Linking Findings in Microfluidics to Membrane Emulsification Process Design: The Importance of Wettability and Component Interactions with Interfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. EDGE Devices
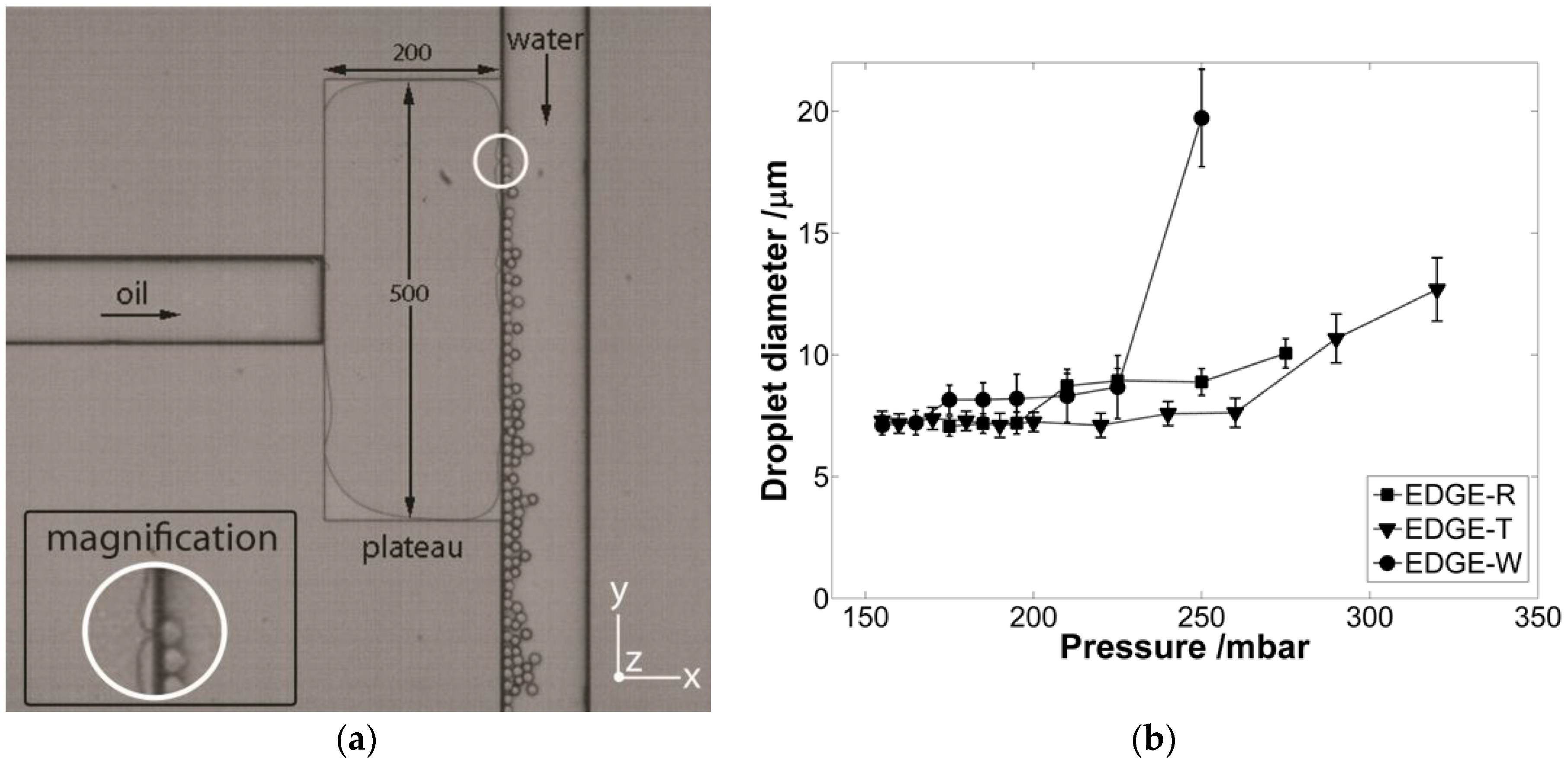
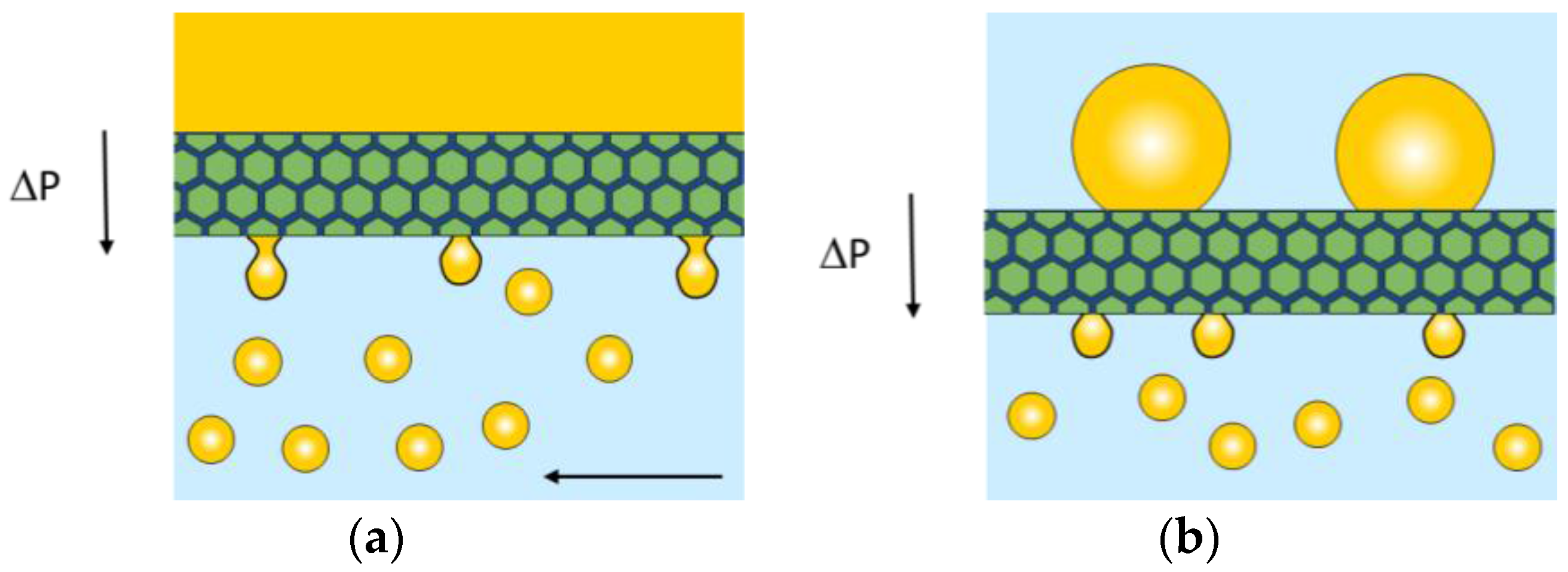
2.1. General Behavior
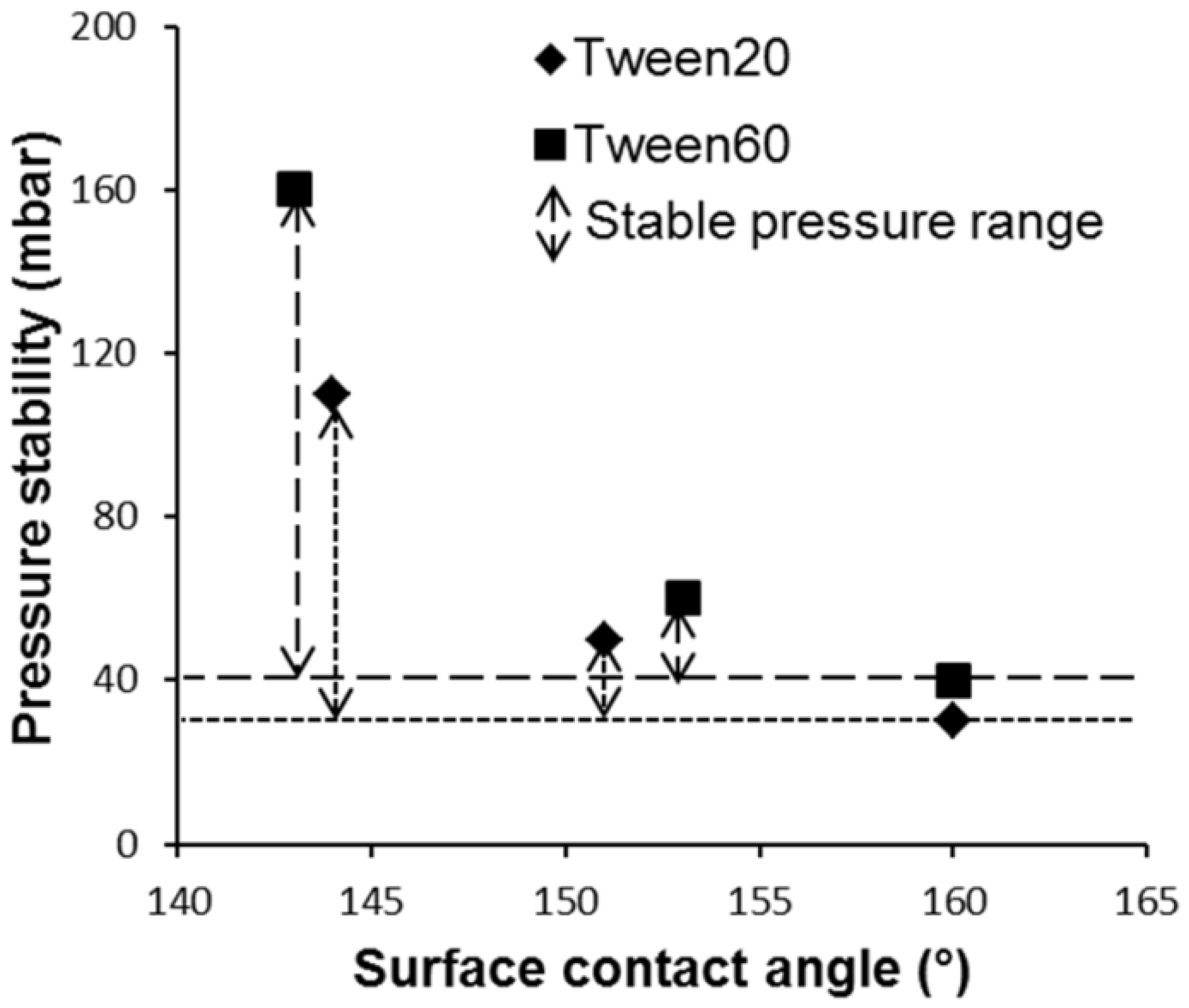
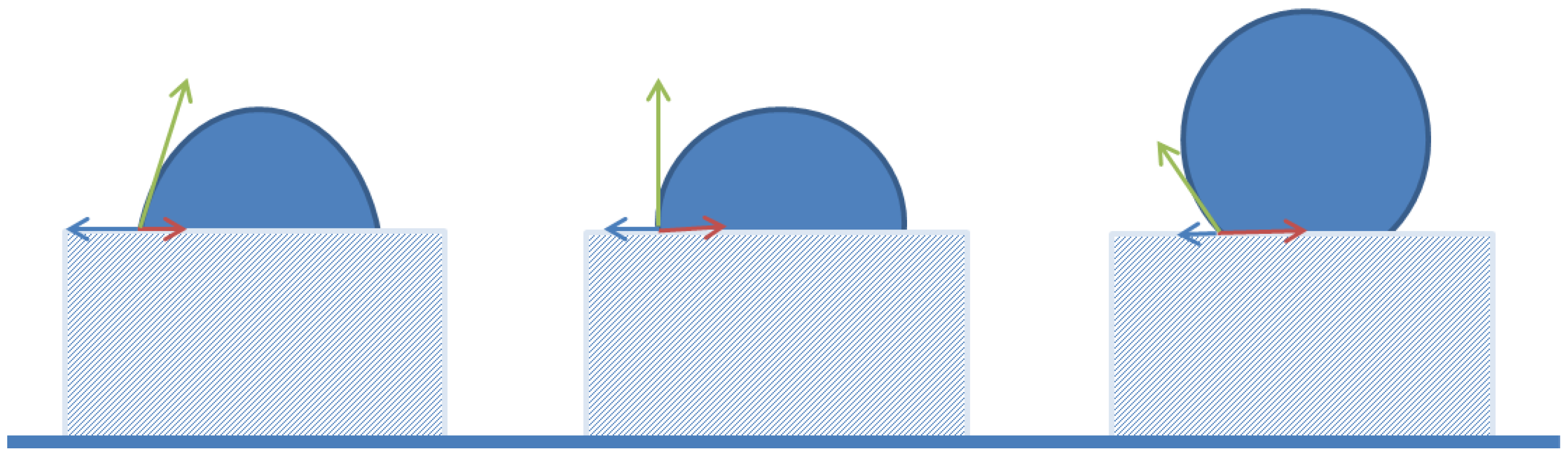
2.2. Contact Angle
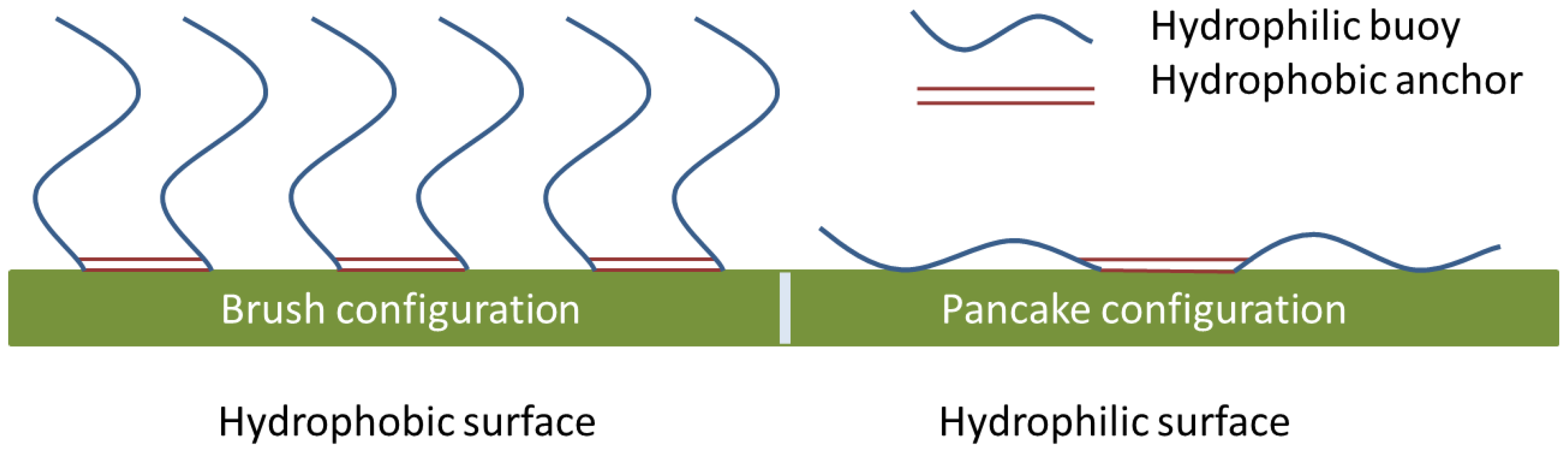
2.3. Component Surface Interactions
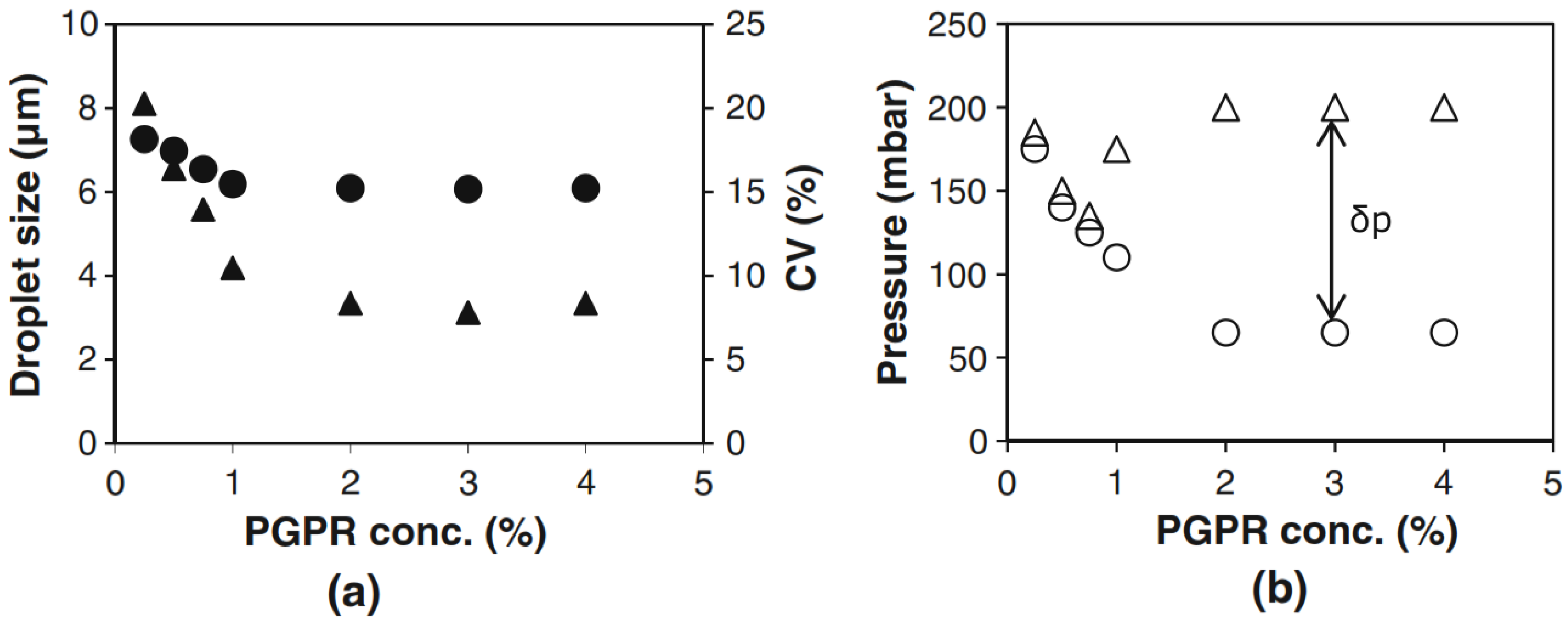
2.3.1. Concentration Effects
2.3.2. Various Components
2.3.3. Surface Roughness
3. Membrane Emulsification
3.1. Cross-Flow or Direct Droplet Formation
3.2. Premix Droplet Formation
3.3. Comparison with Literature
3.4. Process Guide Lines
3.5. Outlook
Acknowledgment
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vladisavljević, G.T.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Production of uniform droplets using membrane, microchannel, and microfluidic emulsification devices. Micro Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremond, N.; Bibette, J. Exploring emulsion science with microfluidics. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10549–10559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroen, K.; Sahin, S.; van Dijke, K.; van der Graaf, S.; Zijffers-Steegmans, M.; Krebs, T.; Boom, R. Emulsion preparation with micro-structured systems. In Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics; Li, D., Ed.; SpringerReference: NewYork, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schroën, K.; Bliznyuk, O.; Muijlwijk, K.; Sahin, S.; Berton-Carabin, C.C. Microfluidic emulsification devices: From micrometer insights to large-scale food emulsion production. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, S.; Schroën, K. Microfluidic EDGE emulsification: The importance of protein/interface interactions on droplet formation and process stability. 2015; accepted for publication in Scientific Reports. [Google Scholar]
- Steegmans, M.L.J.; Warmerdam, A.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Dynamic interfacial tension measurements with microfluidic Y-junctions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9751–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, V.; Behrend, O.; Schubert, H. Effect of dynamic interfacial tension on the emulsification process using microporous, ceramic membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 202, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Graaf, S.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; van der Sman, R.G.M.; Boom, R.M. Influence of dynamic interfacial tension on droplet formation during membrane emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baret, J.-C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engl, W.; Backov, T.; Panizza, P. Controlled production of emulsions and particles by milli- and microfluidic techniques. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2008, 13, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charcosset, C. Preparation of emulsions and particles by membrane emulsification for the food processing industry. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Mukataka, S.; Nakajima, M. Effects of type and physical properties of oil phase on oil-in-water emulsion droplet formation in straight-through microchannel emulsification, experimental and CFD studies. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5722–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, I.; Mukataka, S.; Nakajima, M. Production of monodisperse oil-in-water emulsions using a large silicon straight-through microchannel plate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5852–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, V. Herstellen von Öl-in-Wasser Emulsionen Mit Microporösen Membranen. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hochschule Karlsruhe, Karlsruhe, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, V.; Schubert, H. Influence of emulsifier and pore size on membrane emulsification. Spec. Publ. R. Soc. Chem. 1998, 227, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, A.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Premix emulsification: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Hayakawa, K.; Hagura, Y. Preparation of high concentration O/W and W/O emulsions by the membrane phase inversion emulsification using PTFE membranes. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 1999, 5, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keurentjes, J.T.F.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Brinkman, D.; Schroen, C.G.P.H.; van’t Riet, K. Surfactant-induced wetting transitions: Role of surface hydrophobicity and effect on oil permeability of ultrafiltration membranes. Colloids Surfaces 1990, 51, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsken, L.E.; Oomes, M.; Schroën, K.; Tramper, J.; de Bont, J.A.M.; Beeftink, R. Membrane-facilitated bioproduction of 3-methylcatechol in an octanol/water two-phase. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 96, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, A.J.; van der Padt, A.; Boom, R.M.; de Heij, W.B.C. Process fundamentals of membrane emulsification: Simulation with CFD. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Wijers, M.C.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Padt, A.; van’t Riet, K. Membrane modification to avoid wettability changes due to protein adsorption in an emulsion/membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 80, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Padt, A.; van’t Riet, K. Minimum breakthrough pressure as a measure for wettability changes caused by protein adsorption at hydrophobic membranes. Bioseparation 1994, 10, 151–163. [Google Scholar]
- Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Voort Maarschalk, K.; van der Padt, A.; van’t Riet, K. Influence of preadsorbed block copolymers on protein adsorption: surface properties, layer thickness, and surface coverage. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3068–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Padt, A.; van’t Riet, K. Wettability of tri-block copolymer coated hydrophobic surfaces: Predictions and measurements. Colloids Surfaces A 1994b, 90, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroen, C.; Woodley, J.M. Membrane separation for downstream processing of aqueous-organic bioconversions. Biotechnol. Prog. 1997, 13, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijke, K.C.; Schroën, K.; van der Padt, A.; Boom, R. EDGE emulsification for food-grade dispersions. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijke, K.C.; Veldhuis, G.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Simultaneous formation of many droplets in a single microfluidic droplet formation unit. AIChE J. 2010b, 56, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijke, K.C.; de Ruiter, R.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. The mechanism of droplet formation in microfluidic EDGE systems. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakatsu, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Nakajima, M. Regular-sized cell creation in microchannel emulsification by visual microprocessing method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1997, 74, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M.; Chun, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Fukita, H. Silicon array of elongated through-holes for monodisperse emulsions. AIChE J. 2002, 48, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, X.; Lou, F.; Mukataka, S.; Nakajima, M. Preparation of monodisperse water-in-oil-in-water emulsions using microfluidization and straight-through microchannel emulsification. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2005, 82, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Mukataka, S.; Nakajima, M. Novel asymmetric through-hole array microfabricated on a silicon plate for formulating monodisperse emulsions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7629–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Seki, M. Prediction of droplet diameter for microchannel emulsification. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3854–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakatsu, T.; Tragardh, G.; Tragardh, C.; Nakajima, M.; Oda, N.; Yonemoto, T. The effect of the hydrophobicity of microchannels and components in water and oil phases on droplet formation in microchannel water-in-oil emulsification. Colloids Surfaces A 2001, 179, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M.; Mukataka, S. Preparation characteristics of oil-in-water emulsions using differently charged surfactants in straight-through microchannel emulsification. Colloids Surfaces A 2003, 229, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Iwamoto, S.; Seki, M. Interfacial tension driven monodispersed droplet formation from microfabricated channel array. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5562–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Nakajima, M.; Oda, T.; Satake, M.; Seki, M. Effect of interfacial tension on the dynamic behavior of droplet formation during microchannel emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 269, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangla, R.; Fradet, E.; Lopez, Y.; Baroud, C.N. The physical mechanisms of step emulsification. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijke, K.C.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Microchannel emulsification: From computational fluid dynamics to predictive analytical model. Langmuir 2008, 24, 10107–10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijke, K.C.; Veldhuis, G.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Parallelized edge-based droplet generation (EDGE) devices. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2824–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maan, A.A.; Sahin, S.; Mujawar, L.H.; Boom, R.; Schroën, K. Effect of surface wettability on microfluidic EDGE emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 403, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, S.; Strofyllas, M.; Schroën, K. Upscaling of microfluidic emulsification to industrial throughputs: The importance of structure design. 2016; submitted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Maan, A.A.; Boom, R.; Schroën, K. Preparation of monodispersed oil-in-water emulsions through semi-metal microfluidic EDGE systems. Micro Nanofluid. 2013, 14, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, A.A.; Schroën, K.; Boom, R. Monodispersed water-in-oil emulsions prepared with semi-metal microfluidic EDGE systems. Micro Nanofluid. 2013, 14, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.O.; Biresaw, G. Quartz crystal microbalance investigation of the structure of adsorbed soybean oil and methyl oleate onto steel surface. Thin Solid Films 2010, 519, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.J.; Lu, J.R.; Thomas, R.K.; Cui, Z.F. Effect of pH on the adsorption of bovine serum albumin at the silica/water interface studied by neutron reflection. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 3727–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Schroën, K. Pickering emulsions for food applications: Background, trends and challenges. Ann. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 263–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, I.; Zhang, Y.; Neves, M.A.; Hori, Y.; Uemura, K.; Nakajima, M. Influence of electrolyte concentration on microchannel oil-in-water emulsification using differently charged surfactants. Colloids Surfaces A 2014, 440, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Yin, L.J.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Preparation characteristics of monodispersed oil-in-water emulsions with large particles stabilized by proteins in straight-through microchannel emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Yin, L.J.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Comparison of stability of bovine serum albumin-stabilized emulsions prepared by microchannel emulsification and homogenization. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, S.; Schroën, K. Partitioned EDGE devices for high throughput production of monodisperse emulsion droplets with two distinct sizes. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2486–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joscelyne, S.M.; Trägårdh, G. Membrane emulsification—A literature review. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 169, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charcosset, C.; Limayem, I.; Fessi, H. The membrane emulsification process—A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladisavljevic, G.T.; Williams, R.A. Recent developments in manufacturing emulsions and particulate products using membranes. Adv. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2005, 113, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrich, U.; Schubert, H. Emulsification using microporous systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 257, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, F.; Lloyd, D.M.; Hancocks, R.D.; Pawlik, A.K. Advances in membrane emulsification. Part A: Recent developments in processing aspects and microstructural design approaches. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyropoulos, F.; Lloyd, D.M.; Hancocks, R.D.; Pawlik, A.K. Advances in membrane emulsification. Part B: Recent developments in modelling and scale-up approaches. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Graaf, S.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Preparation of double emulsions by membrane emulsification—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, E.; Drioli, E.; Giorno, L. Membrane emulsification technology: Twenty-five years of inventions and research through patent survey. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadler, V.; Windhab, E.J. Continuous membrane emulsification by using a membrane system with controlled pore distance. Desalination 2006, 189, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryantia, N.; Williams, R.A.; Houa, R.; Vladisavljević, G.T. Performance of rotating membrane emulsification for O/W production. Desalination 2006, 200, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrin, M.Y. Dynamic shear-enhanced membrane filtration: A review of rotating disks, rotating membranes and vibrating systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 324, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Shimizu, M. Porous glass from calcium alumino boro-silicate glass. Ceram. Jpn. 1986, 21, 408–412. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, T.; Shimizu, M.; Kukizaki, M. Membrane emulsification by microporous glass. In Inorganic Membranes, ICIM2–91; Proceedings of the International Conference on Inorganic Membranes, Montpellier, France, 1–4 July 1991; pp. 513–516.
- Joscelyne, S.M.; Trägårdh, G. Food emulsions using membrane emulsification: Conditions for producing small droplets. J. Food Eng. 1999, 39, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchigami, T.; Toki, M.; Nakanishi, K. Membrane emulsification using sol-gel derived macroporous silica glass. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2000, 19, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerken, M.J.; Groenendijk, M.N.W.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Wessling, M. Micro-fabricated metal nozzle plates used for water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsification. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladisavljevic, G.T.; Williams, R.A. Manufacture of large uniform droplets using rotating membrane emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijn, C.J.M. Nano and Micro Engineered Membrane Technology; Membrane Science and Technology Series 10; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Geerken, M.J.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Wessling, M. Tailoring surface properties for controlling droplet formation at microsieve membranes. Colloids Surface A 2007, 292, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, A.J.; van Lierop, R.; van der Sman, R.G.M.; van der Padt, A.; Boom, R.M. Analysis of droplet formation and interactions during cross-flow membrane emulsification. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 204, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Barrow, D. Analysis of droplet size during crossflow membrane emulsification using stationary and vibrating micromachined silicon nitride membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 261, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsbertsen-Abrahamse, A.J.; van der Padt, A.; Boom, R.M. Status of cross-flow membrane emulsification and outlook for industrial application. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 230, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, N.; Naganuma, K.; Nagai, M.; Ma, G.H.; Omi, S. Preparation of W/O (water-in-oil) emulsions using a PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) membrane—A new emulsification device. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2003, 24, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, N.; Yuyama, H.; Nagai, M.; Ma, G.H.; Omi, S. A comparison of membrane emulsification obtained using SPG (Shirasu Porous Glass) and PTFE [poly(tetrafluoroethylene)] membranes. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2002, 23, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Fujiki, I.; Hagura, Y. Preparation of corn oil/water and water/corn oil emulsions using PTFE membranes. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 1998, 4, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerken, M.J.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Wessling, M. Interfacial aspects of water drop formation at micro-engineered orifices. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 312, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.J.; Williams, R.A. Controlled production of emulsions using a crossflow membrane. Part I: Droplet formation from a single pore. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1998, 76, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garstecki, P.; Fuerstman, M.J.; Stone, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction-scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 693–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Graaf, S.; Steegmans, M.L.J.; Van der Sman, R.G.M.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Droplet formation in a T-shaped microchannel junction: A model system for membrane emulsification. Colloids Surface A 2005, 266, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehking, J.D.; Gabany, M.; Chew, L.; Kumar, R. Effects of viscosity, interfacial tension, and flow geometry on droplet formation in a microfluidic T-junction. Micro Nanofluid. 2014, 16, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Graaf, S.; Nisisako, T.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; van der Sman, R.G.M.; Boom, R.M. Lattice Boltzmann simulations of droplet formation in a T-shaped microchannel. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4144–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, M.; Trägårdh, G.; Trägårdh, C.; Dejmek, P. Using the surface evolver to model droplet formation processes in membrane emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 279, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muijlwijk, K.; Berton-Carabin, C.; Schroën, K. Cross-flow microfluidic emulsification from a food perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuno, M.; Nakajima, M.; Iwamoto, S.; Maruyama, T.; Sugiura, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Shono, A.; Satoh, K. Visualization and characterization of SPG membrane emulsification. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 210, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladisavljević, G.T.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M.; Williams, R.A.; Shimizu, M.; Nakashima, T. Shirasu porous glass membrane emulsification: Characterisation of membrane structure by high-resolution X-ray microtomography and microscopic observation of droplet formation in real time. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 302, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zwan, E.A.; Schroën, K.; van Dijke, K.; Boom, R.M. Visualization of droplet break-up in pre-mix membrane emulsification using microfluidic devices. Colloids Surfaces A 2006, 277, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukizaki, M.; Goto, M. Preparation and characterization of a new asymmetric type of Shirasu porous glass (SPG) membrane used for membrane emulsification. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, A.; Güell, C.; López, F.; Ferrando, M. Microfiltration membranes to produce BSA-stabilized O/W emulsions by premix membrane emulsification. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 356, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, A.; Güell, C.; Gelaw, T.; de Lamo, S.; Ferrando, M. Cleaning protocols for organic microfiltration membranes used in premix membrane emulsification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 88, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, A.; de Lamo, S.; Güell, C.; López, F.; Ferrando, M. Protein-stabilized emulsions containing beta-carotene produced by premix membrane emulsification. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.; Güell, C.; Henry, O.; Ferrando, M. Premix membrane emulsification to produce oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with various interfacial structures of whey protein and carboxymethyl cellulose. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 43, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.; Güell, C.; Ferrando, M. A procyanidin-rich extract encapsulated in water-in-oil-in-water emulsions produced by premix membrane emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.; Güell, C.; Ferrando, M. Spray dried double emulsions containing procyanidin-rich extracts produced by premix membrane emulsification: Effect of interfacial composition. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafat, A.; Giesbers, M.; Rosso, M.; Sudhölter, E.J.R.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; White, R.G.; Yang, L.; Linford, M.R.; Zuilhof, H. Covalent biofunctionalization of silicon nitride surfaces. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6233–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steegmans, M.L.J.; Schroën, C.G.P.H.; Boom, R.M. Characterization of emulsification at flat microchannel Y junctions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3396–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muijlwijk, K.; Hinderink, E.; Ershov, D.; Berton-Carabin, C.; Schroën, K. Interfacial tension measured at high expansion rates and within milliseconds using microfluidics. J Colloids Interface Sci. 2016, 470, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawalha, H.; Purwanti, N.; Rinzema, A.; Schroën, K.; Boom, R. Polylactide microspheres prepared by premix membrane emulsification—Effects of solvent removal rate. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Emulsifier | Hexadecane | Sunflower Oil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Range (mbar) | @ Maximum Pressure | Pressure Range (mbar) | @ Maximum Pressure | |||
| Diameter (µm) | Frequency/500 µm Plateau Width (Hz) | Diameter (µm) | Frequency/500 µm Plateau Width (Hz) | |||
| SDS | 60–115 | 12 | 160 | 40–60 | 16 | 12 |
| SDS/WPI a | 40–100 | 12 | 67 | |||
| Tween 20 | 90–210 | 12 | 200 | 60–120 | 10 | 50 |
| WPI | 170–450 | 12 | 1221 | 125–220 | 10 | 28 |
| α-lac | 150–470 | 14 | 5500 | 130–210 | 10 | 33 |
| β-lac | 190–470 | 13 | 1073 | 130–210 | 10 | 28 |
| BSA pH 7 | 190–400 | 14 | 150 | 130–200 | 10 | 8 |
| BSA @ pI | 220–440 | 24 | 526 | 150–260 | 26 | 31 |
| BSA pH 3 | 190–450 | 14 | 1255 | Polydisperse | ||
| Emulsifier | Equilibrium Interfacial Tension (mN/m) | d3,2 (μm) MCE Membrane | d3,2 (μm) PES Membrane |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tween 20 (2%) | 2.87 | 1.05 | 0.67 |
| BSA (1%) | 5.71 | 4.97 | 3.99 |
| BSA (5%) | 3.50 | 2.57 | 2.74 |
| Tween 20 (2%) + BSA (1%) | 0.74 | 1.09 | 0.54 |
| Tween 20 (2%) + BSA (5%) | 0.49 | 1.15 | 0.53 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schroën, K.; Ferrando, M.; De Lamo-Castellví, S.; Sahin, S.; Güell, C. Linking Findings in Microfluidics to Membrane Emulsification Process Design: The Importance of Wettability and Component Interactions with Interfaces. Membranes 2016, 6, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6020026
Schroën K, Ferrando M, De Lamo-Castellví S, Sahin S, Güell C. Linking Findings in Microfluidics to Membrane Emulsification Process Design: The Importance of Wettability and Component Interactions with Interfaces. Membranes. 2016; 6(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchroën, Karin, Montse Ferrando, Silvia De Lamo-Castellví, Sami Sahin, and Carme Güell. 2016. "Linking Findings in Microfluidics to Membrane Emulsification Process Design: The Importance of Wettability and Component Interactions with Interfaces" Membranes 6, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6020026
APA StyleSchroën, K., Ferrando, M., De Lamo-Castellví, S., Sahin, S., & Güell, C. (2016). Linking Findings in Microfluidics to Membrane Emulsification Process Design: The Importance of Wettability and Component Interactions with Interfaces. Membranes, 6(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6020026









