes towards Gas Separation. Membranes, 8(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8020030






