Chirality-Dependent Interaction of d- and l-Menthol with Biomembrane Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. NMR Measurements
2.3. Preparation of Liposomes
2.4. Microscopic Observations
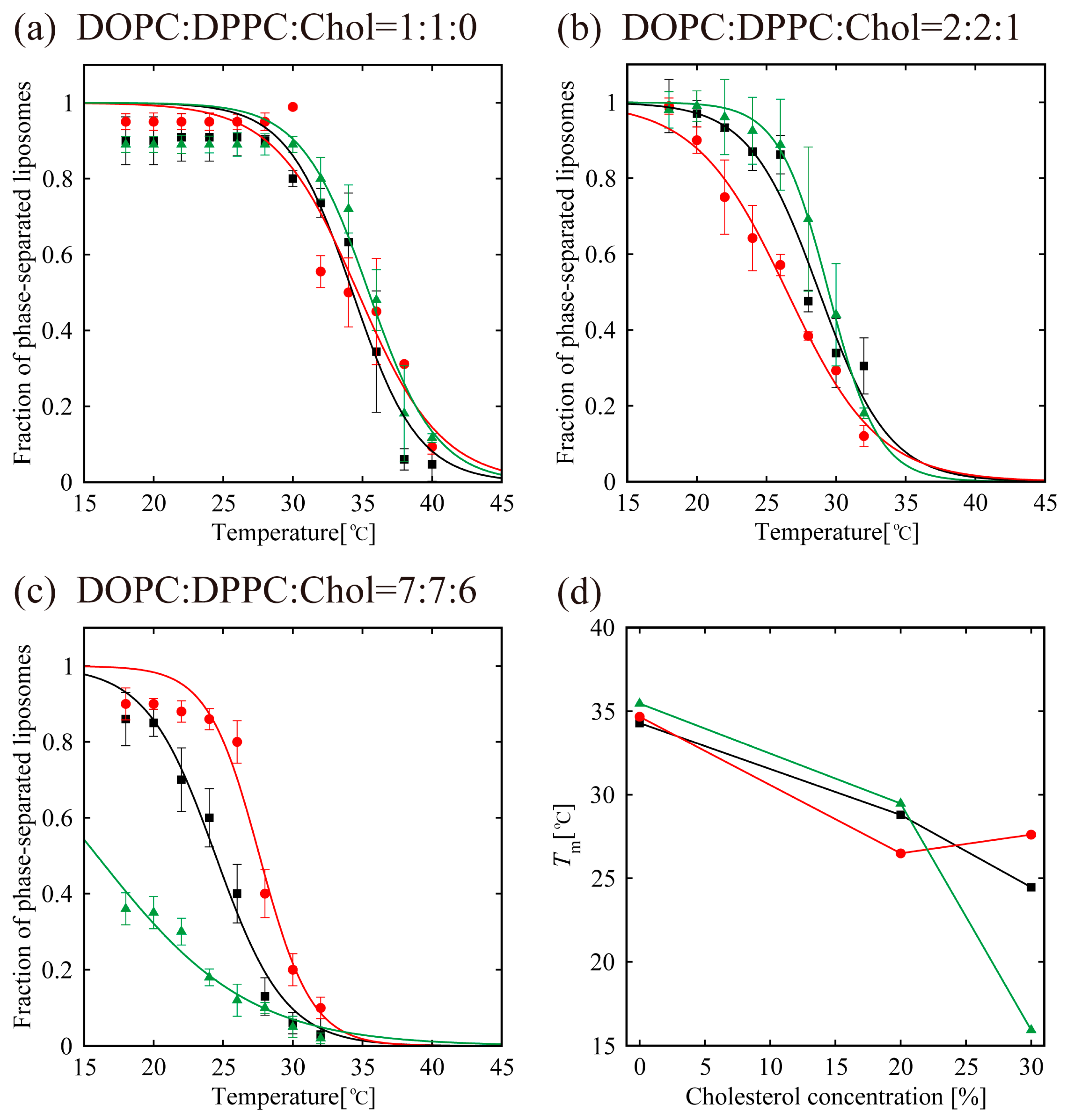
2.5. Miscibility Temperature Measurements
3. Results
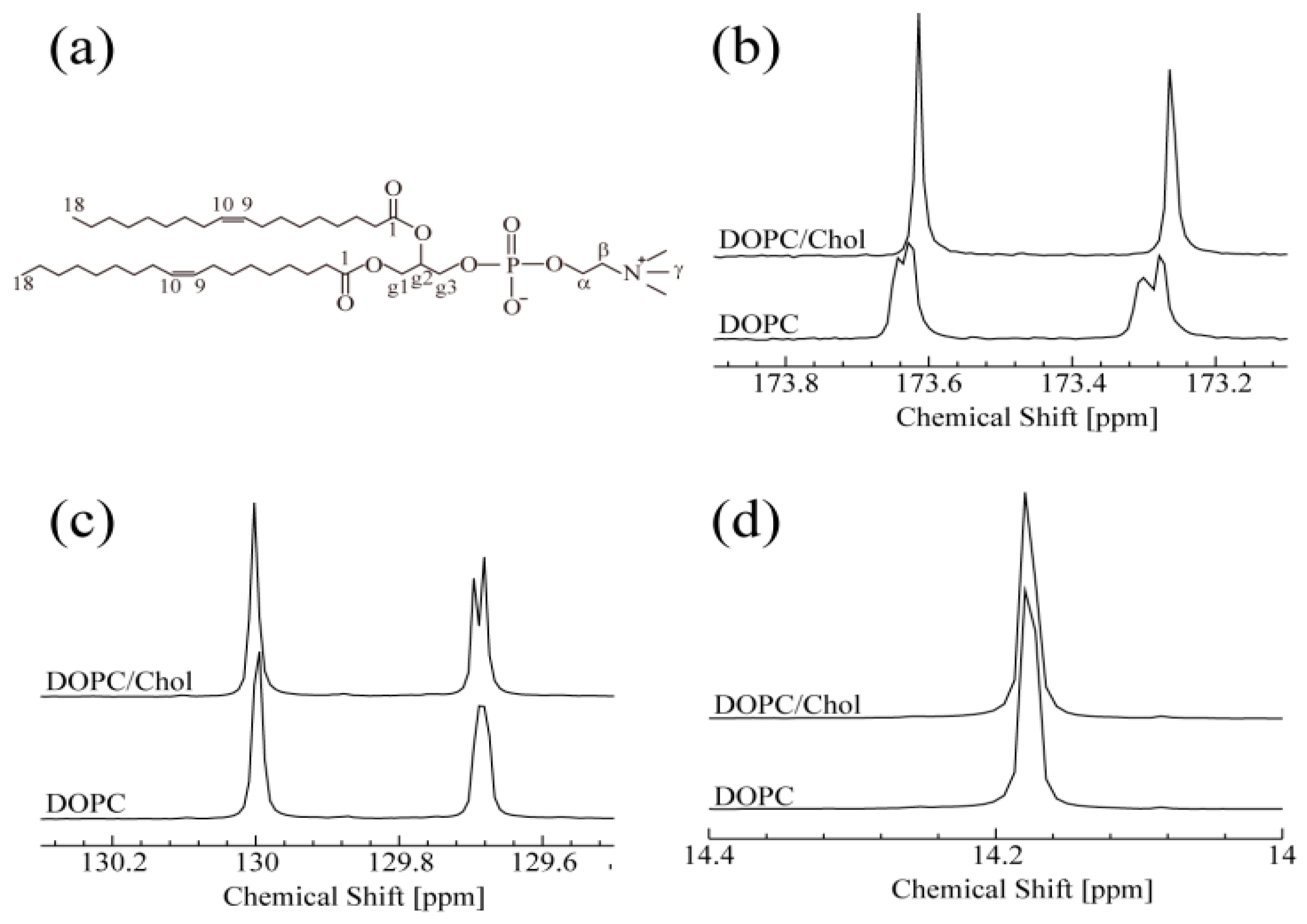
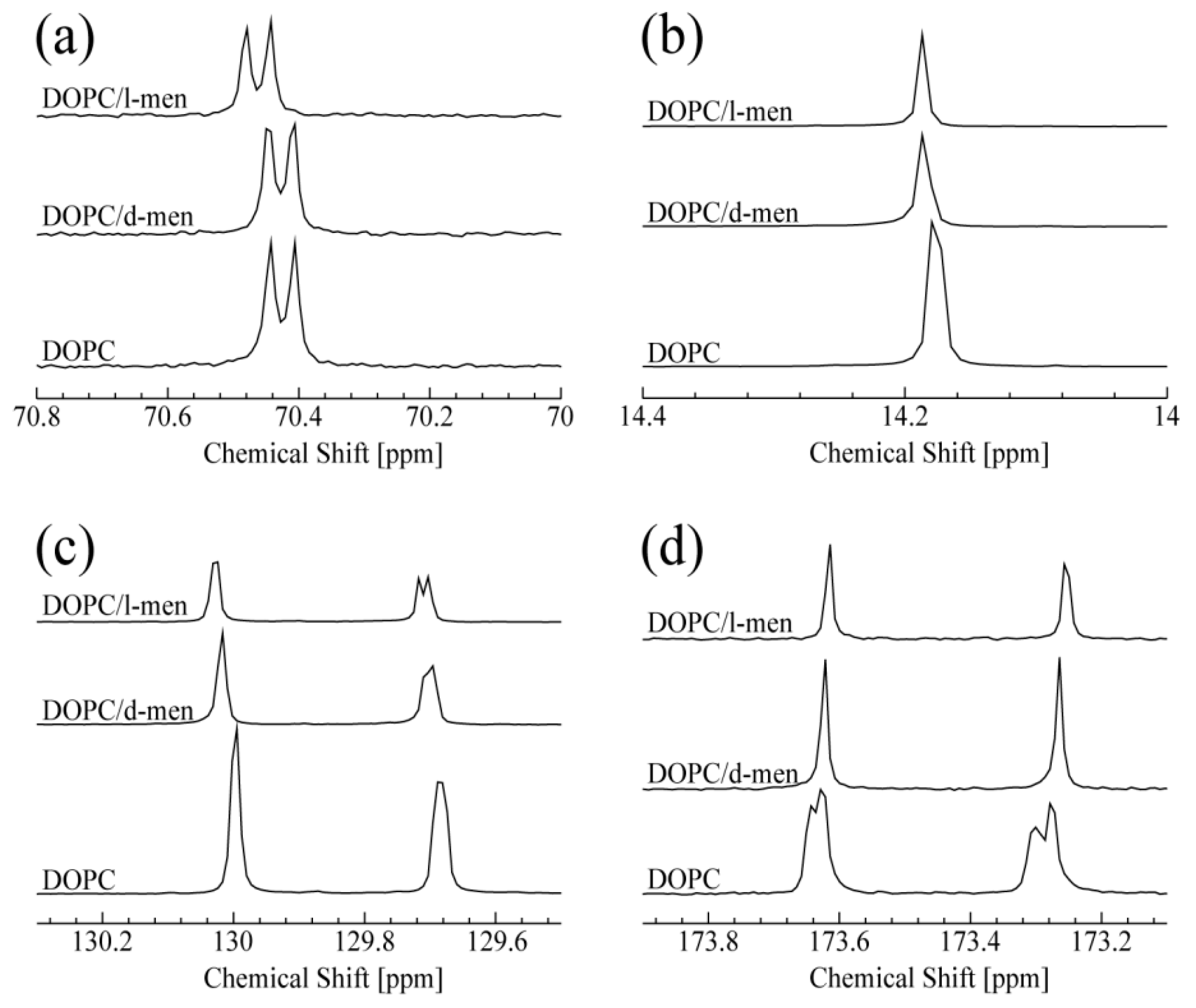
3.1. NMR Spectroscopy
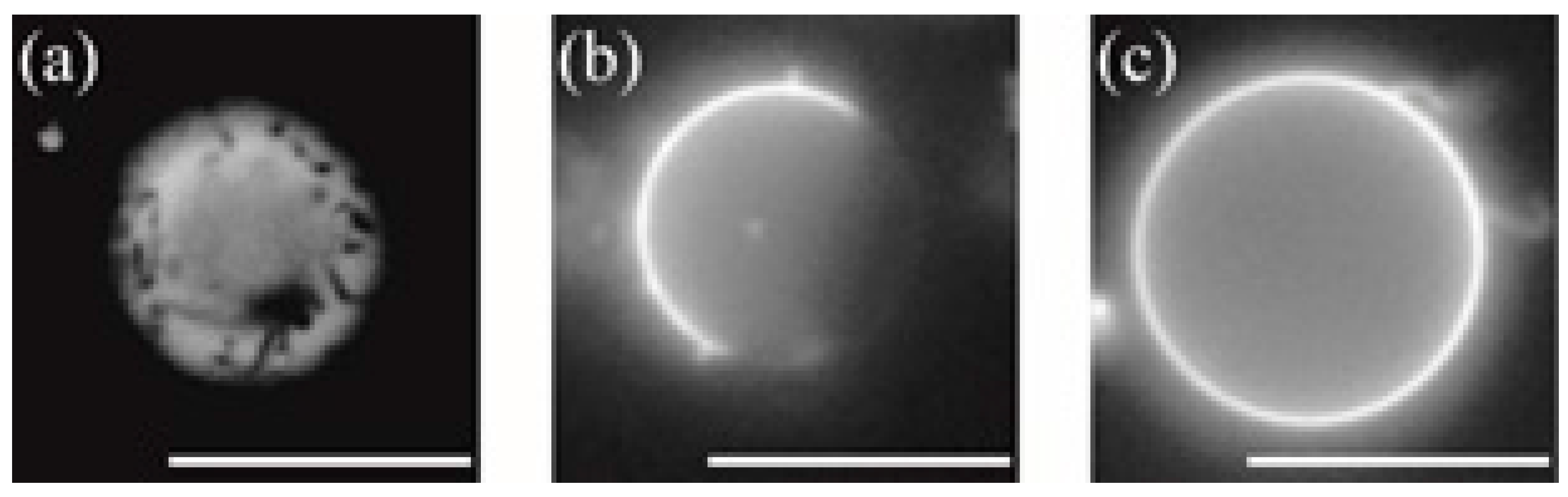
3.2. Phase-Separated Structure Observation by Microscope
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, D.A.; London, E. Structure and Function of Sphingolipid- and Cholesterol-rich Membrane Rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17221–17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanzal-Bayer, M.F.; Hancock, J.F. Lipid rafts and membrane traffic. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2098–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klymchenko, A.S.; Kreder, R. Fluorescent Probes for Lipid Rafts: From Model Membranes to Living Cells. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingwood, D.; Simons, K. Lipid Rafts As a Membrane-Organizing Principl. Science 2009, 327, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, L.J. The challenge of lipid rafts. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pralle, A.; Keller, P.; Florin, E.L.; Simons, K.; Hörber, J.K.H. Sphingolipid–Cholesterol Rafts Diffuse as Small Entities in the Plasma Membrane of Mammalian Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K.; Toomre, D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugahara, K.; Shimokawa, N.; Takagi, M. Destabilization of Phase-separated Structures in Local Anesthetic-containing Model Biomembranes. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 1604–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature 2003, 426, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Haldar, S. Interactions between cholesterol and lipids in bilayer membranes. Role of lipid headgroup and hydrocarbon chain-backbone linkage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2000, 1467, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Mitchell, D.J.; Ninham, B.W. Theory of self-assembly of hydrocarbon amphiphiles into micelles and bilayers. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. II 1976, 72, 1525–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesołowska, O.; Michalak, K.; Maniewska, J.; Hendrich, A.B. Giant unilamellar vesicles—A perfect tool to visualize phase separation and lipid rafts in model systems. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2009, 56, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blosser, M.C.; Horst, B.G.; Keller, S.L. cDICE method produces giant lipid vesicles under physiological conditions of charged lipids and ionic solutions. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 7364–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, M.; Vestergaard, M.; Hamada, T.; Takagi, M. Real-time observation of model membrane dynamics induced by Alzheimer’s amyloid beta. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 147, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionova, I.V.; Livshits, V.A.; Marsh, D. Phase Diagram of Ternary Cholesterol/Palmitoylsphingomyelin/Palmitoyloleoyl-Phosphatidylcholine Mixtures: Spin-Label EPR Study of Lipid-Raft Formation. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Phase Separation in Lipid Membranes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, T.; Kishimoto, Y.; Nagasaki, T.; Takagi, M. Lateral phase separation in tense membranes. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9061–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.V.; Andersen, H.H.; Møller, H.G.; Eskelund, P.W. Somatosensory and vasomotor manifestations of individual and combined stimulation of TRPM8 and TRPA1 using topical l-menthol and trans-cinnamaldehyde in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, G.; Strohbeck, M.; Koch, S.; Caglioti, L.; Zucchi, C.; Palyi, G. Molecular elements of ion permeation and selectivity within calcium chennels. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 34, 181–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandini, M.A.; Sandoval, A.; Felix, R. Toxins targeting voltage-activated Ca2+ channels and their potential biochemical applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, L.J.; Hwang, S.W.; Miyamoto, T.; Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A.; Story, G.M. More than cool: Promiscuous relationships of menthol and other sensory compounds. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2006, 32, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliff, M.A.; Green, B.G. Sensory irritation and coolness produced by menthol: Evidence for selective desensitization of irritation. Physiol. Behav. 1994, 56, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.G. Menthol modulates oral sensations of warmth and cold. Physiol. Behav. 1985, 35, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R. Menthol and Related Cooling Compounds. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.O.; Glantz, S.A. Menthol: Putting the pieces together. Tob. Control 2011, 20, ii1–ii7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.J. Menthol cigarettes and smoking cessation behaviour: A review of tobacco industry documents. Tob. Control 2011, 20, ii49–ii56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, M.V.; Glantz, S.A. Direct disease-inducing effects of menthol through the eyes of tobacco companies. Tob. Control 2011, 20, ii44–ii48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausner, K. Menthol cigarettes and smoking initiation: A tobacco industry perspective. Tob. Control 2011, 20, ii12–ii19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKemy, D.D. TRPM8: The Cold and Menthol Receptor. in: Heller S (Ed.), Southern California, n.d. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK5238/ (accessed on 20 October 2017).
- Chuang, H.; Neuhausser, W.M.; Julius, D. The Super-Cooling Agent Icilin Reveals a Mechanism of Coincidence Detection by a Temperature-Sensitive TRP Channel. Neuron 2004, 43, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.C.; Turcotte, C.M.; Betts, B.A.; Yeung, W.Y.; Agyeman, A.S.; Burk, L.A. Modulation of human GABAA and glycine receptor currents by menthol and related monoterpenoids. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 506, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrar, A.; Nordman, J.C.; Veltri, D.; Yang, K.-H.S.; Al Kury, L.; Shuba, Y.; Mahgoub, M.; Howarth, F.C.; Sadek, B.; Shehu, A.; et al. Menthol Binding and Inhibition of α7-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67674. [Google Scholar]
- Palyi, G.; Alberts, K.; Bartik, T.; Boese, R.; Fráter, G.; Herbrich, T.; Herfurth, A.; Kriebel, C.; Sorkau, A.; Tschoerner, M.C.; et al. Intermolecular transmission of chiral information. Conformational enantiomers in crystalline organocobalt complexes generated by self-organization. Orhanomettalics 1996, 15, 3253–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, C.; Turrini, D.; Boese, R.; Bencze, L.; Kurdi, R.; Caglioti, L.; Palyi, G. Alkylcobalt carbonyls, XIV. Generation of chiral conformations by centres of chirality in organocobalt complexes. Can. J. Chem. 2005, 83, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warschawski, D.E.; Devaux, P.F. Order parameters of unsaturated phospholipids in membranes and the effect of cholesterol: A 1H–13C solid-state NMR study at natural abundance. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 34, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordani, C.; Wakai, C.; Yoshida, K.; Okamura, E.; Matubayasi, N.; Nakahara, M. Cholesterol Location and Orientation in Aqueous Suspension of Large Unilamellar Vesicles of Phospholipid Revealed by Intermolecular Nuclear Overhauser Effect. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 2622–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Nanz, D. Study of phospholipid structure by 1H, 13C, and 31P dipolar couplings from two-dimensional NMR. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huster, D.; Arnold, K.; Gawrisch, K. Influence of Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cholesterol on Lateral Lipid Organization in Phospholipid Mixtures. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 17299–17308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzorati, M.; Bigler, P.; Vermathen, M. Interactions between selected photosensitizers and model membranes: An NMR classification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, G.; Dai, X.; Yin, Q.; Shi, X.; Qiao, Y. Interaction of menthol with mixed-lipid bilayer of stratum corneum: A coarse-grained simulation study. J. Mol. Graph Model. 2015, 60, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veatch, S.L.; Soubias, O.; Keller, S.L.; Gawrisch, K. Critical fluctuations in domian-forming lipid mixtures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17650–17655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veatch, S.L.; Cicuta, P.; Sengupta, P.; Honerkamp-Smith, A.; Holowka, D.; Baird, B. Critical Fluctuations in Plasma Membrane Vesicles. ACS. Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H. A structural model for the cholesterol-phosphatidylcholine complexes in bilayer membranes. Lipids 1977, 12, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, M.; Huang, W.; Wu, D.; Priestley, J.V. TRPV1, but not P2X, requires choles-terol for its function and membrane expression in rat nociceptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gusain, P.; Ohki, S.; Hoshino, K.; Tsujino, Y.; Shimokawa, N.; Takagi, M. Chirality-Dependent Interaction of d- and l-Menthol with Biomembrane Models. Membranes 2017, 7, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7040069
Gusain P, Ohki S, Hoshino K, Tsujino Y, Shimokawa N, Takagi M. Chirality-Dependent Interaction of d- and l-Menthol with Biomembrane Models. Membranes. 2017; 7(4):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7040069
Chicago/Turabian StyleGusain, Pooja, Shinya Ohki, Kunihide Hoshino, Yoshio Tsujino, Naofumi Shimokawa, and Masahiro Takagi. 2017. "Chirality-Dependent Interaction of d- and l-Menthol with Biomembrane Models" Membranes 7, no. 4: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7040069
APA StyleGusain, P., Ohki, S., Hoshino, K., Tsujino, Y., Shimokawa, N., & Takagi, M. (2017). Chirality-Dependent Interaction of d- and l-Menthol with Biomembrane Models. Membranes, 7(4), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7040069




