Hollow Fiber Supported Liquid Membrane Extraction Combined with HPLC-UV for Simultaneous Preconcentration and Determination of Urinary Hippuric Acid and Mandelic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions and Real Samples
2.3. Chromatographic Conditions
2.4. Extraction Procedure by HF-LPME
3. Result and Discussion
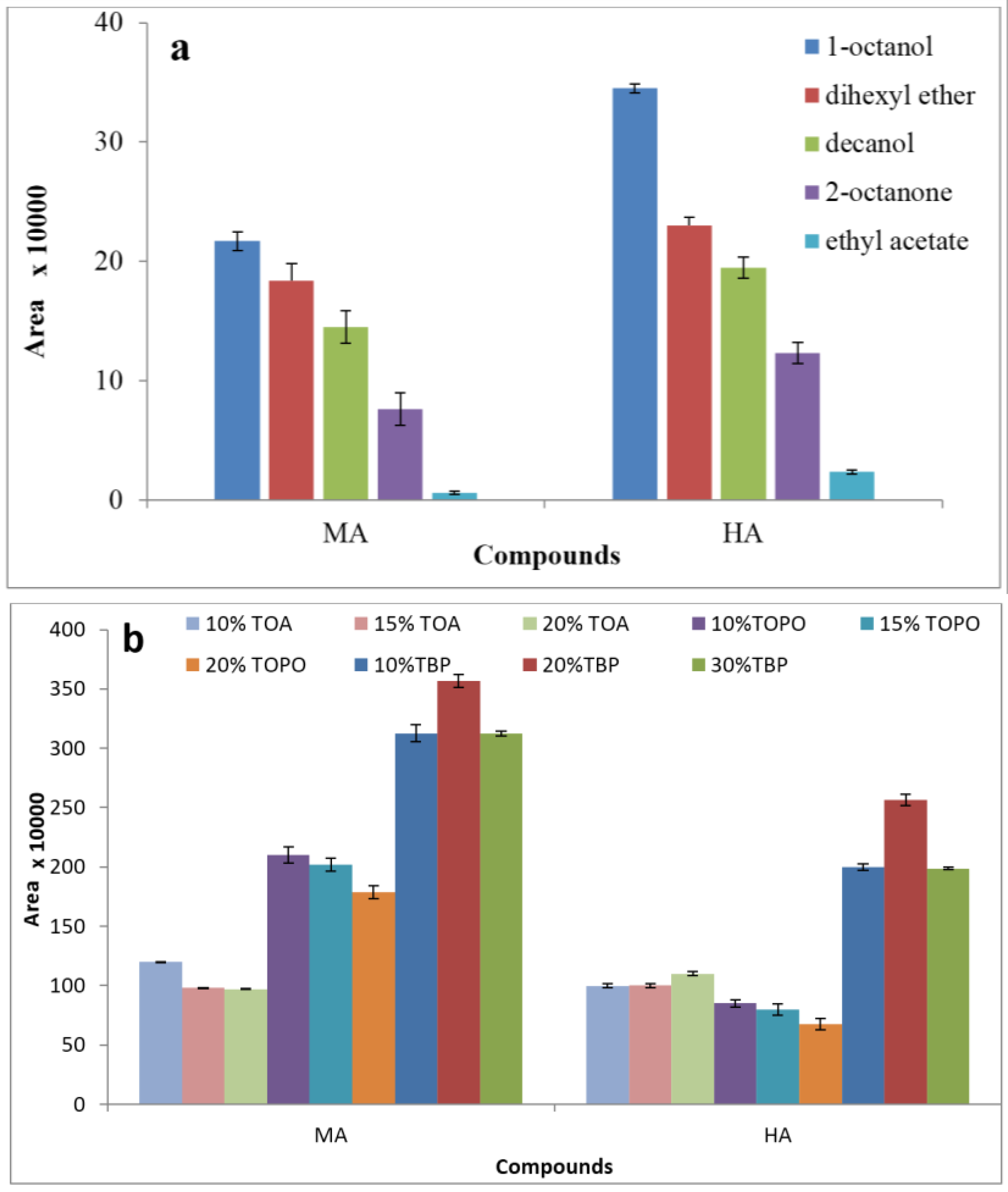
3.1. Effect of Extraction Solvent
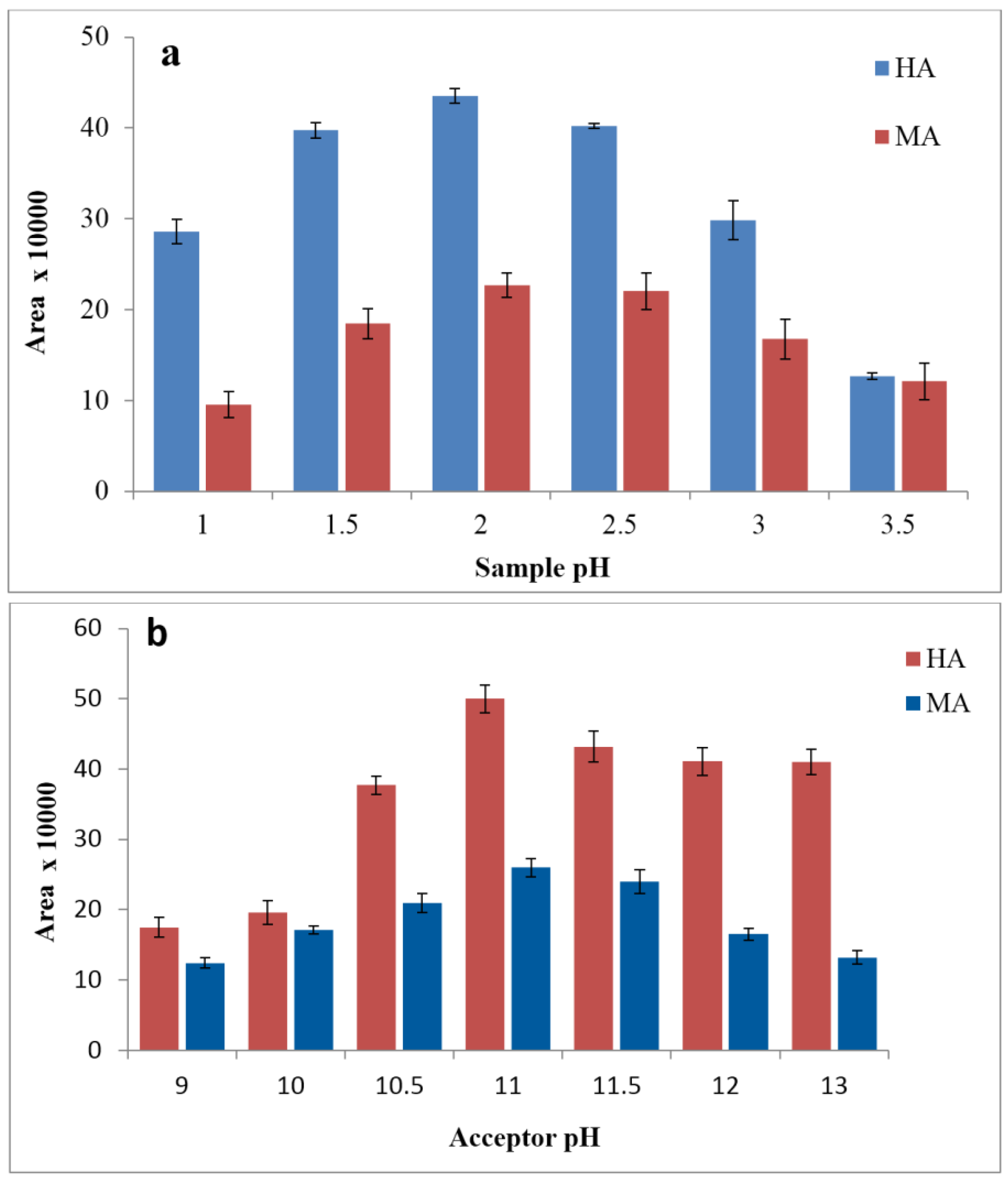
3.2. Effects of Donor and Acceptor pH
3.3. Effects of Agitation and Salinity
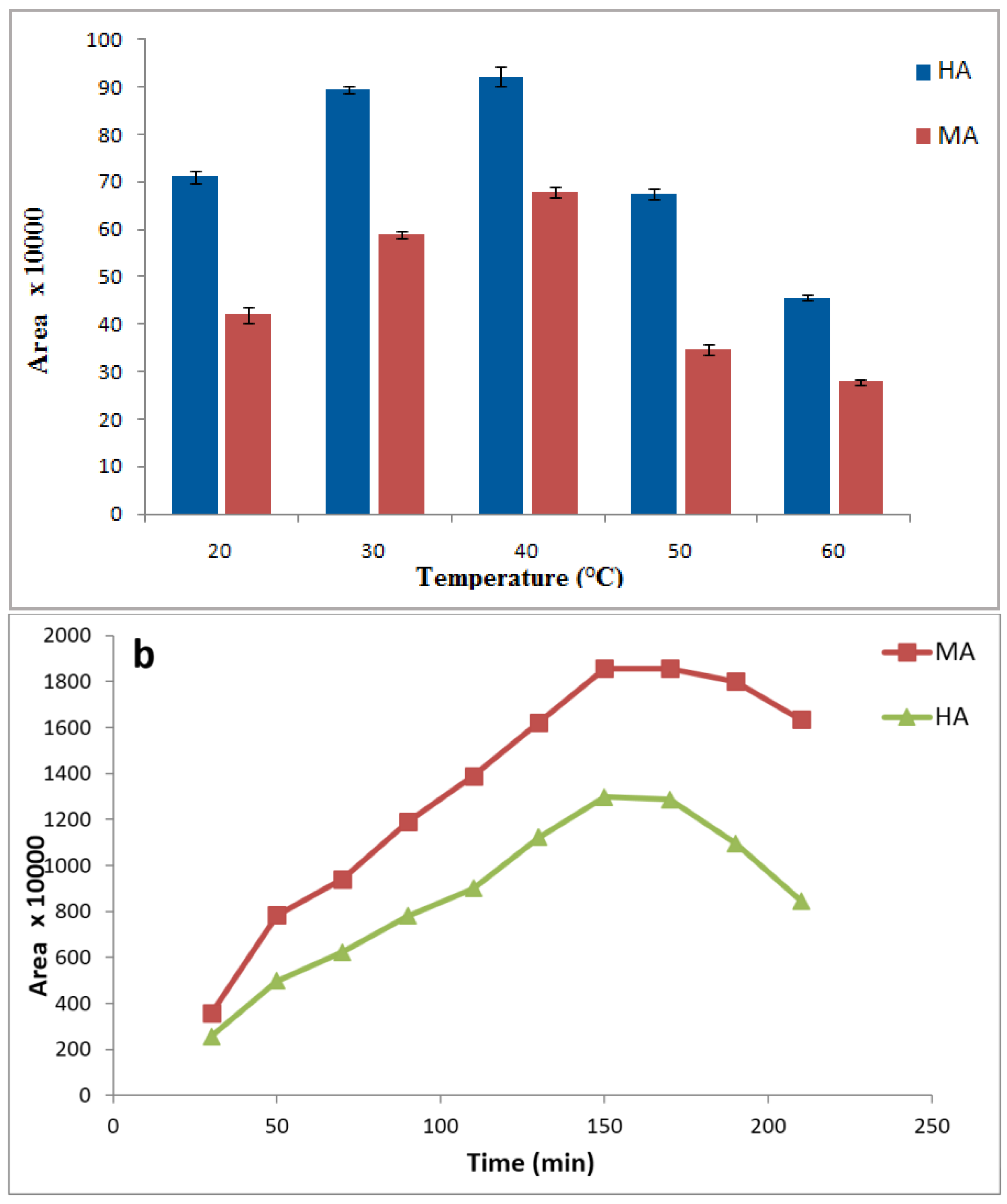
3.4. Effects of Sample Temperature and Extraction Time
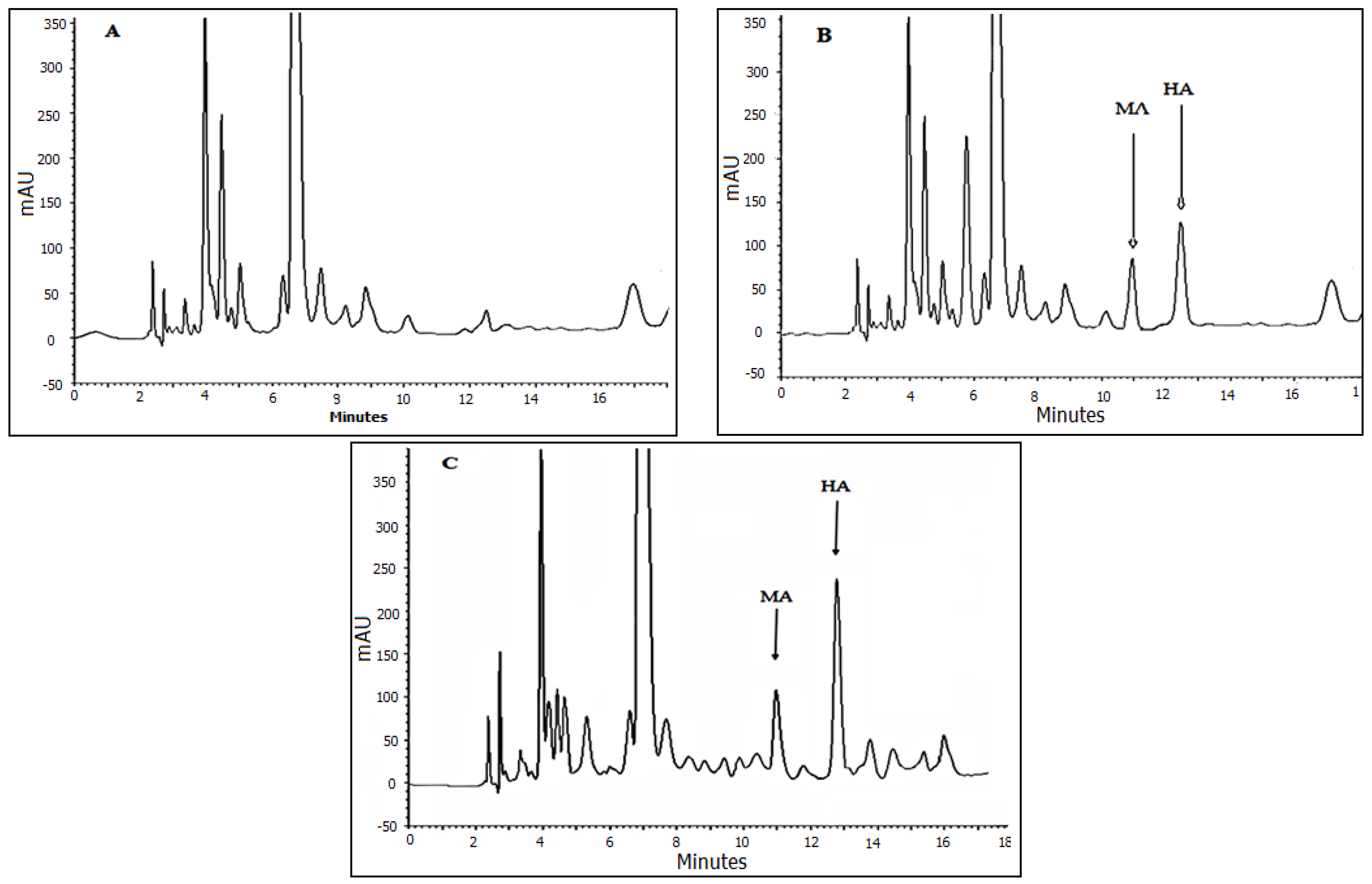
3.5. Method Validation and Application
3.6. Analysis of Real Samples Applicability
3.7. Comparison of the Proposed Method with Other Conventional Reported Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keymeulen, R.; Görgényi, M.; Héberger, K.; Priksane, A.; Van Langenhove, H. Benzene, toluene, ethyl benzene and xylenes in ambient air and Pinus sylvestris L. needles: A comparative study between Belgium, Hungary and Latvia. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 6327–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szucs, S.; Tóth, L.; Legoza, J.; Sárváry, A.; Ádány, R. Simultaneous determination of styrene, toluene, and xylene metabolites in urine by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Arch. Toxicol. 2002, 76, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Toluene; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2000.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease (ATSDR). Interaction profile for Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylenes (BTEX); U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2004.
- Chen, R.; Seaton, A. A Meta-analysis of Mortality among Workers Exposed to Organic Solvents. Occup. Med. 1996, 46, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACGIH. TLVs and BEIs: Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices; American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, Y.; Mamiya, T.; Mitani, K.; Wang, B.; Takigawa, T.; Kira, S.; Kataoka, H. Simultaneous determination of urinary hippuric acid, o-, m- and p-methylhippuric acids, mandelic acid and phenylglyoxylic acid for biomonitoring of volatile organic compounds by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 566, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Ansari, M. Exposure of Sweepers to Volatile Organic Compounds Using Urinary Biological Exposure Index. Health 2007, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Lee, J.; Eom, H. Rapid HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Eight Urinary Metabolites of Toluene, Xylene and Styrene. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 2021–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, T.; Kawabe, S.; Horike, T.; Taguchi, T.; Ogata, M. Simultaneous determination of the urinary metabolites of toluene, xylene and styrene using high-performance capillary electrophoresis: Comparison with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 730, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-T.; Hsieh, Y.-Z. Determination of metabolites of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene by β-cyclodextrin modified capillary electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2003, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, T.-C.; Lee, H.-L.; Lin, Y.-W. Fast and simple screening for the simultaneous analysis of seven metabolites derived from five volatile organic compounds in human urine using on-line solid-phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2015, 132, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, S.; Curini, R.; Gentili, A.; Perret, D.; Rocca, L.M. Simultaneous determination of the urinary metabolites of benzene, toluene, xylene and styrene using high-performance liquid chromatography/hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2004, 18, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffon, B.; Lema, M.; Méndez, J. Simultaneous high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of urinary mandelic and phenylglyoxylic acids as indirect evaluation of styrene exposure. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 753, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahtaheri, S.J.; Abdollahi, M.; Golbabaei, F.; Rahimi-Froushani, A.; Ghamari, F. Optimization of SPE for Analysis of Mandelic Acid as a Biomarker of Exposure to Ethyl Benzene. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2004, 1, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, C.N.; Chua, S.C.; Lee, B.L.; Liau, L.S. Determination of Mandelic Acid and Phenylglyoxylic Acid in the Urine and Its Use in Monitoring of Styrene Exposure. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1993, 17, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Hander, G.M.; Makahleh, A.; Saad, B.; Saleh, M.I.; Cheng, K.W. Sequential hollow-fiber liquid phase microextraction for the determination of rosiglitazone and metformin hydrochloride (anti-diabetic drugs) in biological fluids. Talanta 2015, 131, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Yamini, Y.; Ara, K.M.; Kamarei, F. Three-phase hollow fiber microextraction based on carrier-mediated transport combined with HPLC-UV for the analysis of dexamethasone sodium phosphate in biological samples. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-López, M.Á.; Ramos-Payán, M.; Ocaña-González, J.A.; Fernández-Torres, R.; Callejón-Mochón, M. Analytical Applications of Hollow Fiber Liquid Phase Microextraction (HF-LPME): A Review. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 804–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, M.; Hou, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S. Calibration of pre-equilibrium HF-LPME and its application to the rapid determination of free analytes in biological fluids. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 980, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payán, M.R.; López, M.A.B.; Fernández-Torres, R.; Mochón, M.C.; Ariza, J.L.G. Application of hollow fiber-based liquid-phase microextraction (HF-LPME) for the determination of acidic pharmaceuticals in wastewaters. Talanta 2010, 82, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, M.; Dinpanah, H. Three phases hollow fiber LPME combined with HPLC-UV for extraction, preconcentration and determination of valerenic acid in Valeriana officinalis. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Amiri, A.H.; Es’haghi, Z. BTEX determination in water matrices using HF-LPME with gas chromatography-flame ionization detector. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangiri, S.; Hatami, M.; Farhadi, K.; Bahram, M. Hollow-fiber-based LPME as a reliable sampling method for gas-chromatographic determination of pharmacokinetic parameters of valproic acid in rat plasma. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, R.A.; de Oliveira, A.R.M.; Bonato, P.S. Hollow fiber-based liquid-phase microextraction (HF-LPME) of isradipine and its main metabolite followed by chiral HPLC analysis: Application to an in vitro biotransformation study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2435–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-Navarro, M.; Ramos-Payán, M.; Fernández-Torres, R.; Callejón-Mochón, M.; Bello-López, M.Á. A novel application of three phase hollow fiber based liquid phase microextraction (HF-LPME) for the HPLC determination of two endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs), n-octylphenol and n-nonylphenol, in environmental waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-Navarro, M.; Ramos-Payán, M.; Luis Pérez-Bernal, J.; Fernández-Torres, R.; Callejón-Mochón, M.; Bello-López, M.Á. Application of three phase hollow fiber based liquid phase microextraction (HF-LPME) for the simultaneous HPLC determination of phenol substituting compounds (alkyl-, chloro- and nitrophenols). Talanta 2012, 99, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasheminasab, K.S.; Fakhari, A.R.; Shahsavani, A.; Ahmar, H. A new method for the enhancement of electromembrane extraction efficiency using carbon nanotube reinforced hollow fiber for the determination of acidic drugs in spiked plasma, urine, breast milk and wastewater samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1285, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Hian, K.L. Hollow fiber-protected liquid-phase microextraction of triazine herbicides. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Shao, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, A.; Chen, Y. Determination of Sulfonylurea Herbicides in Pears Using Hollow Fiber-Protected Magnetized Solvent-Bar Liquid-Phase Microextraction HPLC. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.-F.; Liu, J.-F.; Hu, X.-L.; Jiang, G.-B. Direct determination of chlorophenols in environmental water samples by hollow fiber supported ionic liquid membrane extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1139, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Albanis, T.A. Application of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction for the determination of insecticides in water. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1072, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghamari, F.; Bahrami, A.; Yamini, Y.; Shahna, F.G. Development of Hollow-Fiber Liquid-Phase Microextraction Method for Determination of Urinary trans, trans-Muconic Acid as a Biomarker of Benzene Exposure. Anal. Chem. Insights 2016, 11, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, L. Application of Three Phase Hollow Fiber LPME Using an Ionic Liquid as Supported Phase for Preconcentration of Bisphenol A and Diethylstilbestrol from Water Sample with HPLC Detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Adlnasab, L.; Shekari, N. Optimization of ion-pair based hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction combined with HPLC-UV for the determination of methimazole in biological samples and animal feed. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Abedi, H.; Kamarei, F. Optimization of carrier-mediated three-phase hollow fiber microextraction combined with HPLC-UV for determination of propylthiouracil in biological samples. Talanta 2011, 85, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardell, J.; King, C. Solvent equilibriums for extraction of carboxylic acids from water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1978, 23, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudthavorasit, S.; Chiaochan, C.; Leepipatpiboon, N. Simultaneous determination of multi-class antibiotic residues in water using carrier-mediated hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Microchim. Acta 2010, 172, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, M.; Genberg, J.; Jönsson, J.Å. Application of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction for pinic acid and pinonic acid analysis from organic aerosols. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 713, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, J.Å.; Lövkvist, P.; Audunsson, G.; Nilvé, G. Mass transfer kinetics for analytical enrichment and sample preparation using supported liquid membranes in a flow system with stagnant acceptor liquid. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 277, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili, A.; Yamini, Y.; Ghambarian, M.; Shariati, S.; Moradi, M. Measurement of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics From Human Plasma Using Hollow Fiber Liquid-Phase Microextraction Based on Carrier Mediated Transport. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjmohammadi, M.R.; Soltani, M.; Sharifi, V. Use of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction and HPLC for extraction and determination of apigenin in human urine after consumption of Satureja sahendica Bornm. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 900, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, F.; Lin, Z.; Lu, Q.; Lin, F.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L. Novel multifunctional acceptor phase additive of water-miscible ionic liquid in hollow-fiber protected liquid phase microextraction. Talanta 2012, 88, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Su, X.; Ma, M.; Chen, B.; Yao, S. Carrier-mediated liquid phase microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for determination of illicit drugs in human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 621, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Metabolite | Chemical Structure | Log p (O/W) | pka | Solubility in Water (g·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hippuric acid |  | 0.23 | 3.68 | 3.75 |
| Mandelic acid | 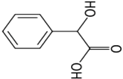 | 0.66 | 3.75 | 16.8 |
| Metabolite | Concentration (µg·mL−1) | Intra-Day RSD% N = 6 | Inter-Day RSD% N = 18 | LOD (µg·mL−1) | DLR (µg·mL−1) | EF | RR% | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA | 0.02 | 8.2 | 10.7 | 0.009 | 0.02–20 | 172 | 88–91 | 0.998 |
| 0.2 | 5.6 | 7.2 | ||||||
| 2 | 2.5 | 4.1 | ||||||
| MA | 0.02 | 2.9 | 7.5 | 0.007 | 0.02–10 | 195 | 84–94 | 0.997 |
| 0.2 | 4.7 | 8.2 | ||||||
| 2 | 3.6 | 8.6 |
| No. of Sample Urine | Workplace | Mean ± SD (mg/g Creatinine) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA | MA | ||
| 1 | Petrol station | 376 ± 30 | 101 ± 10 |
| 2 | Petrol station | 483 ± 33 | 85 ± 9 |
| 3 | Petrol station | 221 ± 11 | 128 ± 12 |
| 4 | Car painting | 791 ± 78 | 180 ± 38 |
| 5 | Car painting | 344 ± 27 | 98 ± 38 |
| 6 | Car painting | 598 ± 47 | 125 ± 38 |
| 7 | Petrochemical plant | 287 ± 24 | 75 ± 21 |
| 8 | Petrochemical plant | 532 ± 42 | 121 ± 14 |
| 9 | Petrochemical plant | 435 ± 46 | 98 ± 18 |
| Analyte | Extraction | Determination | LOD (µg·mL−1) | LOQ (µg·mL−1) | RSD% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA | LPME | HPLC-UV | 0.009 | 0.02 | 2.5–10.7 | Proposed method |
| Derivatization | GC-MS | 0.017 | 0.05 | 6.2 | [7] | |
| Dilution & filtration | HPLC-UV | 1.5 | 4.5 | 0.2–0.5 | [14] | |
| SPE | GC-MS | 10 | 40 | 4.1–4.9 | [2] | |
| SPE | LC/MS/MS | 0.005 | 0.015 | 3–10 | [13] | |
| MA | LPME | HPLC-UV | 0.007 | 0.02 | 3.6–8.6 | Proposed method |
| SPE | HPLC-UV | 4 | 50 | 1.1–11.7 | [15] | |
| Derivatization | GC-MS | 0.008 | 0.05 | 7.7 | [7] | |
| Dilution &filtration | HPLC-UV | 7.6 | 22.8 | 0.4–2.6 | [14] | |
| SPE | GC-MS | 1 | 10 | 2.5–7.4 | [2] | |
| LLE | HPLC-UV | 5 | – | 3.9–4.4 | [16] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahrami, A.; Ghamari, F.; Yamini, Y.; Ghorbani Shahna, F.; Moghimbeigi, A. Hollow Fiber Supported Liquid Membrane Extraction Combined with HPLC-UV for Simultaneous Preconcentration and Determination of Urinary Hippuric Acid and Mandelic Acid. Membranes 2017, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010008
Bahrami A, Ghamari F, Yamini Y, Ghorbani Shahna F, Moghimbeigi A. Hollow Fiber Supported Liquid Membrane Extraction Combined with HPLC-UV for Simultaneous Preconcentration and Determination of Urinary Hippuric Acid and Mandelic Acid. Membranes. 2017; 7(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahrami, Abdulrahman, Farhad Ghamari, Yadollah Yamini, Farshid Ghorbani Shahna, and Abbas Moghimbeigi. 2017. "Hollow Fiber Supported Liquid Membrane Extraction Combined with HPLC-UV for Simultaneous Preconcentration and Determination of Urinary Hippuric Acid and Mandelic Acid" Membranes 7, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010008
APA StyleBahrami, A., Ghamari, F., Yamini, Y., Ghorbani Shahna, F., & Moghimbeigi, A. (2017). Hollow Fiber Supported Liquid Membrane Extraction Combined with HPLC-UV for Simultaneous Preconcentration and Determination of Urinary Hippuric Acid and Mandelic Acid. Membranes, 7(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010008







